OTD 317 Exam 3
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
symptoms and behaviors of personality disorders
Inflexibility, rigid response to life changes, dysfunctional relationships, maladaptive thinking and behaviors, distorted self-image. Includes paranoid, schizoid, antisocial, borderline, histrionic, narcissistic, avoidant, dependent, and obsessive-compulsive personality disorders. Common symptoms include suspicion, emotional instability, grandiosity, avoidance of social contact, and compulsive perfectionism.
functional impact from personality disorders
Impaired interpersonal relationships, difficulty maintaining employment, social withdrawal, impulsivity, poor coping mechanisms.
occupational performance impact from personality disorders
Difficulty in engaging socially, maintaining employment, performing ADLs, and self-care. Affects time management, emotional regulation, and collaboration in group settings.
OT assessment and intervention for personality disorders
Focus on social skills training, behavior modification, developing self-awareness, self-esteem building, structured group interaction, DBT (especially for BPD), and coping strategies. May use role-play, journaling, mindfulness, and group-based therapy.
occurring disorders
Often found with substance use disorders due to self-medication.
symptoms/behaviors of anxiety
GAD, panic disorder, OCD, phobias, social anxiety, agoraphobia, selective mutism. Symptoms include excessive worry, restlessness, avoidance behaviors, hypervigilance, and compulsions.
symptoms/behaviors of depresion
symptoms/behaviors of bipolar disorder
Characterized by manic (or hypomanic) and depressive episodes. Symptoms include mood swings, impulsive behavior, sleep disturbance, and grandiosity.
functional impact from anxiety and mood disorders
Decision-making difficulties, social and occupational withdrawal, ADL/IADL impairment, disrupted sleep and eating routines.
occupational performance impact from anxiety and mood disorders
Low participation in daily life tasks, decreased productivity, self-isolation.
OT assessment & intervention for anxiety and mood disorders
Facilitate meaningful activity engagement, cognitive-behavioral approaches, mindfulness, emotional regulation training, stress management, and sensory-based interventions. Support return to work/school.
statistics for domestic violence (DV) and human trafficking (HT)
1 in 4 women and 1 in 7 men experience IPV; high rates of underreporting.
impacts of domestic violence (DV) and human trafficking (HT)
Psychological and physical injuries, PTSD, anxiety, depression, fear, learned helplessness, substance abuse.
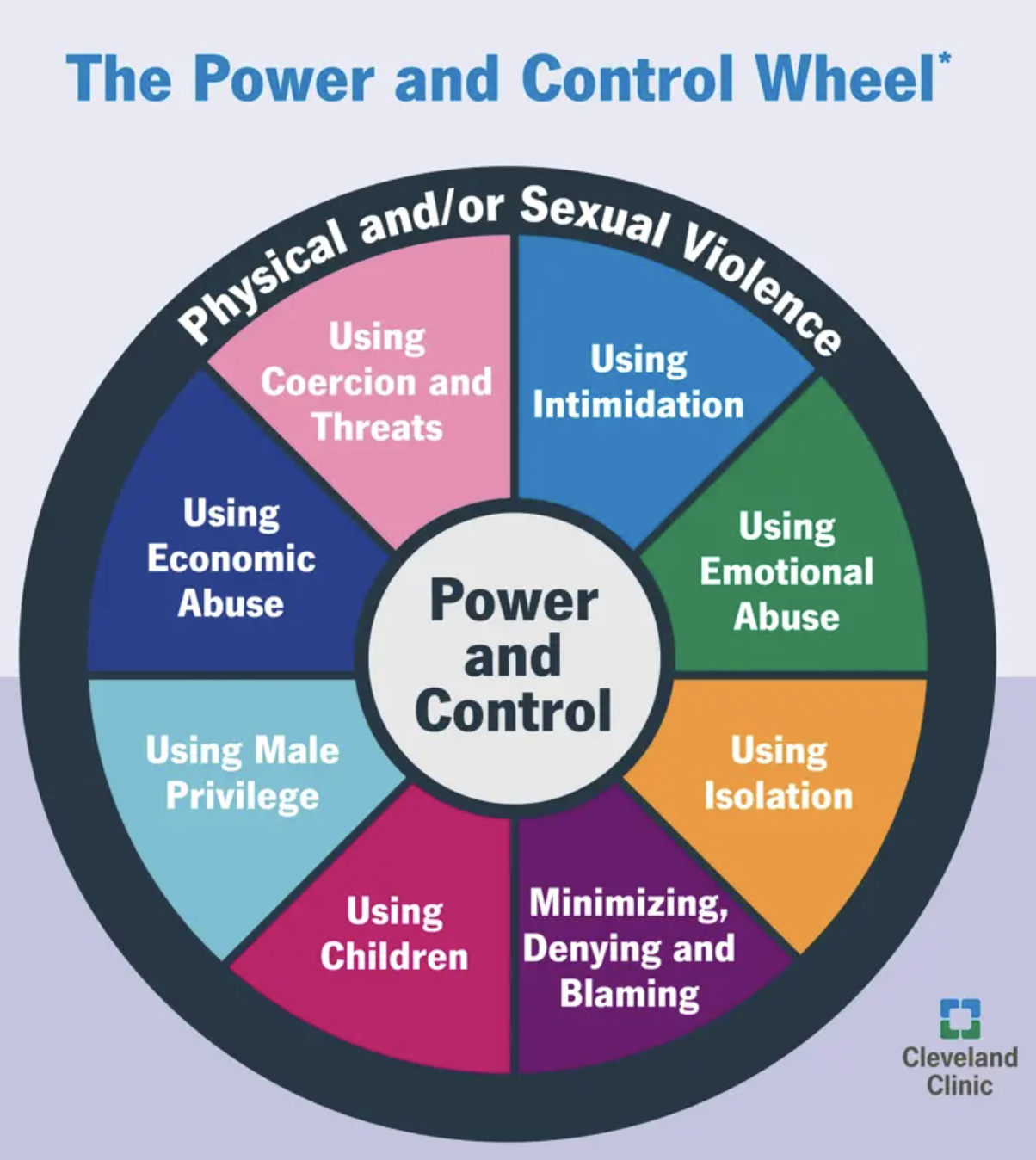
power and control wheel/cycle of violence
Illustrates the use of intimidation, emotional abuse, isolation, minimizing/denying/blaming, using children, privilege, economic abuse, and coercion/threats.
3 P’s protocol
Prevention, Protection, Prosecution
domestic violence (DV)
Pattern of coercive behavior involving power and control.
human trafficking
Exploitation through force, fraud, or coercion for labor or sex.
what is OT’s role in domestic violence (DV) and human trafficking (HT)?
Provide trauma-informed care, facilitate empowerment through occupation, assess safety, identify community supports, provide psychoeducation, and develop safety plans.
barriers to victims of DV and HT help-seeking
Fear, manipulation, economic dependence, lack of awareness or resources.
spotting victims of DV and HT
Inconsistent explanations for injuries, fearfulness, signs of control by another individual, limited independence.
statistics of mental illness & incarceration
Up to 44% in jails and 37% in prisons have mental illness.
what is the role of OT in the criminal justice system?
Focus on life skills training, emotional regulation, social skills, coping strategies, vocational rehab, and reentry planning.
barriers to OT in the criminal justice system
Lack of awareness of OT’s role, funding constraints, stigma, institutional policies.
settings in the criminal justice system
Jails, prisons, forensic hospitals, diversion programs, community reintegration services.
anorexia nervosa
Characterized by restriction of energy intake, intense fear of gaining weight, and a distorted body image. Subtypes include restricting type (no bingeing/purging) and binge-eating/purging type. Often associated with amenorrhea, bradycardia, and osteoporosis.
bulimia nervosa
Involves cycles of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors such as vomiting, excessive exercise, or laxative use. Individuals often maintain normal body weight, making the disorder less noticeable.
binge eating disorder
Marked by recurrent episodes of eating large quantities of food with a sense of loss of control. Not followed by purging behaviors. Often associated with shame and significant distress.
avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID)
Characterized by a lack of interest in eating or avoidance due to sensory characteristics or fear of consequences (e.g., choking). Not related to body image.
orthorexia
Obsession with "clean" or "pure" eating. Not officially recognized in the DSM but can lead to significant nutritional deficiencies and social impairment.
diabulimia
A dangerous practice seen in individuals with Type 1 diabetes who reduce or omit insulin to lose weight. Involves both an eating disorder and manipulation of insulin treatment.
side effects of eating disorders
Electrolyte imbalance, cardiac arrhythmias, renal damage, dental erosion, amenorrhea, GI issues, osteoporosis.
functional impact from eating disorders
Distorted body image, disordered eating behaviors, social withdrawal, perfectionism, avoidance of food-related activities.
OT assessments and intervention for eating disorders
Focus on body image, identity, adaptive routines, mindfulness, emotional regulation, meal prep, stress management, and re-engaging in valued occupations.
diagnoses of perinatal mood and anxiety disorders (PMADs)
include postpartum depression, anxiety, OCD, PTSD, and postpartum psychosis.
what is the OT role for maternal mental health, grief, loss
Screen for PMADs, support identity transformation, manage role overload, address co-occupations (e.g., feeding, sleep routines), provide caregiver education.
grieft
Includes perinatal loss, disenfranchised grief, anticipatory grief. Can lead to PTSD, depression, and identity disruption.
intervention strategies for maternal mental health, grief, loss
Coping skills, therapeutic journaling, group therapy, self-care planning, role restoration, environmental adaptations.
Licensed Mental Health Professional (LMHP)
Typically includes psychiatrists, psychologists, licensed clinical social workers, and licensed professional counselors. These professionals are authorized to diagnose and treat mental illness independently.
Qualified Mental Health Professional (QMHP)
A broader category often used by state Medicaid programs and community mental health systems. It includes professionals who have training and supervised experience in mental health services but may not hold a license for independent practice. In some states, occupational therapists can qualify as QMHPs based on their education and mental health experience.
OT’s role in advocacy and parity
While not typically LMHPs, OTs may be considered QMHPs in states such as Illinois, Oregon, and Michigan. This status allows them to provide reimbursable mental health services under Medicaid and contribute to interdisciplinary mental health teams. Advocacy is ongoing to expand recognition of OTs as QMHPs nationwide. not LMHPs but can qualify as QMHPs in some states based on experience and training
parity
Ensures equal treatment of mental and physical health conditions under insurance laws.
mental health parity act (MHPA)
Prohibits lifetime/annual dollar limits on mental health.
mental health parity and addiction equity act (MHPAEA)
Covers treatment limits, deductibles, out-of-pocket costs.
affordable care act (2010/2014)
Expands MHPAEA protections to individual/marketplace plans.
how can ot advocate for mental health?
Promote mental health OT, participate in legislation (e.g., RISE Act, Medicaid Reentry Act), educate communities, use AOTA resources.