The circulatory system
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
circulatory system other names
cardiovascular system
vascular system
circulatory system function
allows blood to circulate around the body
transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, waste and blood cells to and from each cell in the body
what is the circulatory system made up of?
heart, blood, blood vessels
role of the heart
pumps blood around the body by contracting and relaxing
role of the blood
pumped around the body and heart via a network of vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries)
double circulatory system
blood travels through two circuits: the pulmonary and systematic
types of blood vessels
arteries, veins, capillaries
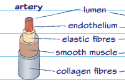
arteries structure and function
carry oxygenated blood at higher pressure from the heart to parts of the body so they have a thick layer of tissue in the wall
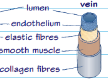
veins structure and function
carry deoxygenated blood at lower pressure from the body back to the heart so have less elastic tissue than arteries
valve function
open and close to allow blood flow due to pressure changes in the chambers
stop blood from flowing backwards (backflow)
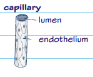
capillary structure and function
thin walls to allow exchange of compounds e.g. nutrients, glucose, oxygen and co2 between blood and tissues
artery diagram
vein diagram
capillary diagram
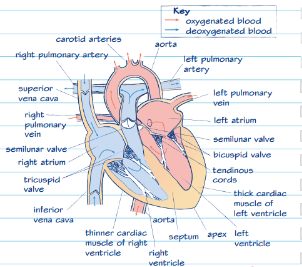
how many chambers in mammal and bird hearts?
four
structure of mammal and bird hearts
4 chambers
efficient - does not allow oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to mix
aorta - very elastic and thick as it has to withstand large pressures as it carries oxygenated blood away from the heart
vena cava - transports deoxygenated blood to the heart. not as thick as not under as much pressure (made up of superior and inferior vena cava)
oxygenated colour
red
deoxygenated colour
blue
largest artery
aorta
aorta function
carries oxygenated blood away from the heart
vena cava function
transports deoxygenated blood to the heart
types of vena cava
superior and inferior
types of heart chambers
atria and ventricles
compare atria and ventricles
both have muscular walls that helps them pump blood
ventricles are more muscular as blood must be forced out of the heart at a higher pressure and around the body
left side of heart vs right side
left is more muscular as it pumps blood around the body
right side just pumps blood to the lungs
heart diagram