L23 The Auditory System (Imported from Quizlet)
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
The vibration of air particles that gets passed along until it eventually reaches our ears
What is sound?
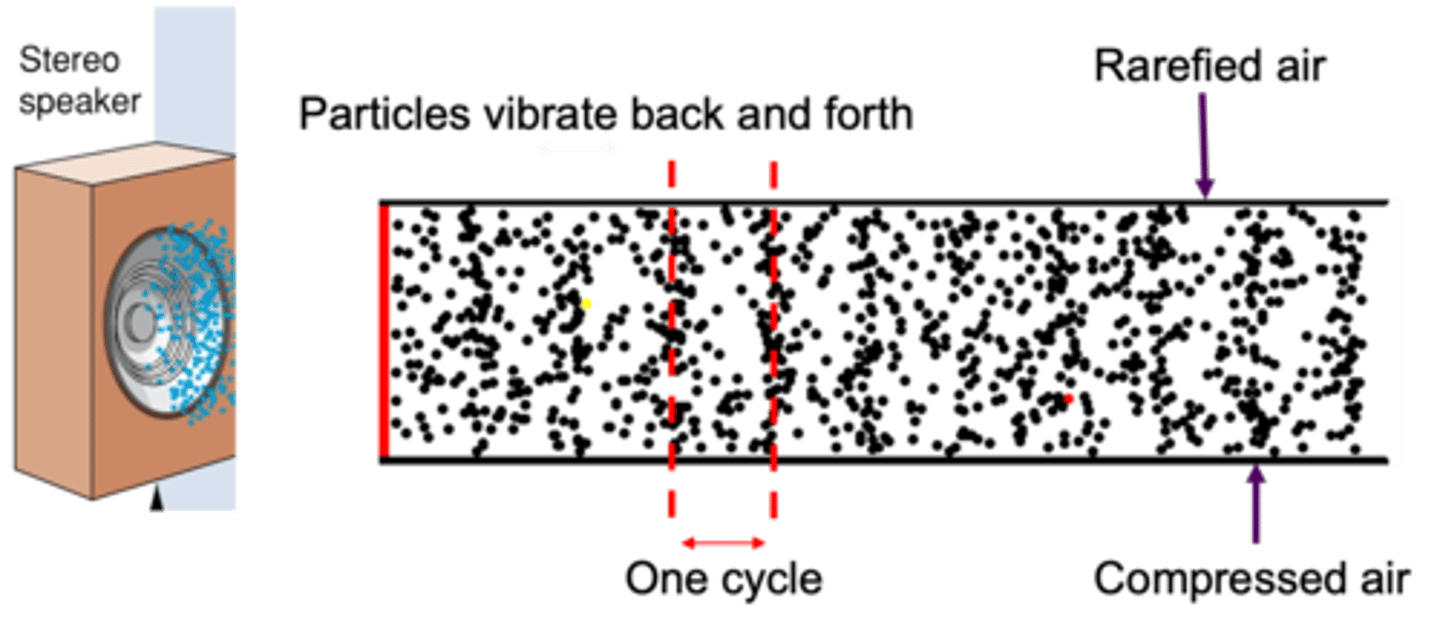
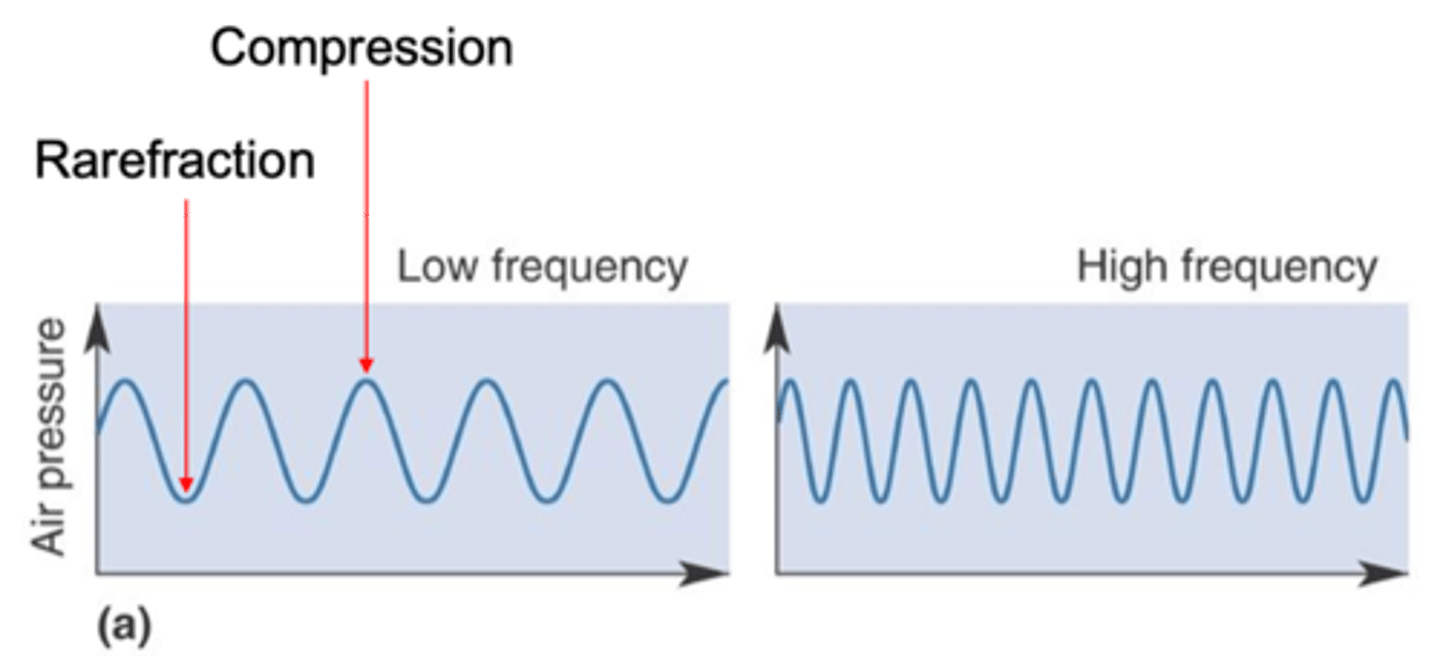
Number of compressed or rarefied patches of air that pass by our ears each second
What is frequency?
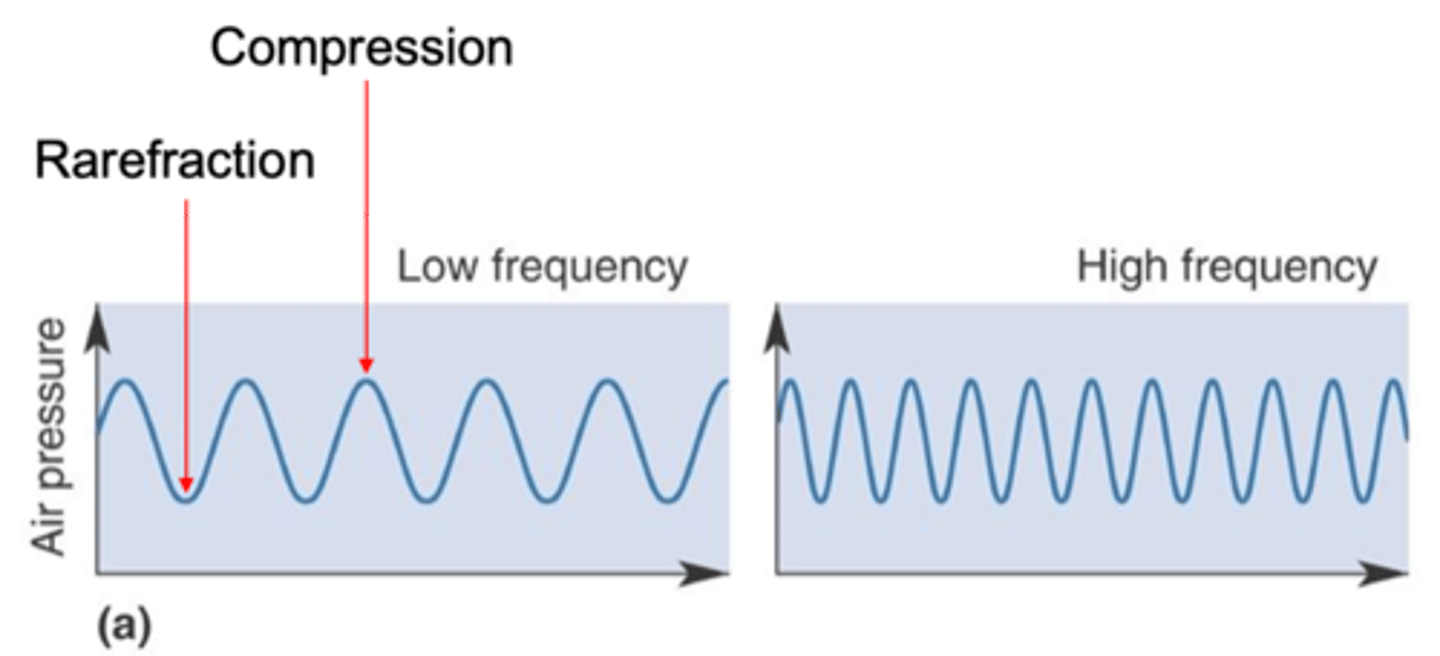
Hertz (Hz)
What is frequency expressed as?
Air pressure difference between peaks and troughs
What is intensity (or amplitude)?
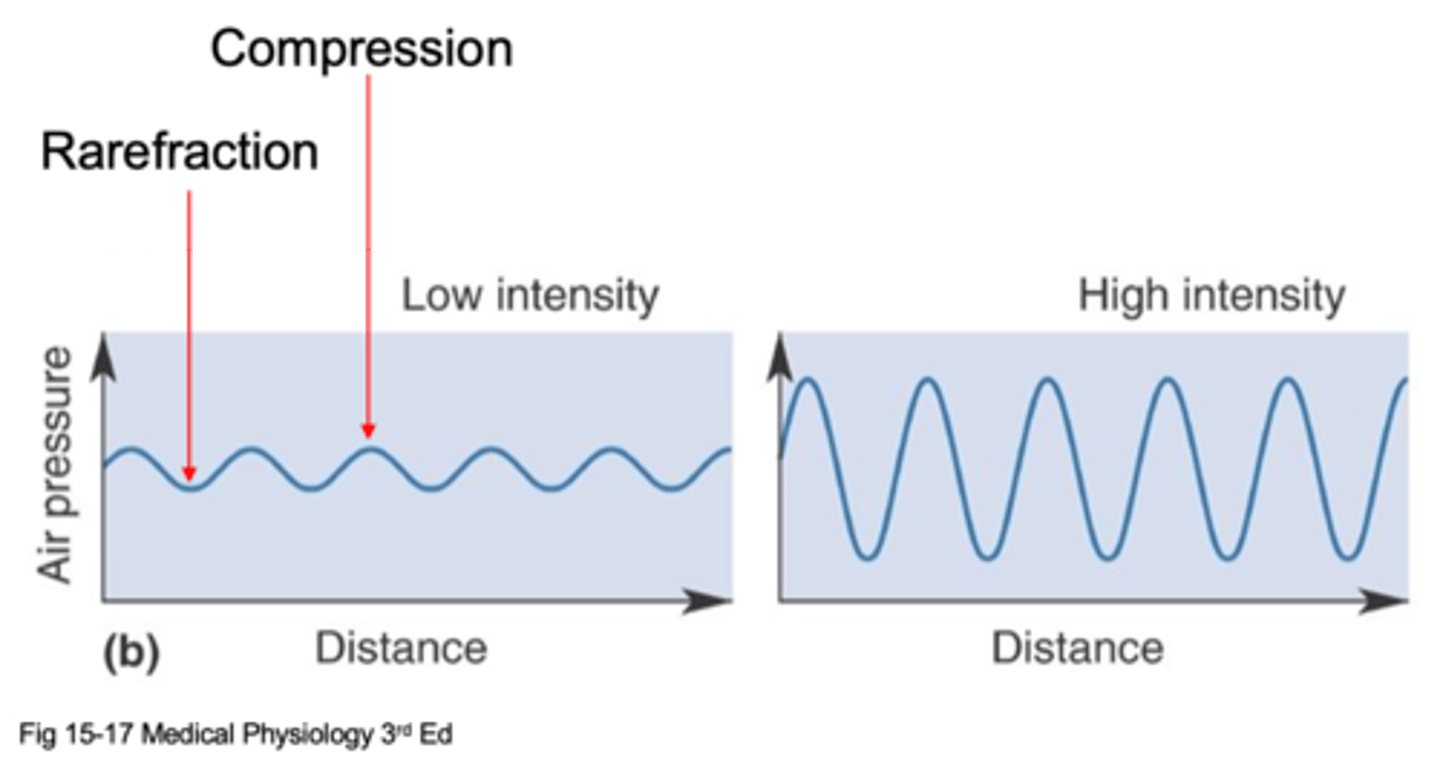
Decibels (dB)
What is intensity/amplitude expressed as?
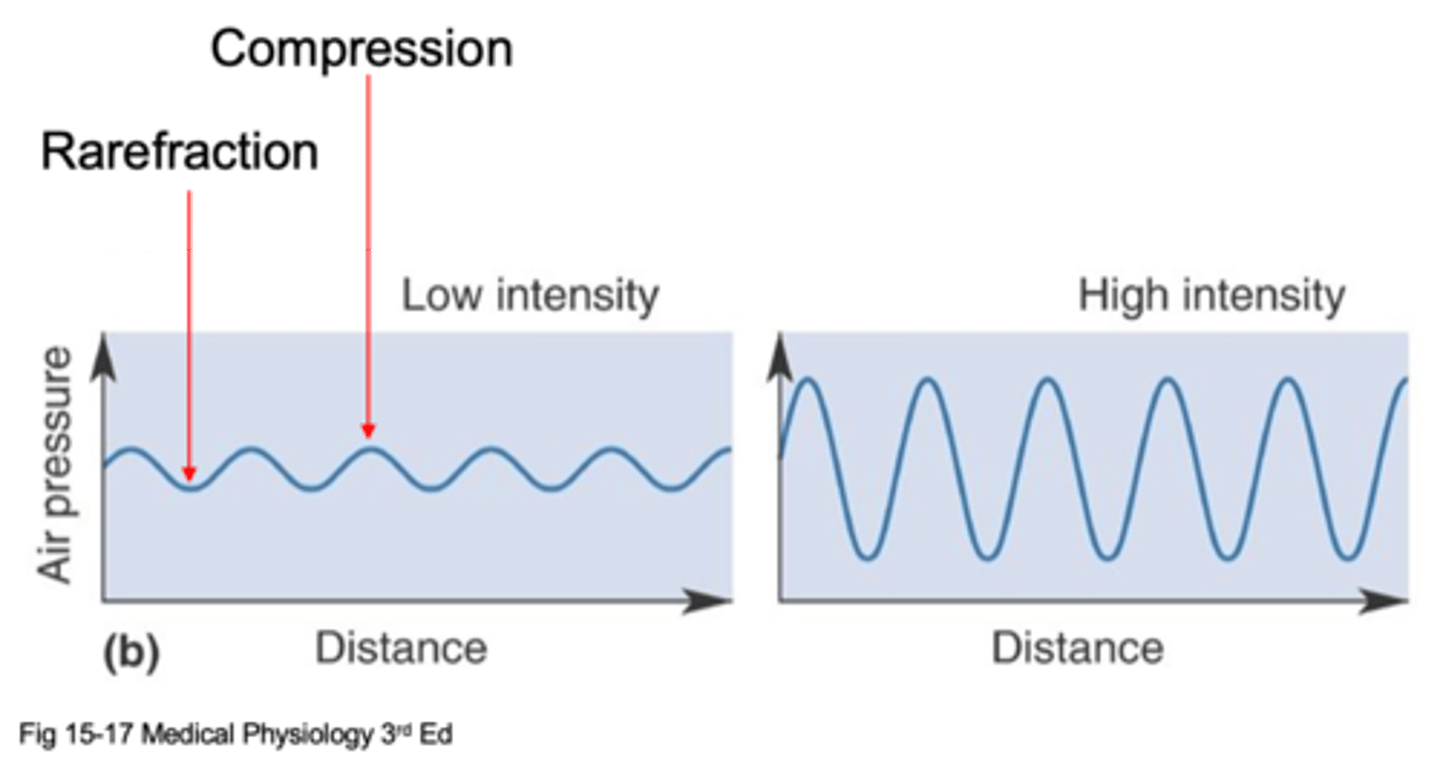
Logarithmic
What kind of scale is decibels?
20, 20000
Human hearing range = __Hz to _____Hz
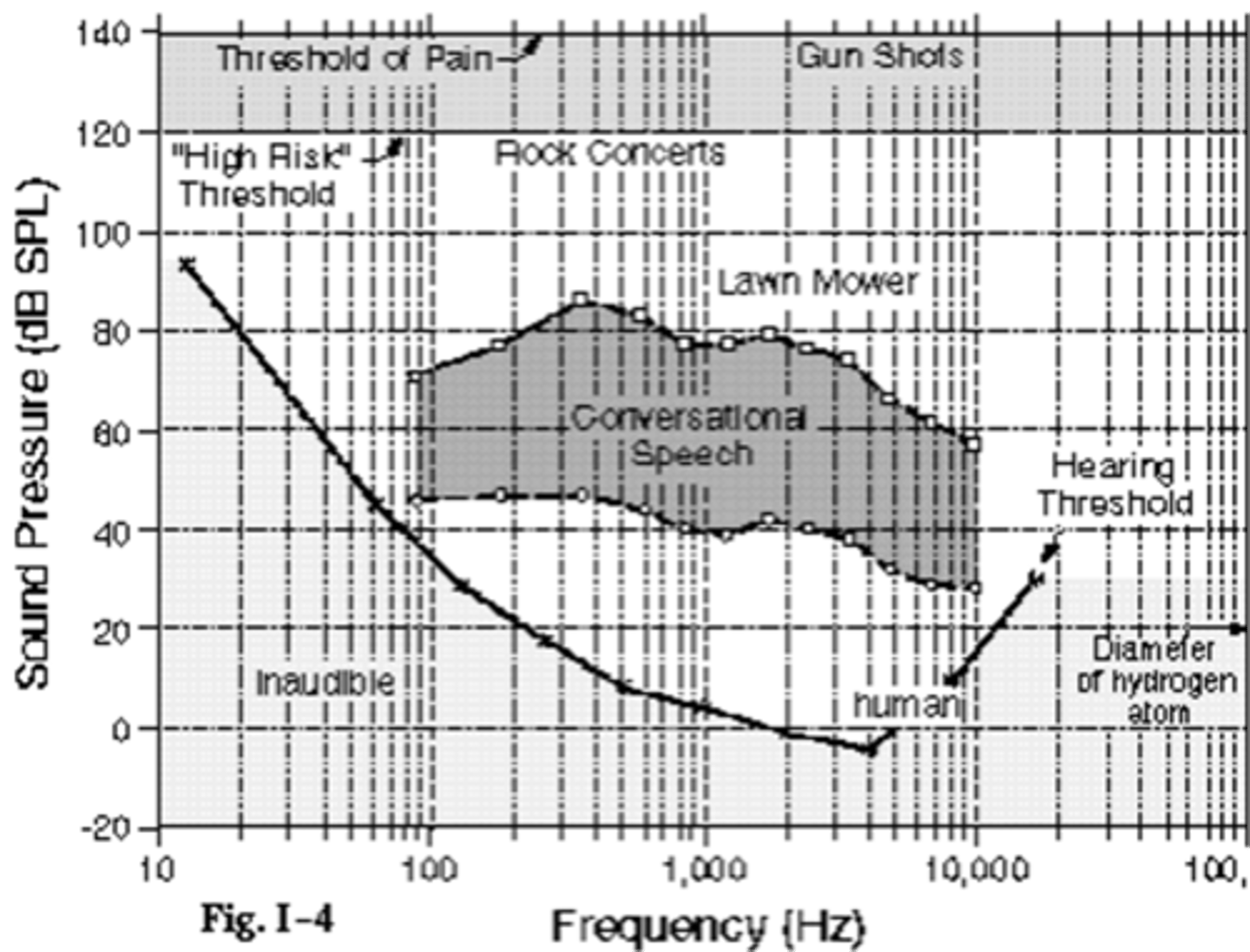
The frequency
Sound intensity depends on what?
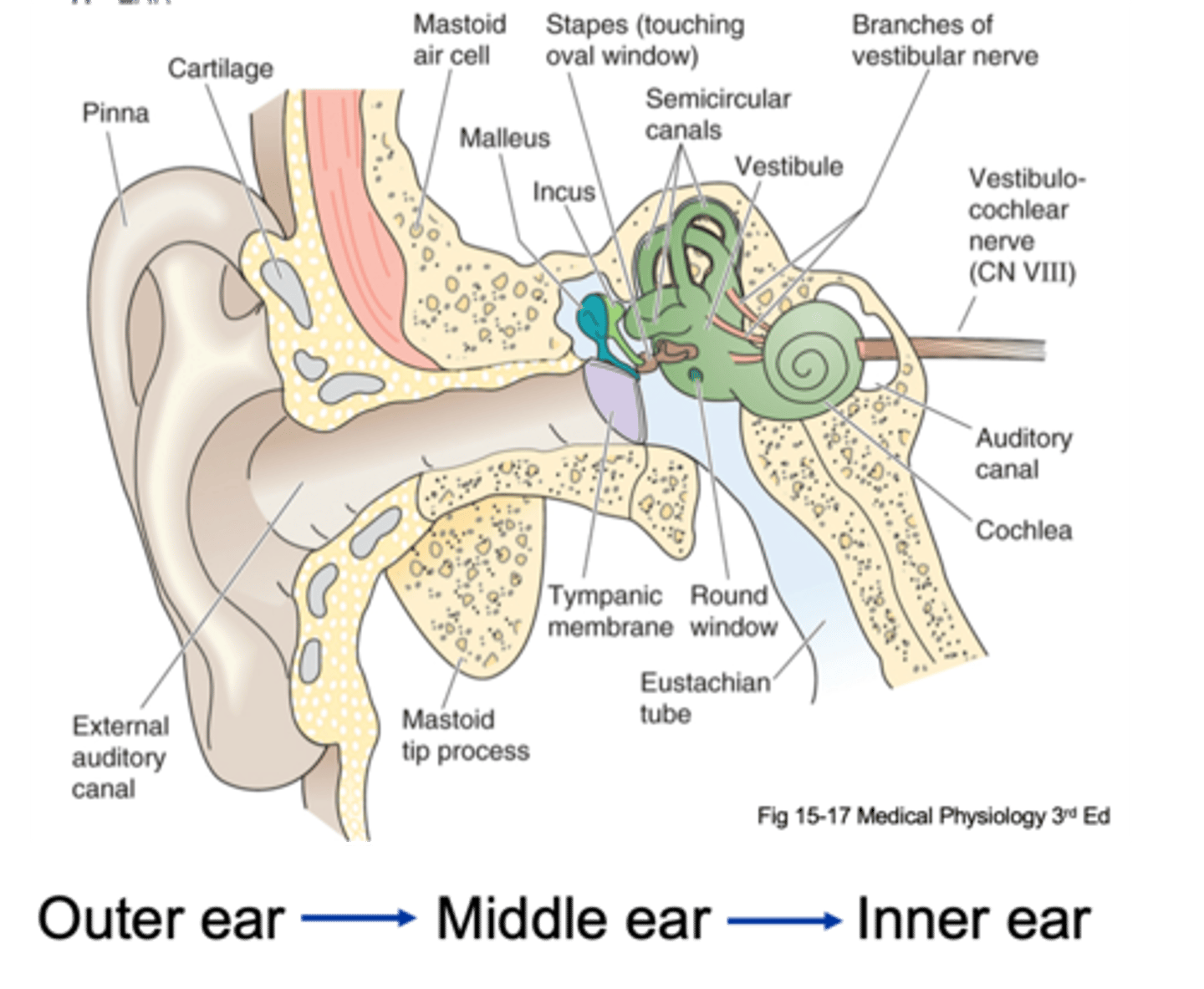
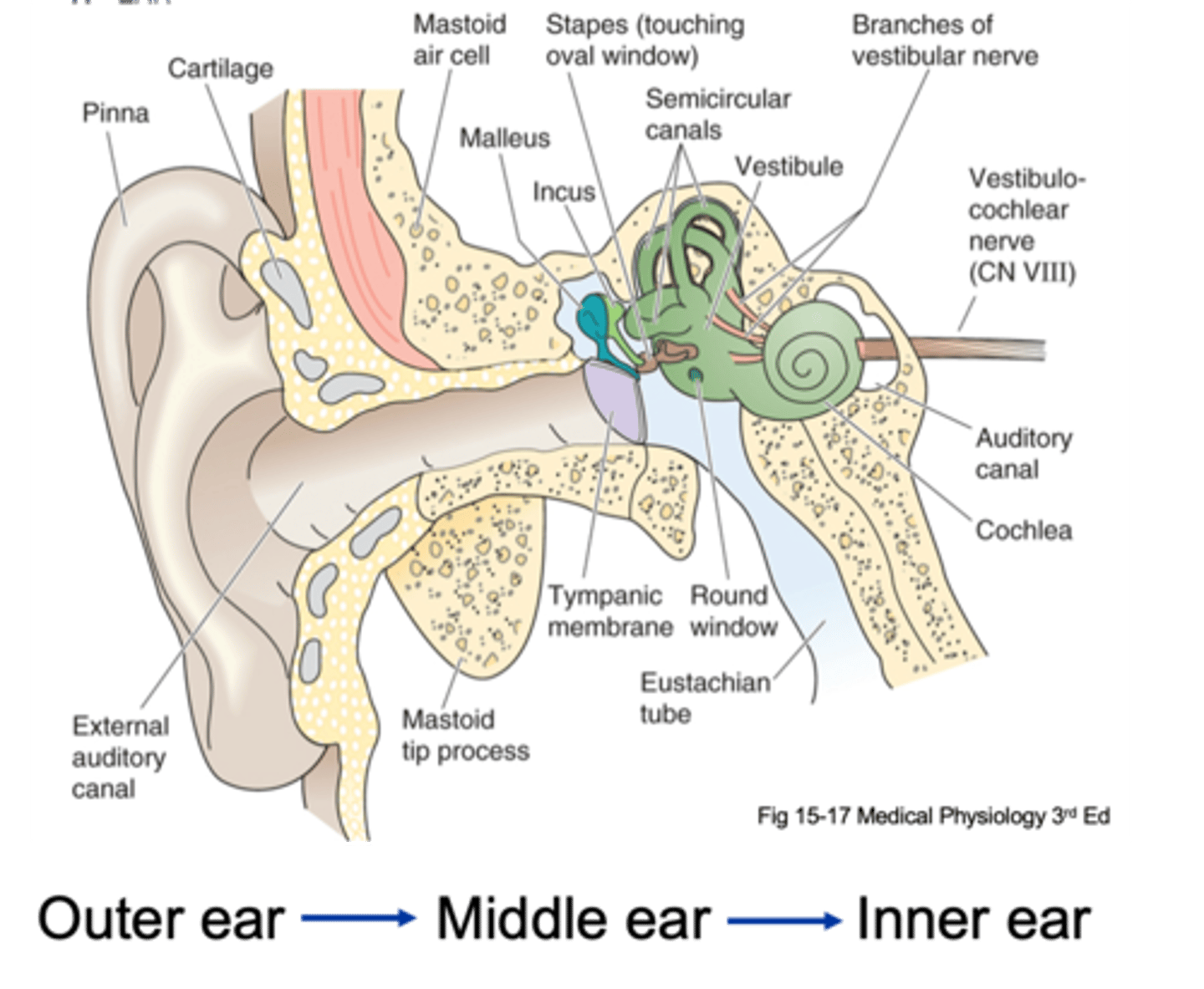
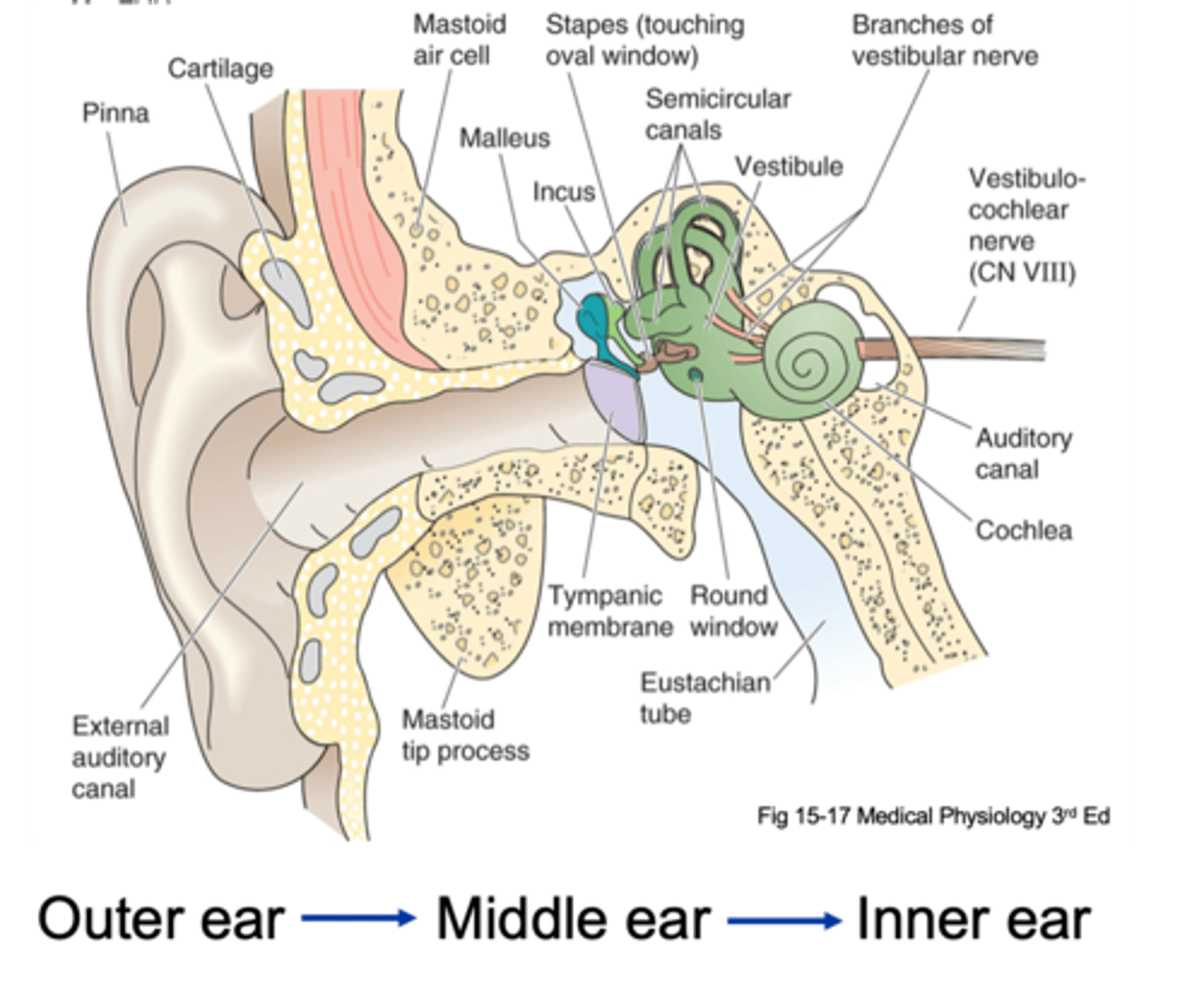
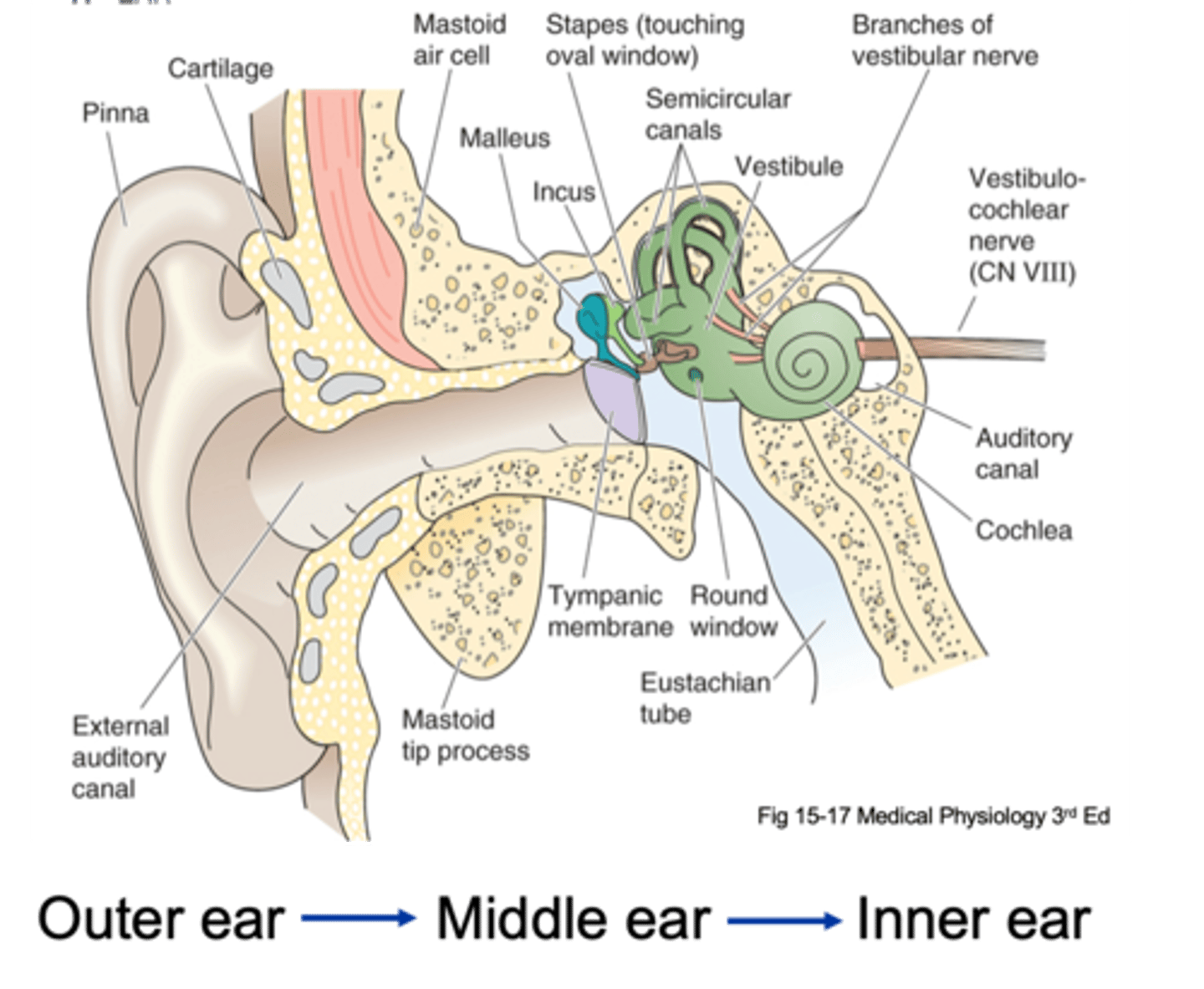
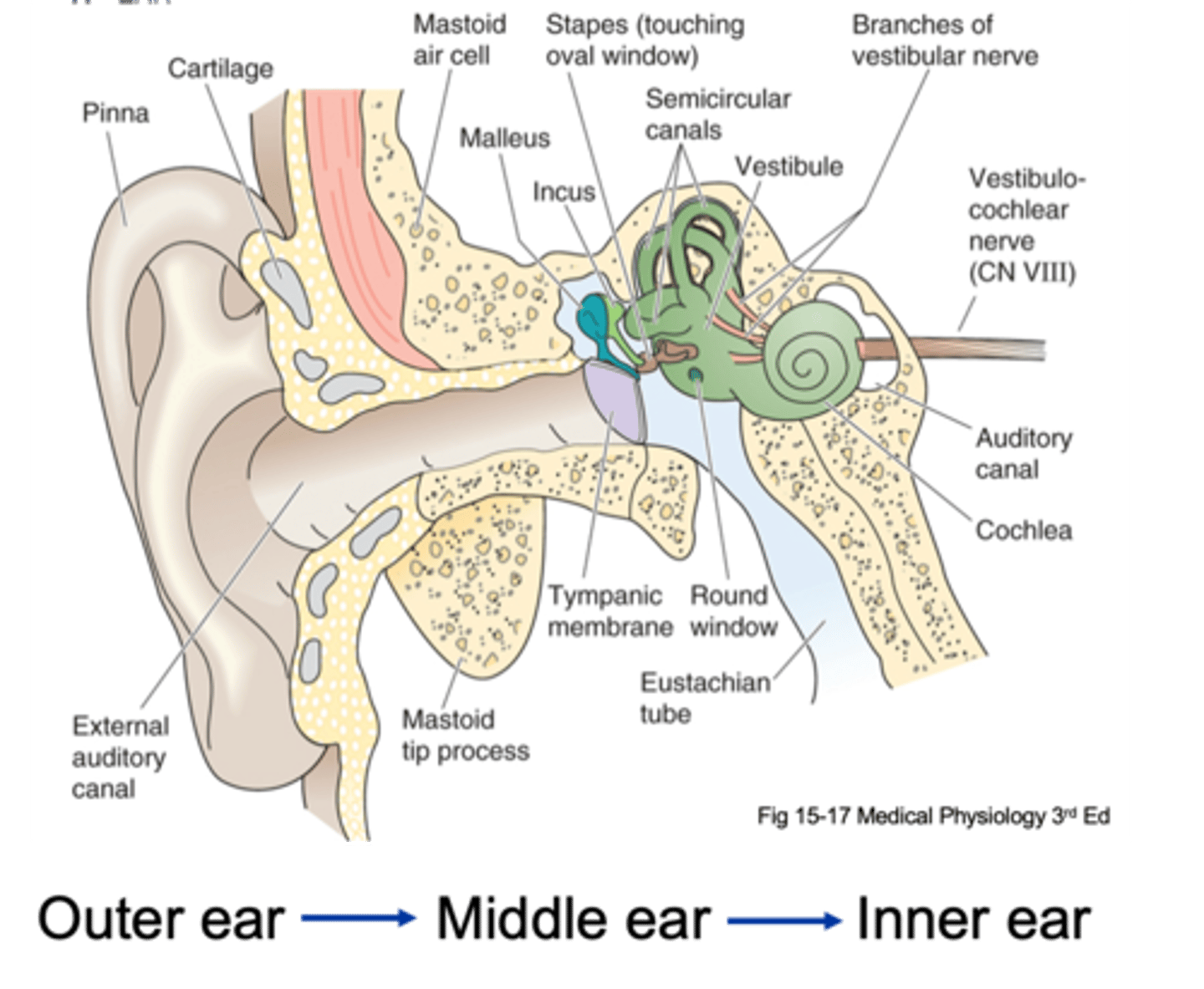
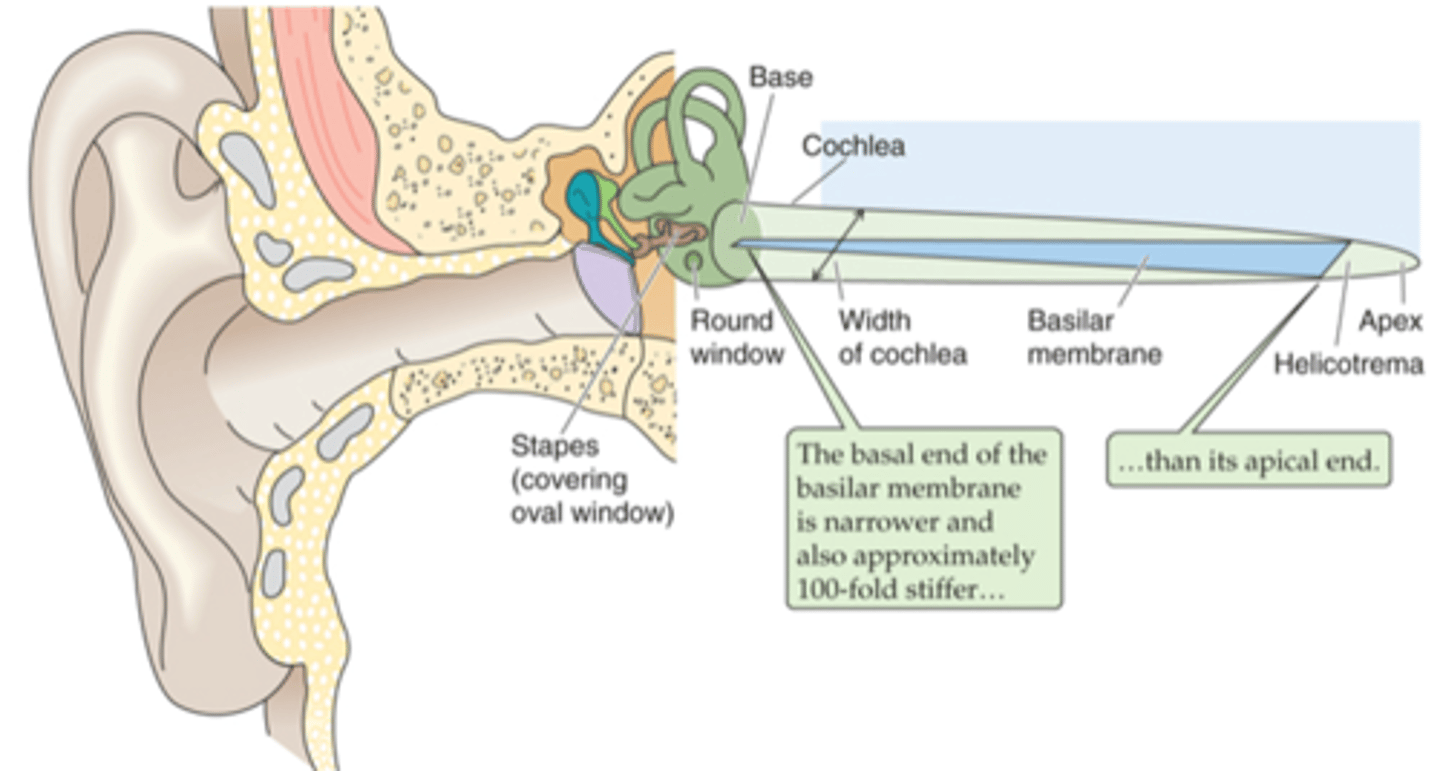
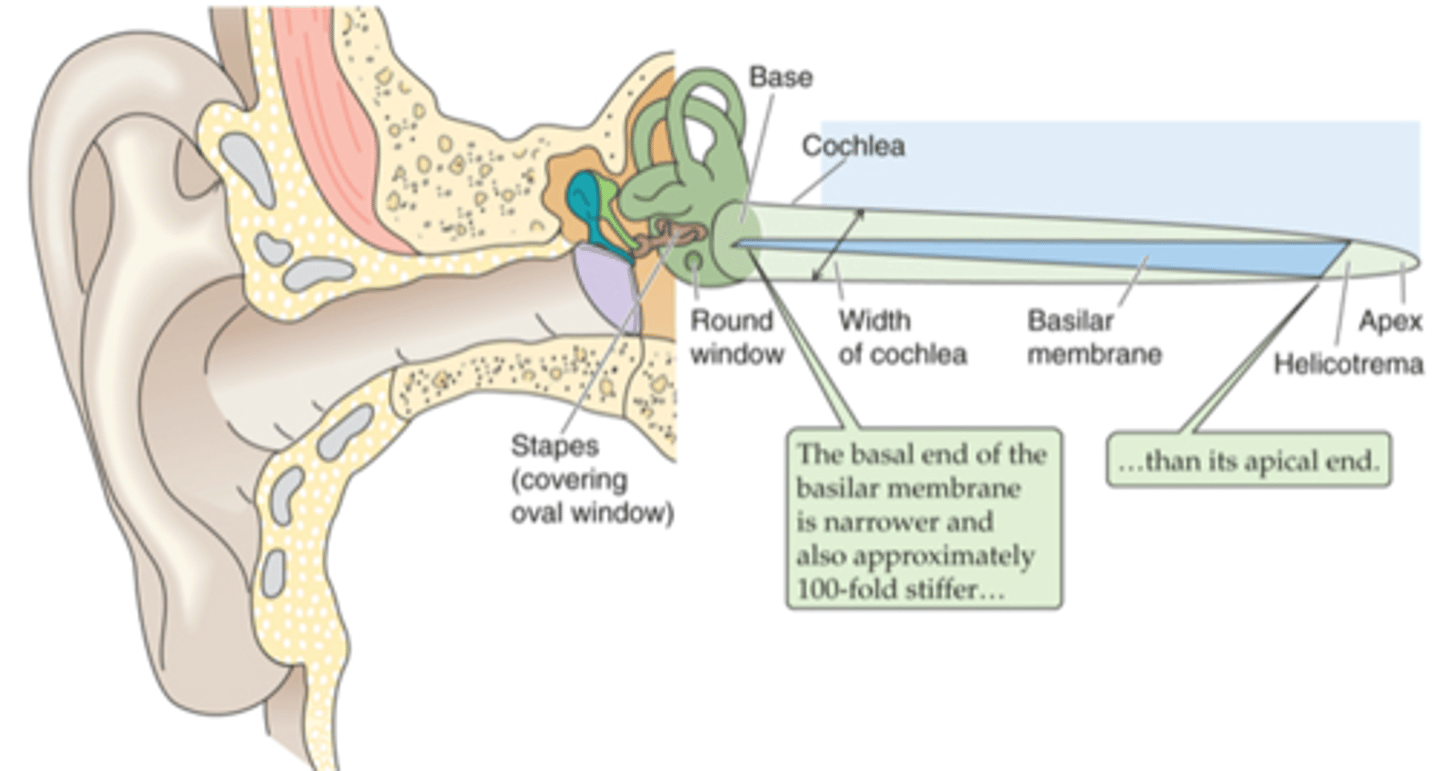
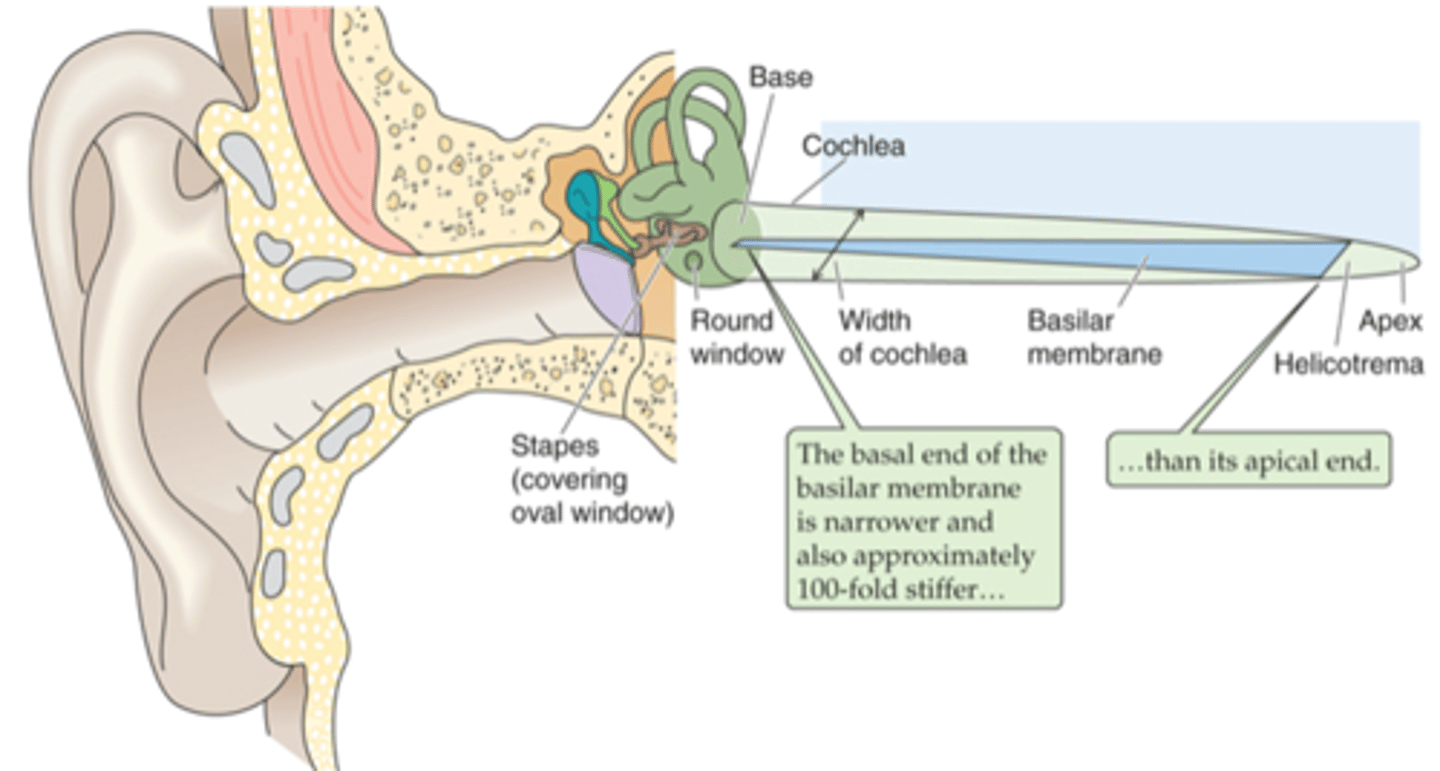
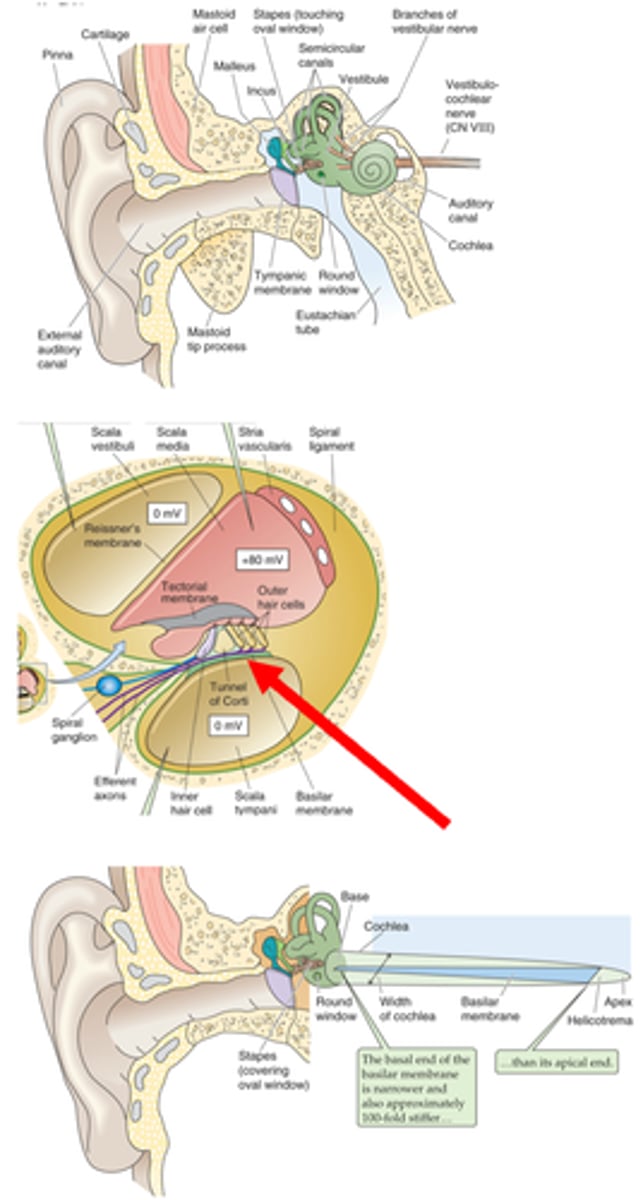
Pinna, tympanic membrane
The outer ear is from the _______ to the __________ ____________
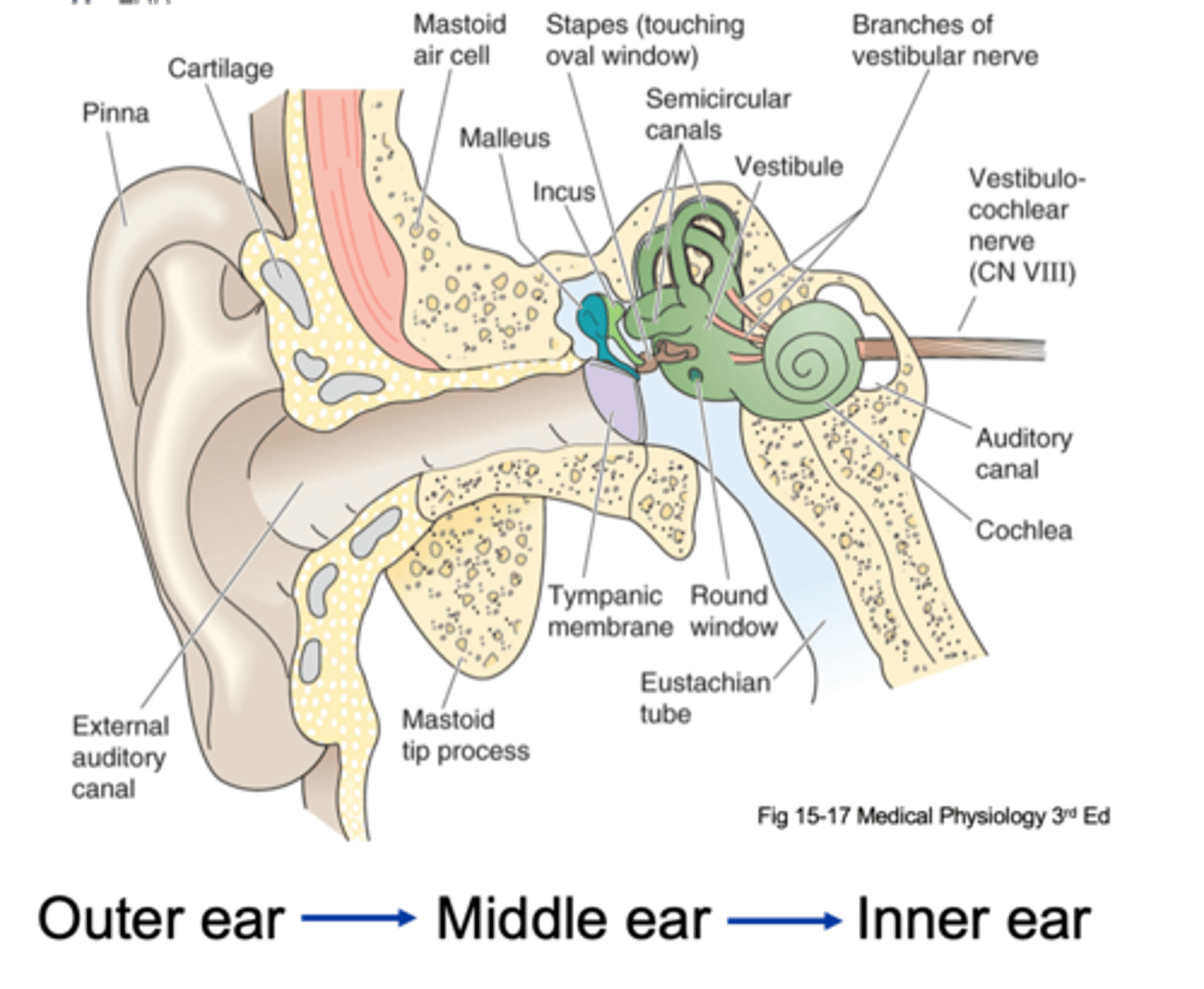
Tympanic membrane, oval window
The middle ear is from the ____________ __________ to a small membrane behind a bone called the _____ ___________ (the entirety of the air filled compartment)
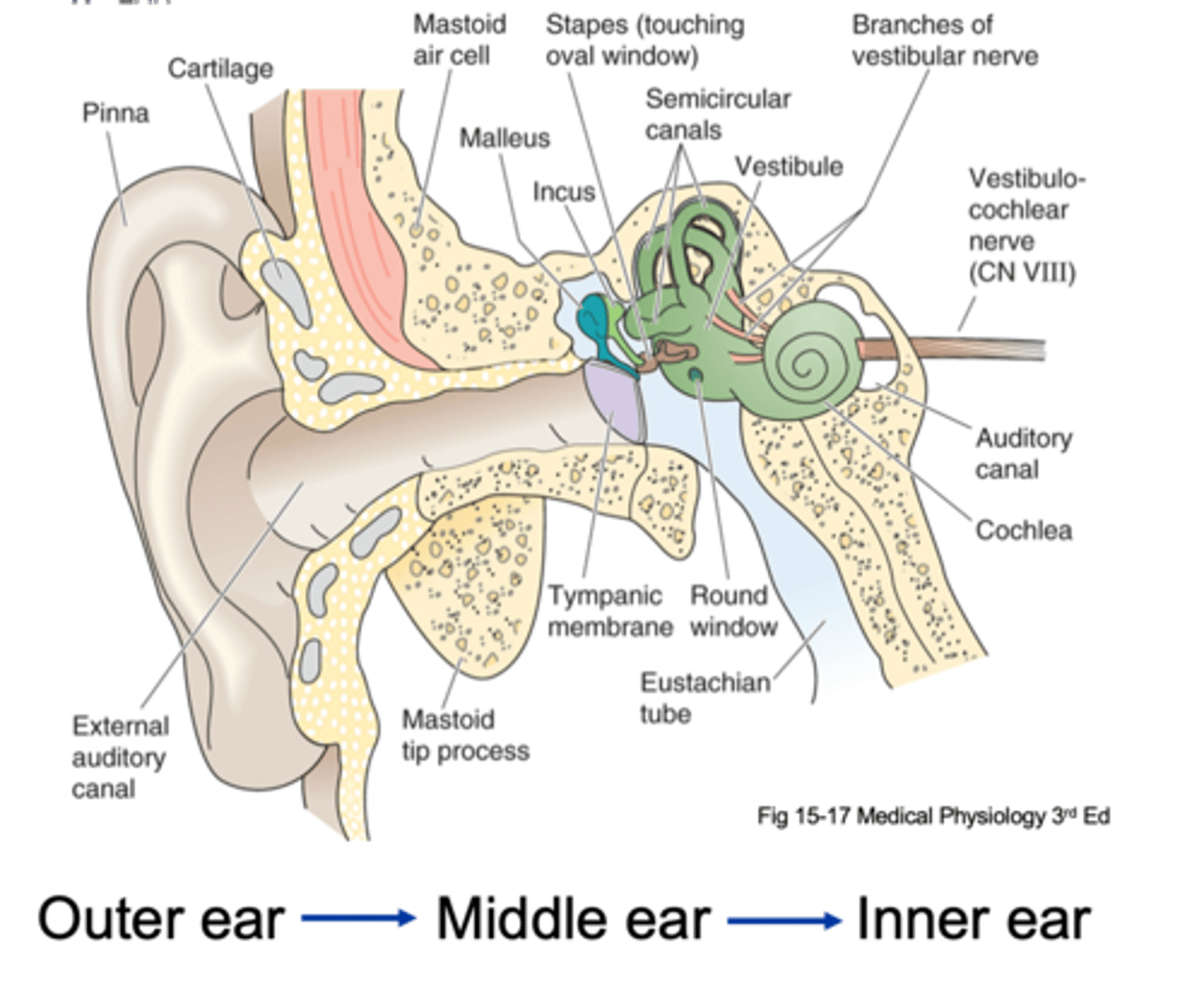
Inner ear
Inside the oval window (the green part of the diagram) is known as the _________ ____
In front, behind
More sensitive to sounds from ____ ________ than from ___________
Sound localisation
Convolutions of pinna play a role in what?
~2.5cm
How much does the auditory canal extend into the skull?
Allow the brain to perceive where (in terms of the vertical plane) the sound is coming from
What do the different lumps and bumps of the outer ear do?
Localisation in the vertical plane
Most of the convulsions of the pinna are to do with ...?
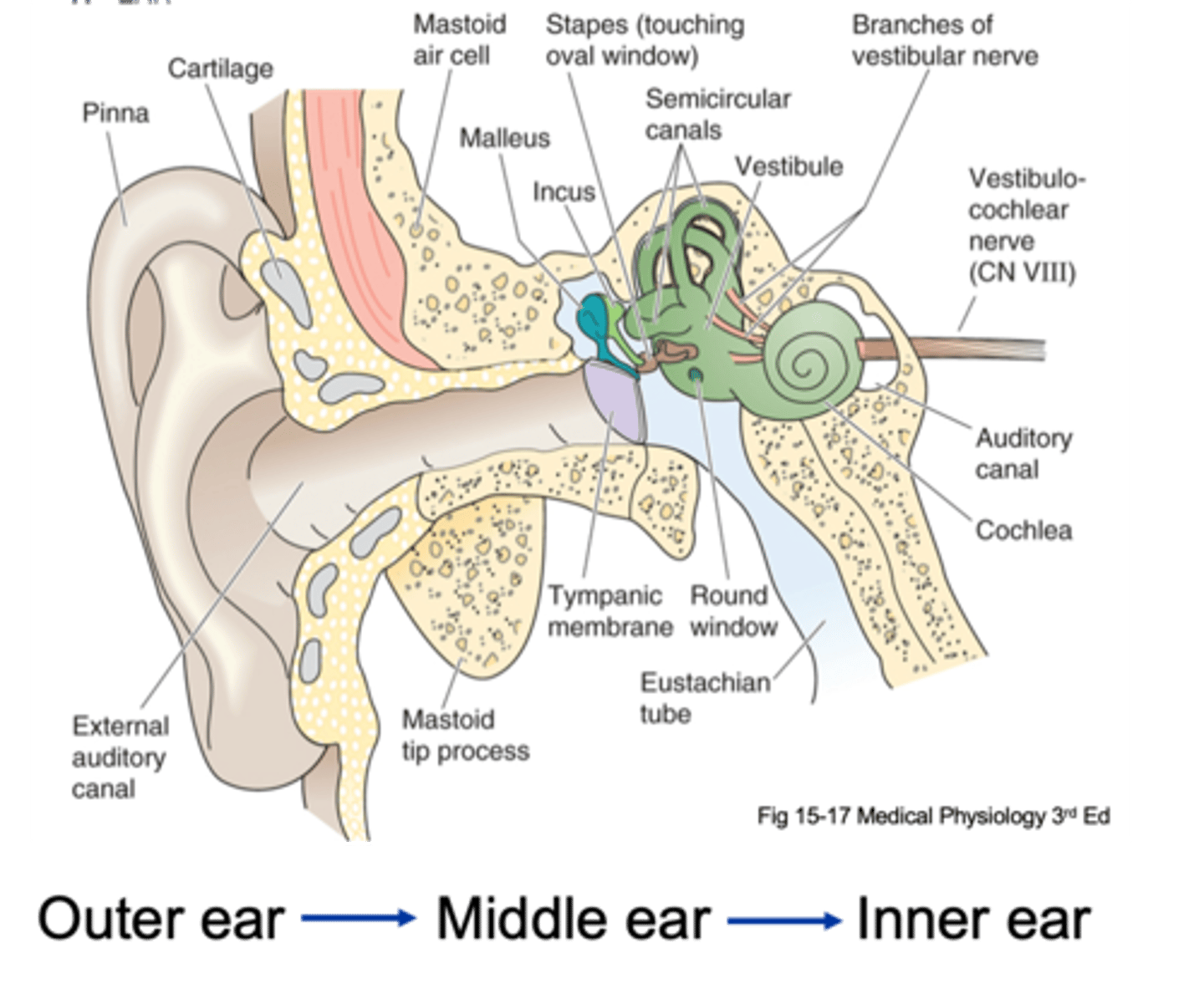
External auditory canal, tympanic membrane, ossicles, oval membrane
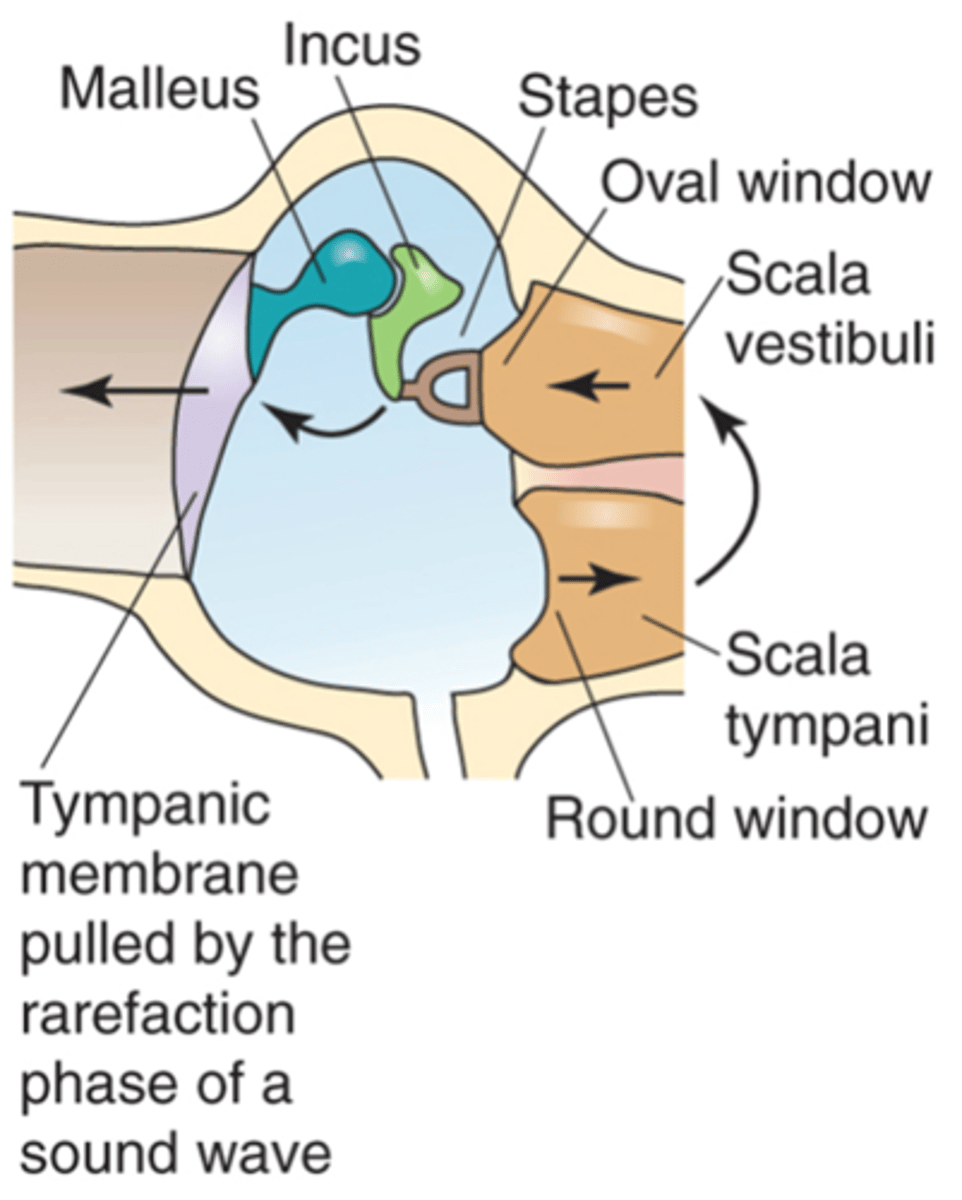
Sound in funnelled in through __________ ___________ _____ and hits __________ _________ (which is a large drum that vibrates backwards and forwards with each sound wave) and as it does that it causes movement of 3 tiny bones in the ear known as your ______________ and these kind of move in a certain arrangement, which as the membrane pushes and pulls the tympanic membrane backwards and forwards, it causes the ______ ___________ to move backwards and forwards
Mechanoelectical transducers
The cochlea is a fluid filled compartment that contains cells that are transducers: ______________________ ___________
Take mechanical energy of sound and transduce it into electrical energy
What do mechanoelectrical transducers do?
Rigid
Malleus to incus has a ________ connection
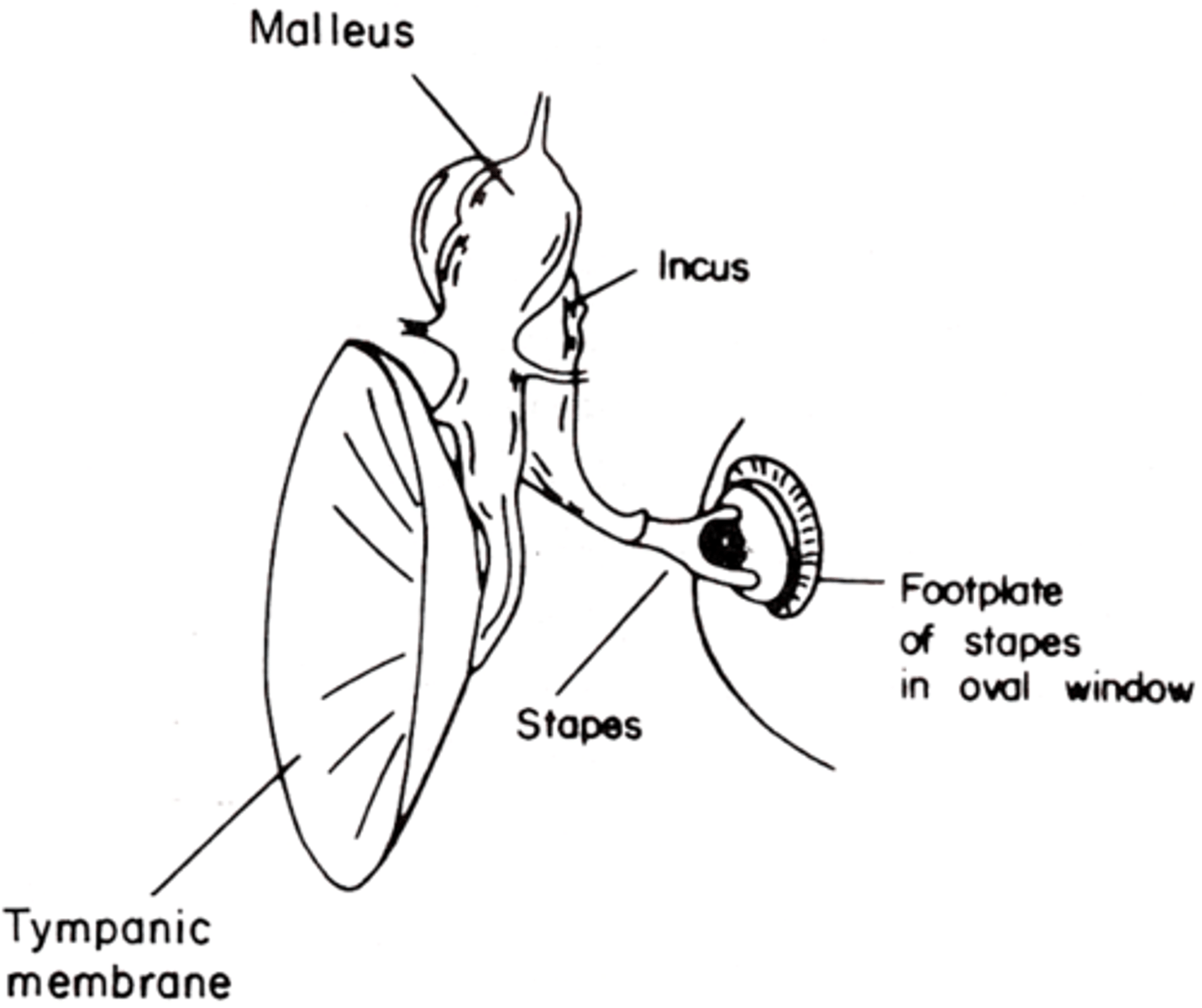
Flexible
Incus to stapes has a __________ connection
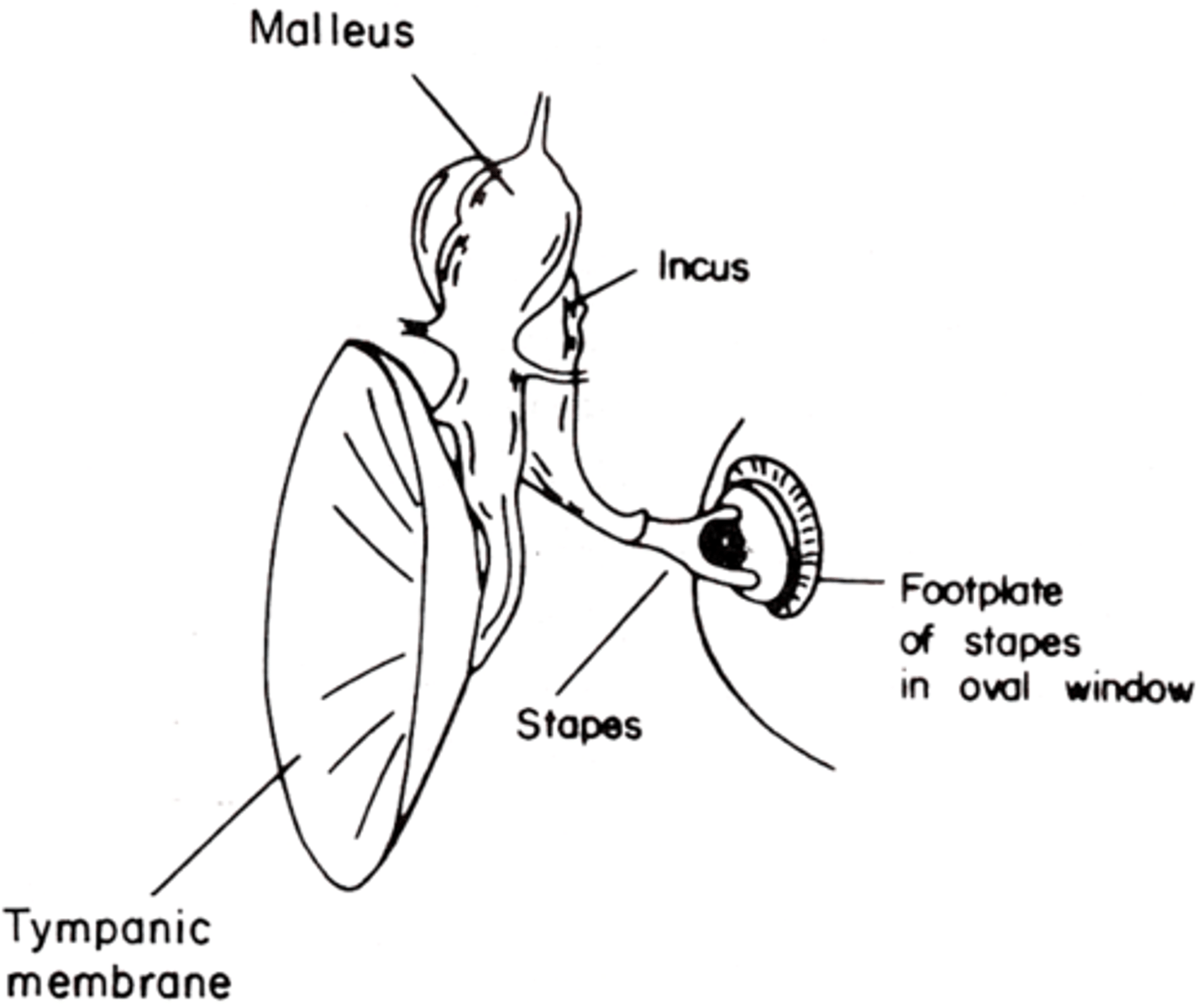
When the malleus moves the incus has to move in the same orientation
What does a rigid connection mean?
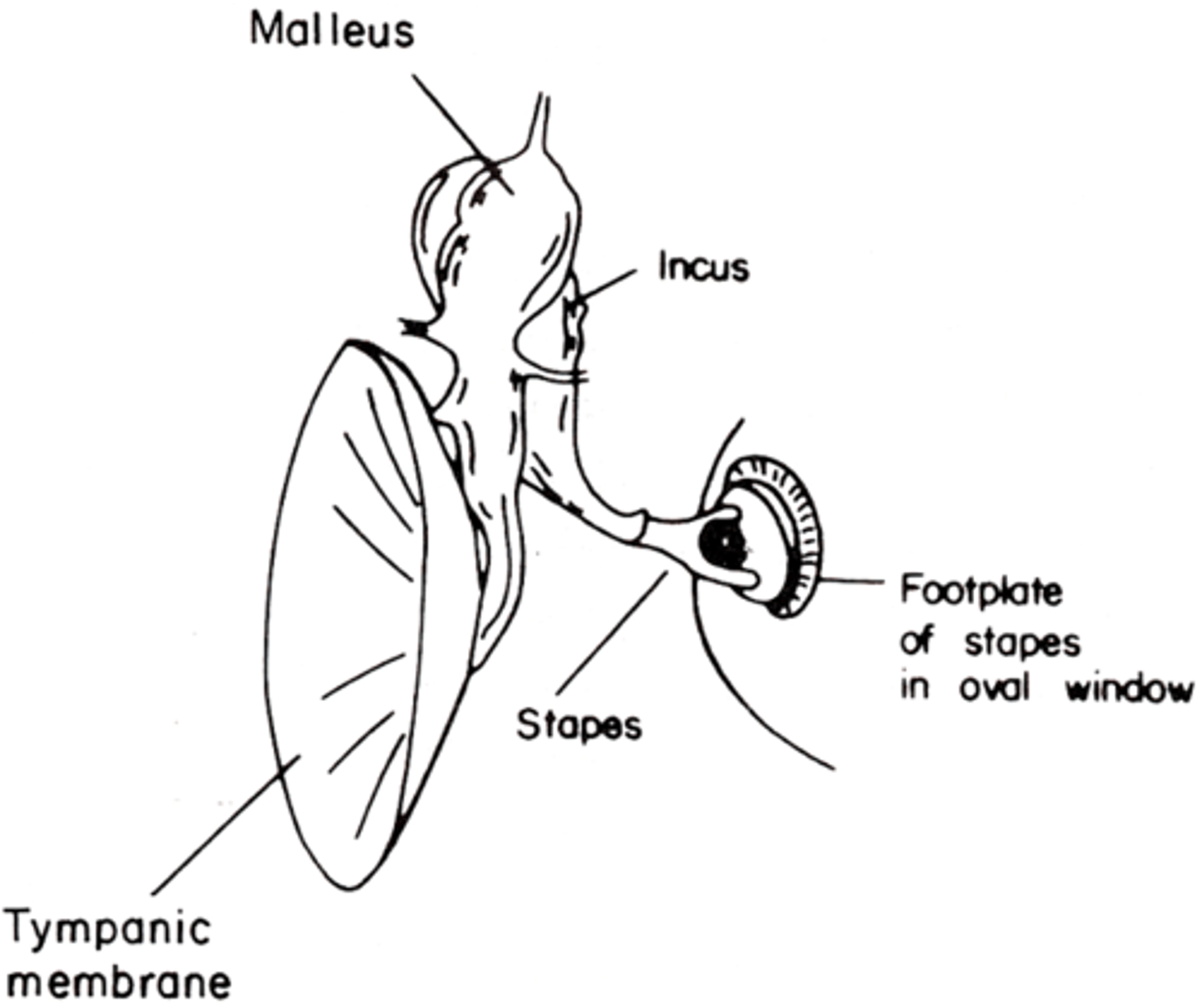
When the incus moves in one direction it can cause small swinging, a leverage of the stapes so it can push it into and out of the oval window
What does a flexible connection mean?
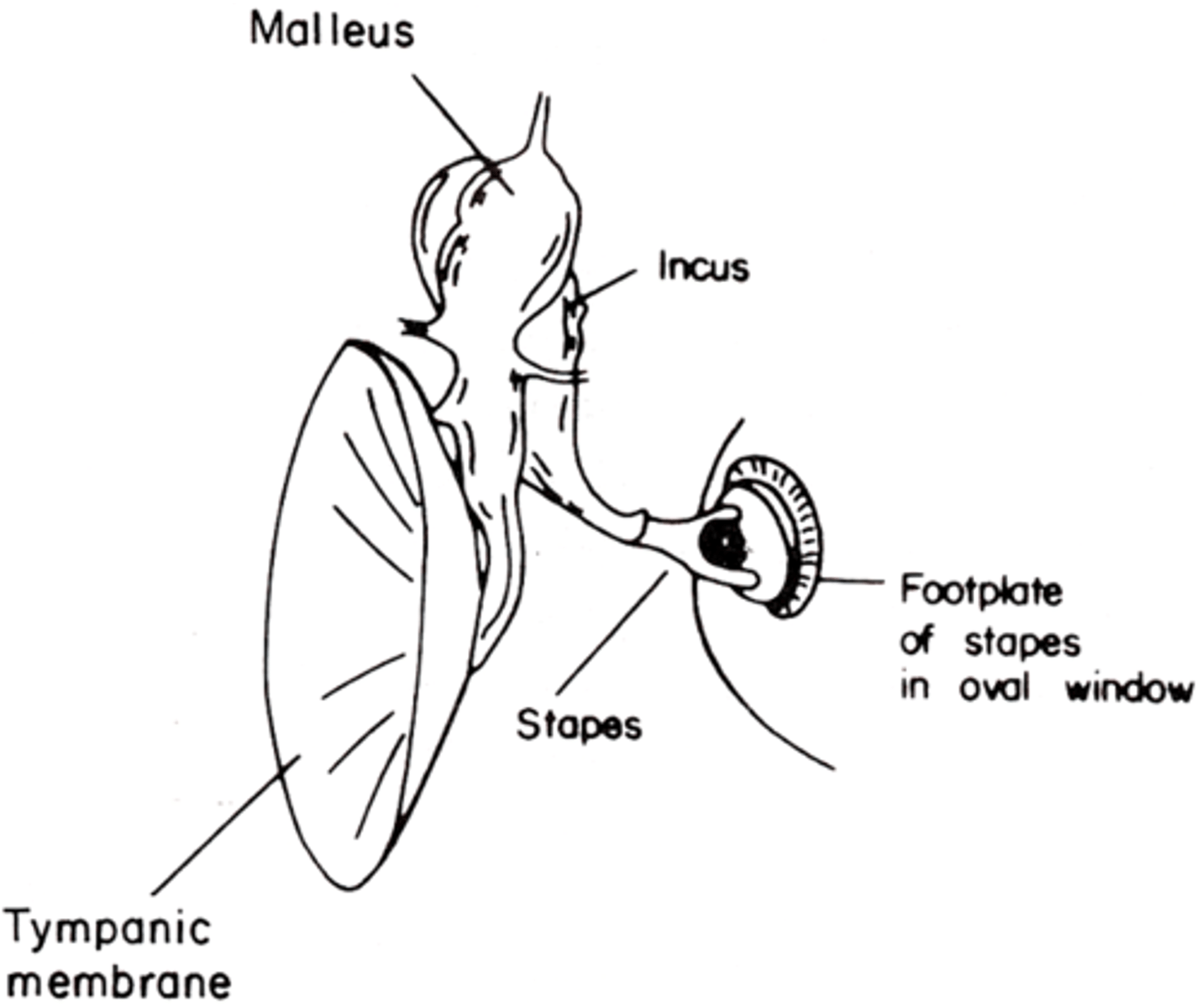
By taking in pressure over a large surface area and concentrating it into a small surface area (the oval window) so it concentrates the force of each sound wave onto the oval window
How does the middle ear transfer sound?
The bottom of the malleus moves down and causes the point of the incus to push forward and push the stapes into the oval window and this causes fluid movement right along the compartment of the cochlea
If you've got a sound wave pushing the tympanic membrane inwards, what happens?
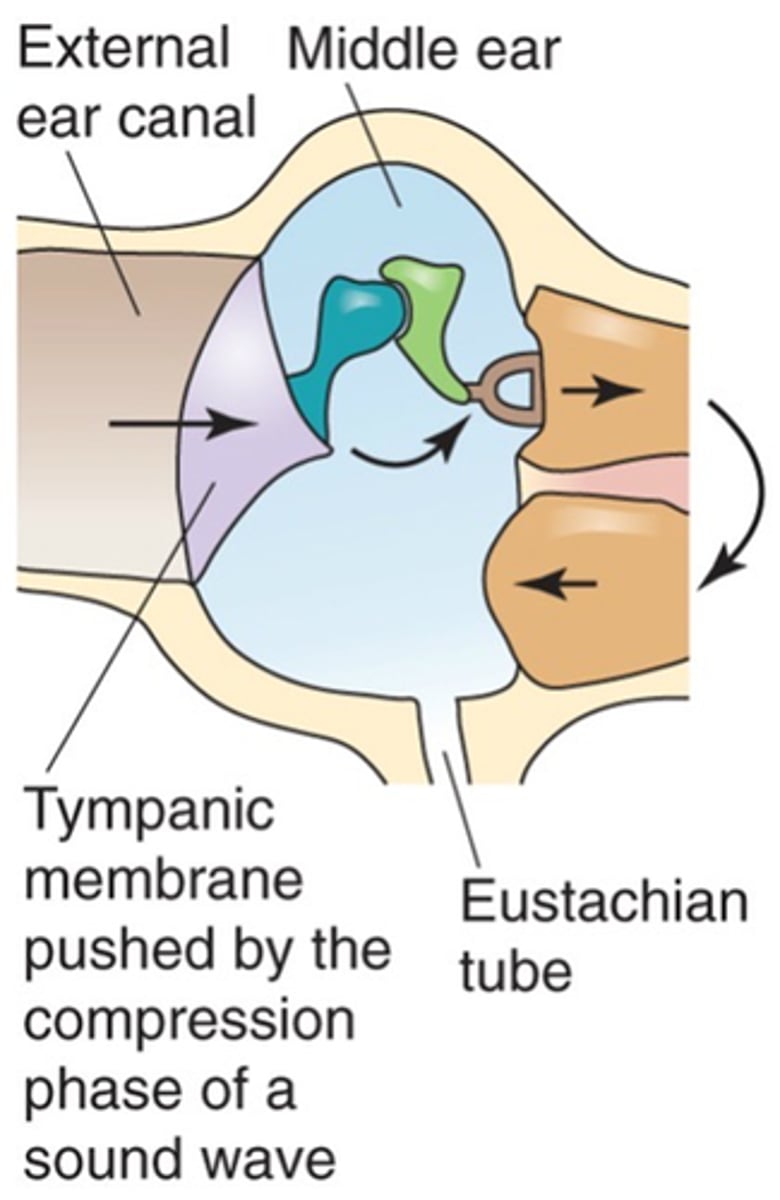
Allows the cochlea to push fluid out (allows the fluid of movement to still occur because without fluid being able to escape the oval window would be meeting too much resistance)
What does the round window (another part of the cochlea) do?
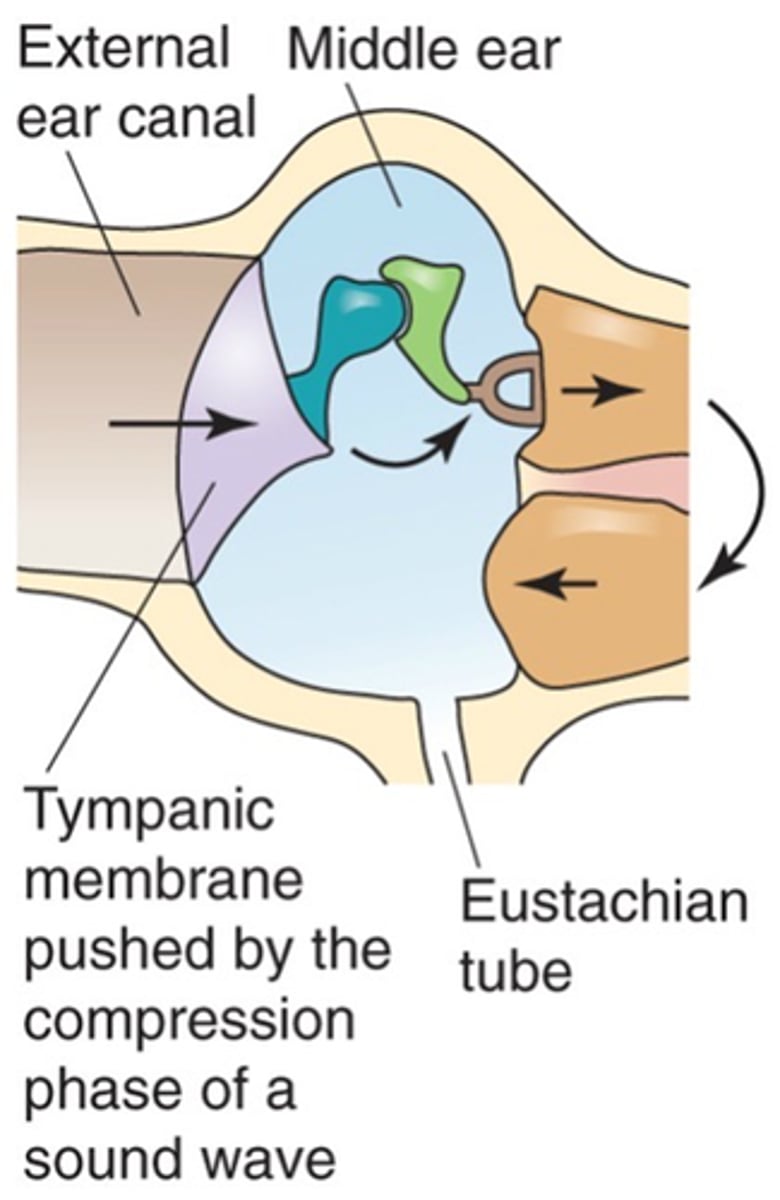
The base of the malleus moves upwards, the bottom of the incus pulls backwards and pulls the stapes with it which means the oval window moves out and we get fluid moving in the opposite direction
If the tympanic membrane is pulled to the outside of the ear, what happens?
20, impedance
Ossicles amplify sounds to exert ~__ times more pressure on the oval window than on the tympanic membrane - overcoming the greater ____________ of the cochlear fluid
Air-fluid interface, inertia
The oval would barely move if it was moved directly by sound due to the ___-______ __________, as fluid has a greater ___________ (impedance)
The tendency of each medium to oppose movement brought about by a pressure wave
Air and water have difference impedances, what does this mean?
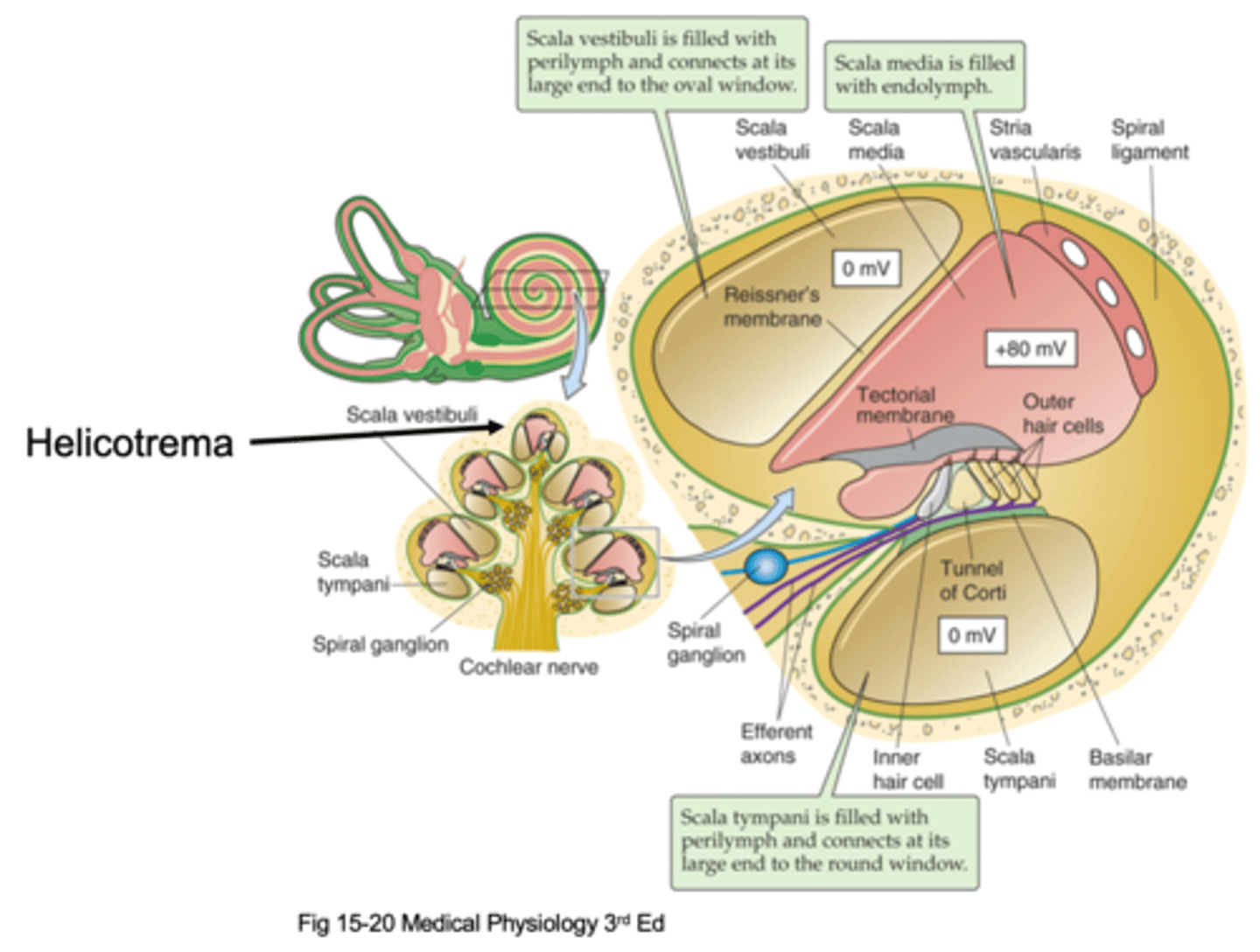
Helicotrema
The oval window attaches at the bottom and causes movement of fluid up and up the apex where it meets the _________________ (the very top of the cochlea) and that is where fluid stops moving and moves through a compartment down into a different compartment and starts moving down
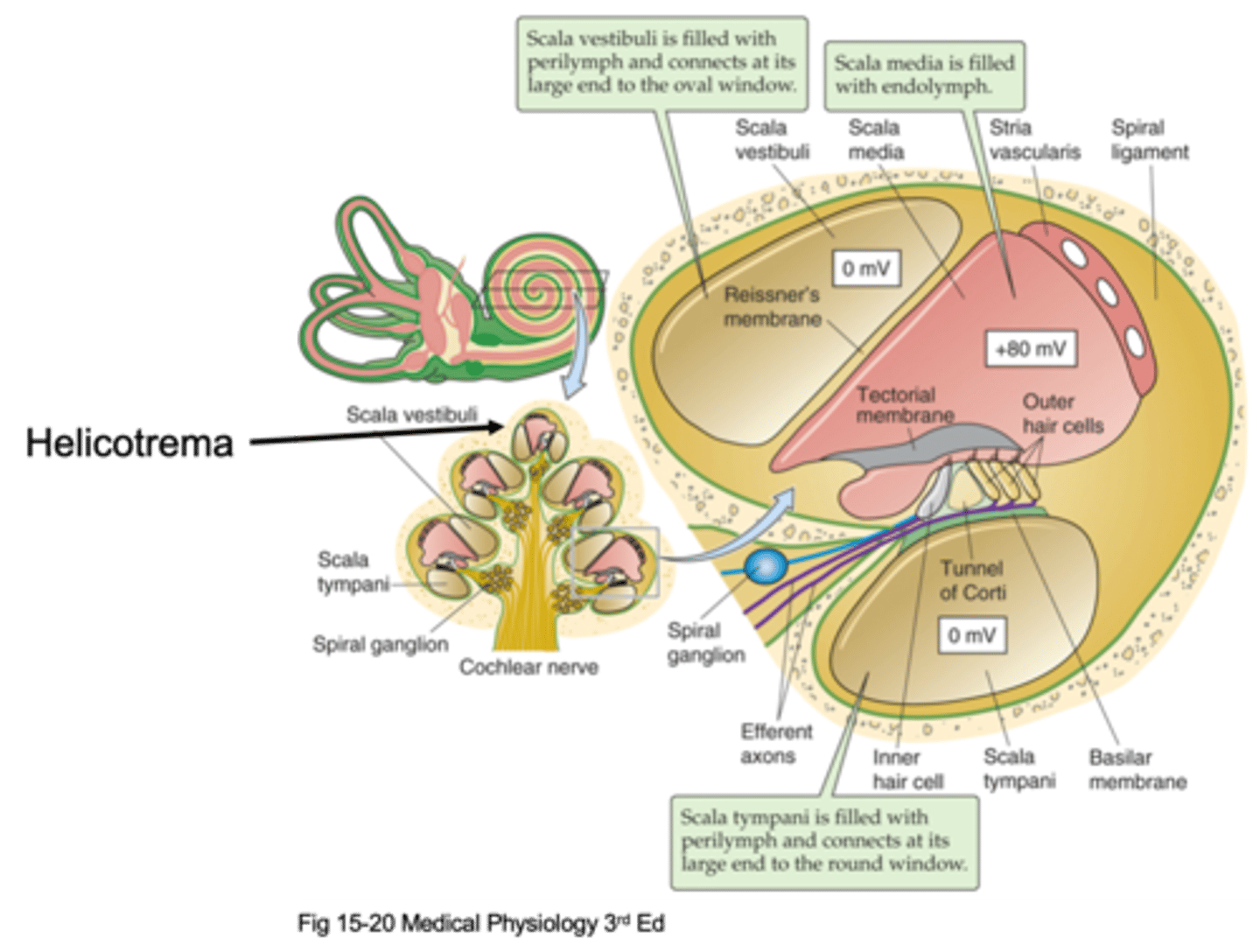
Scala vestibuli, scala media, scala tympani
There are 3 different compartments, what are they?
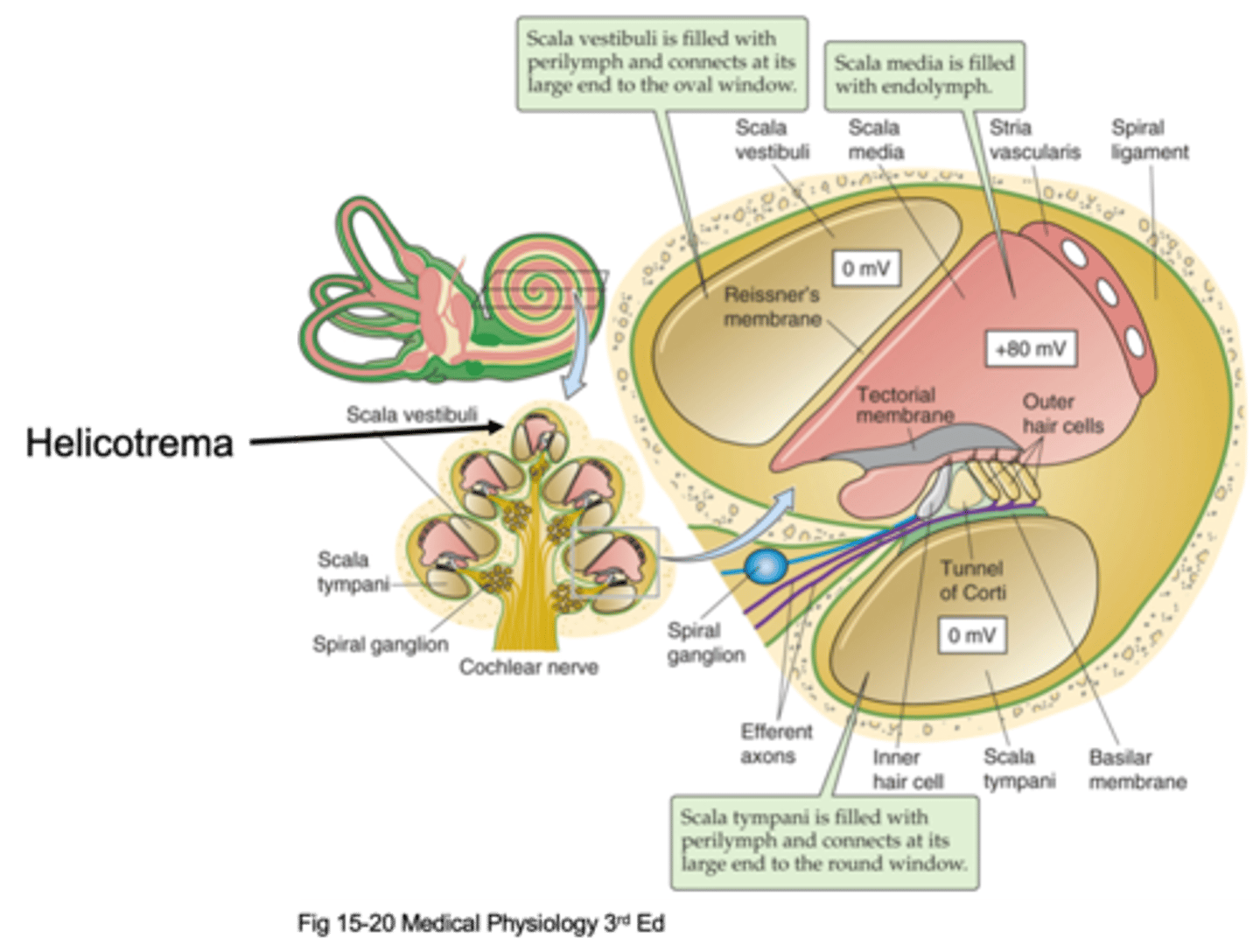
The compartment that is initially pushed, the fluid is initially pushed from the oval window
What is the Scala vestibuli compartment?
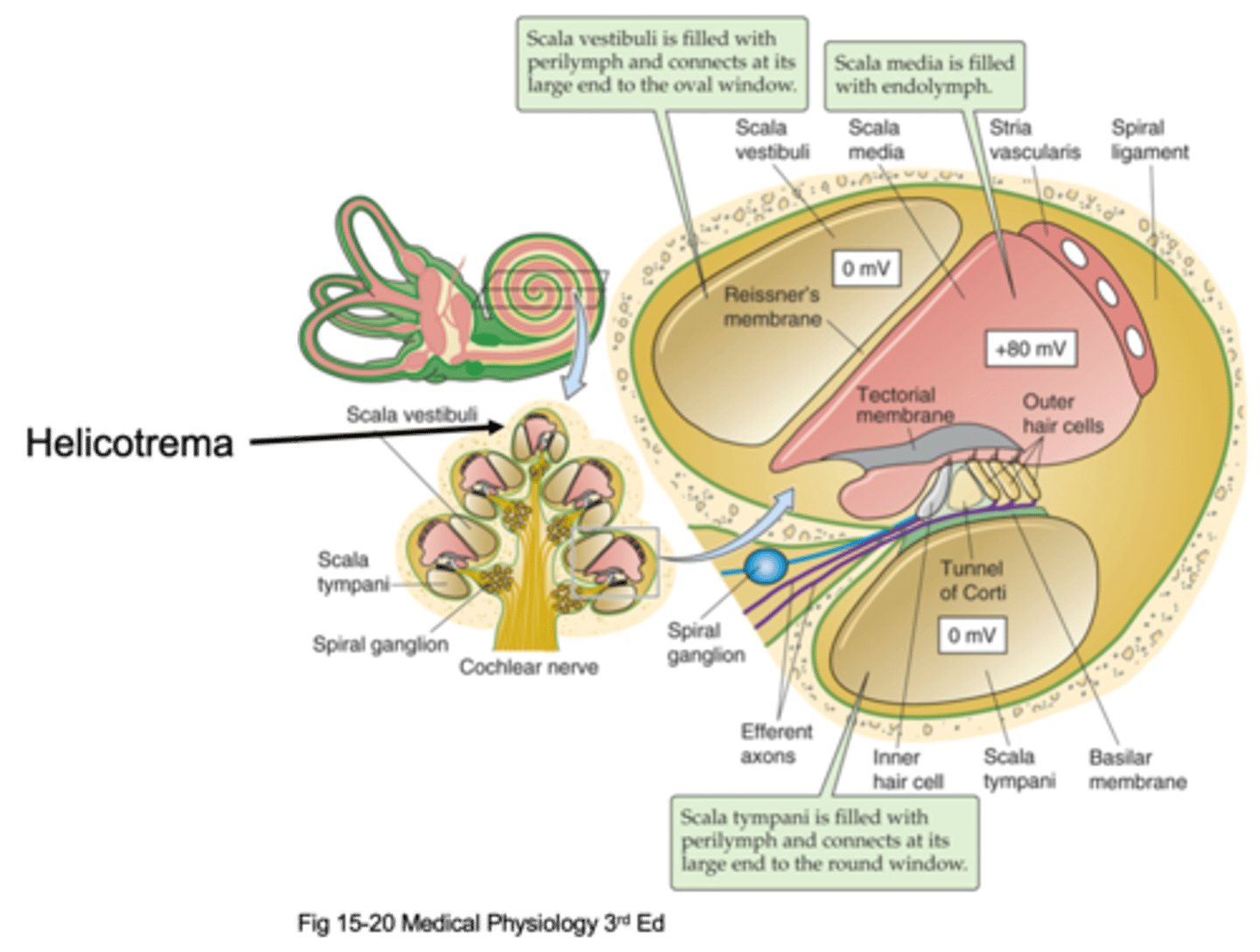
At the bottom to the round window
Where is the Scala tympani compartment connected to?
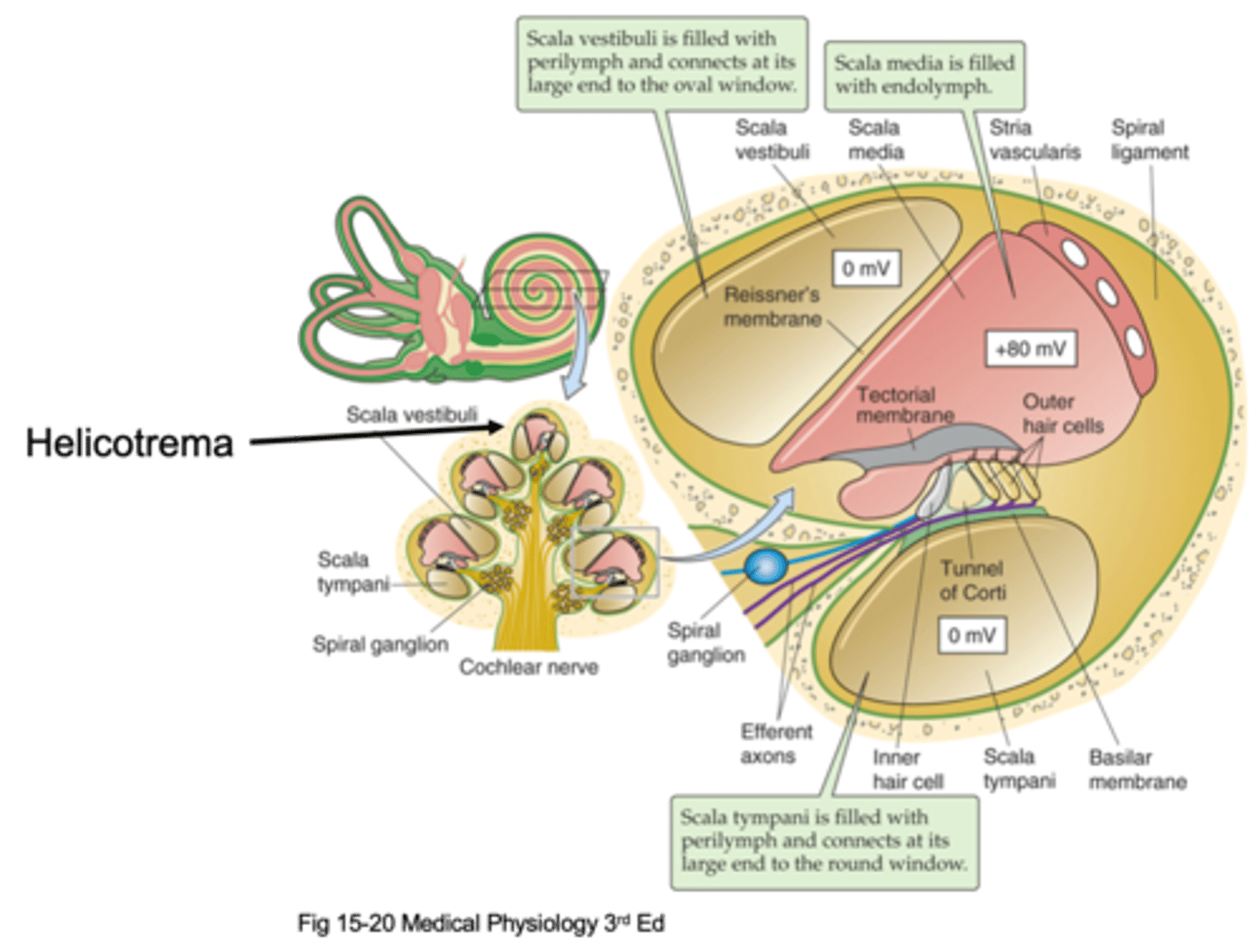
Scala vestibuli, scala tympani
Things move up through the _______ ___________, hit the helicotrema and move down through the ______ ____________
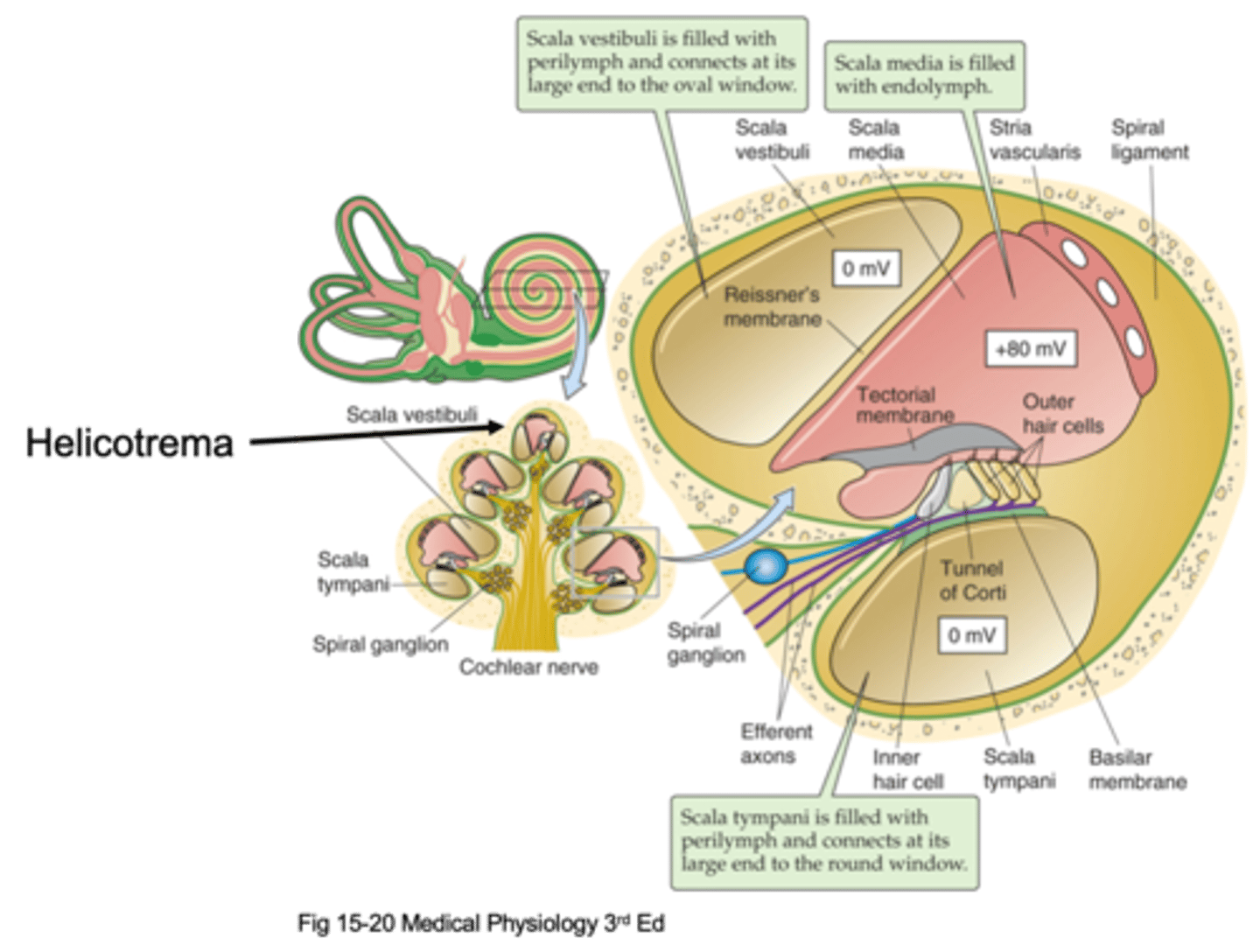
Perilymph
The scala vestibuli and scala tympani are filled with an extracellular solution known as ...?
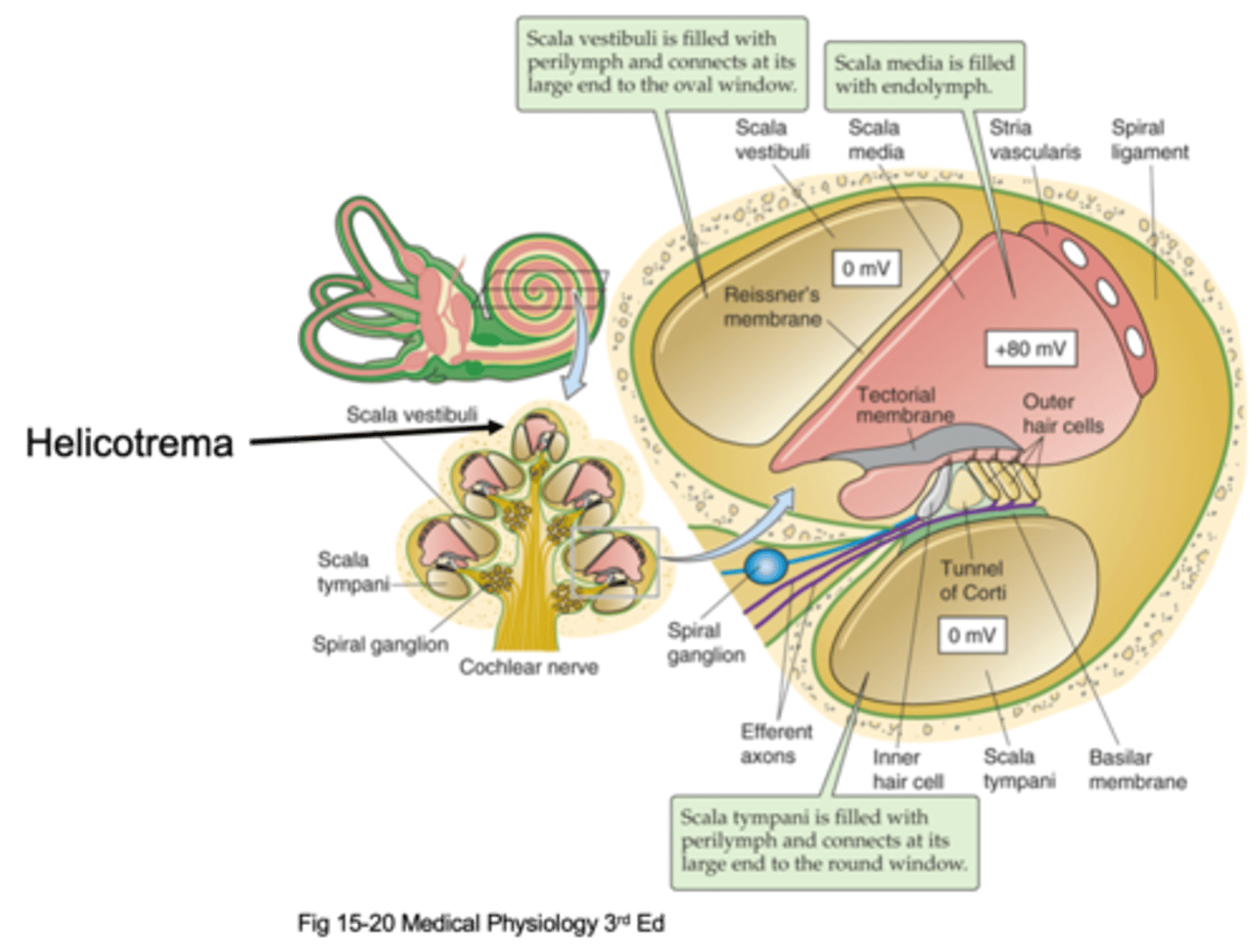
Transduction and hearing
What is the scala media important in?
You start to have problems with hearing and start to go deaf
When things go wrong in the scala media compartment, what happens?
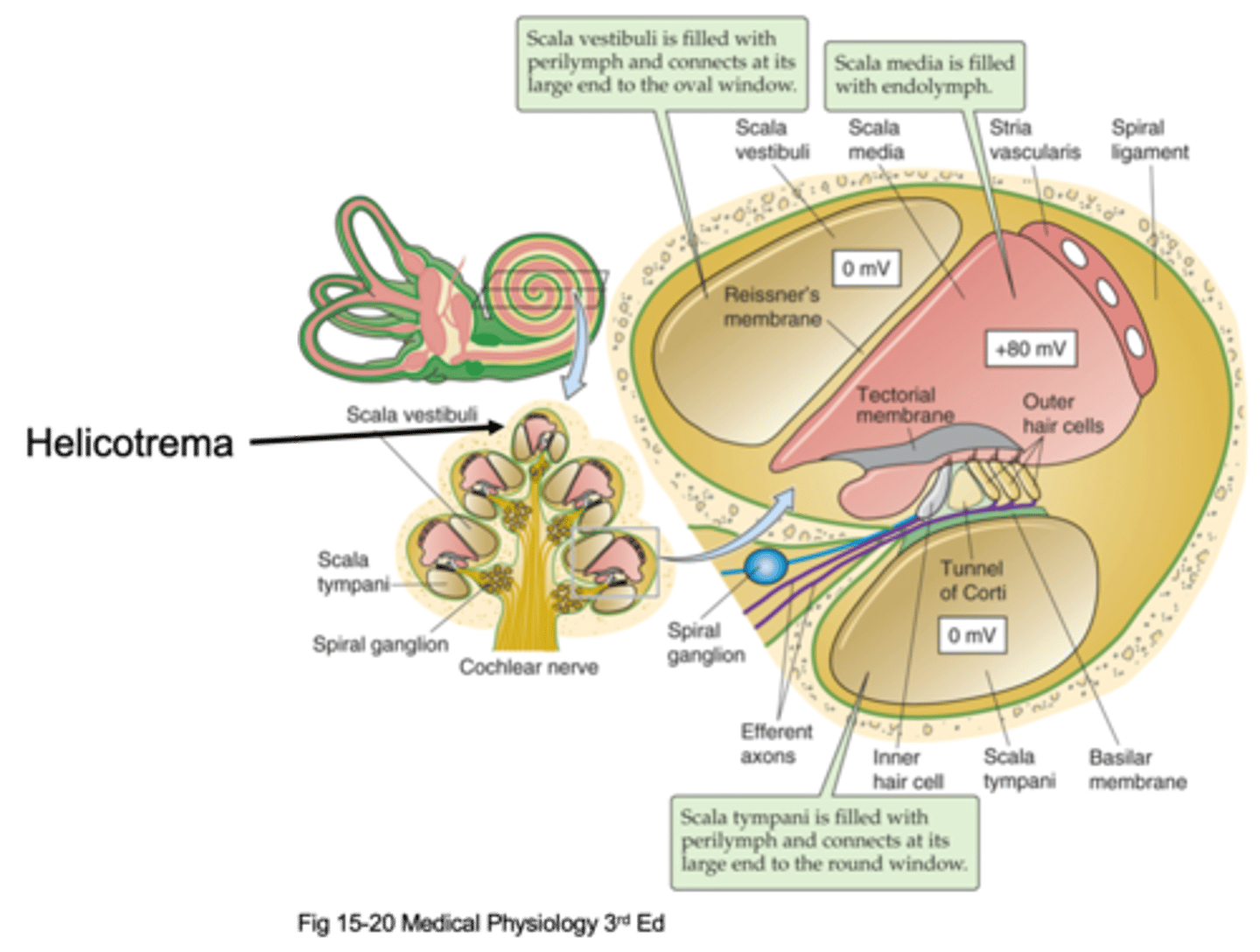
Endolymph
The scala media is filled with ____________ which is found in the auditory system in the inner ear and in the vestibular system and nowhere else, it is a specialised solution and has super high potassium concentration
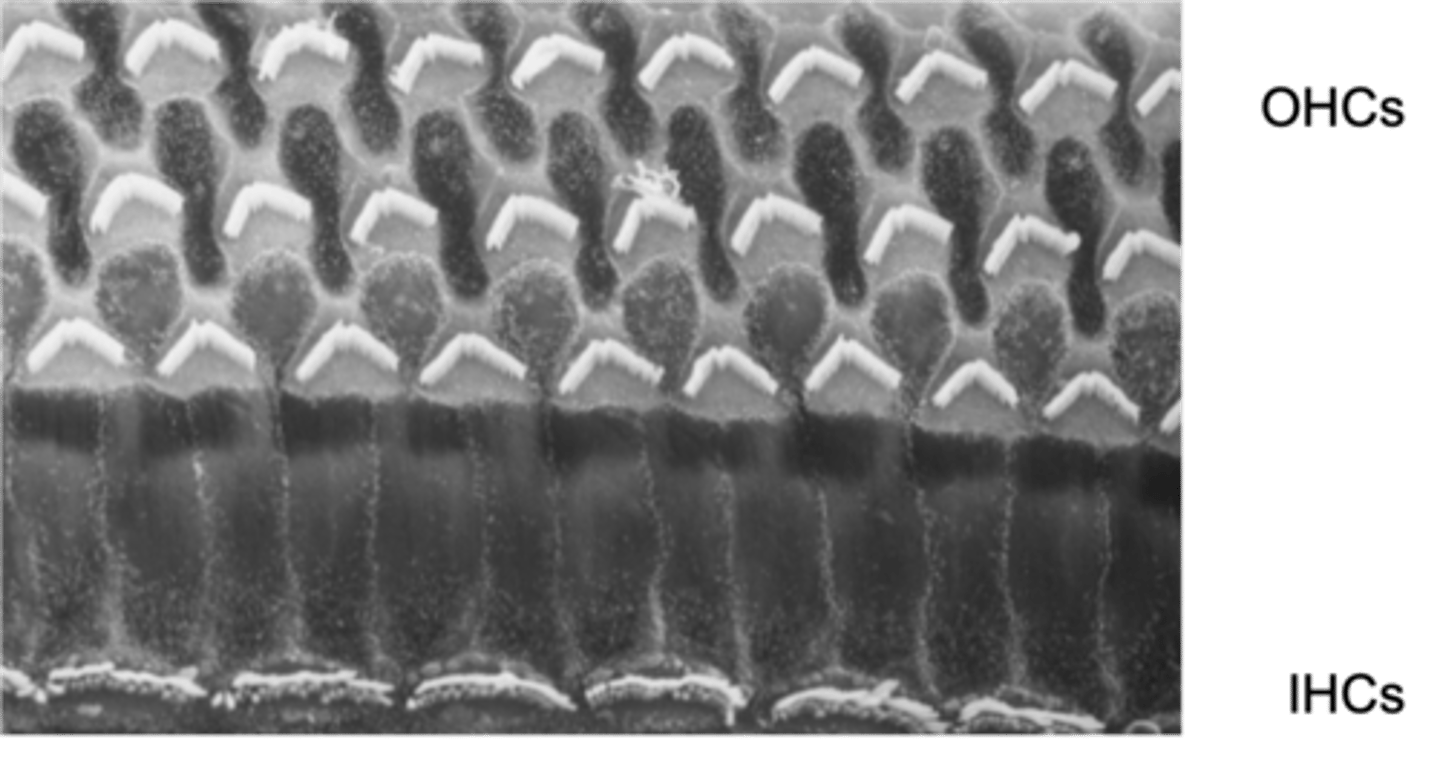
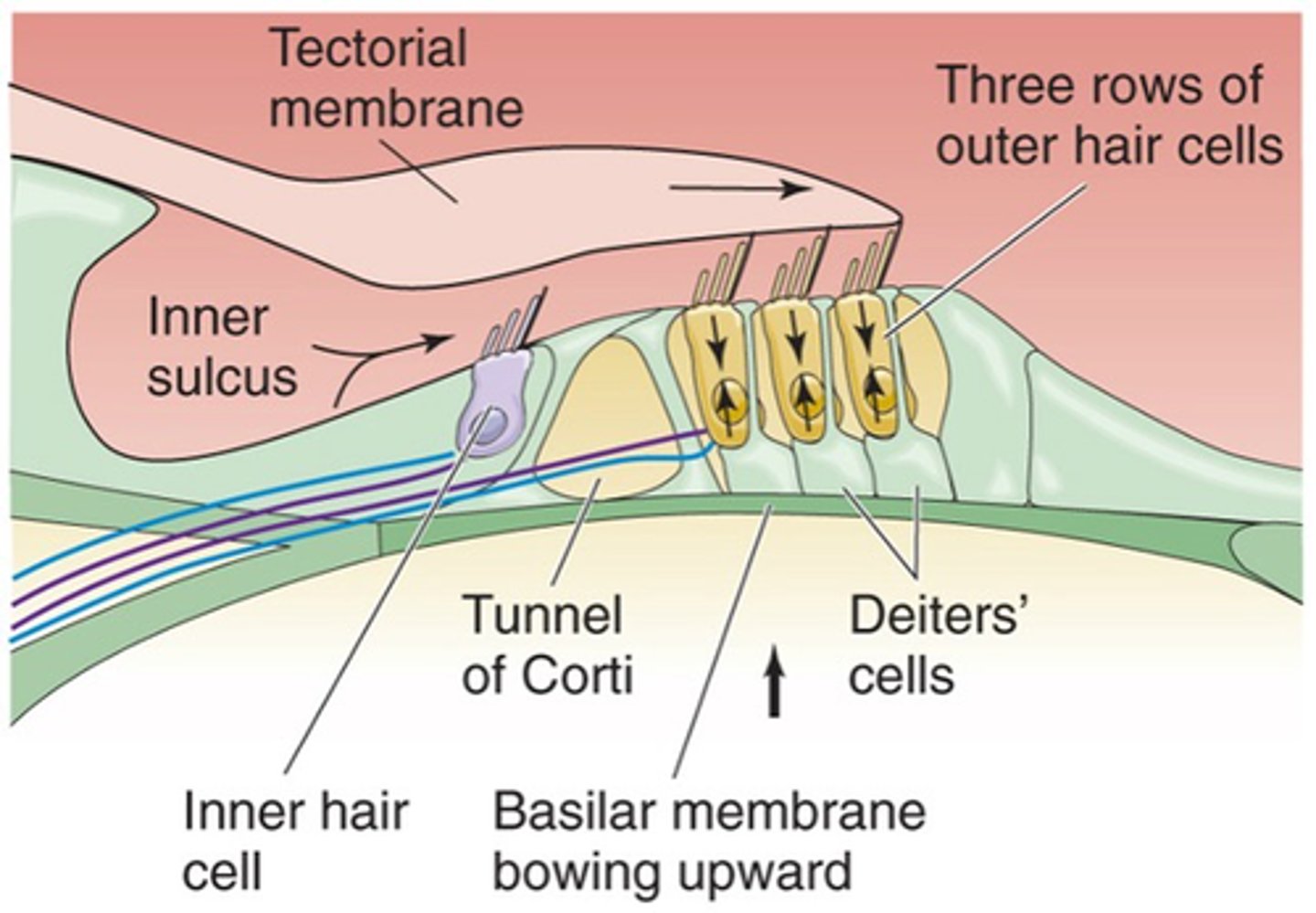
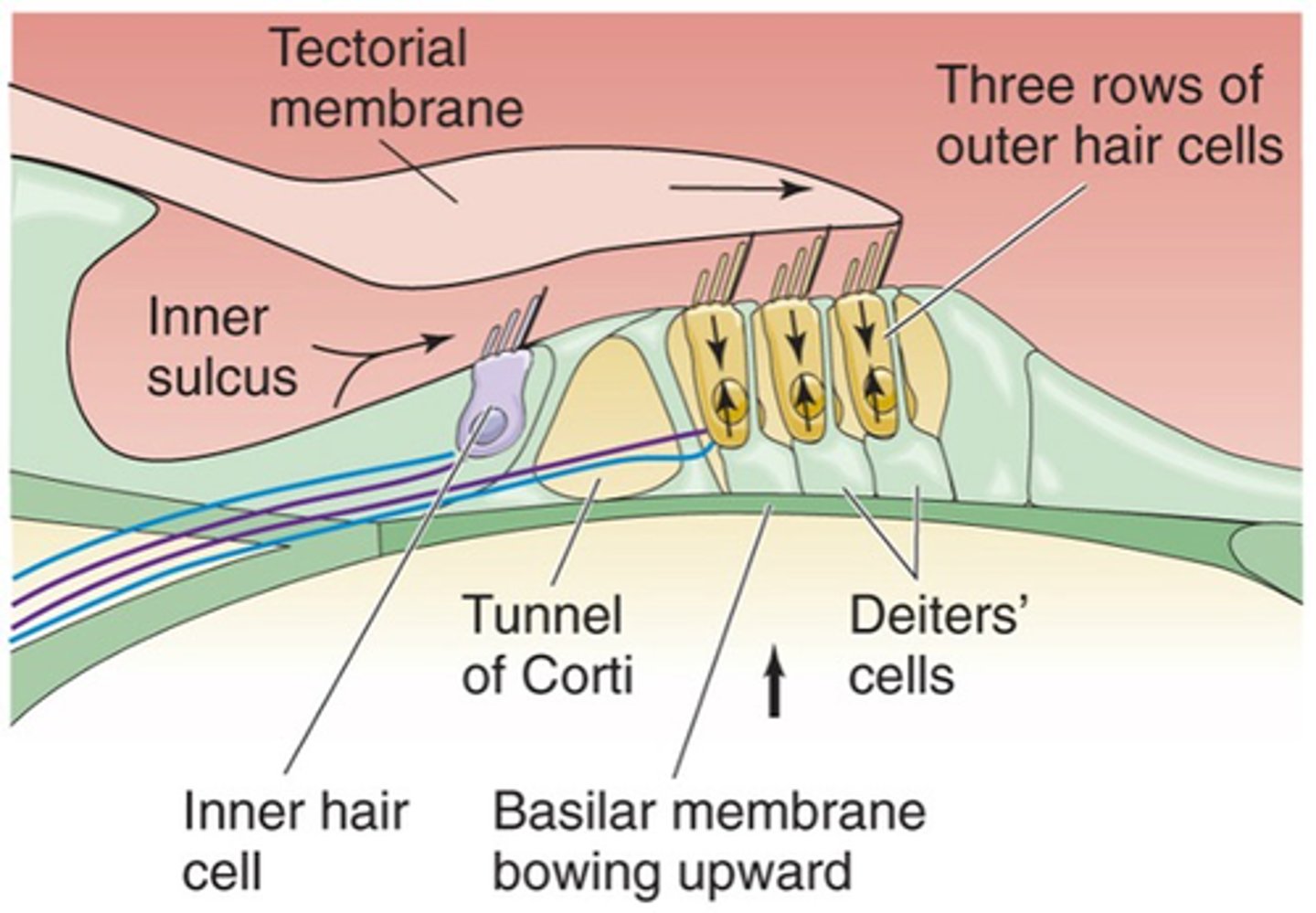
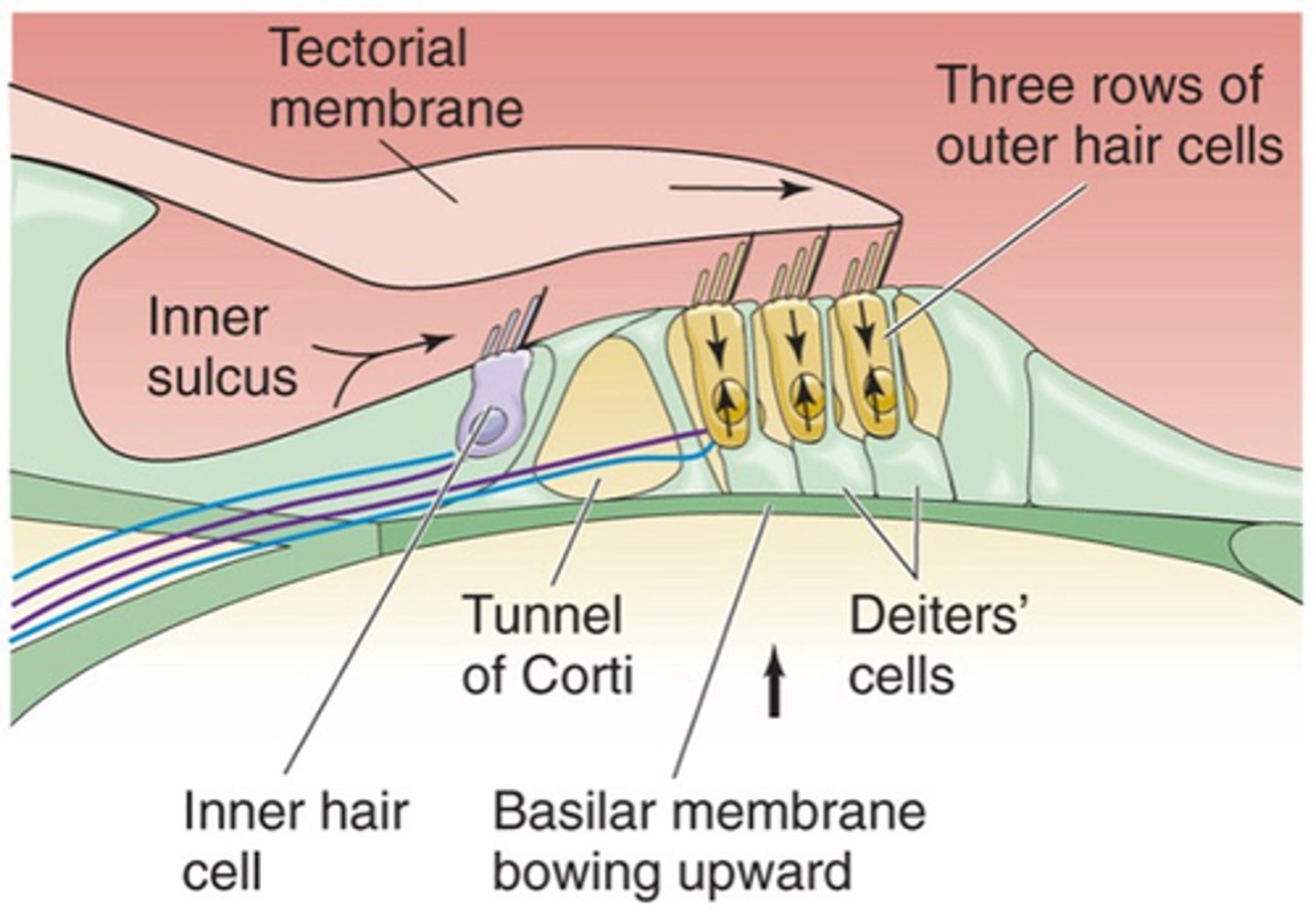
This is where our cells transduce the stimuli/the sound and these cells sit on a basilar membrane and on top of the basilar membrane are our hair cells (our transducers) and then above our hair cells we have another membrane known as the tectorial membrane
What happens in the organ of corti?
Move back and forth in response to fluid movement
All outer and inner hair cells have cilia that stick up known as stereo cilia, what do stereo cilia do?
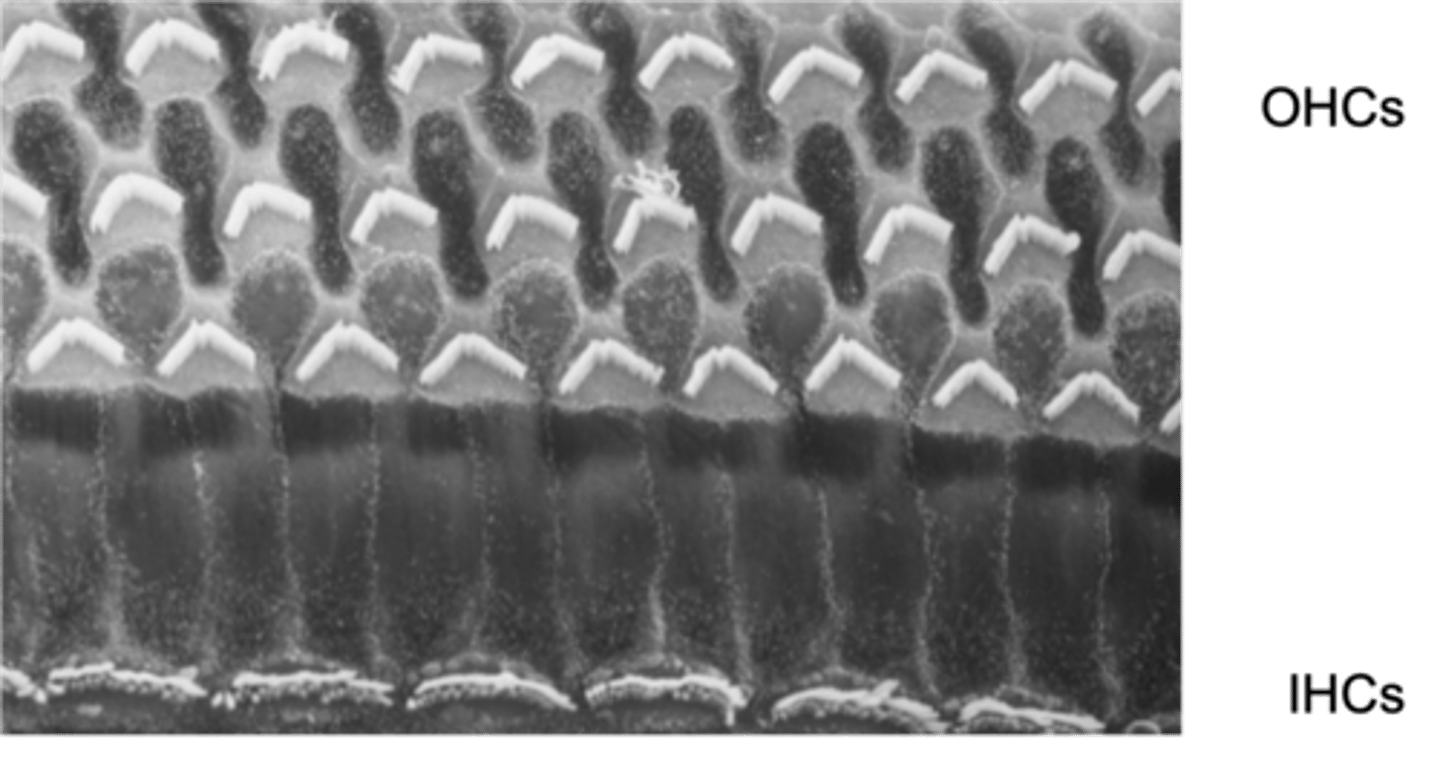
They cant move properly and so you cant transduce sound anymore
What happens if there is a problem with your stereo cilia or they're damaged?
Move it a lot
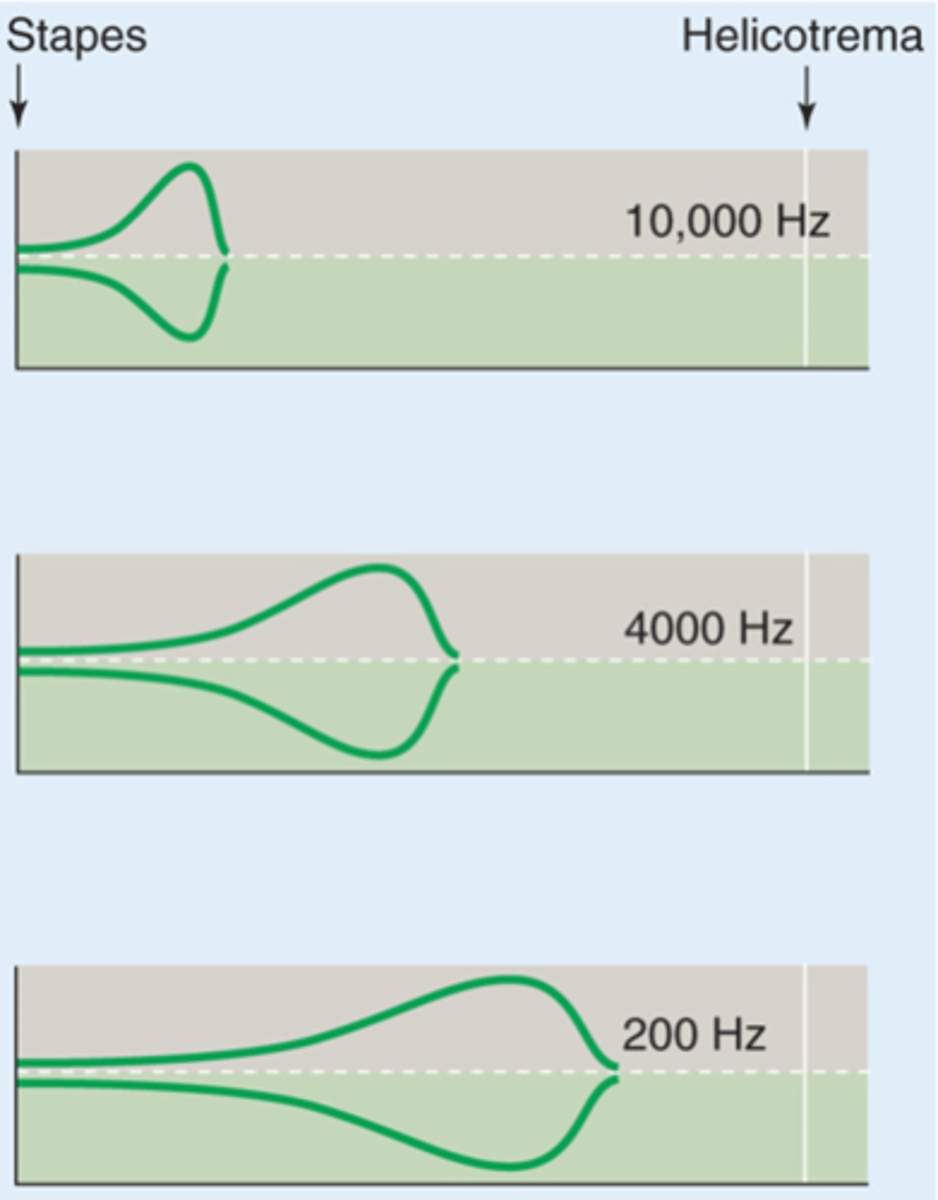
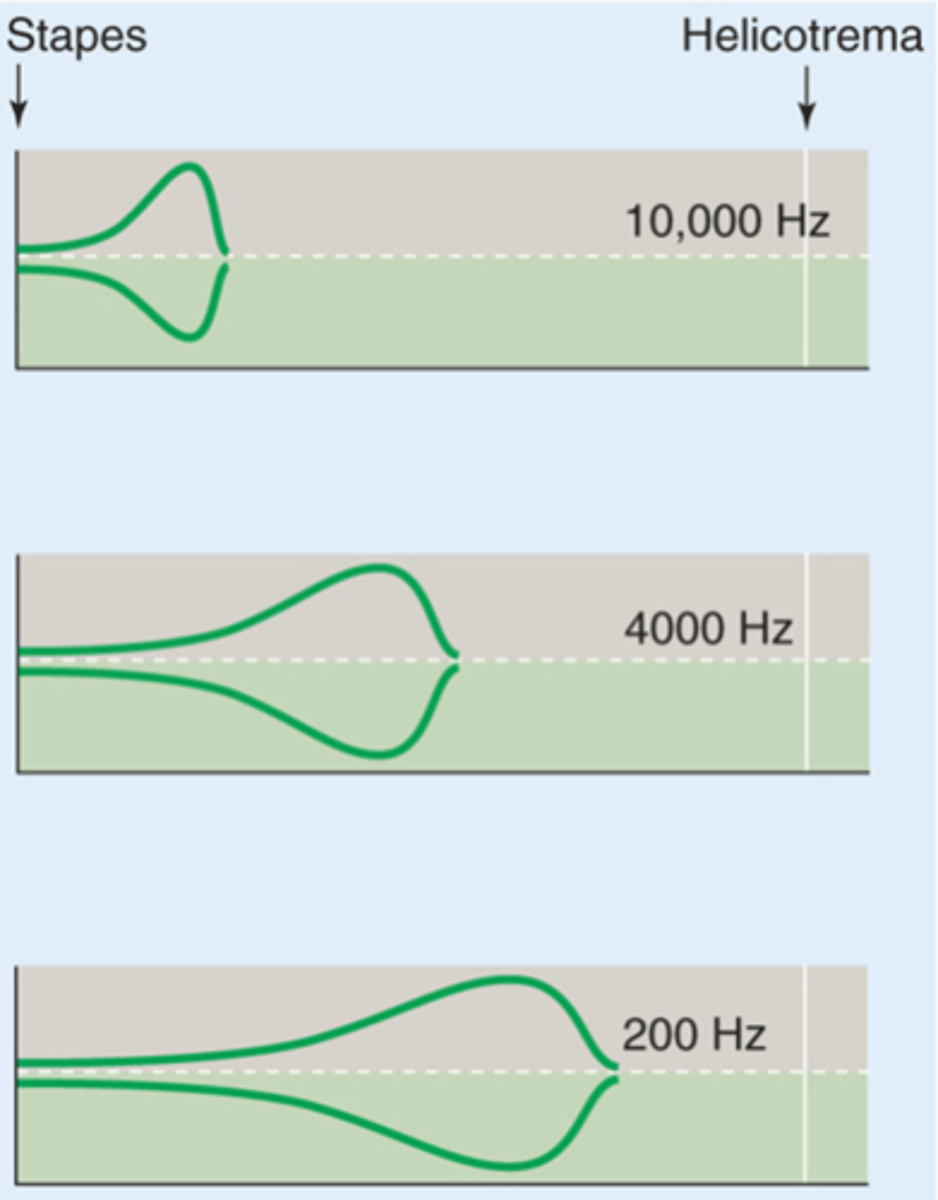
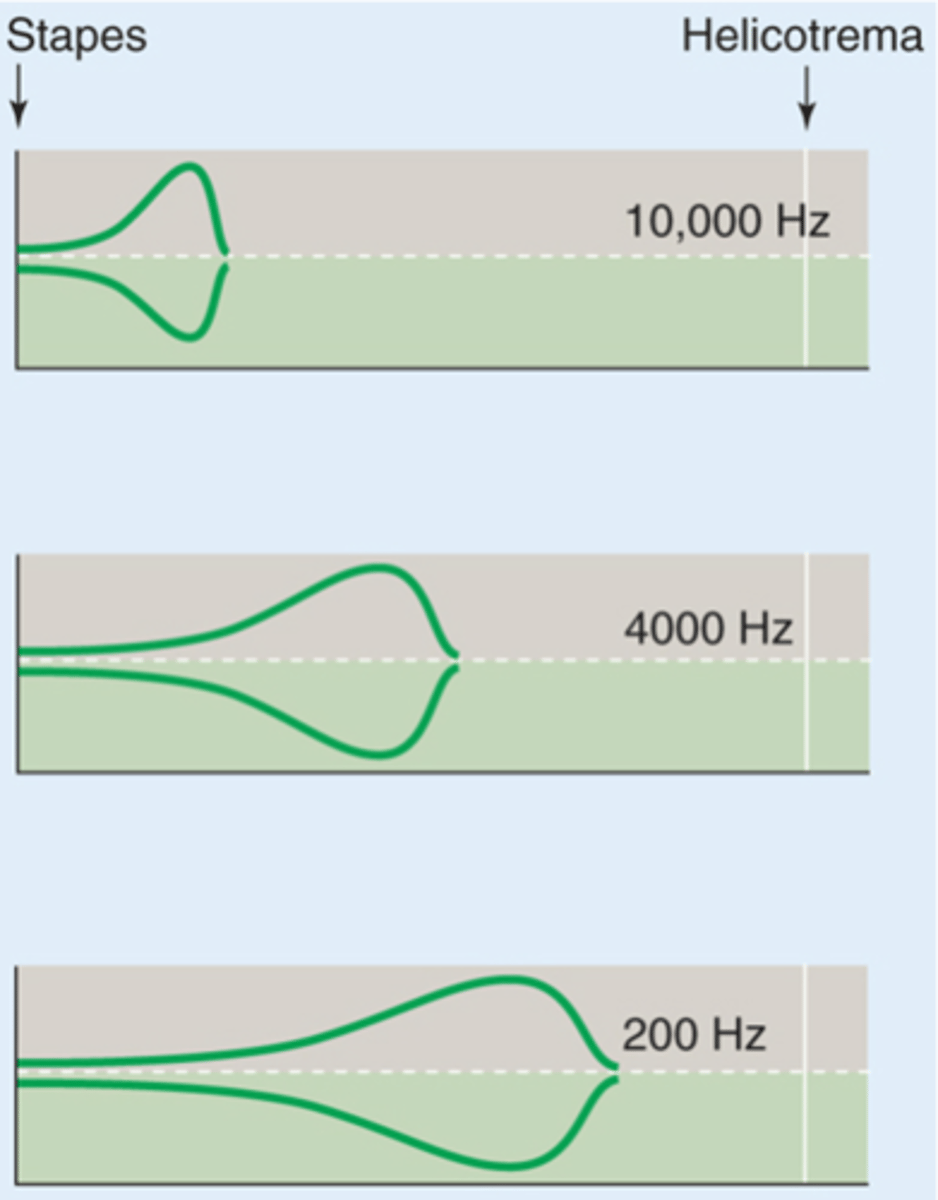
What do high frequency sounds do to the basilar membrane?
Anatomy
The reason the basilar membrane can respond to different frequencies is due to its ...?
Narrower, stiffer, thicker, wider, floppier
The bottom of the basilar membrane is _________ and ___________ and kind of _________ whereas at the apex it is _________ and ___________, different frequencies stimulate it better at different areas due to these anatomical properties
Anatomy of the basilar membrane
Displacement, basilar
Different frequency sounds cause maximal ___________ of the _______ membrane in different regions
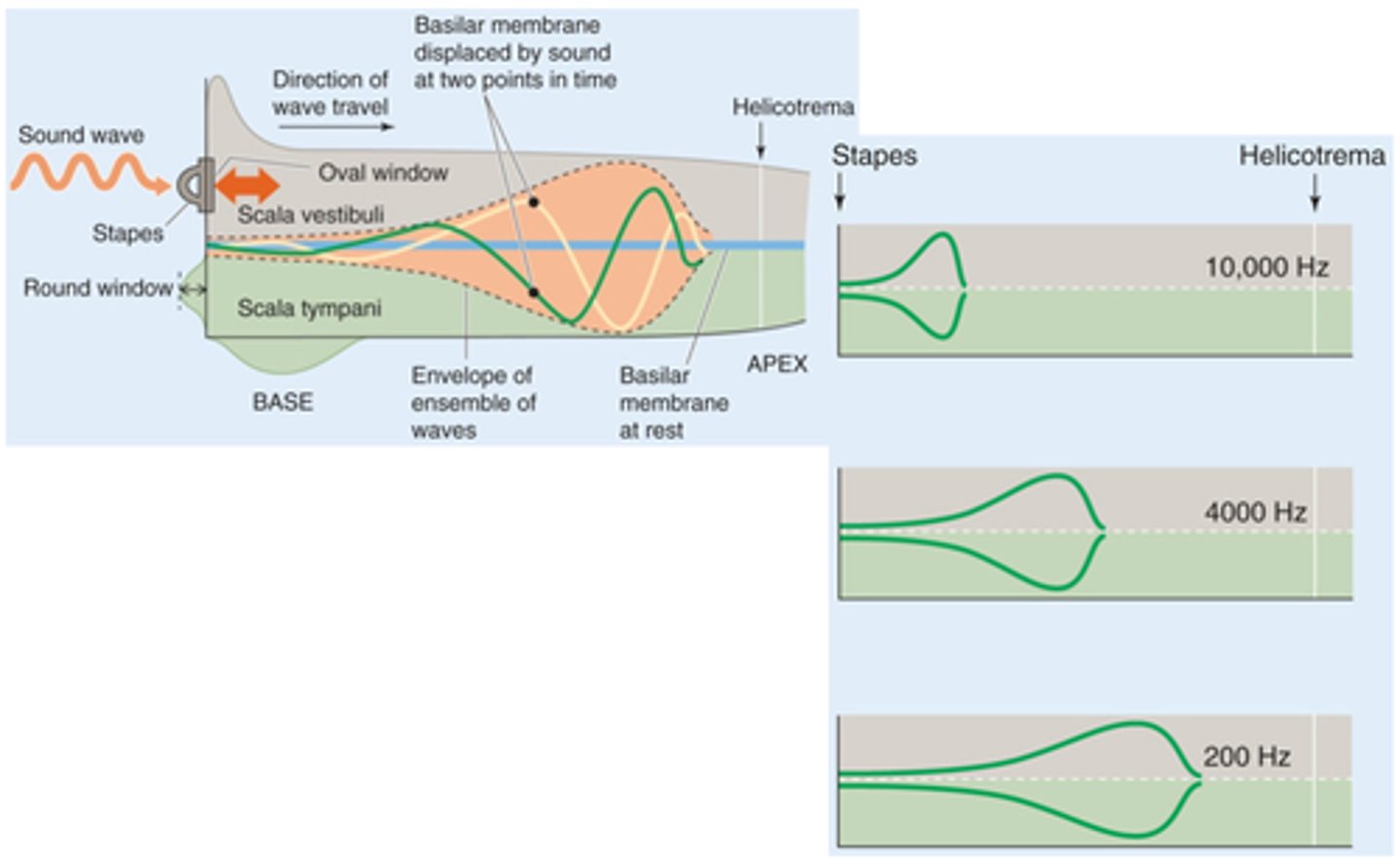
No sound coming in
What does the blue line represent?
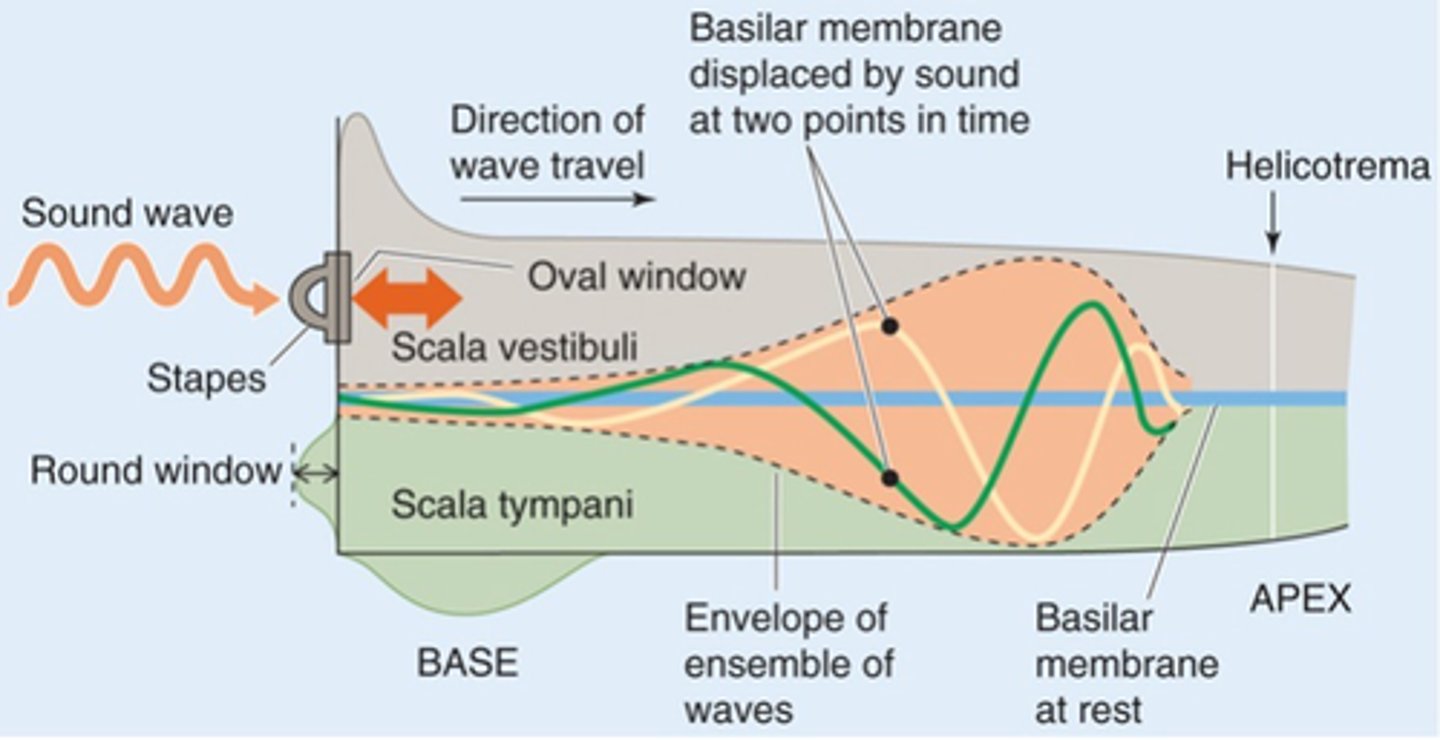
Different frequency of sound causing different movement
What does the green line represent?
Cause maximal movement of the basilar membrane at the base
What would a high frequency sound do?
Cause maximum displacement of the basilar membrane up towards the apex
What would a low frequency sound do?
Tonotropic
What is this kind of map called?
Because of fluid movement in and out of the cochlea
How does the basilar membrane move up and down?
Stereo cilia
Movement of the basilar membrane and tectorial membrane causes ________ _______ (on top of hair cells) to move backwards and forwards
Outwards, upwards, outwards, depolarise
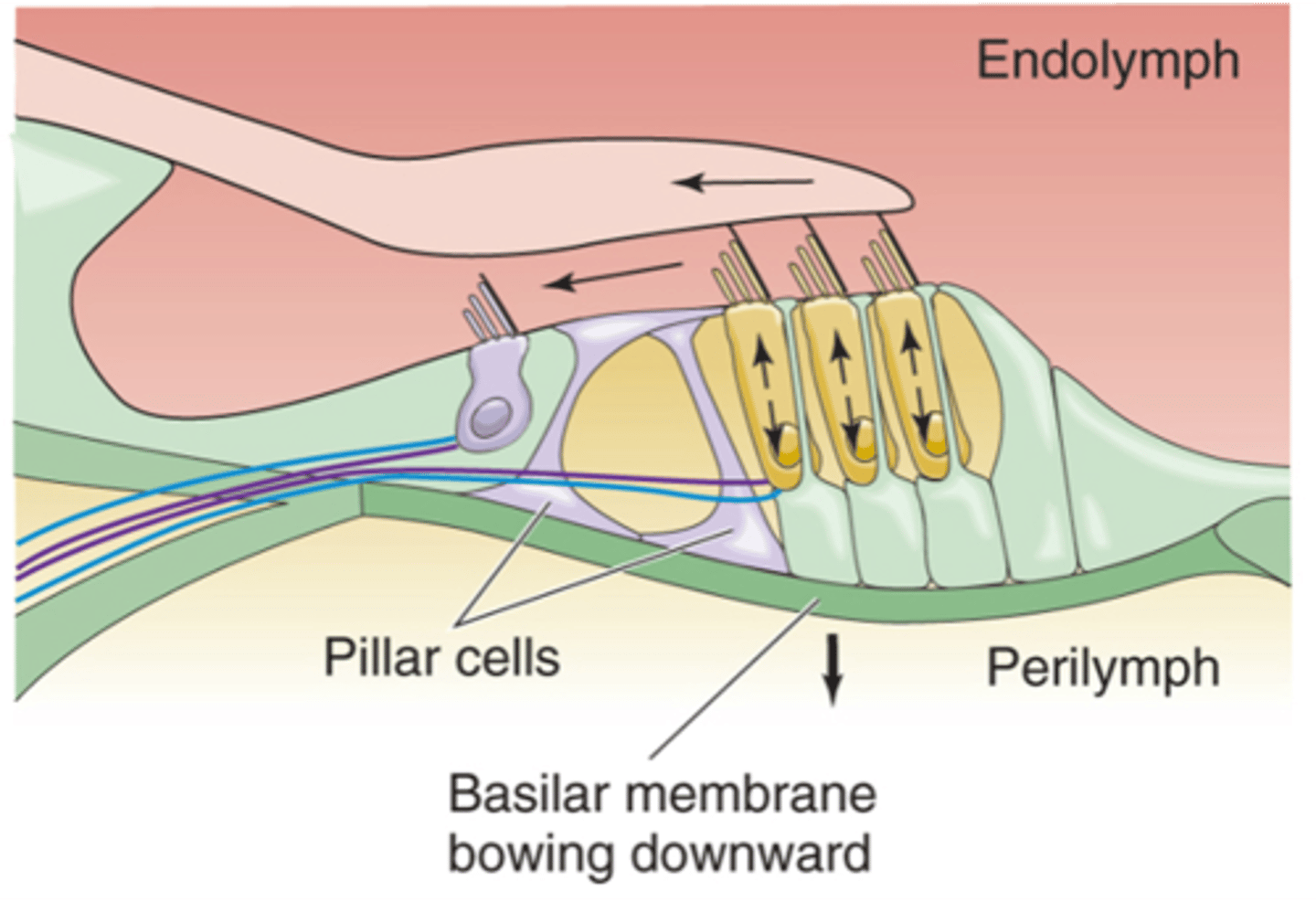
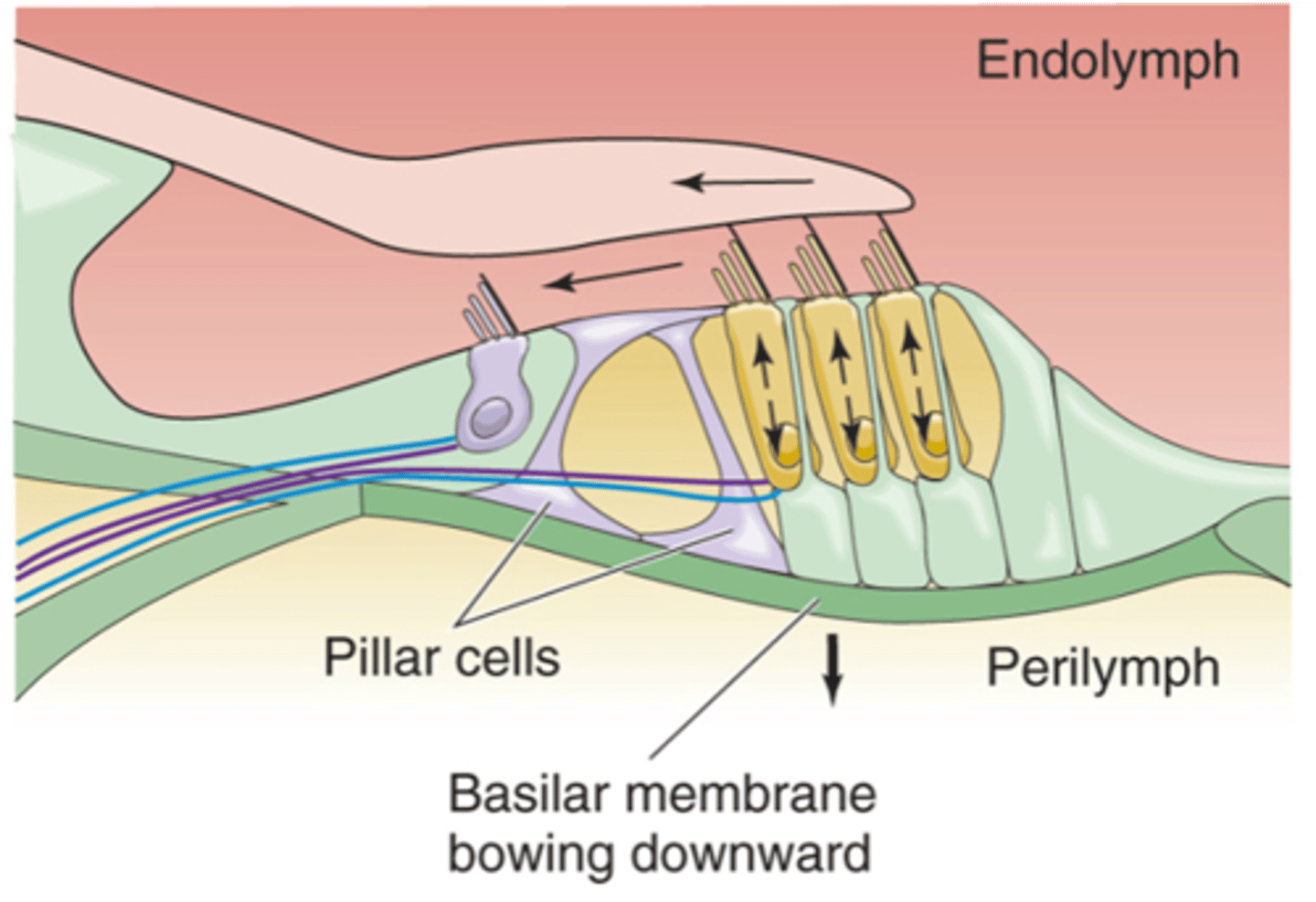
If the stapes is pulled outwards, we've got fluid moving __________, the upshot of that is that the basilar membrane pushes ____________ and as it does that the tectorial membrane moves slightly ___________ and pushes the stereo cilia a little bit towards the taller stereo cilia which causes the hair cells to _______________
Downwards, hyperpolarise
If your stapes moves inwards, it causes the basilar membrane to move ____________ and the hair cells/hair bundles move in the opposite direction which makes the hair cells ______________
Signals will be sent into the primary afferent nerve of the auditory nerve
If there is depolarisation, what is happening?
No signal going down the auditory nerve
If there is hyper polarisation, what happens?
They're the sensory receptors that are transfusing sound and sending information on down the nerve
The inner hair cells are the primary receptors, what does this mean?
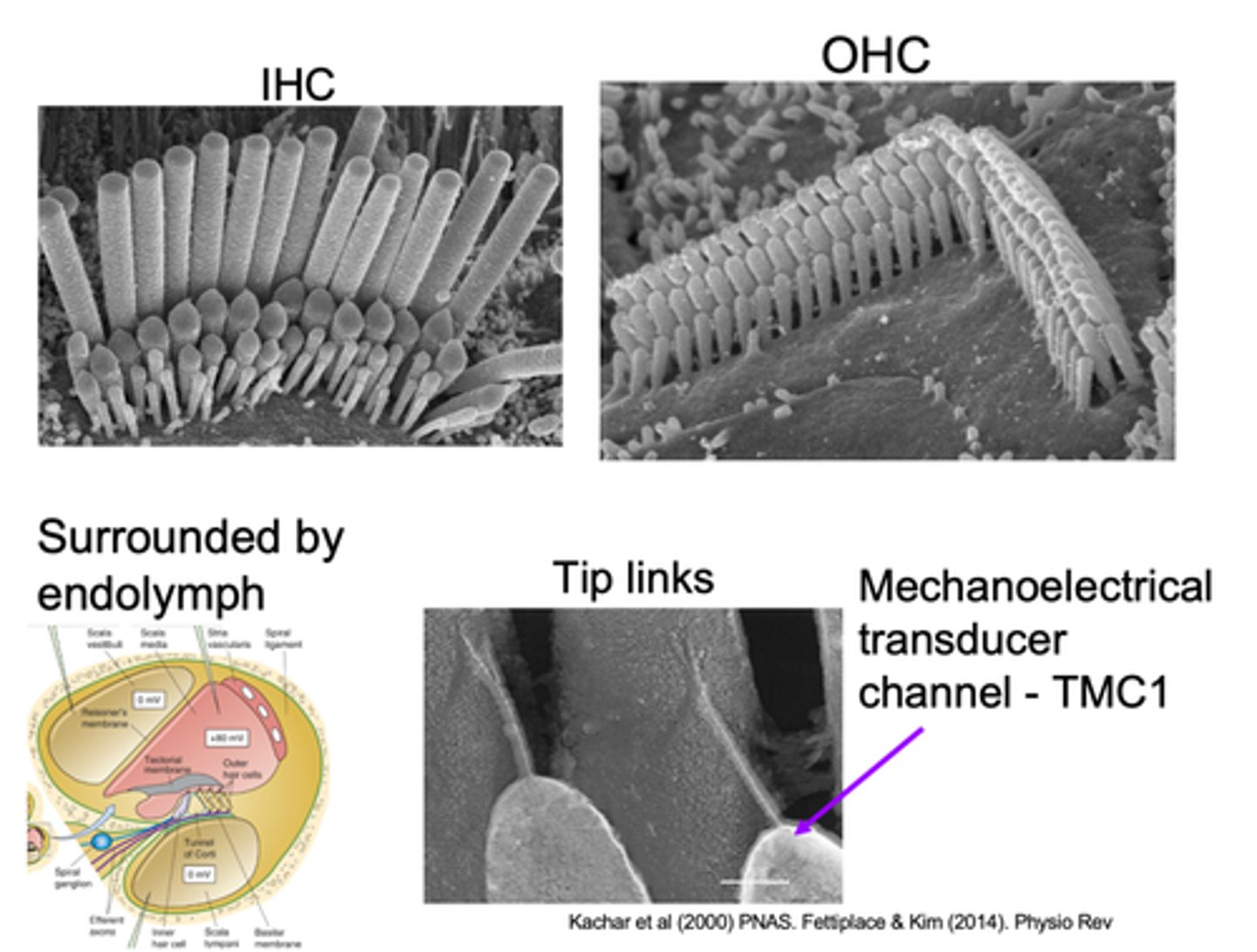
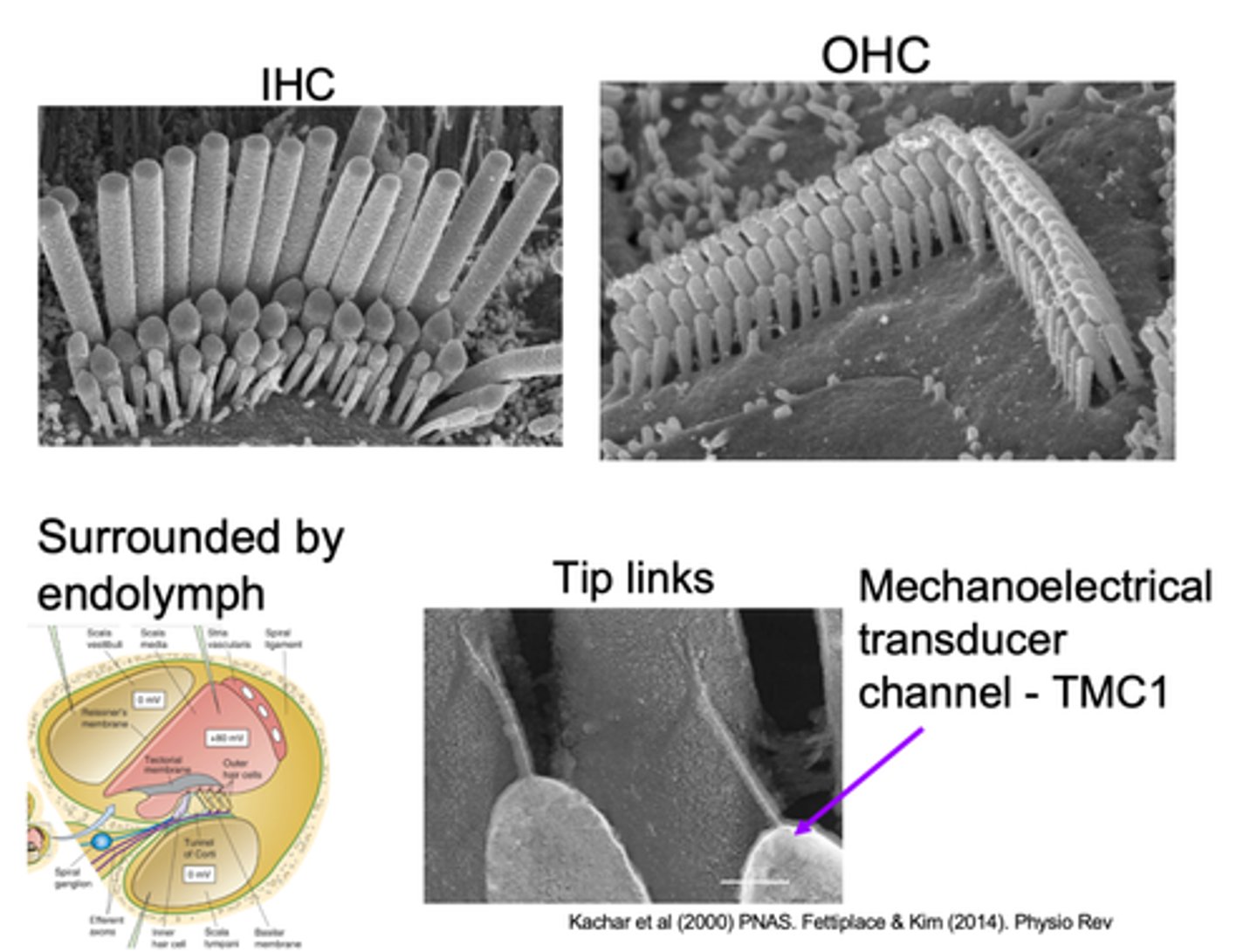
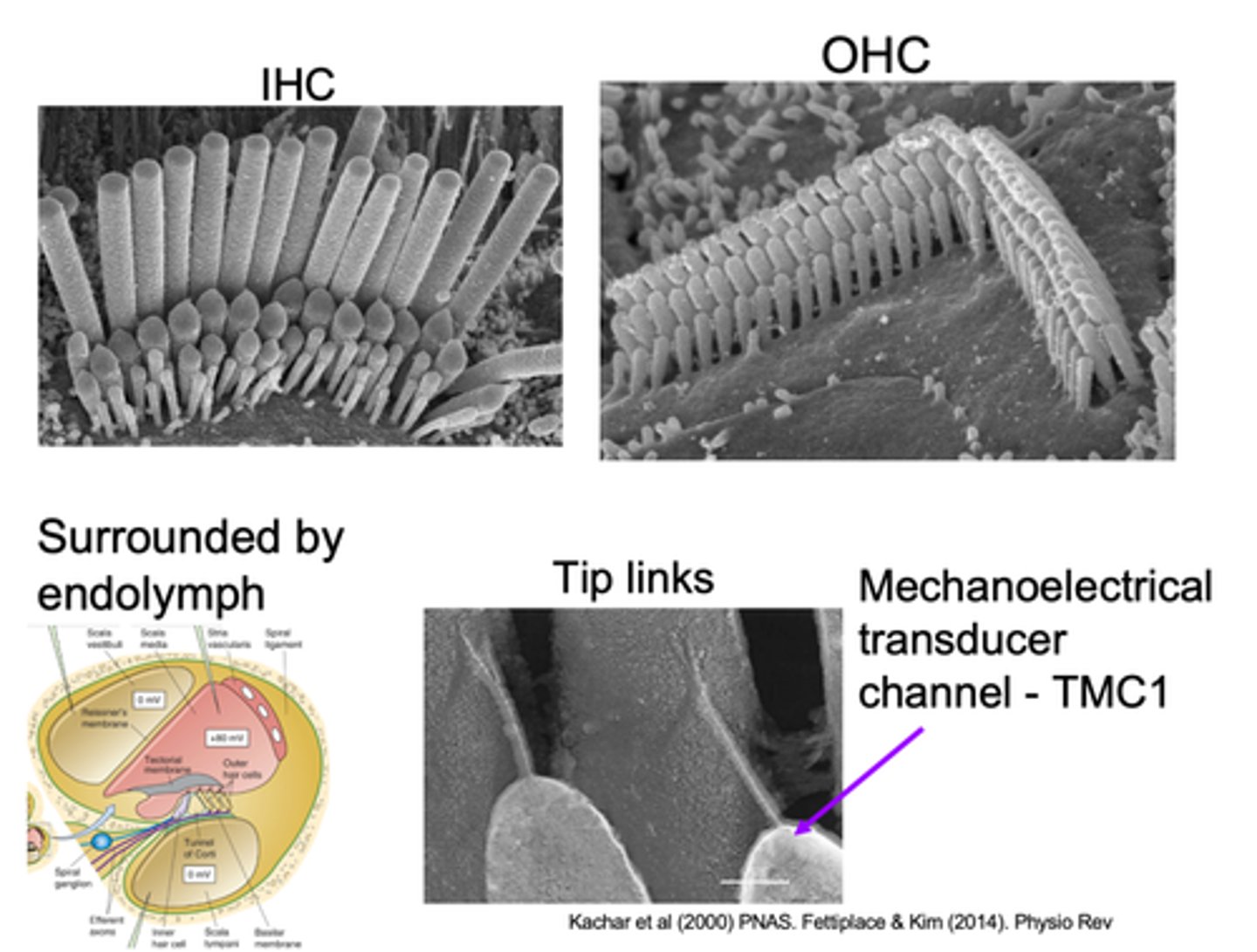
Tip links
What are hair bundles connected by?
Become broken/ripped off because they've been overstimulated
What happens to tip links in noise induced hearing loss?
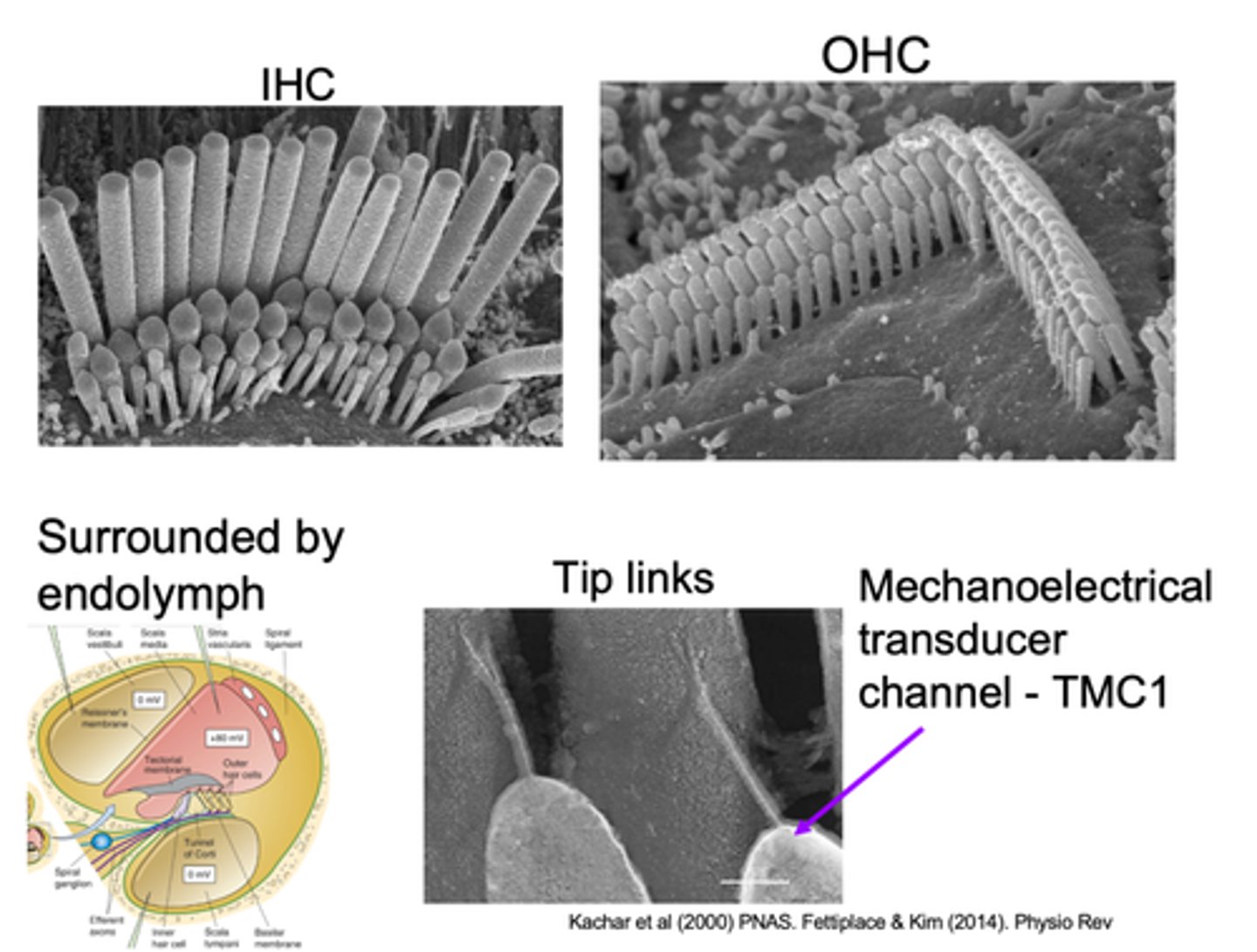
Pull open a channel at the top of the stereo cilia which allow sound to be transduced
What do tip links do?
Shorter, cation, cations
Mechanoelectrical transducer channel - TMC1 is found on top of the __________ stereo cilia and this is a _______ channel so it lets ________ move in
Potassium, potential
Stereo cilia is surrounded by endolymph which has high _____________ and ____________ in relation to the perilymph that surrounding the cell body

Perilymph
At the bottom we have ____________ surrounding the cell body
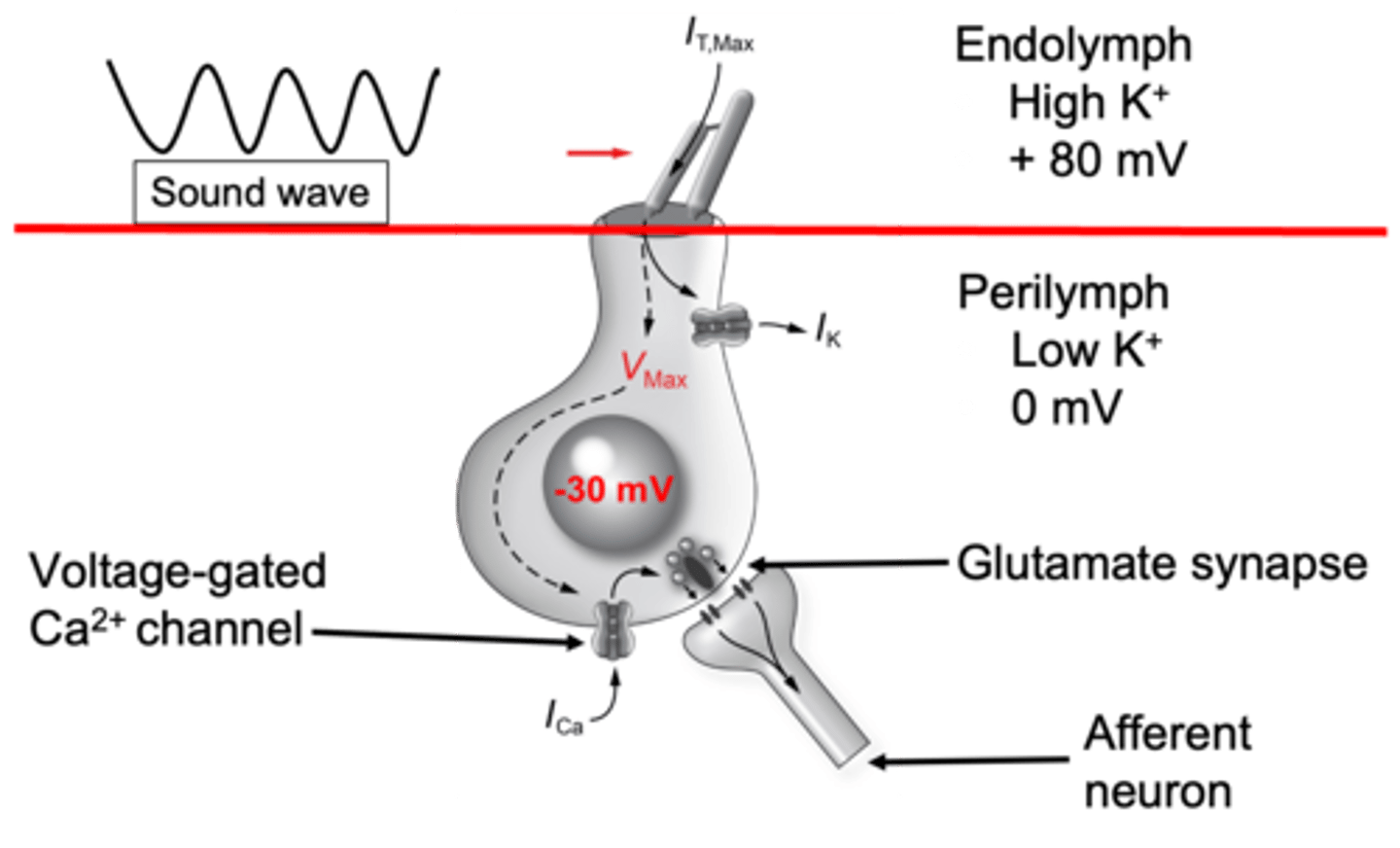
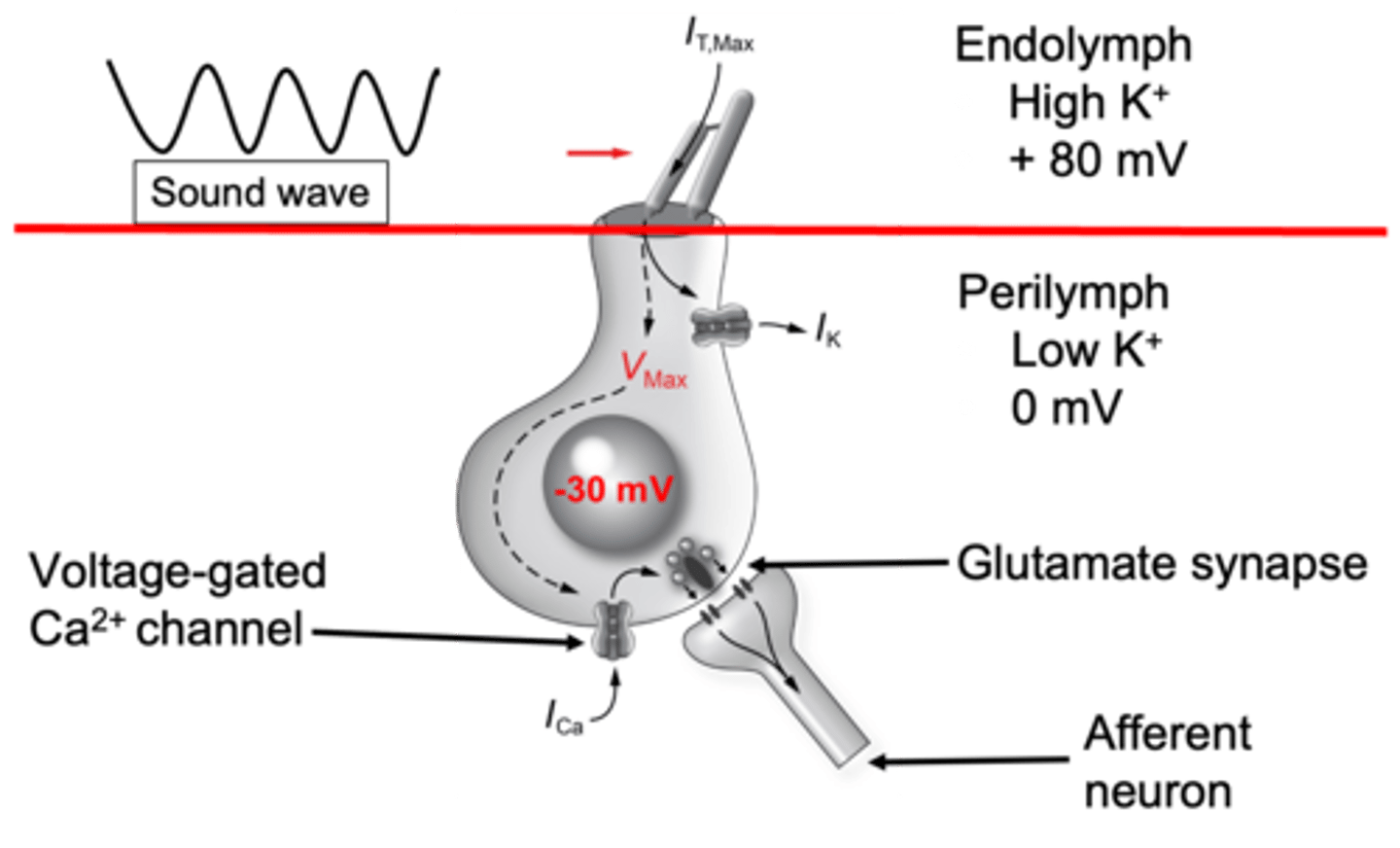
Stretched, opened, potassium, voltage gated calcium, exocytosis
When a stereo cilia is pushed towards a taller one, the tip link is __________ and the channel is ___________ all __________ floods in which causes depolarisation of hair cells
The depolarisation moves towards the base of the cell where it opens your _________ _________ __________ channels and because there's more calcium on the outside it floods into the cell and causes ____________ of vesicles containing glutamate so these travel across the synapse and activate glutamate receptors on the primary afferent neuron of the auditory nerve
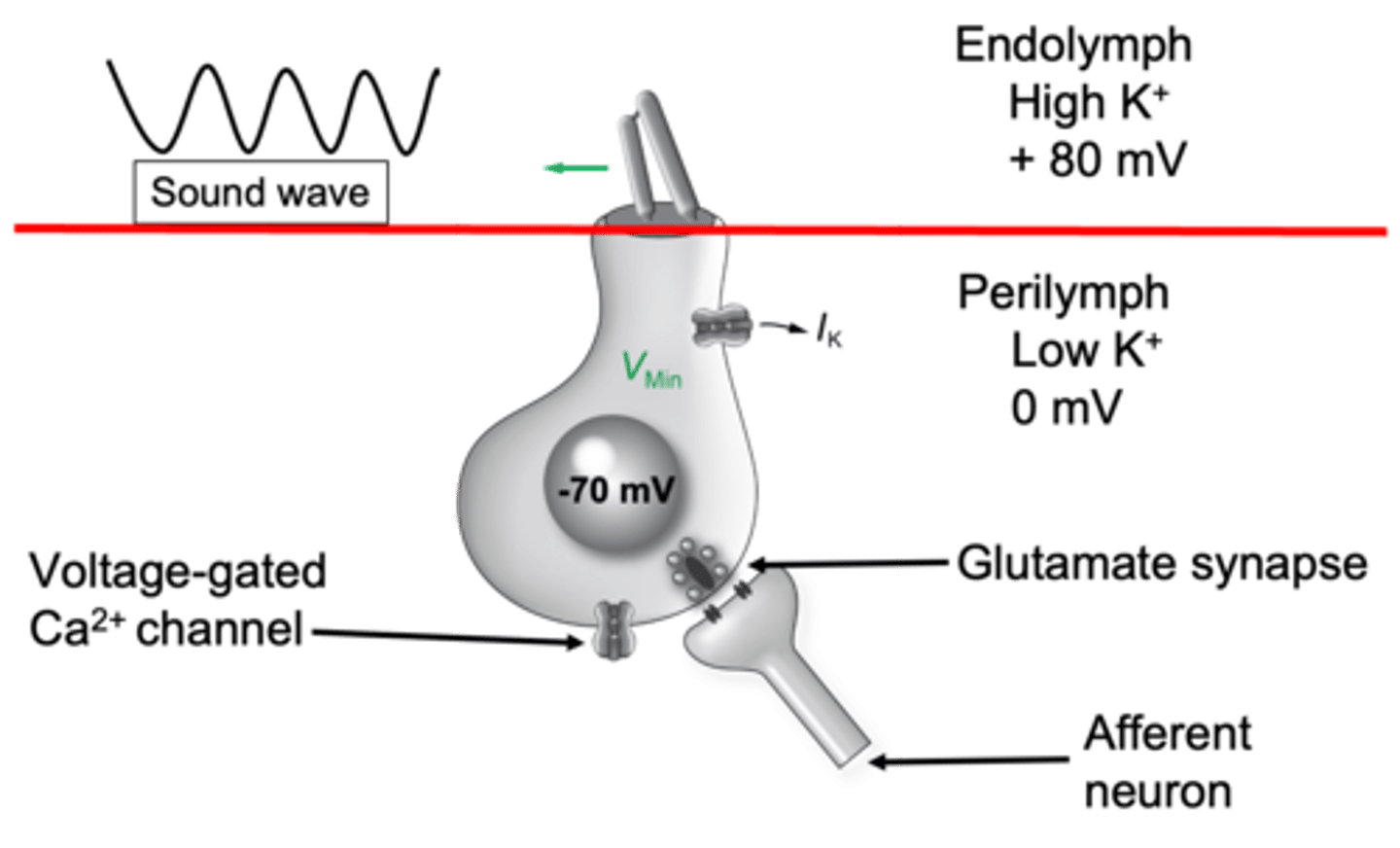
Slackened, closes, hyperpolarised, closed, glutamate, action potential
When the sound wave pushes this way, the tip link is ___________ which _______ the channel and so potassium cant come in, if potassium cant come in then your cell becomes _________________ (becomes more negative) that means the voltage gated calcium channels are ___________ which means _____________ isn't released which means your afferent neurone isn't stimulated and won't produce an _______ ____________
Electromotile, cochlear amplifier
Outer hair cells (OHCs) are _______________ and act as the __________ ____________
They help amplify the signal that comes in
What is meant by cochlear amplifier?
Electromotility
Because of a change in electrical profile, OHCs become motile, what is this known as?