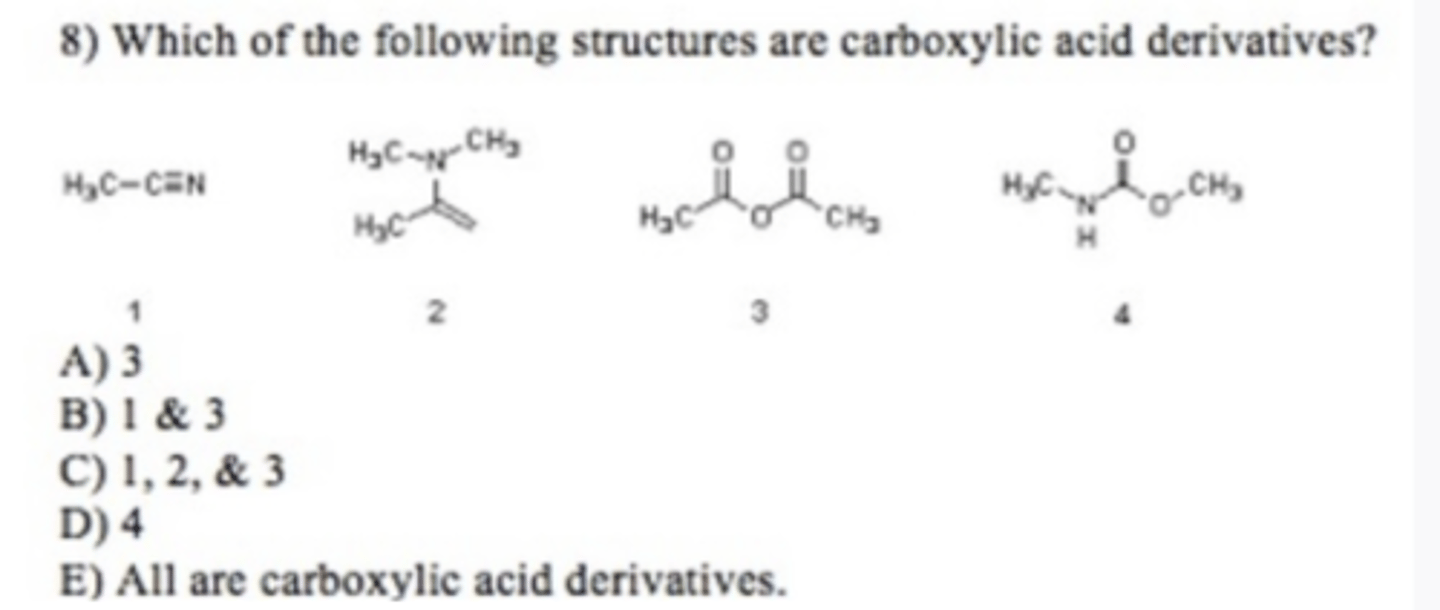
Summer Orgo 2 Exam 3 MC
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
C
Which of the following amines could be formed by reduction of an amide?
1) benzylamine
2) isopropylamine
3) aniline
4) triethylamine
A) 1
B) 3 & 4
C) 1 & 4
D) 2 & 3
E) 1, 3, & 4
C
Secondary amines react with the nitrosonium ion to generate ________
A) diazonium salts
B) oximes
C) N-nitrosoamines
D) imines
E) anilines
A
Heating a(n) ________ results in a Cope elimination.
A) amine oxide
B) imine
C) enamine
D) oxime
E) quaternary ammonium salt
E
Pyridine typically undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution ________ rapidly than benzene, and its preferred site of substitution is the ________ - position.
A) more; 2
B) more; 3
C) more; 4
D) less; 2
E) less; 3
A
A nitrile can be made by dehydrating an amide. However, for this reaction to occur, the amide must be ________.
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) N-methylated
E) part of a lactam
E
What reagent is used to convert pentanamide to 1-pentanamine?
A) POCl3
B) CuCN
C) CH3MgBr
D) SOCl2
E) LiAlH4
A
What type of compound results from the reaction of an acid chloride and a 2° amine?
A) amide
B) 1° amine
C) ester
D) nitrile
E) carboxylate
D
Phthalic acid produces what acid derivative upon heating?
A) an ester
B) a carboxylate
C) an acid chloride
D) an anhydride
E) an amide
A
Two equivalents of methyl magnesium bromide will add to ________.
A) lactones
B) aldehydes
C) ketones
D) imines
E) secondary amines
D
Which of the following compounds containing a tertiary amine?
1) 2-methyl-2-propanamine
2) N-ethylpyrrolidine
3) N-methylcyclohexylamine
4) 2-(dimethylamino)butanal
A) 1
B) 4
C) 3
D) 2 and 4
E
When a 1° amine reacts with an alkyl sulfonyl chloride, the major organic product is __________.
A) a tosylhydrazone
B) a nitrile
C) a sulfoxide
D) an oxime
E) a sulfonamide
C
Which of the following compounds is a 2° amine?
A) cyclohexylamine
B) t-butylamine
C) N-ethylaniline
D) N,N-diethylaniline
E) N-butylpyridinium bromide
B
When pyridine is treated with a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids, the major product is:
A) 2-nitropyridine
B) 3-nitropyridine
C) 4-nitropyridine
D) 3-aminopyridine
E) 4-aminopyridine
B
In 1H NMR protons on the α-carbon of amines typically absorb between θ:
A) 1.0 and 2.0 ppm
B) 2.0 and 3.0 ppm
C) 3.0 and 4.0 ppm
D) 6.0 and 7.0 ppm
E) 9.0 and 10.0 ppm
E
Which of the following is a secondary amine?
A) cyclohexylamine
B) 3-pentanamine
C) methylamine
D) N,N-dimethylaniline
E) N-ethyl-1-propanamine
D
Which of the following is a tertiary amine?
A) cyclohexylamine
B) 3-pentanamine
C) methylamine
D) N,N-dimethylaniline
E) N-ethyl-1-propanamine
E
Which of the following amines is most soluble in water?
A) pyrrolidine
B) PhNH2
C) (CH3)3N
D) (CH3CH2CH2)2NH
E) ethylamine
C
Which of the following amines can be resolved into enantiomers?
A) trimethylamine
B) 3-pentanamine
C) 2-pentanamine
D) dimethylammonium chloride
E) 4-(dimethylamino) pyridine
E
The nitrogen atom of trimethylamine is ________ hybridized which is reflected in the CNC bond angle of ________.
A) sp, 180°
B) sp2, 120°
C) sp2, 108°
D) sp3, 120°
E) sp3, 108°
B
The nitrogen's lone pair in pyrrolidine is best described as occupying what type of orbital?
A) s
B) sp3
C) sp2
D) sp
E) p
D
Which of the following amines is most basic?
A) aniline
B) N-ethylaniline
C) N,N-diethylaniline
D) piperidine
E) pyrrole
D
Which of the following amines is the strongest base?
A) cyclohexylamine
B) pyrrole
C) p-iodoaniline
D) piperidine
E) imidazole
C
In the mass spectrum of dipropylamine, the base peak appears at m/z ________.
A) 101
B) 86
C) 72
D) 58
E) none of the above
B
The α-carbon atom bonded to the nitrogen of an alkylamine usually appears in what chemical shift (δ) range?
A) 5-20
B) 30-50
C) 80-100
D) 120-150
E) 180-220
D
A three-carbon, nitrogen-containing compound exhibits 3 13C NMR peaks (d 11.2, 27.3, and 44.9). Which of the following compounds best matches this spectral data?
A) H2NCH2CH2CH2OH
B) (CH3)2CHNH2
C) CH3NHCH2CH3
D) CH3CH2CH2NH2
E) CH3CH2C≡N
C
When pentanal reacts with ethylamine under conditions of acid catalysis, the major organic product is ________.
A) a ketone
B) a nitrile
C) an imine
D) an oxime
E) a hydrazone
E
When CH3CH2CHO reacts with PhNHNH2 under conditions of acid catalysis, the major organic product is ________.
A) a ketone
B) a nitrile
C) an imine
D) an oxime
E) a hydrazone
D
Which of the following chloropyridines readily undergo nucleophilic substitution upon treatment with NaCN?
A) 2-chloropyridine
B) 3-chloropyridine
C) 4-chloropyridine
D) both A and C
E) both A and B
B
When pyridine is treated with a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids, the major product is:
A) 2-nitropyridine.
B) 3-nitropyridine.
C) 4-nitropyridine.
D) 3-aminopyridine.
E) 4-aminopyridine.
B
Which compound would react most rapidly with sodium methoxide and heat?
A) chlorobenzene
B) 2-chloropyridine
C) 3-chloropyridine
D) 3-chloropyrrole
A
The Hofmann elimination proceeds via a(n) ________ pathway.
A) E2
B) E1
C) SN1
D) SN2
E) none of the above
B
Sec-Butylamine is the common name of what compound?
A) 1-butanamine
B) 2-butanamine
C) N-methyl-1-propanamine
D) N-methyl-2-propanamine
E) N-ethylethanamine
B
Which of the following is not an alkaloid?
A) cocaine
B) mesitylene
C) nicotine
D) mescaline
E) morphine
B

A
Physostigmine is used in the treatment of glaucoma. Within the structure, the atom indicated by _______ is most basic, while atom ______ is least basic.
A)1 (most basic), 4 (least basic)
B)2 (most basic), 3 (least basic)
C)1 (most basic), 3 (least basic)
D)2 (most basic), 4 (least basic)
E)None of the above
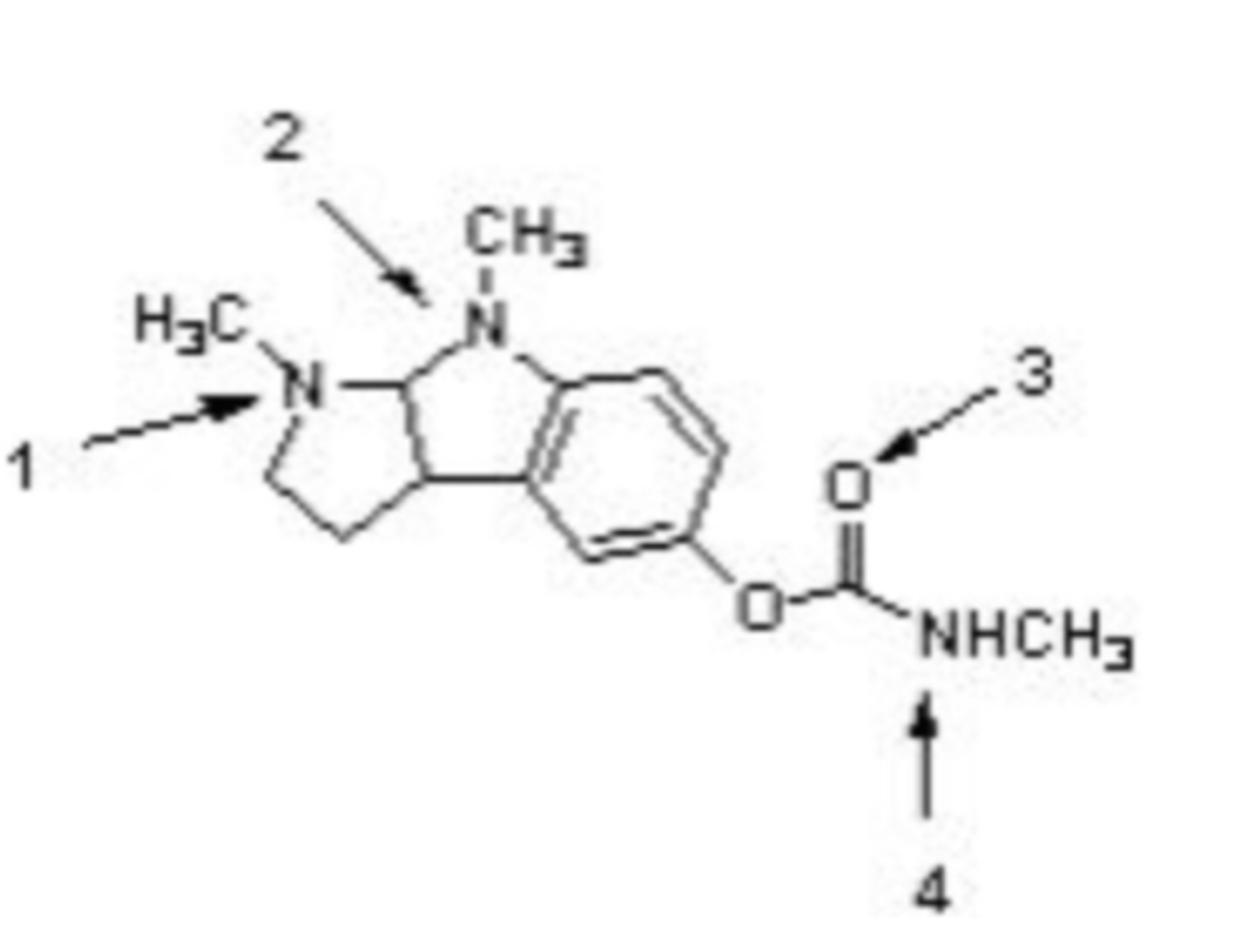
E
N-Methylacetamide is an example of:
A) a primary amide
B) a secondary amide
C) a tertiary amide
D) an N, N-disubstituted amide
E) an imine
B
Cyclic amides are called:
A) lactones.
B) lactams.
C) aminals.
D) animals.
E) imines.
B
Amides are less basic than amines because:
A) the carbonyl group donates electrons by resonance.
B) the carbonyl group withdraws electrons by resonance.
C) the nitrogen does not have a lone pair of electrons.
D) the nitrogen has a full positive charge.
E) amides do not contain nitrogen.
A
Cyclic esters are called:
A) lactones.
B) lactams.
C) lacrimals.
D) imides.
E) enamines.
C
The correct priority of functional groups in IUPAC nomenclature is:
A) ester > amide > ketone > acid.
B) ketone > acid > ester > amide.
C) acid > ester > amide > ketone.
D) amide > acid > ester > ketone.
E) amide > ester > acid > ketone.
C
Which of the following are strongly hydrogen bonded in the liquid phase?
A) nitriles
B) esters
C) secondary amides
D) tertiary amides
E) acid chlorides
C
While the carbonyl stretching frequency for simple aldeydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids is about 1710 cm-1, the carbonyl stretching frequency for esters is about:
A) 1660 cm-1
B) 1700 cm-1
C) 1735 cm-1
D) 1800 cm-1
E) 2200 cm-1
C
While the carbonyl stretching frequency for simple aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids is about 1710 cm-1, the carbonyl stretching frequency for acid chlorides is about:
A) 1700 cm-1
B) 1735 cm-1
C) 1800 cm-1
D) 1660 cm-1
E) 2200 cm-1
D
While the carbonyl stretching frequency for simple aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids is about 1710 cm-1, the carbonyl stretching frequency for amides is about ________.
A) 1700 cm-1
B) 1735 cm-1
C) 1800 cm-1
D) 1660 cm-1
E) 2200 cm-1
D
The most characteristic IR stretch of butanenitrile occurs at approximately what wavenumber?
A) 3500 cm-1
B) 3100 cm-1
C) 2600 cm-1
D) 2200 cm-1
E) 1750 cm-1
A
The chemical shifts for protons α to a carbonyl group:
A) are similar for all acid derivatives.
B) are farthest downfield for carboxylic acids.
C) are farther downfield than those α to a nitrile.
D) fall between δ 3.1 and δ 4.2 (ppm).
E) fall between δ 1.3 and δ 1.8 (ppm).
D
In the proton NMR spectrum of a secondary amide, the amide proton's signal is:
A) sharp, around δ 5.0 (ppm).
B) sharp, around δ 10.0 (ppm).
C) broad, around δ 9.0 (ppm).
D) broad, around δ 7.0 (ppm).
E) usually not observed.
B
Which compound has a carbonyl stretch in its IR spectrum at the lowest wavenumber?
A) acetic anhydride
B) formamide
C) cyclohexanone
D) propanoyl chloride
E) ethyl acetate
D
Which of the following is the most reactive carboxylic acid derivative?
A) ester
B) anhydride
C) nitrile
D) acid chloride
E) amide
E
A correct order of reactivity of acid derivatives towards nucleophilic attack is:
A) esters > acid anhydrides > amides.
B) anhydrides > amides > esters.
C) carboxylates > esters > amides.
D) anhydrides > acids > acid chlorides.
E) anhydrides > amides > carboxylates.
C
In nucleophilic acyl substitution, :
A) protonation of the carbonyl is followed immediately by loss of the leaving group.
B) loss of the leaving group is followed by rearrangement of the carbocation.
C) addition to the carbonyl by a nucleophile is followed by loss of the leaving group.
D) ester hydrolysis is followed by deprotonation.
E) an SN2 reaction occurs.
E
The hydrolysis of esters in base is called:
A) the Fischer esterification.
B) the Hunsdiecker reaction.
C) the Dieckmann condensation.
D) transesterification.
E) saponification.
A
Typically, amides will hydrolyze under __________ conditions than esters.
A) stronger
B) more dilute
C) milder
D) less vigorous
E) more saline
A
The hydrolysis of esters, amides, and nitriles:
A) can be carried out under acidic or basic conditions.
B) must be acid-catalyzed.
C) must be base-catalyzed.
D) should be carried out at pH 7.0 for optimum efficiency.
E) is not pH dependent.
E
Which of the following compounds is(are) hydrolyzed to butanoic acid upon heating in
H2O, H2SO4?
A) ethyl butanoate
B) butyl acetate
C) N-methylbutanamide
D) both A and B
E) both A and C
B
Lithium aluminum hydride reduces carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, and esters to:
A) aldehydes.
B) primary alcohols.
C) secondary alcohols.
D) tertiary alcohols.
E) ketones.
B
Acids can be reduced to aldehydes by:
A) treatment with LiAlH4
B) conversion to the acid chloride followed by treatment with LiAlH[OC(CH3)3]3.
C) conversion to the amide followed by treatment with NaBH4.
D) conversion to the ester followed by treatment with LiAlH4.
E) conversion to the anhydride followed by treatment with Mg and H3O+.
E
Acids can be converted to primary amines by:
A) conversion to the nitrile followed by treatment with LiAlH4.
B) conversion to the diazonium salt followed by treatment with NaBH4.
C) conversion to the primary amide followed by treatment with LiAlH4.
D) both A and B.
E) both A and C.
D
What compound is produced when N,N-dimethylpropanamide is treated with LiAlH4?
A) CH3CH2CONH2
B) CH3CH2CH2NH2
C) CH3CH2CH2OH
D) CH3CH2CH2N(CH3)2
E) CH3CH2N(CH3)2
H
Starting with an acid chloride and any other chemical reagent you've learned in organic chemistry, which of the following functional groups can be synthesized in three steps or less?
A) primary alcohol
B) tertiary alcohol
C) ester
D) aldehyde
E) amine
F) only A and C
G) only C, D and E
H) all of the above (A - E)
A
Which of the following statements is/are true?
A) Two equivalents of Grignard reagent react with acid chlorides to yield tertiary alcohols after hydrolysis.
B) LiAlH4 reacts with acid chlorides to yield secondary alcohols after hydrolysis. Still primary
C) LiAlH[OC(CH3)3]3 reacts with acid chlorides to yield primary alcohols after hydrolysis.
D) both A and B
E) both B and C
C
Which of the following reagents convert(s) benzoyl chloride to phenyl propyl ketone?
A) CH3CH2CH2MgBr
B) CH3CH2CH2Li
C) (CH3CH2CH2)2CuLi
D) both A and B
E) both A and C
D
Which of the following compounds, when reacted with aniline, yield(s) acetanilide?
A) acetyl chloride
B) acetic anhydride
C) methyl butanoate
D) both A and B
E) both A and C
A
What type of compound results from the reaction of ethyl formate with cyclohexylamine?
A) amide
B) 1° amine
C) acid anhydride
D) nitrile
E) carboxylate
A, C, D
Assuming equal molecular weights, mark all of the following compounds, indicated by their functional group, that would have a higher boiling point than an alcohol. (More than one answer is possible.)
A) carboxylic acid
B) ester
C) nitrile
D) 3° amide
D

A
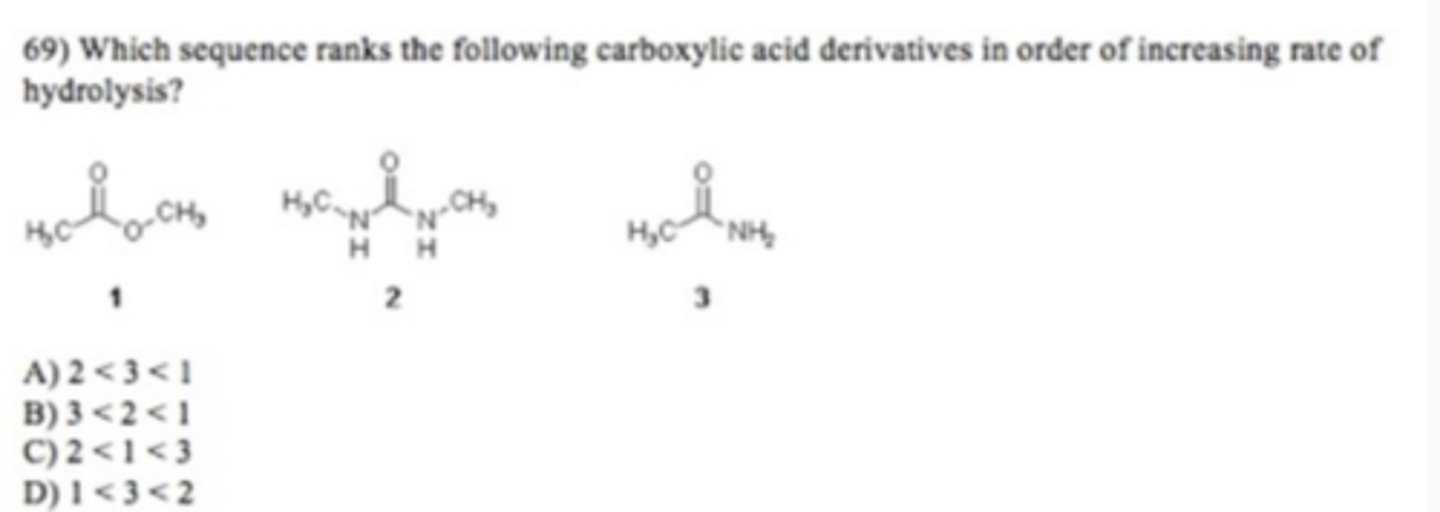
A
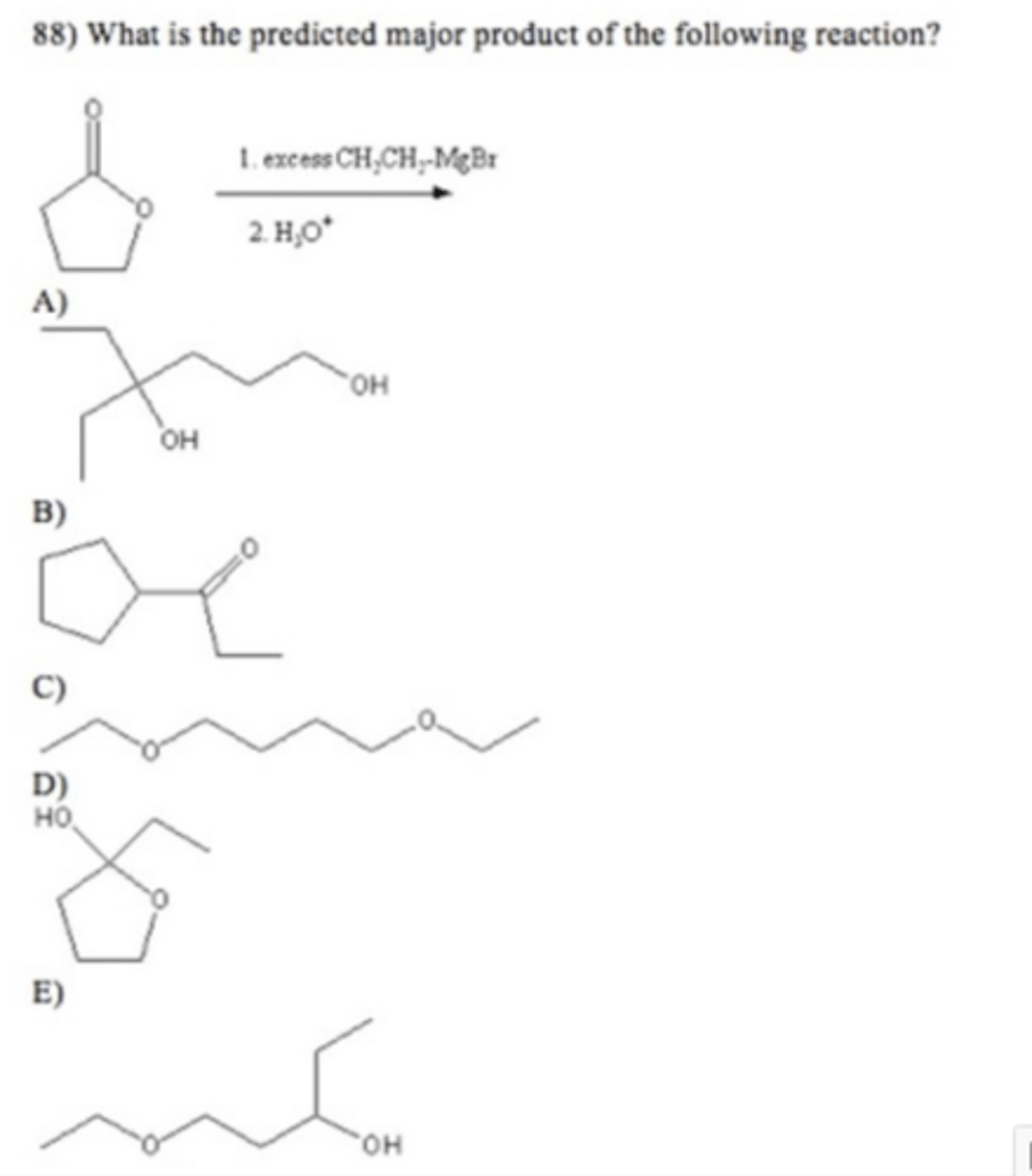
C
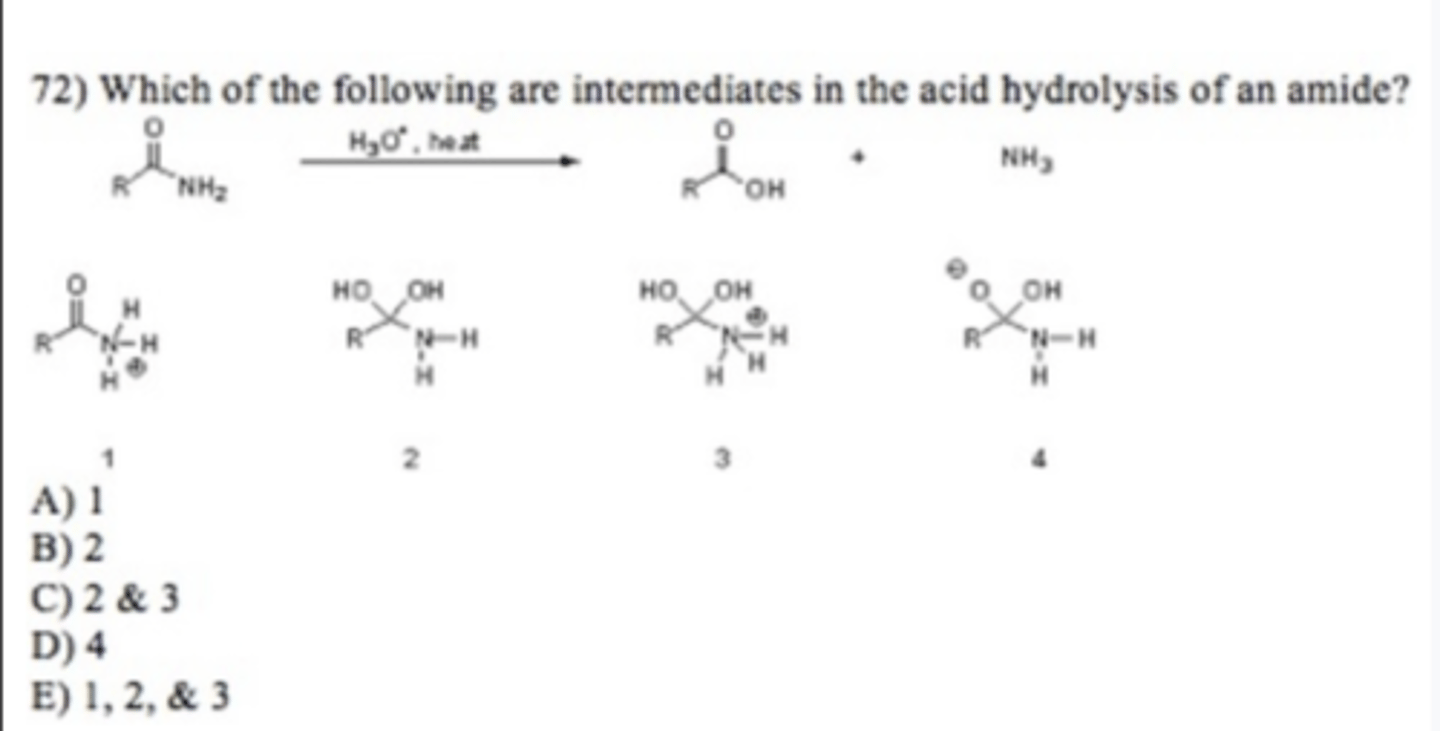
A
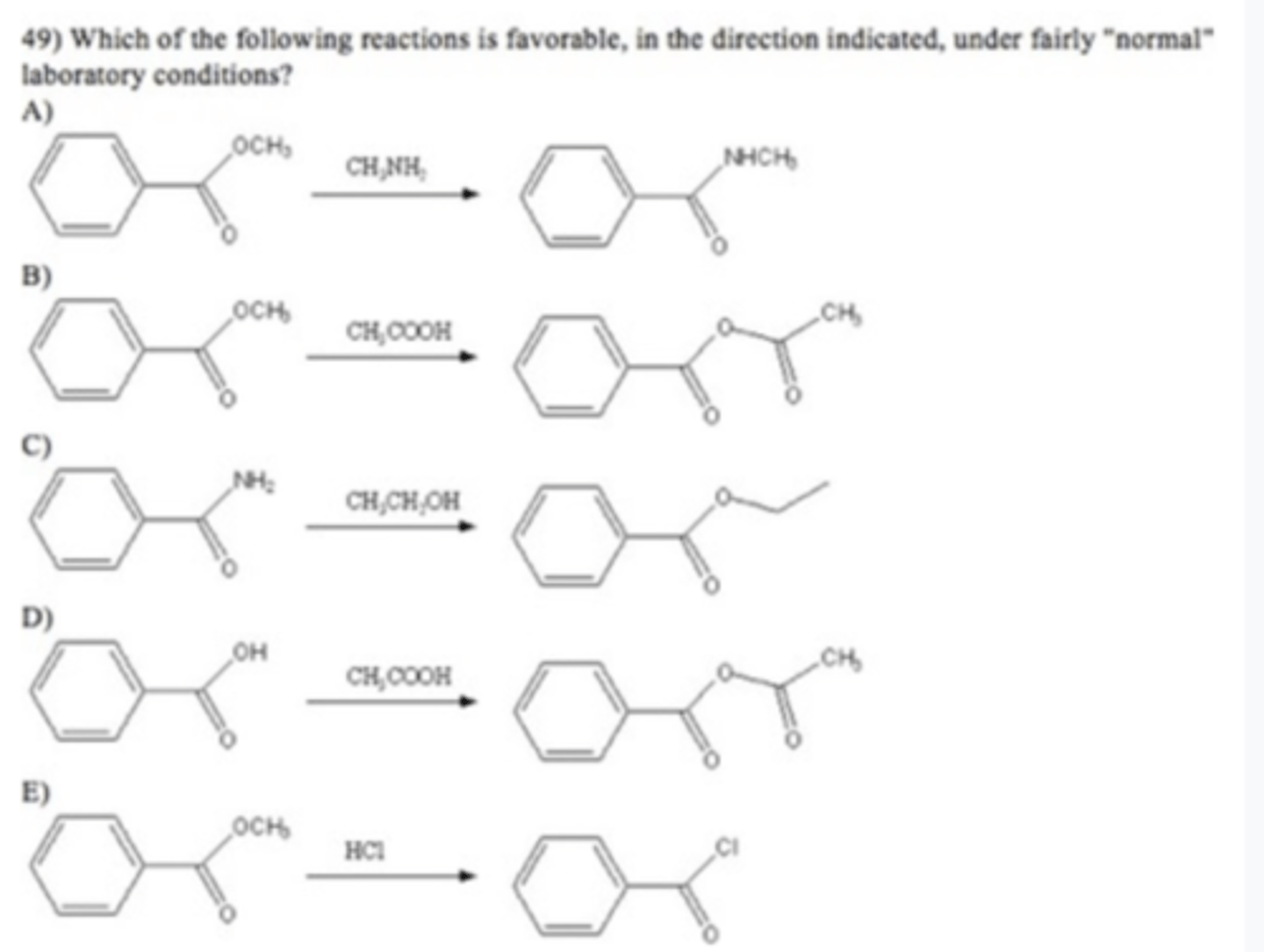
A
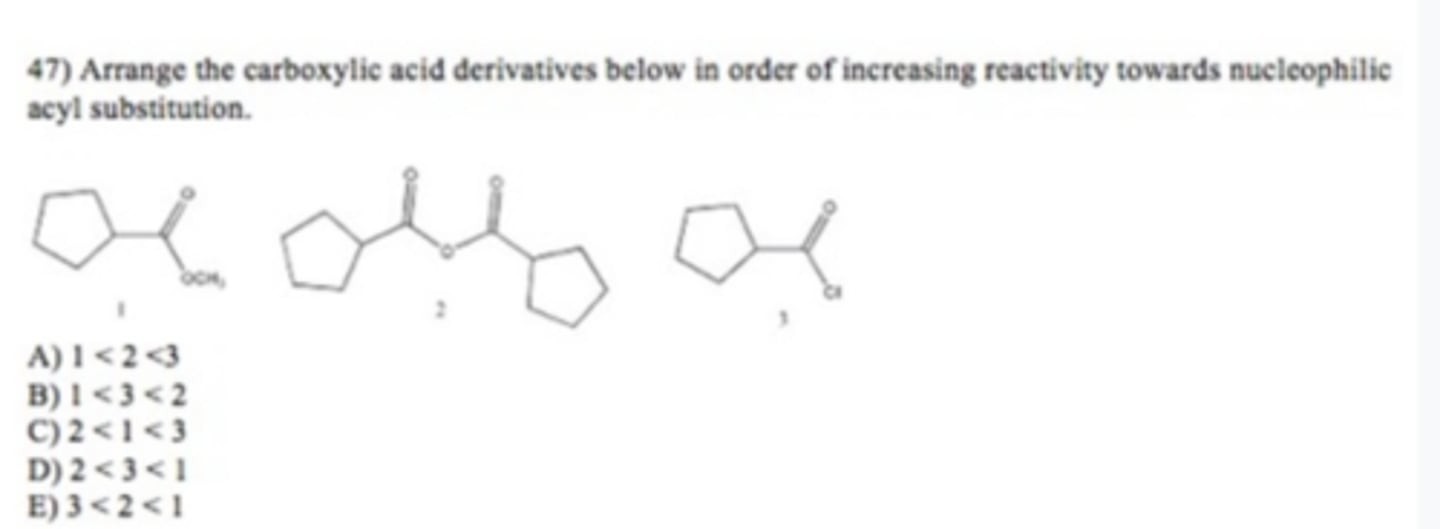
A

C

C