Topic 1 - Particles and Radiation
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
How do we know that the nucleus contains most of the mass of an atom?
from Rutherford's alpha-scattering experiment
What are isotopes?
atoms with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
What is the nucleon number? (other name, symbol?)
the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom (mass number)
symbol = A
What is a nuclide?
a general term for a specific isotope of an element
What is specific charge?
This is the ratio of charge to its mass of a particle. It is measured in CKg-1 and you work it out by
specific charge= charge/mass
What force stops nuclei in stable isotopes disintegrating?
strong nuclear force
What are the features of the strong nuclear force?
- between ranges of 0.5fm- (3-4)fm it acts as an attractive force to overcome the repulsion between protons and neutrons
- below 0.5fm it acts as a repulsive force to stop protons and neutrons being pushed into each other
- it has the same effect on 2 neutrons, 2 protons or a neutron and a proton
Describe alpha radiation.
- 2 protons and 2 neutrons
What is the symbol for atomic number?
Z
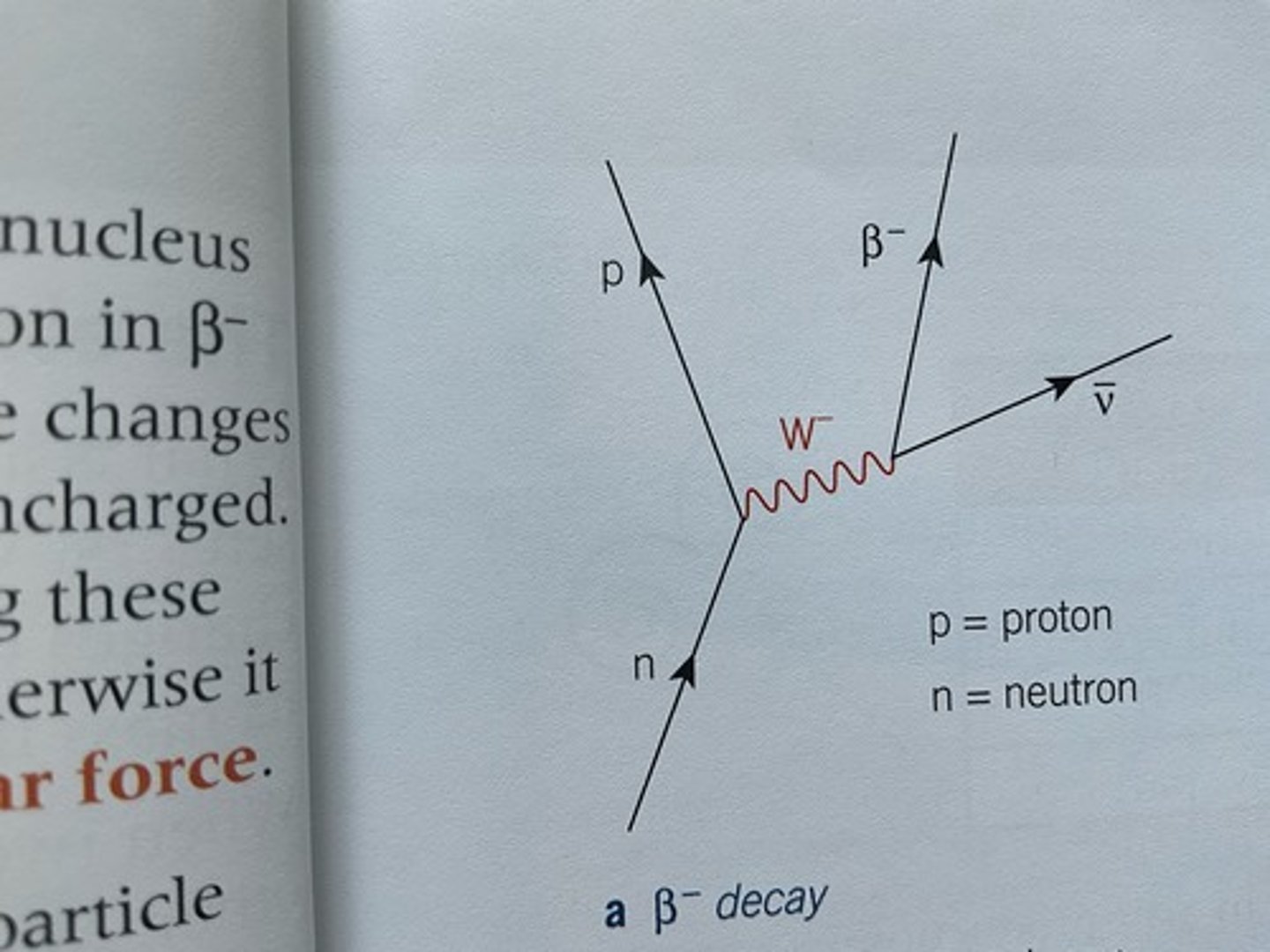
Describe beta decay. What particles are produced/emitted?
neutron decays into a proton to release a B- particle, which is immediately emitted from the nucleus.
An antineutrino is also produced and emitted during this decay.
What is an antineutrino?
A kind of uncharged antimatter particle
How do the mass and atomic numbers change in beta decay?
mass: no change
atomic: +1
Why are antineutrinos needed during beta decay? (as in how did scientists know that an antineutrino must have been produced)
- experiments showed that the KE of the B- particle emitted by a particular radioisotope varied up to a max value (unlike a-decay where a particular radioisotope produces a-particles of a particular energy)
- if E is conserved in B-decay, the remaining energy must be carried away by another particle. The particle have a very small mass, and must be neutral.
- therefore it was called a neutrino (Italian for "small neutral one")
Describe gamma radiation.
- high frequency EM radiation emitted by an unstable nucleus
- has no charge or mass and can pass through thick metal plates
- emitted by a nucleus that has too much energy following an alpha or beta decay
What is a photon?
a packet of EM waves,
What is the formula for photon energy?
E = hf
h = the planck constant
What is a laser beam?
Photons of the same frequency
What is the power of a laser?
P = nhf
where n = number of photons
f = frequency
h = planck constant
What happens when matter and antimatter meet?
they annihilate
When does positron emission occur?
When a proton changes into a neutron in an unstable nucleus with too many protons.
A neutrino is also emitted
These isotopes that decay by positron emission are not naturally occurring so must be manufactured for this process
How does a PET scan work?
- patient gven a positron-emitting isotope, some of which travels to area under investigation
- emitted positrons will meet and annihilate with an electron within a few mm of travel
- 2 gamma photons are produced which travel in opposite directions and are detected outsode the patient
What is rest energy?
The amount of energy that would be produced if all of its mass was transformed into energy
What did paul dirac do?
in 1928 he predicted that antimatter particles woud release their rest energy whenever a particles meets and annihilates its corresponding antimatter particle
he also predicted the process of pair production
What 3 things did Dirac predict about antimatter?
For every particle, there is a corresponding antiparticle that:
- annihilates the particle and itself when they meet, converting their total mass into photons
- has exactly the same rest mass as the particle
- has exactly the opposite charge of the particle if the particle has a charge
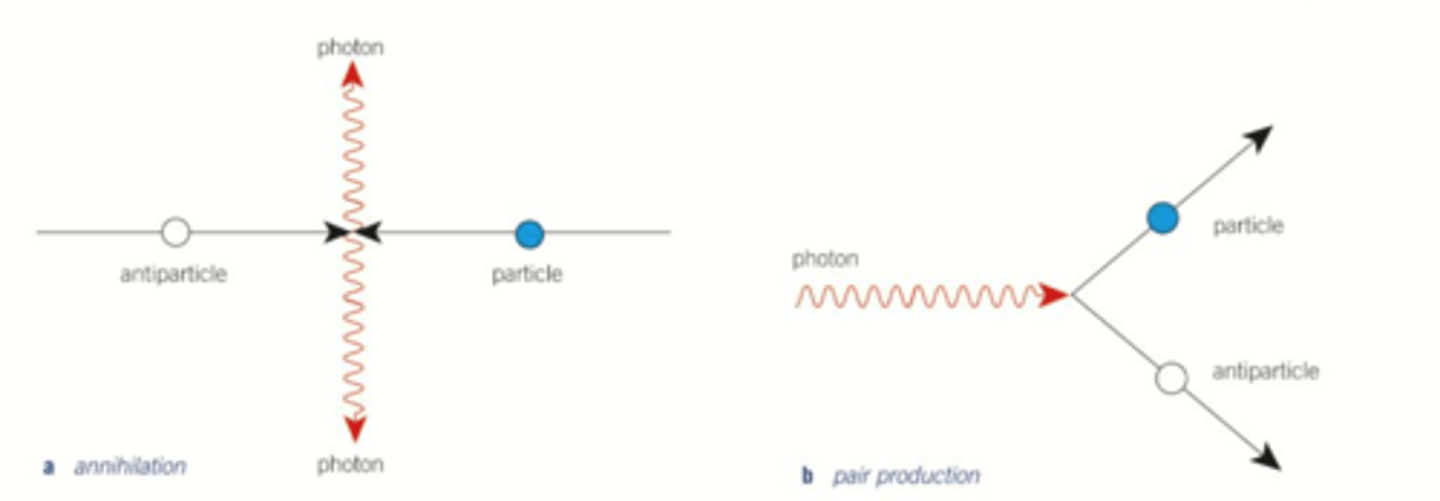
Draw diagrams of pair production
What is a megaelectron volt? (MeV)
1.6 x 10^-13J
Define 1 Electron volt
the energy transferred when an electron is moved through a potential difference of one volt
Define annihilation.
When a particle and its antiparticle meet, they destroy each other and become radiation energy.
What is the minimum energy of each photon produced from annihilation equal to?
the rest energy of the particle
What is the minimum energy of each photon needed for pair production equal to?
2 x the rest energy of the particle
What happens in pair production?
A photon creates a particle and a corresponding antiparticle and vanishes in the process
What are the four fundamental forces?
gravity, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, weak nuclear
What did Richard Feynman say?
The EM force between two charged particles is due to the exchange of virtual protons.
Why are virtual protons described as virtual?
Because we can't detect them directly. If we did detect them, we would block the exchange and stop the EM force from occurring.
How do we know that there is a weak nuclear force?
Strong nuclear force doesn't change neutrons into protons or vice versa in B-decay, and these changes can't be due to the EM force bc the neutron is uncharged. So, there must be another force weaker than the strong nuclear force (otherwise it would affect stable nuclei).
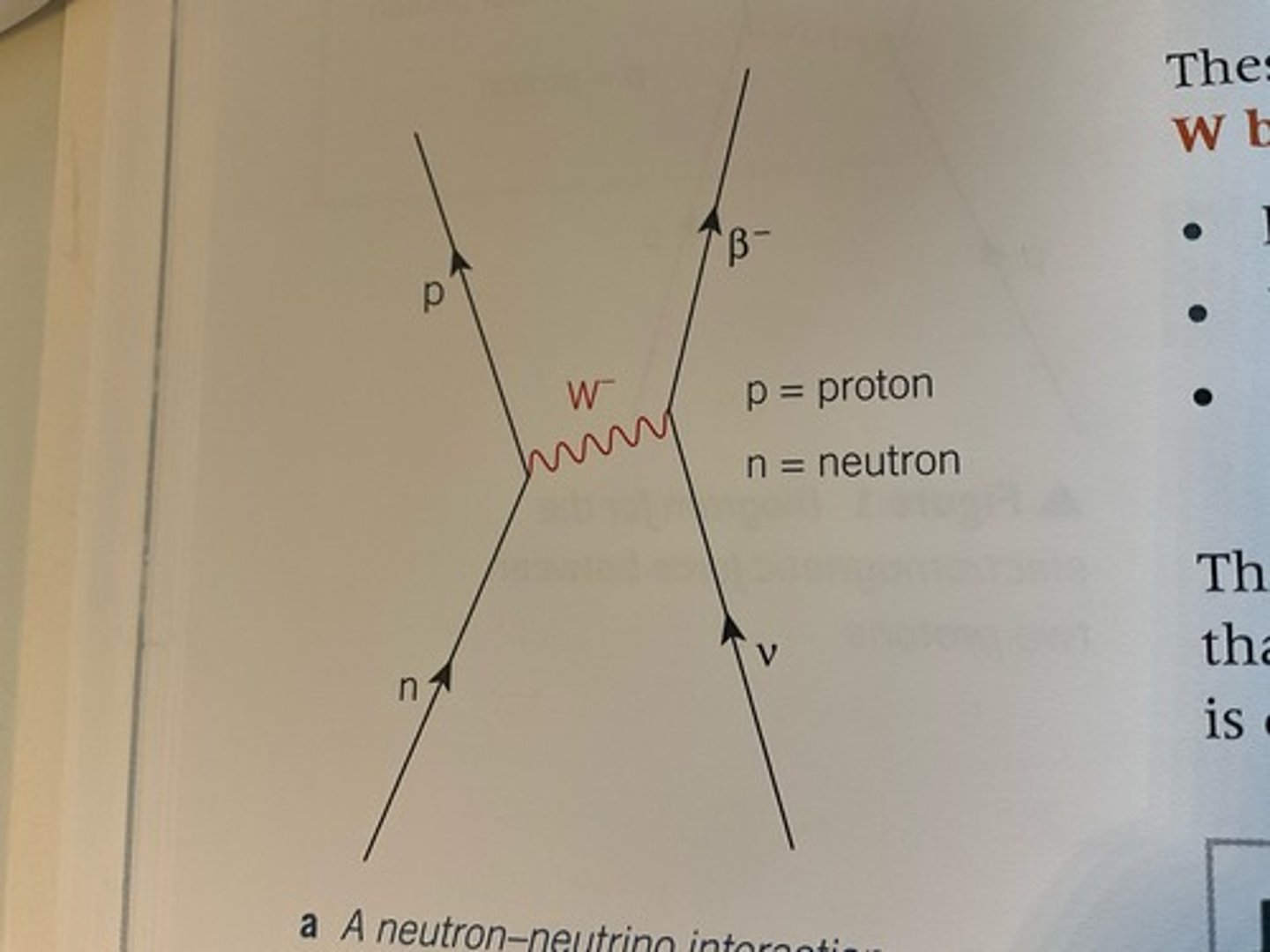
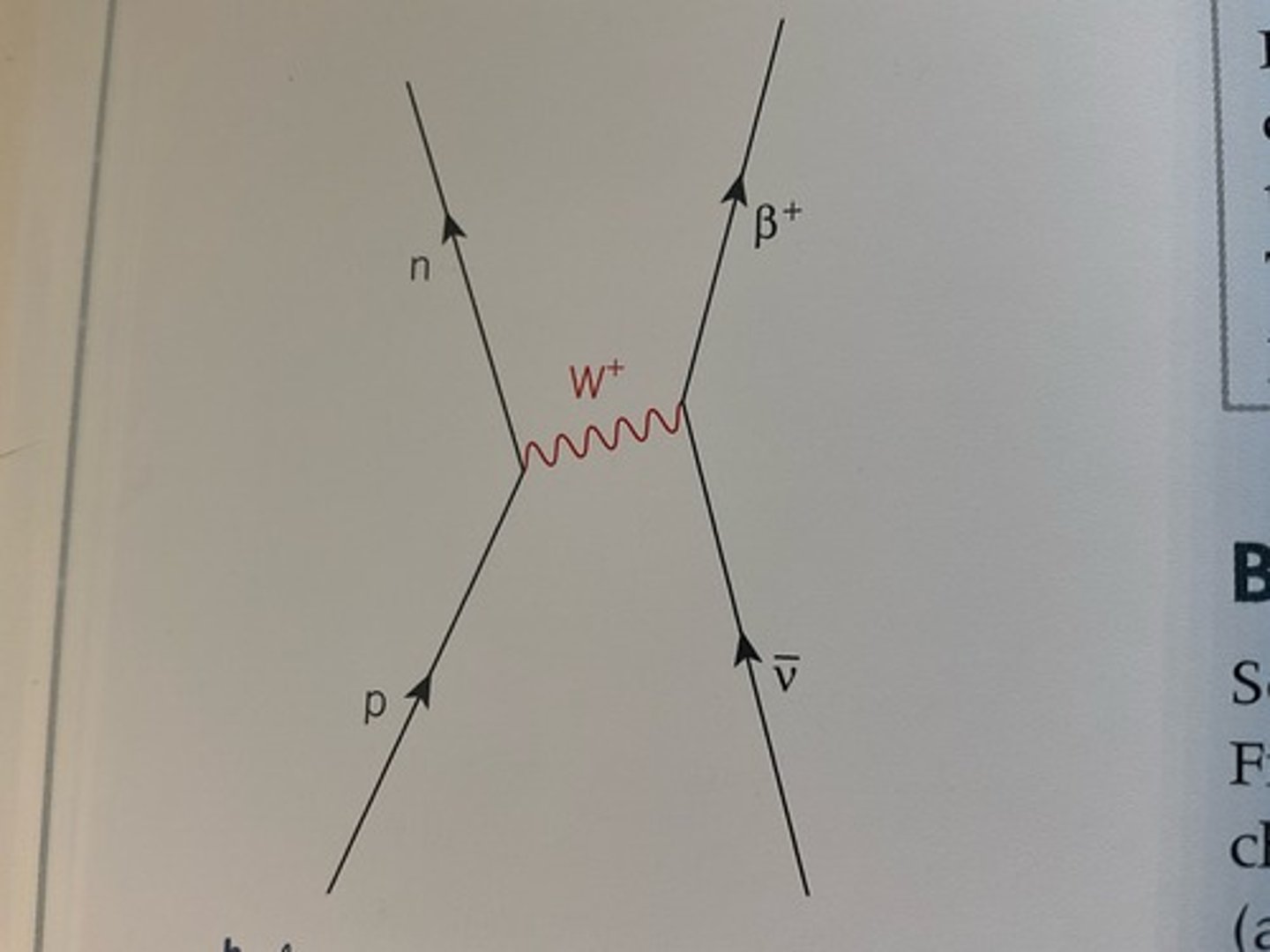
What happens when neutrinos or antineutrinos interact with other particles?
- a neutrino can interact with a neutron and make it change into a proton. A B- particle is created and emitted.
- an antineutrino can interact with a proton and change it into a neutron. A B+ particle is created and emitted.
- These interactions are due to the exchange of W bosons.
Describe W-bosons.
- non-zero rest mass
- short range of less than 0.001fm
- are positively charged (W+ boson) or negatively charged (W- boson)
Draw a diagram to represent a neutron-neutrino interaction
Draw a diagram to represent a proton-antineutrino interaction.
Draw a diagram to represent B- decay.
Draw a diagram to represent B+ decay

What are cosmic rays?
high energy particles that travel through space.
Arrange these particles from smallest to greatest mass:
kaon, proton, electron, pion, muon
electron, muon, pion, kaon, proton
What is the muon? symbol?
negatively charged particle with a rest mass of over 200x the electron
symbol: μ
What is the pion?
particle that can be +ely (π+), neutral (π0), or -ely (π-) charged
it has a rest mass greater than a muon but less than a proton
What is a kaon?
It can also be + (K+), - (K-) or neutrally (K0) charged like a pion. It ha a rest mass greater than a pion but less than a proton.
How are pions and kaons produced?
In pairs through the strong interaction when protons moving at high speed collide with nuclei
How did we figure out that kaons decay by weak interaction?
They decay much slower than pions and decay into pions. This means their decay must include the weak interaction.
Why are particle accelerators useful?
- new particles can be created by using particle accelerators to collide protons head-on with other protons at high speeds
- the KE of the protons can be converted into rest-mass energy of new particles
- this means theyu can be studied under controlled conditions so the rest masses, charges and lifetimes of the particles can e studied
What can a kaon decay into?
Pions OR a muon and an antineutrino OR an antimuon and a neutrino
What can a charged pion decay into?
A muon and an antineutrino OR an antimuon and a neutrino
What can a neutral pion decay into?
high energy photons
What can a muon decay into?
An electron and an antineutrino
What can an antimuon decay into?
positron and neutrino
What are the two main groups of particles?
hadrons and leptons
What are hadrons?
particles or antiparticles that can interact by strong interaction, including positrons, neutrons, pions and kaons.
What are leptons?
particles that can't interact by strong interaction, including electrons, muons and neutrinos.
What are the two classes of hadrons?
baryons and mesons
What are baryons?
protons and all hadrons that decay into protons, either directly or indirectly
What are mesons?
hadrons that don't include protons in their decay products, including kaons and pions.
How did we know there must be two classes of hadrons?
- when kaons are created, other short-lived particles with greater rest masses may be produced at the same time.
- these particles are created through strong interaction so much be hadrons
- however, unlike kaons, these other particles can decay into protons as well as pions
What occurs when leptons and antileptons collide?
a quark-antiquark pair is produced.
they move off in opposite directions to produce a shower of hadrons
How do we know there are different types of neutrinos and antineutrinos?
When the neutrinos and antineutrinos produced when muons and antimuons decay interact with protons and neutrons they only create muons. This means there must be different types of neutrinos and antineutrinos because otherwise equal numbers of electrons and muons would be created.
What are the two types of neutrino?
electron neutrino (ve) and muon neutrino (vμ)
What can leptons not do that suggests they are fundamental particles?
Although they can change into other leptons by the weak interaction, and they can be produced or annihilated in particle-antiparticle interactions, they cannot decay into non-leptons.
What happens when an electron neutrino interacts with a neutron?
an electron and proton can be produced:
Ve + n -> p + e-
Why can't an electron neutrino and a neutron change into an antiproton and a positron?
even though charge would be conserved, lepton number would not.
(+1) + (0) does not equal 0 + (-1)
What are the rules for lepton number?
lepton: +1
antilepton: -1
non-lepton: 0
What is muon decay?
when a muon changes into a muon neutrino, an electron and an electron antineutrino
How do we apply conservation of lepton number?
We apply it separately to muons and electrons
What are strange particles that decay into pions called?
kaons
How are strange particles created?
they are always created in pairs
What are hadrons made from?
quarks and antiquarks
What do mesons consist of?
a quark and an antiquark
there are 9 possible combos
What do baryons consist of?
3 quarks
What do antibaryons consist of?
3 antiquarks
What is a proton made up from?
uud
What is a neutron made from?
udd
What is the sigma (Σ) particle?
A baryon containing a strange quark
What properties are conserved in interactions?
baryon number, strangeness (except in weak interaction), charge, lepton number and energy
How are numbers for strangeness assigned?
strange quark: -1
antistrange quark: +1
other quarks: 0
How are baryon numbers assigned?
+1 for baryons
-1 for antibaryons
0 for mesons and leptons
Define the photoelectric effect.
The emission of electrons from a metal when light of a sufficiently high frequency is incident on the metal
What observations of the photoelectric effect could not be explained by the wave model of light?
- it doesn't occur unless the frequency of light is high enough, wave theory wouldn tell us that it could occur at any frequency
- no. of e- emitted/second is proportional to intensity of incident radiation, in wave theory intesity would be proportional to KE of electrons emitted
- it occurs immediately when threshold frequency is reached (wave theory tells us there should be a time delay)
What is the threshold frequency? What does it depend on?
the minimum frequency of light required to produce the photoelectric effect
depends on the metal it is incident upon
When can ionisation occur?
- when alpha, beta or gamma radiation passes through a substance, colliding with atoms of that substance
- when electrons pass through a fluorescent tube, colliding with atoms of the gas or vapour in tube
How do you measure ionisation energy?
- electrons are emitted from a heated filament and attracted to the anode
- the p.d. between the filament and the anode is increased to increase the speed of the electrons
- when the electrons gain enough KE to ionise atoms close to the anode, a larger current is measured by the ammeter
- the p.d. required to cause this increase in current is measured and used in E=eV to give the ionisation energy
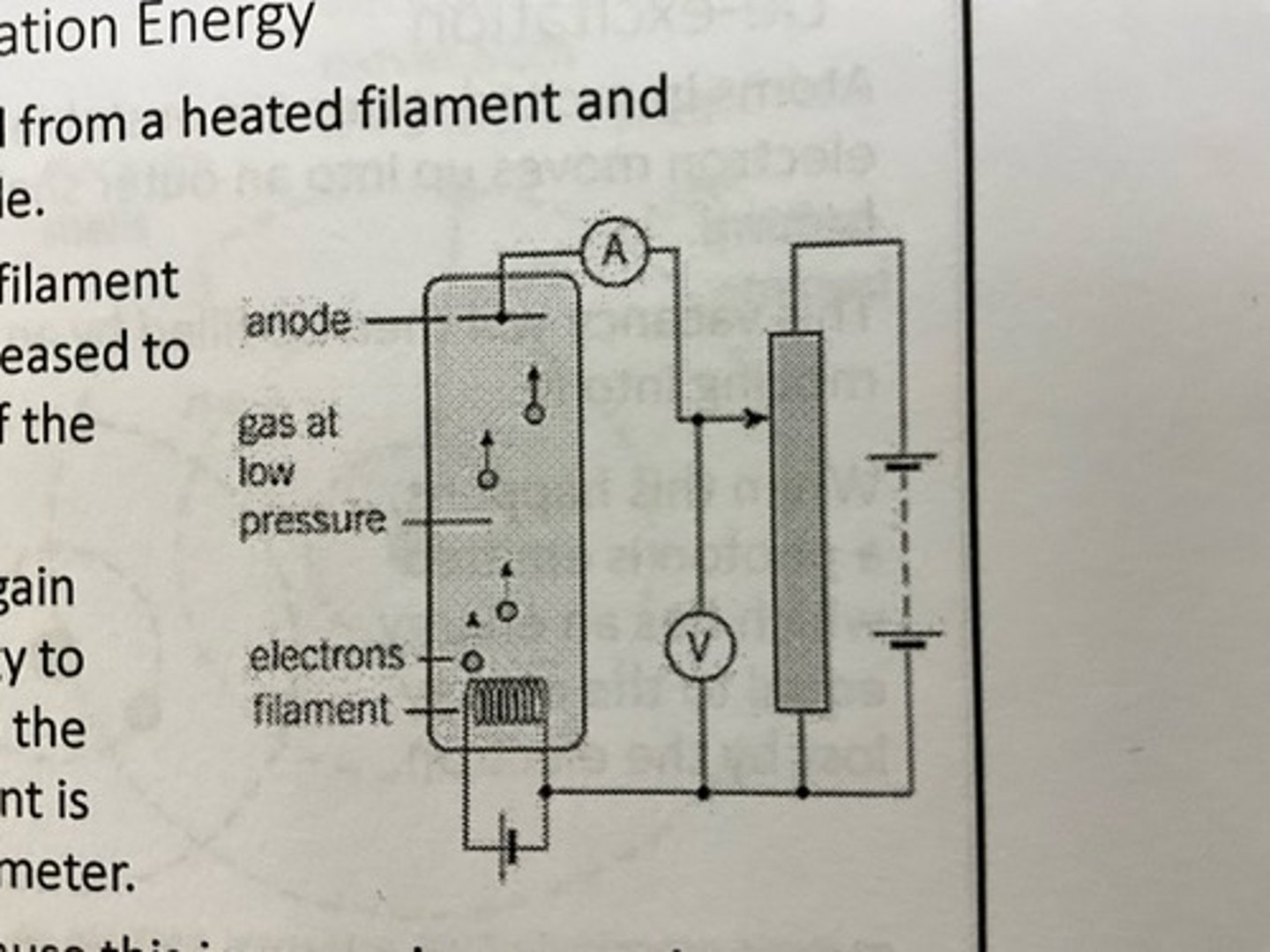
How can we show excitation occurs?
- using apparatus like that used to measure ionisation but with a metal grid between the filament and the ammeter, we see that gas atoms can absorb energy from colliding with electrons without being ionised
- as the p.d. is increased between the filament and the anode, the current due to electrons arriving at the anode will decrease for certain p.d.s. These correspond to the energies which can be absorbed by an atom and are called excitation energies.
Are excitation energies higher or lower than ionisation energies?
lower
If an electron is in a shell closer to the nucleus, does it have more or less energy?
less
What is an atom's ground state?
when all the electrons in an atom are in the lowest possible shells
What is an atom's excited state?
when an atom absorbs energy and one of its electrons moves into a shell at a higher energy
What is an energy level diagram?
A diagram that shows measurements of excitation energies
What is de-excitation of an electron?
The return of an electron from an outer shell to the ground state. A photon with energy equal to the energy lost by the electron is emitted.
What is the difference between direct and indirect de-excitation?
Directly - one photon is emitted
Indirectly - more than one photon is emitted
Why do substances fluoresce?
absorb UV light and emit visible light
Draw a diagram of a fluorescent tube.
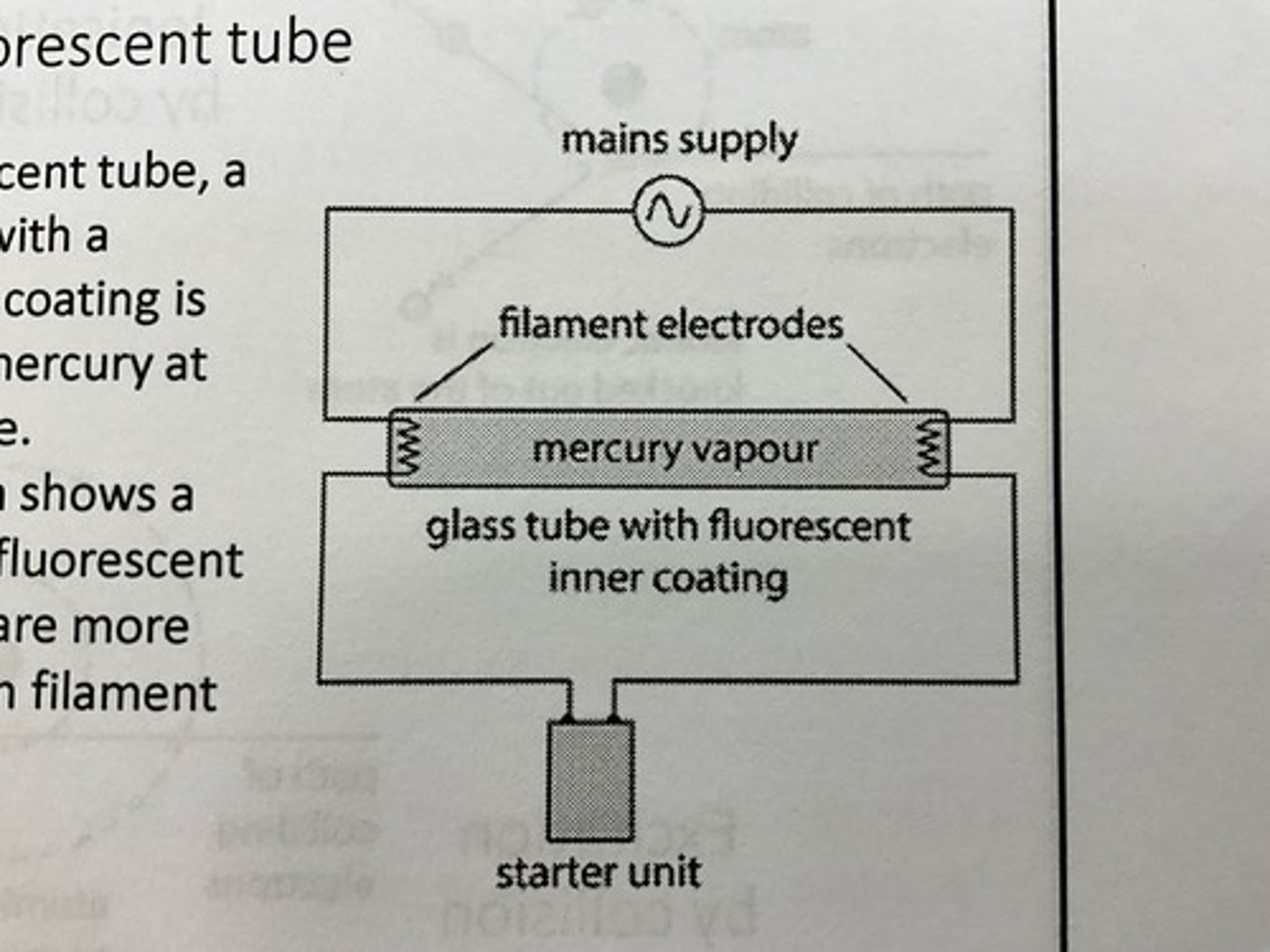
How do fluorescent tubes work?
1) ionisation and excitation of mercury atoms occur as they collide with each other and electrons in the tube.
2) Mercury atoms de-excite emitting UV photons, as well as visible and lower energy photons when they de-excite
3) UV photons are absorbed by atoms in fluorescent coating causing excitation
4) atoms in the coating de-excite, emitting visible light photons.
What is a line spectrum?
contains only specific wavelengths of visible light that are characteristics of the element producing them
What is the energy of an emitted photon equal to?
For an electron moving from energy level E1 to E2, the energy of the emitted photon, hf = E1 - E2