Bio: Unit 12 DNA Structure, Transcription, Translation, Mutation
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.(made of nucleotides)
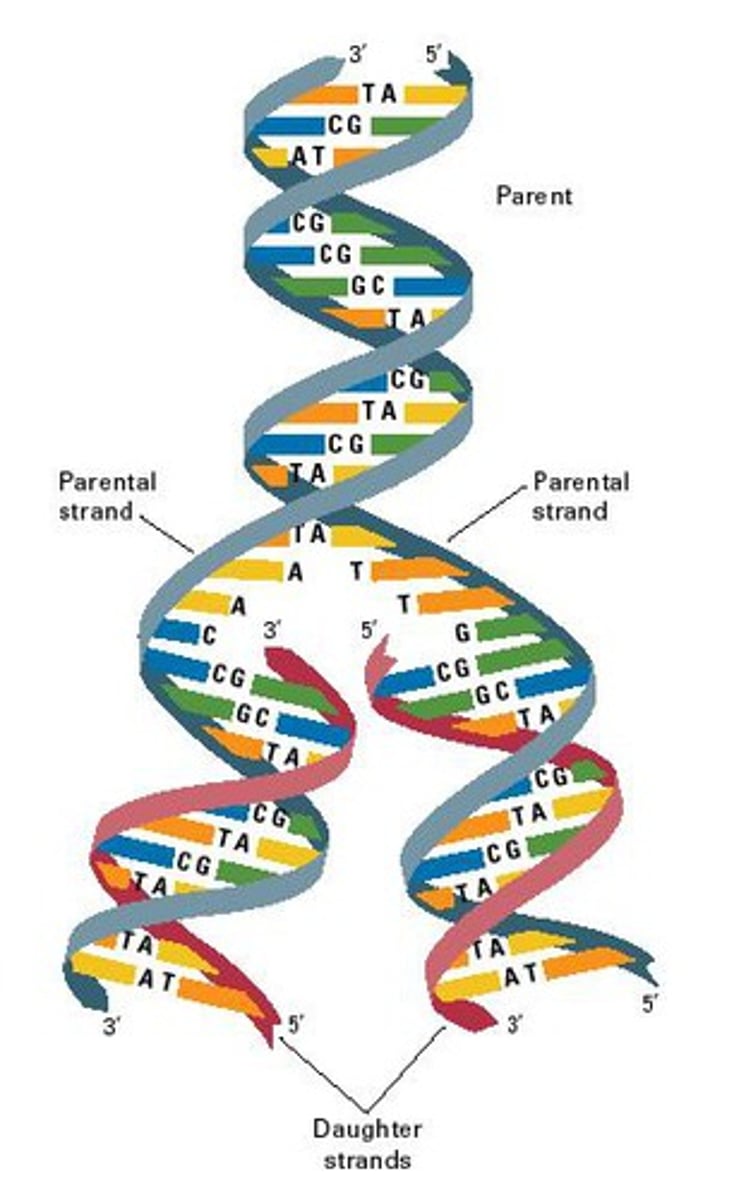
DNA Replication
the process of making identical copies of DNA before cell division, occurs during S phase of interphase
Nucleotide
a subunit that consists of a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base (monomer of DNA & RNA)
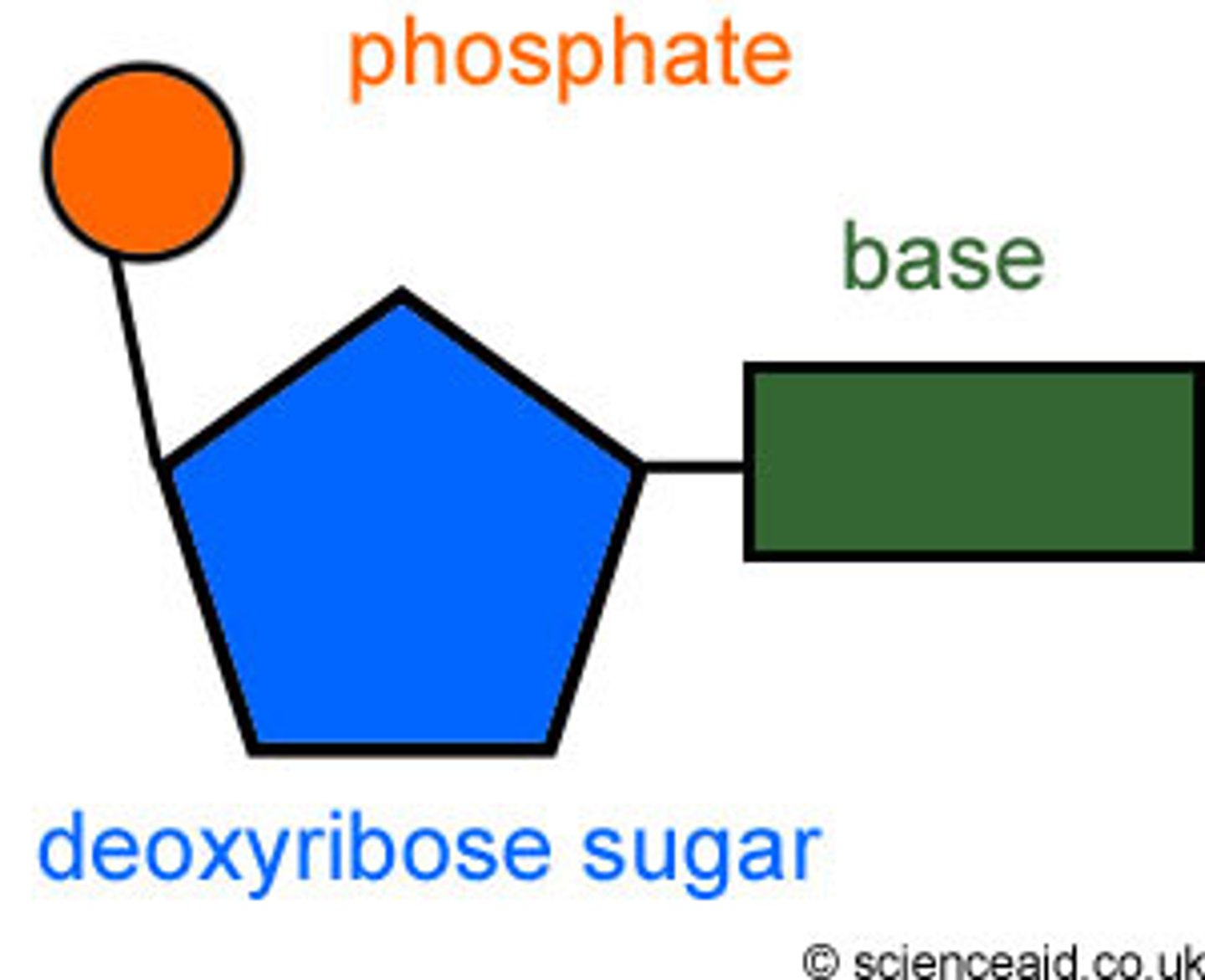
nitrogen base
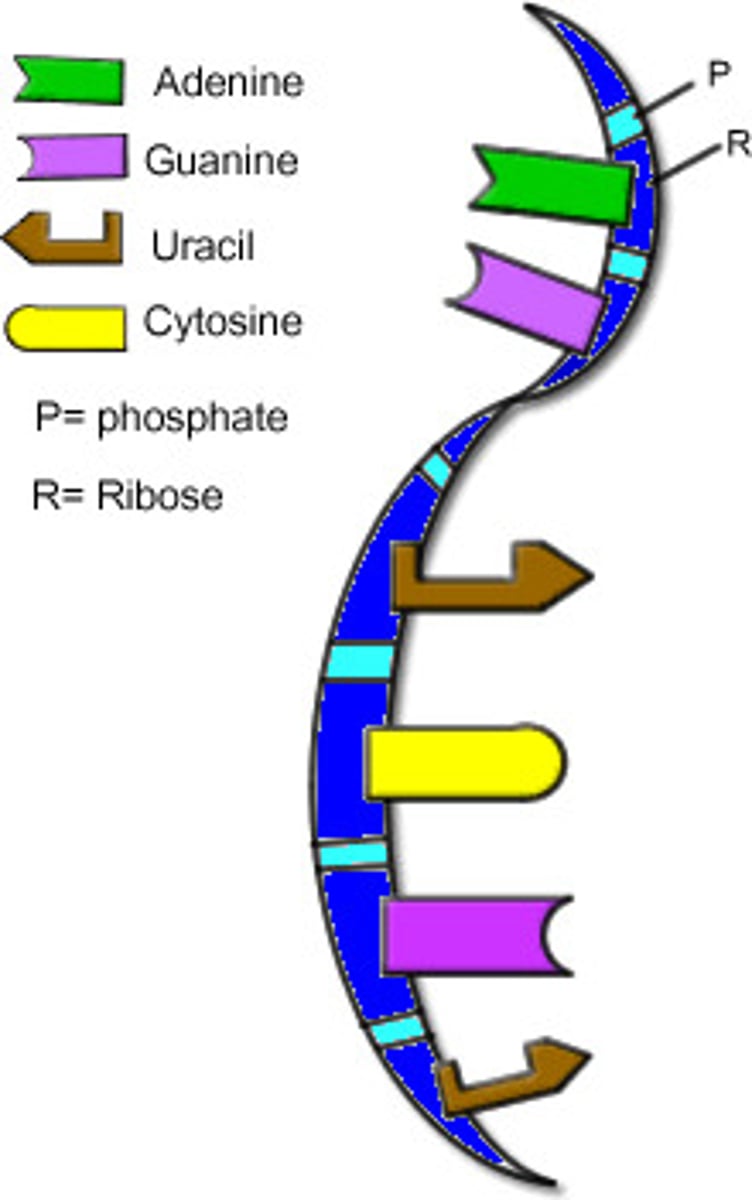
The chemicals that make up the rungs of the DNA ladder. A-T and C-G pair up. (RNA has U in place of T)
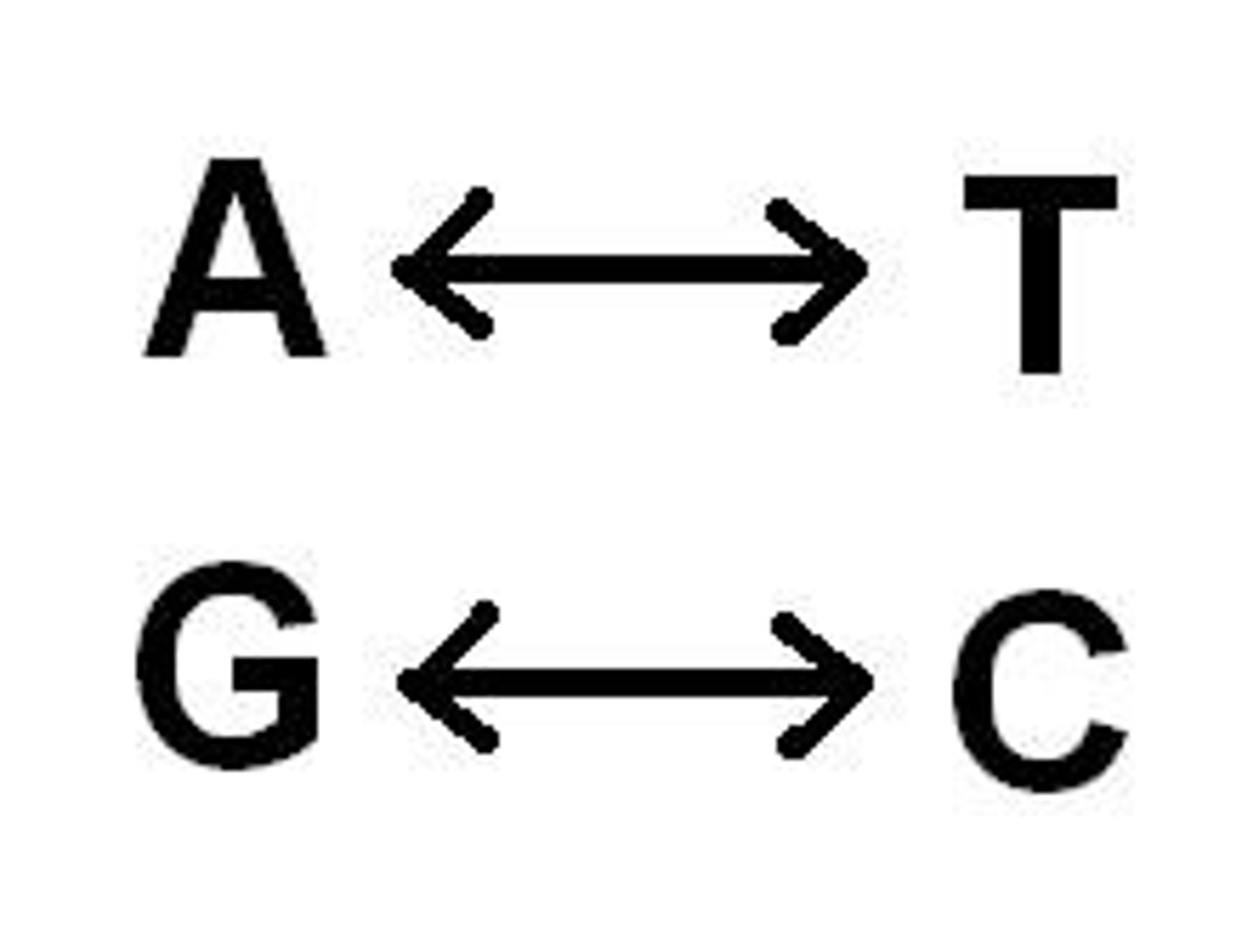
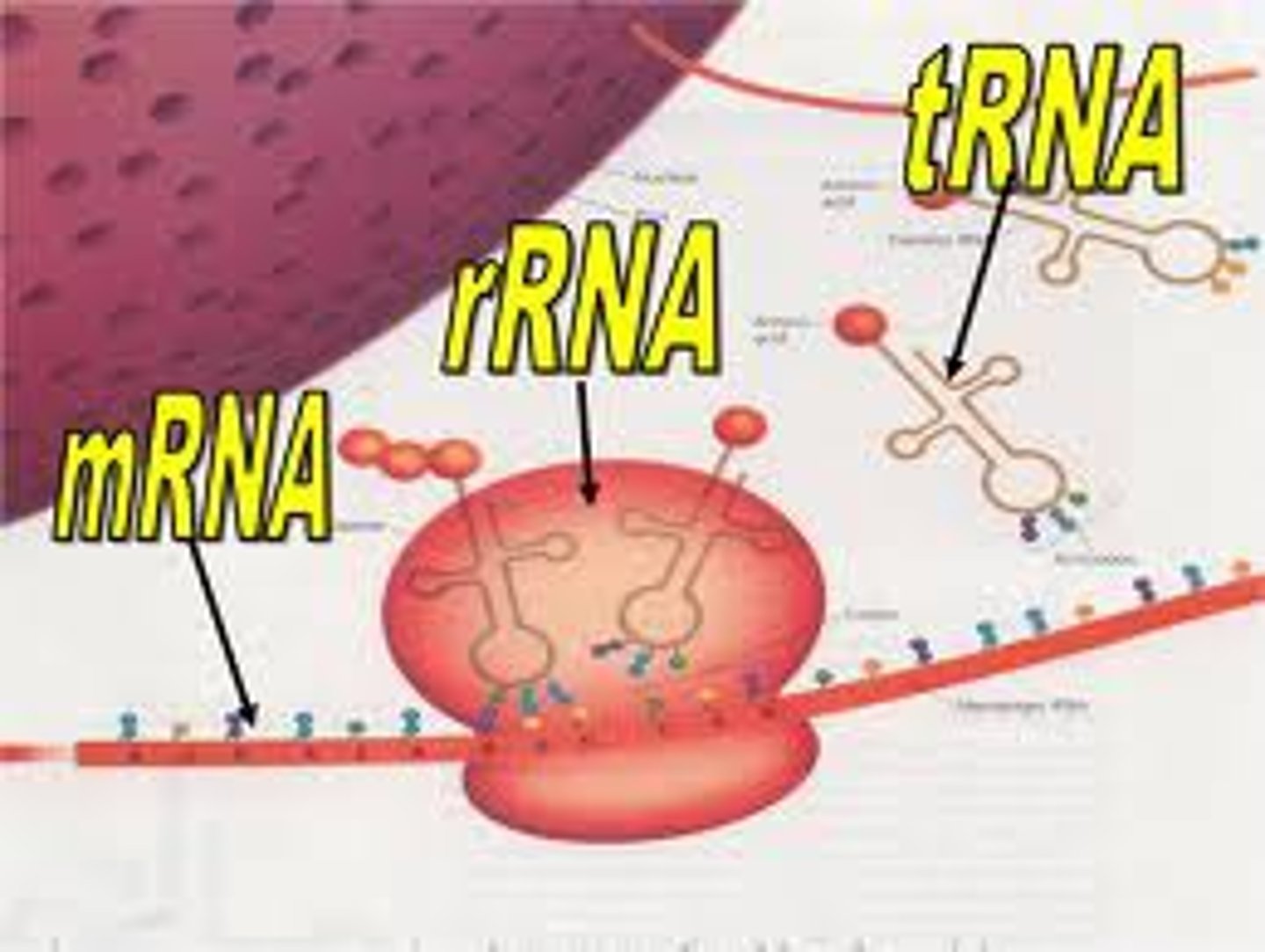
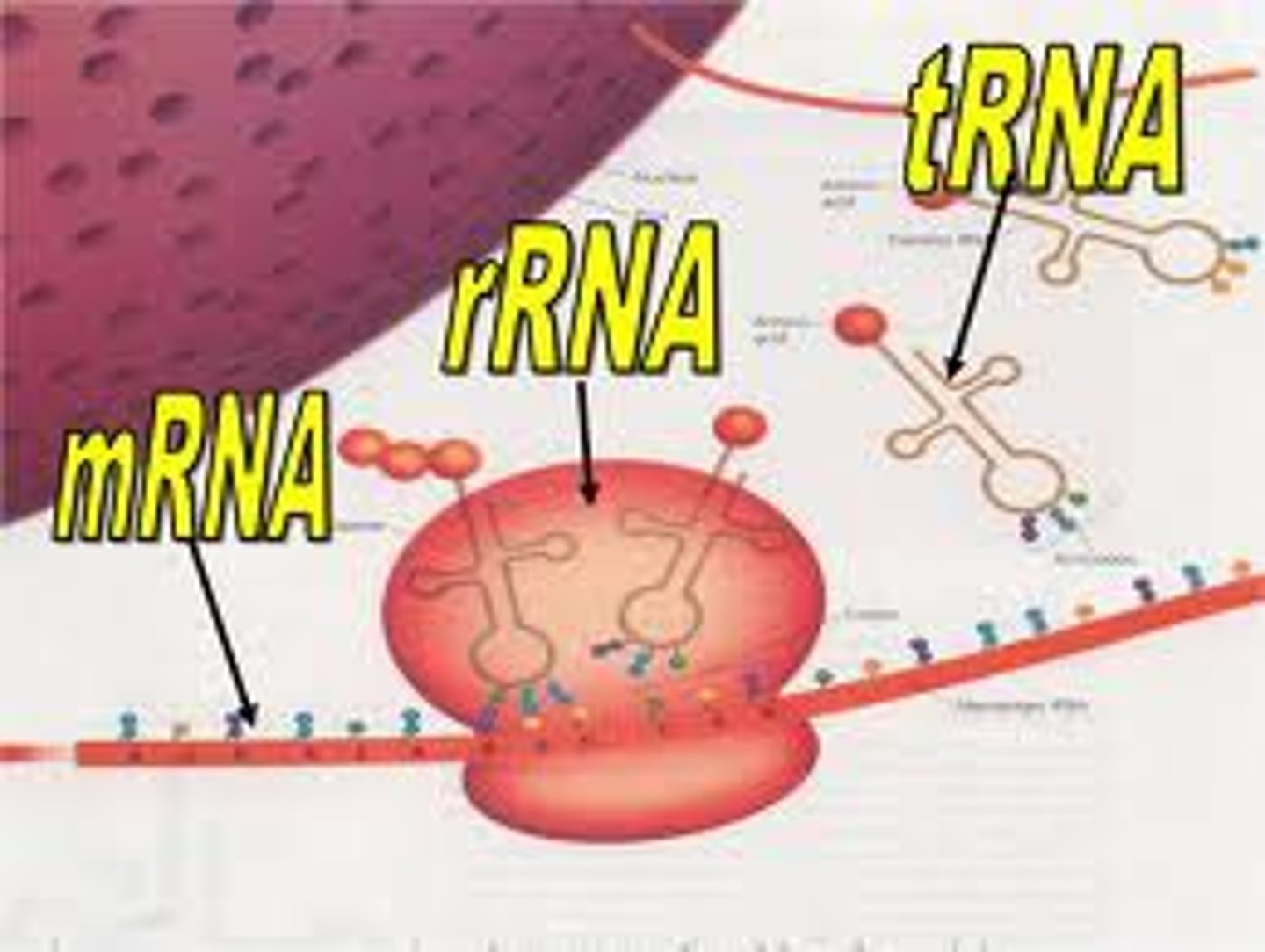
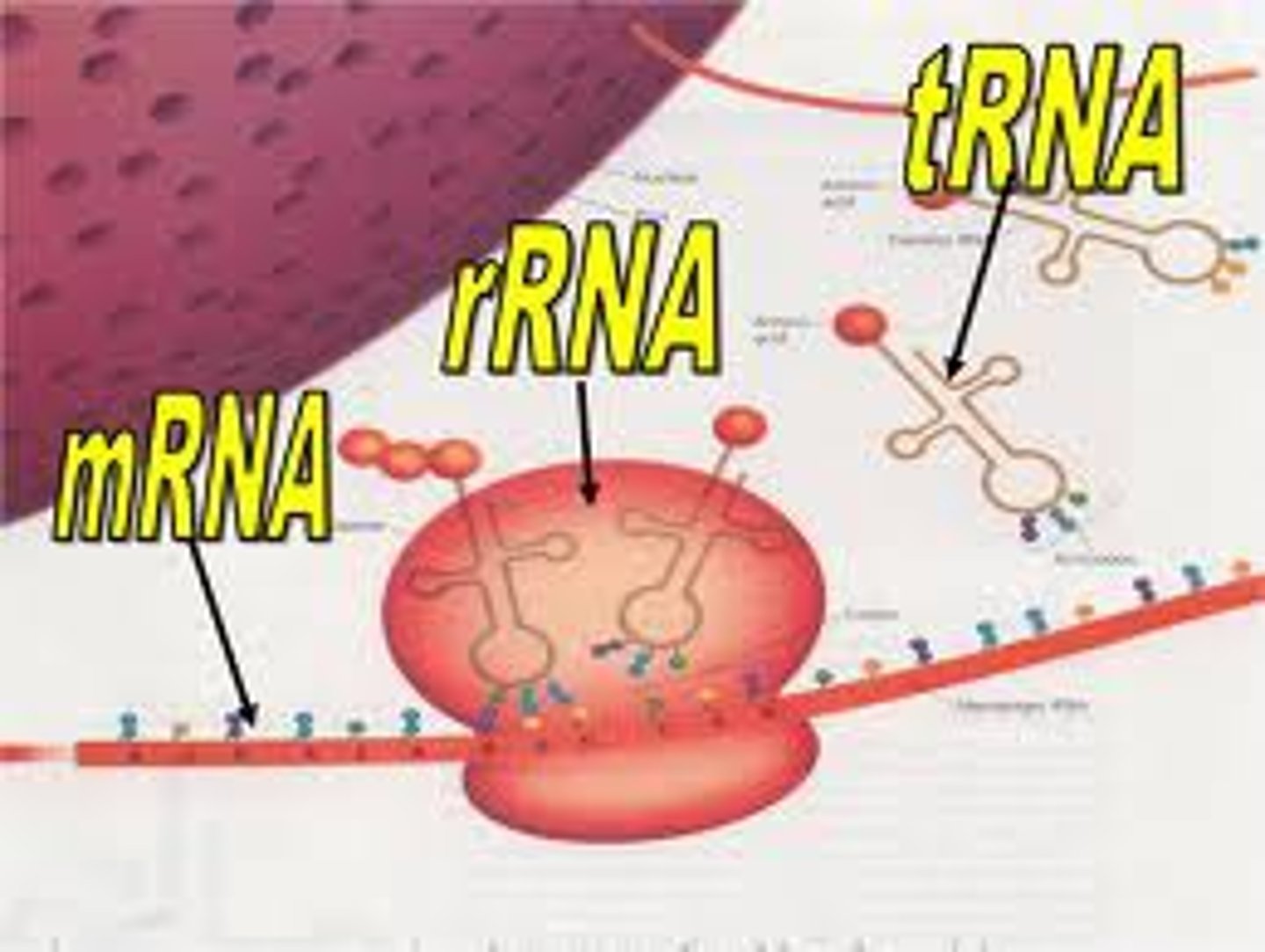
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome (made in transcription)
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids in the cytoplasm to the ribosome during translation
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome where protein is made during translation
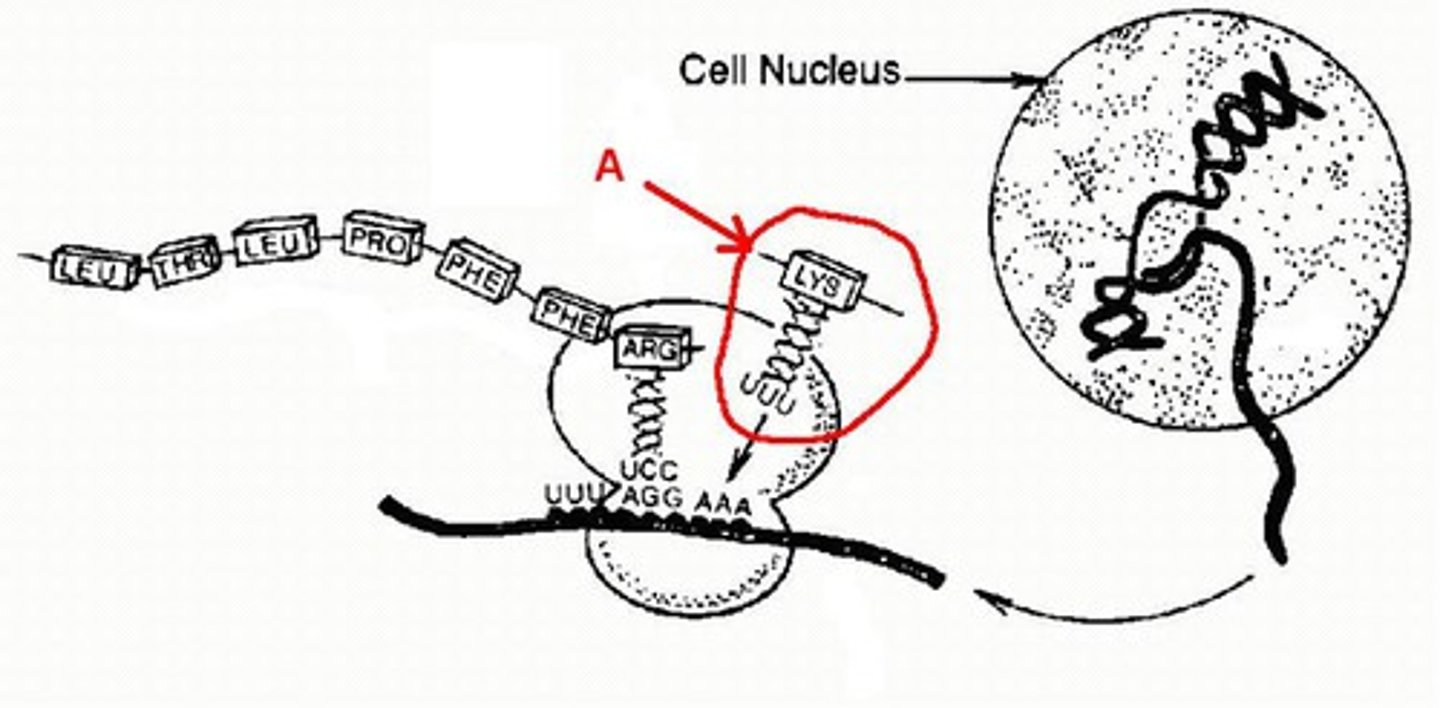
transcription
process where part of a DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA (like copying a recipe from a large book, happens in the Nucleus of eukaryotic cells)
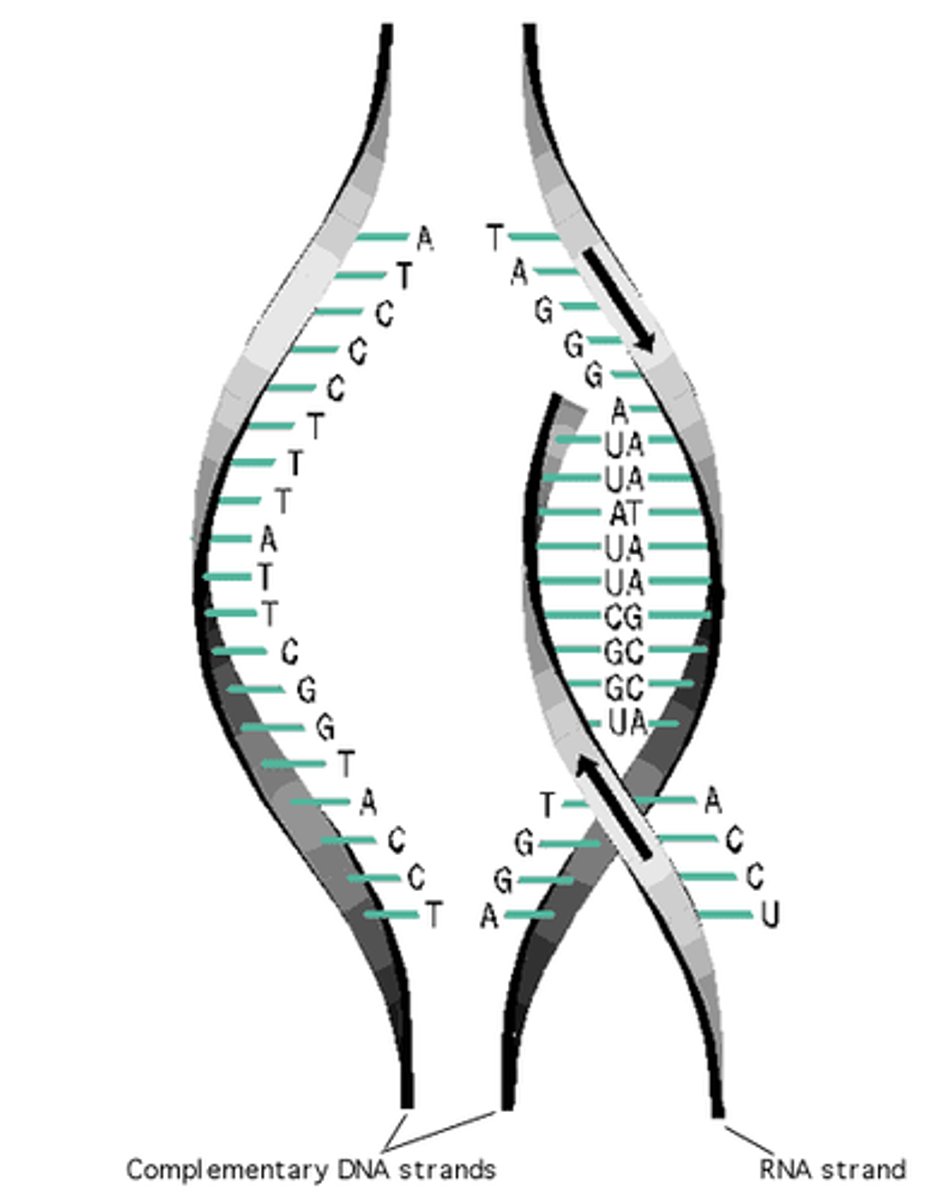
codon
3 nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid (we use the chart for this)

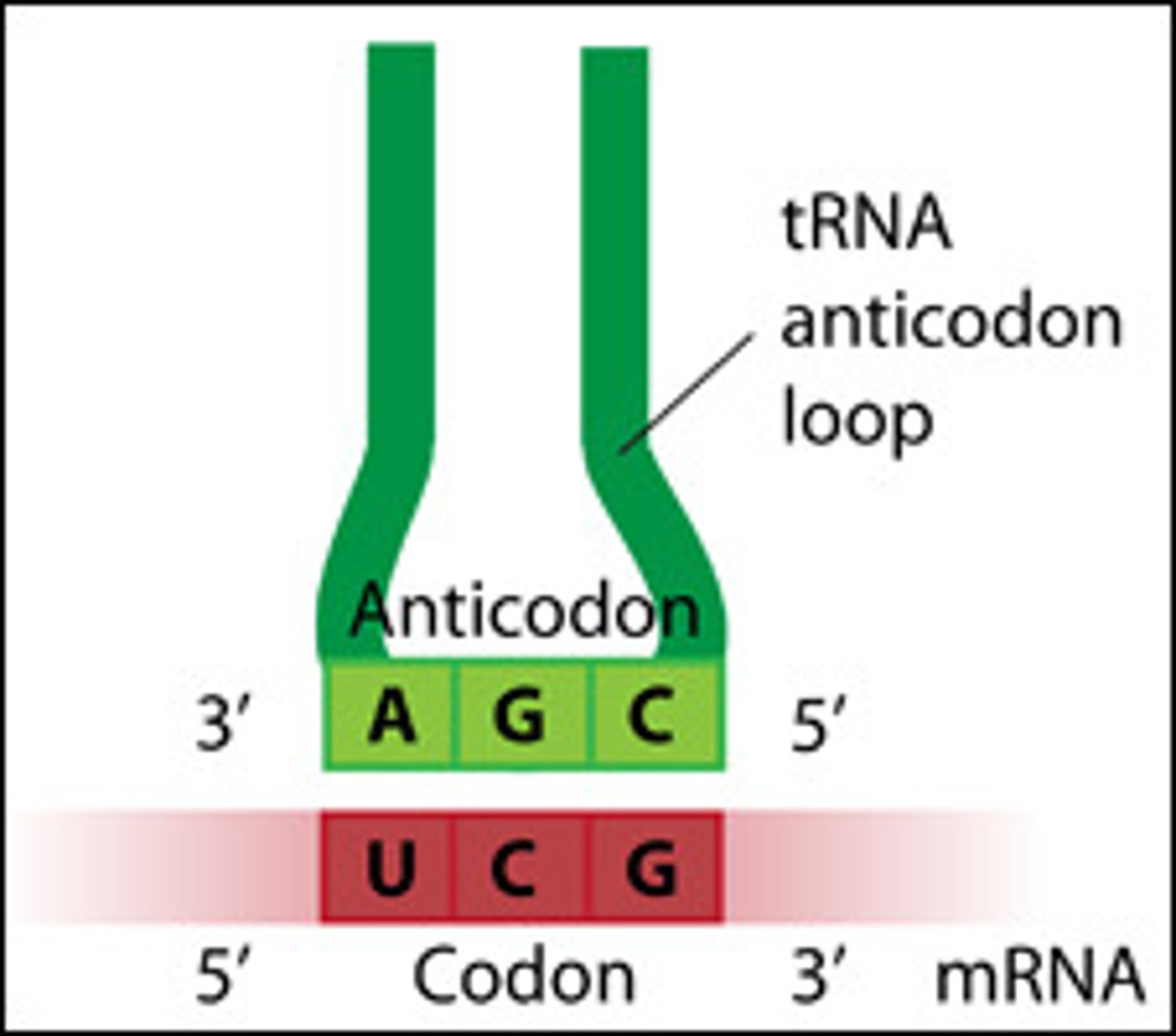
anticodon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
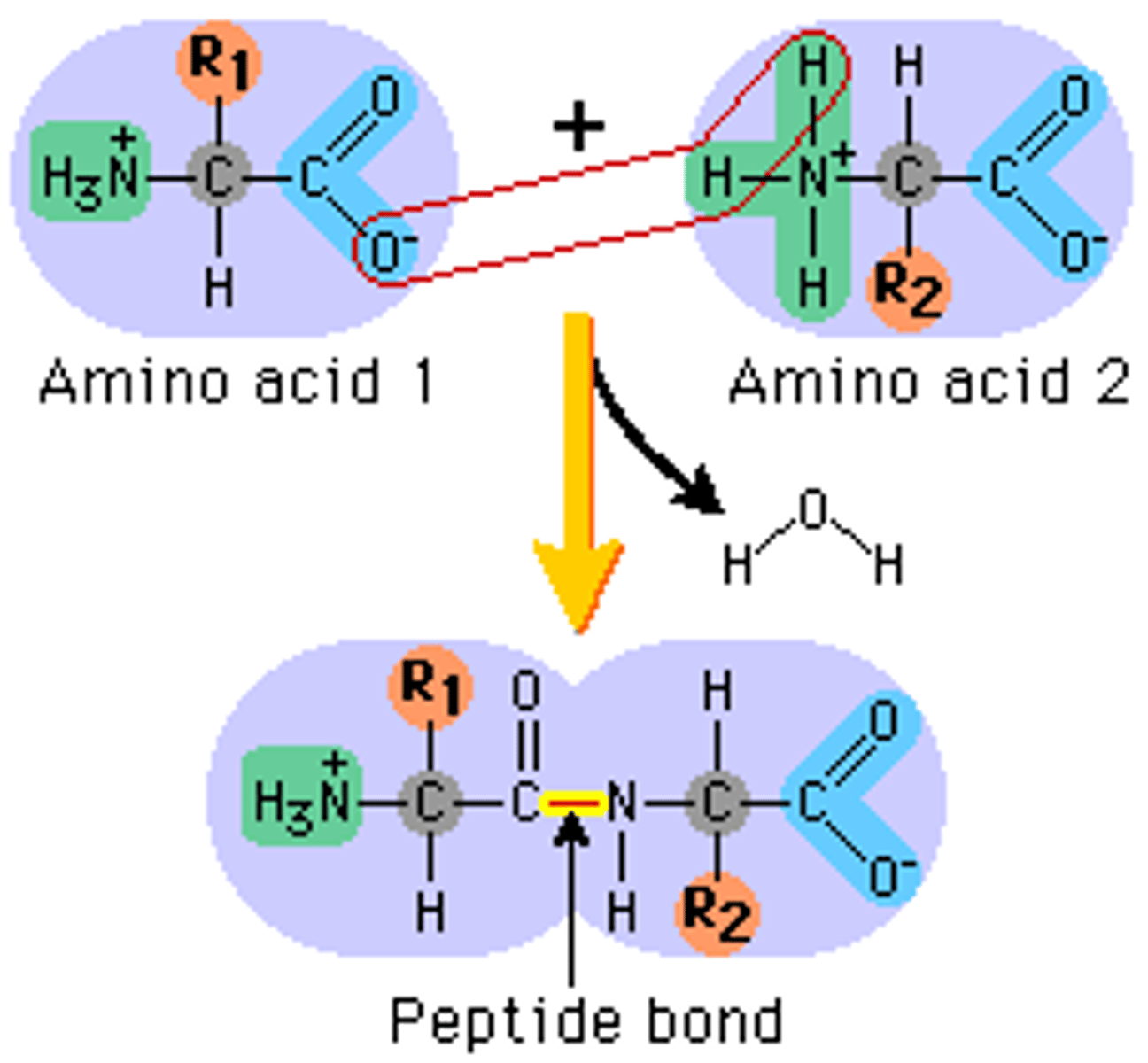
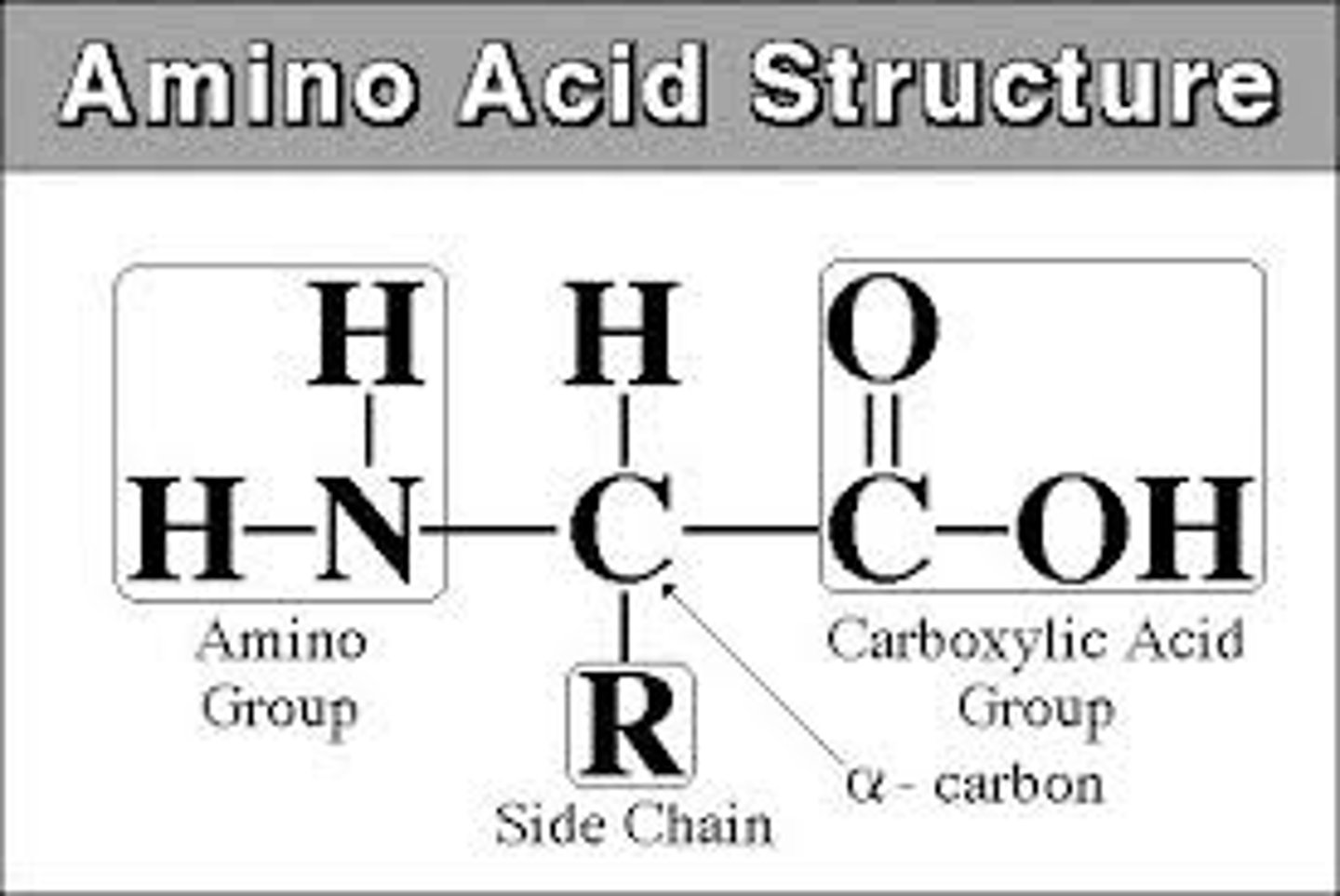
amino acids
Building blocks of proteins (monomers of proteins) these are put together at the ribosomes during protein synthesis
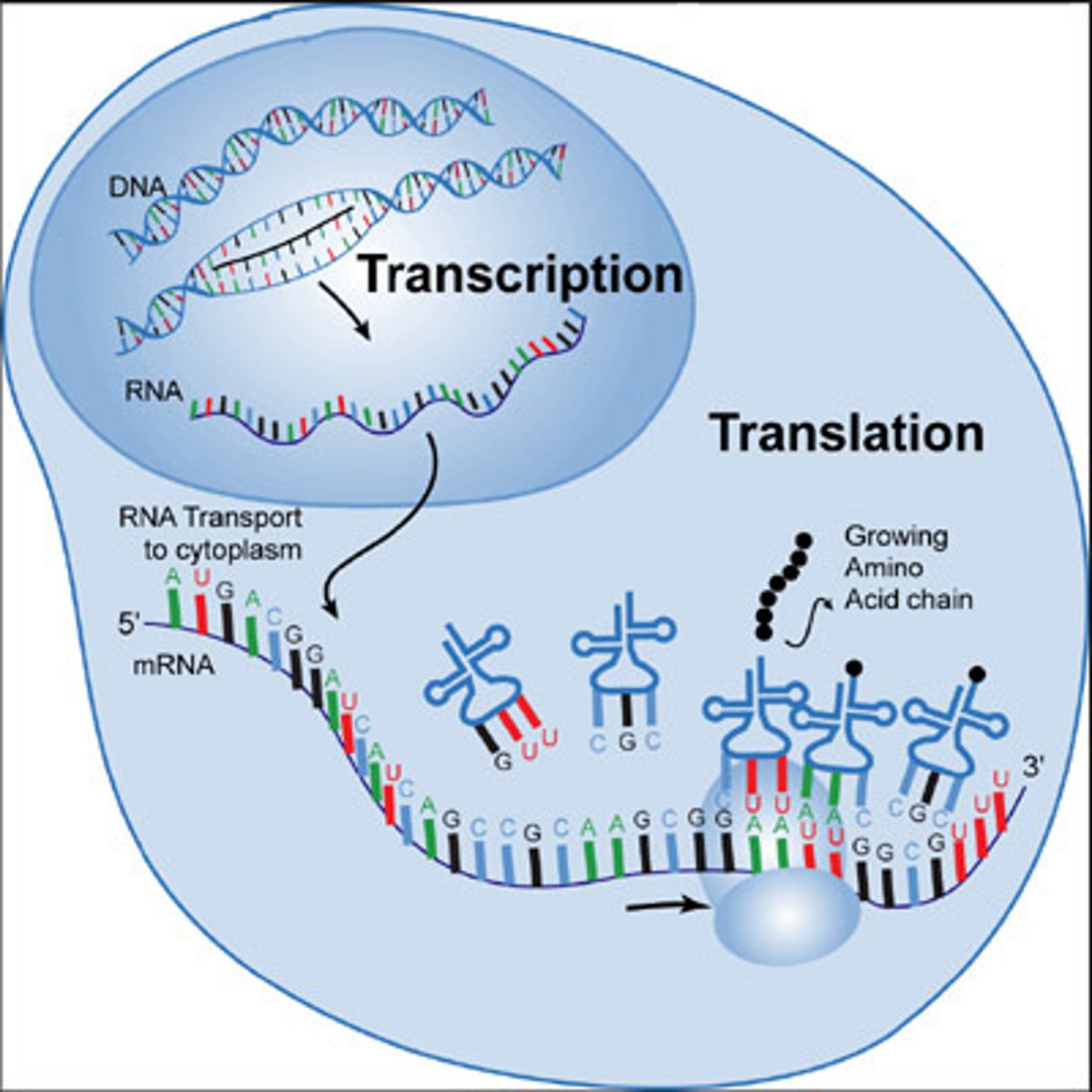
protein synthesis
process in which cells make proteins that includes transcription of DNA and translation of mRNA
nucleic acid
a long chain of smaller molecules called nucleotides; DNA and RNA

mutation
A change in a gene or chromosome that can change the protein.
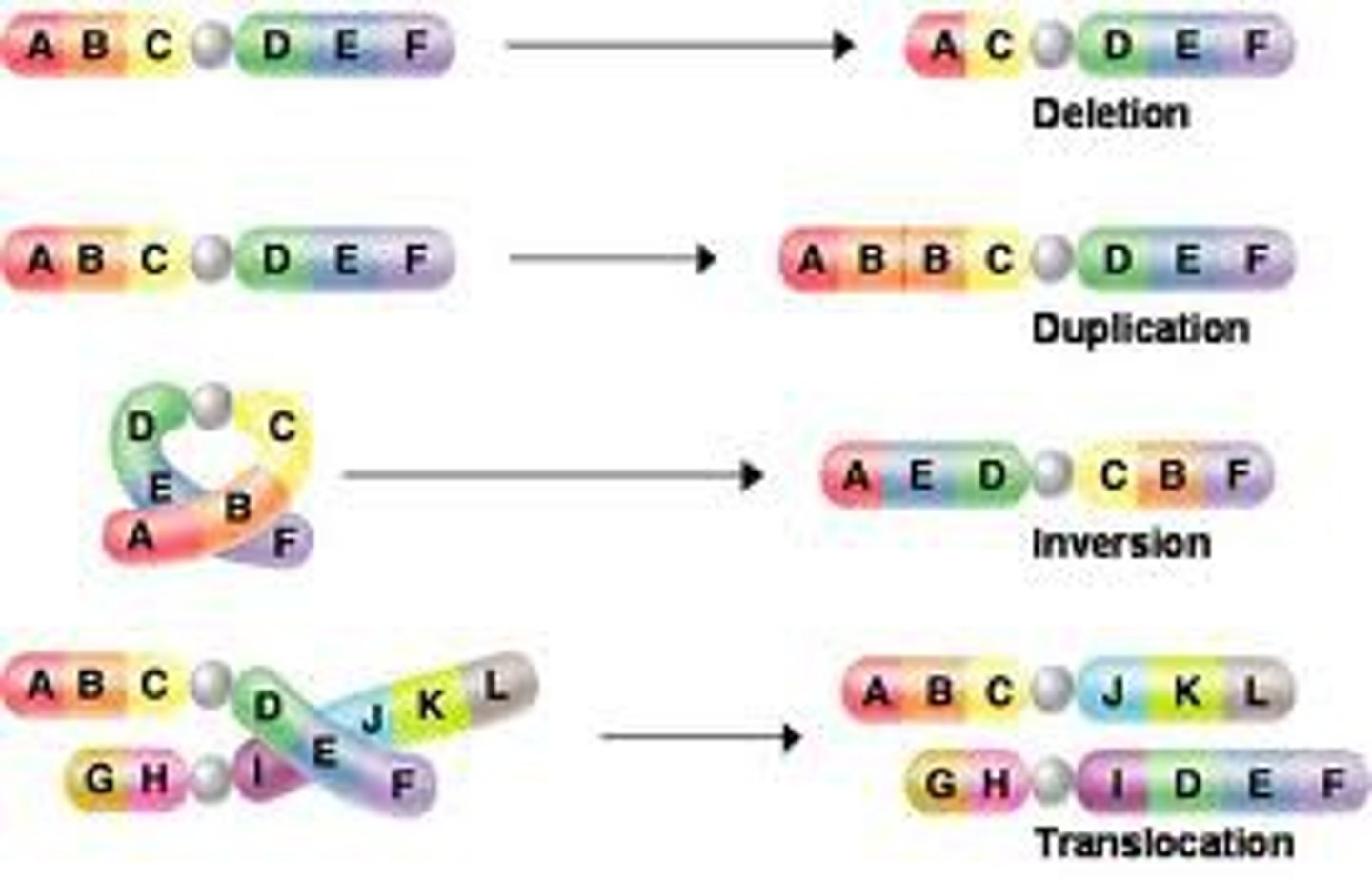
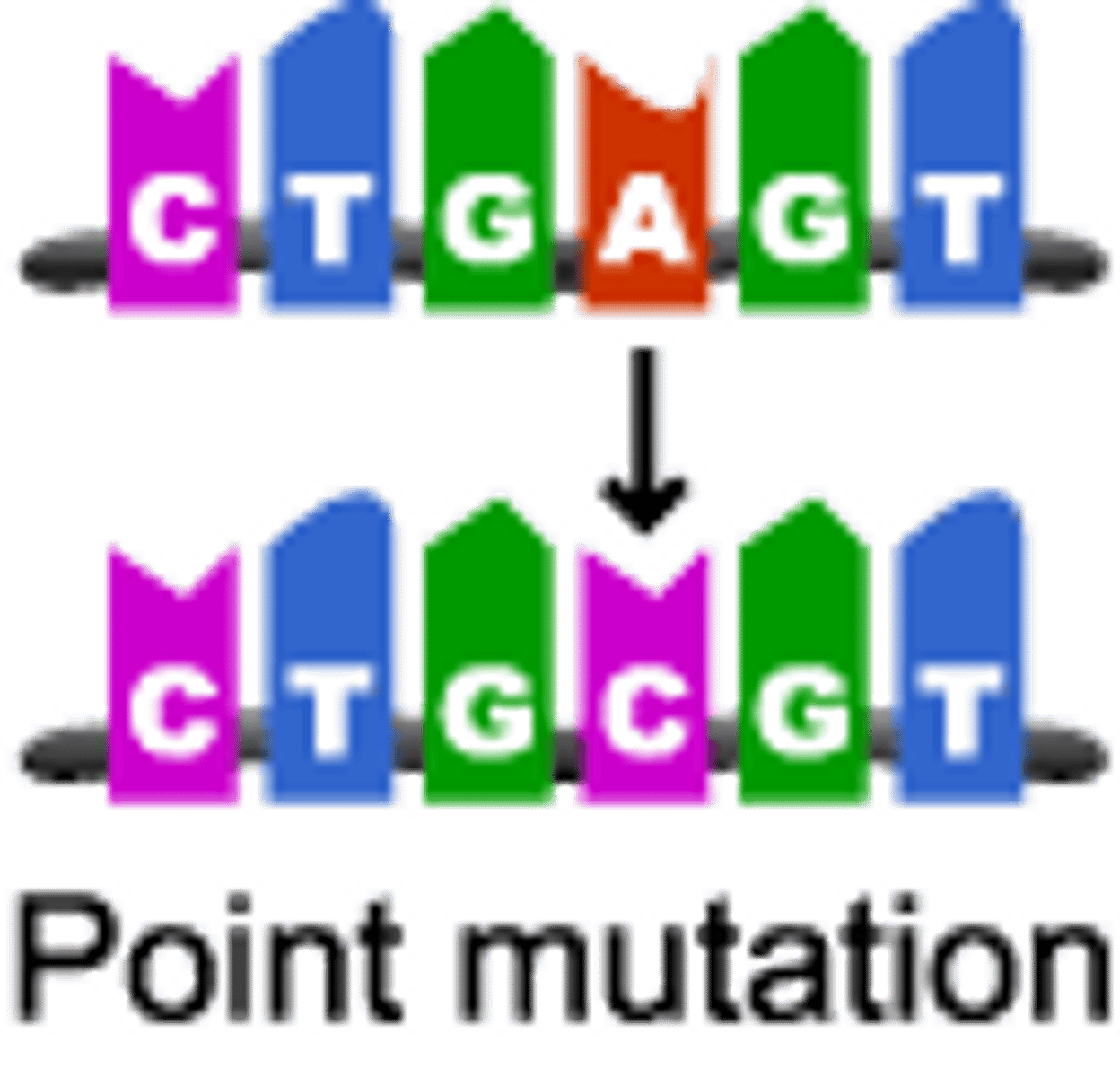
point mutation (substitution)
gene mutation in which a single base pair in DNA has been changed or substituted
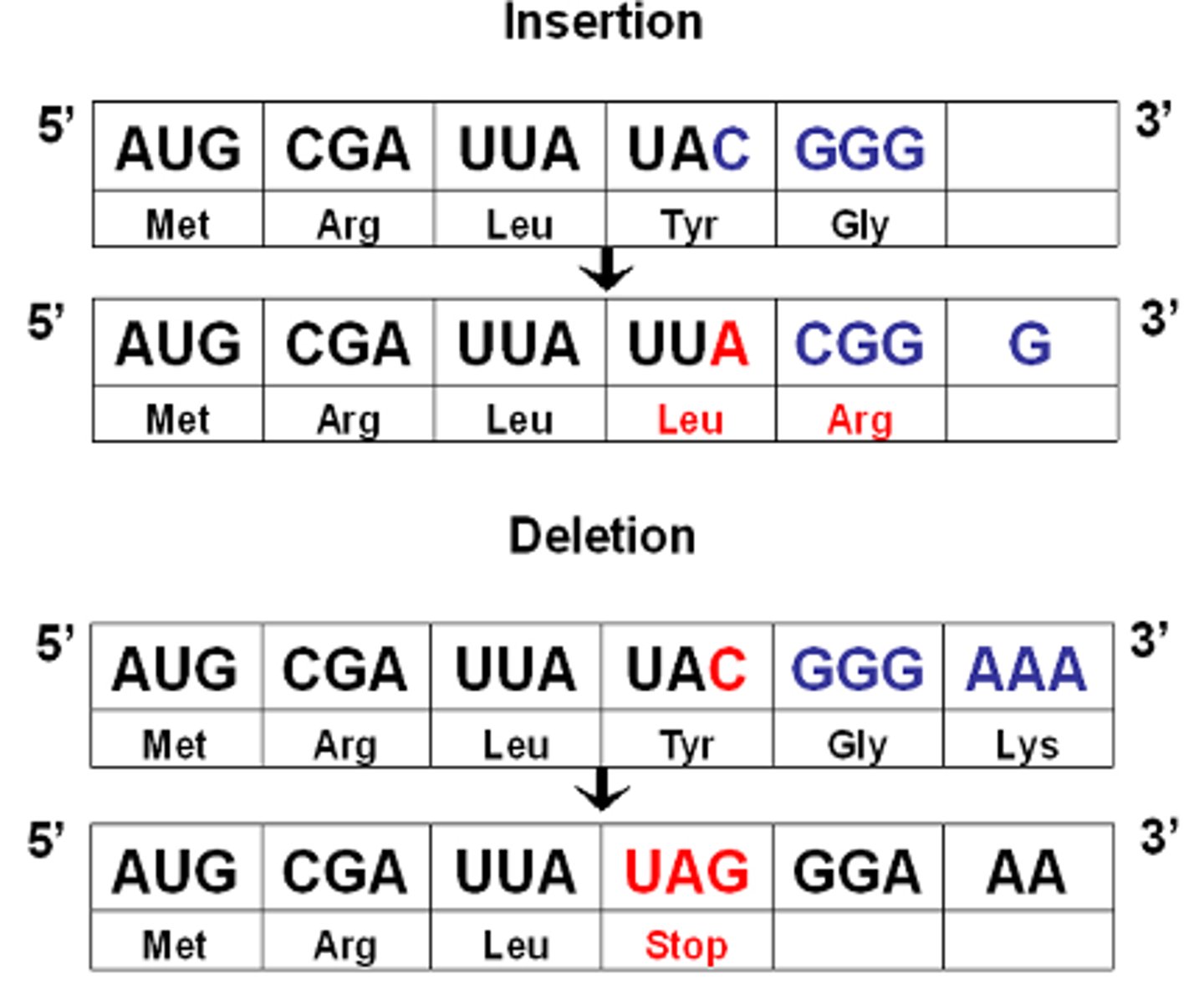
frame shift mutation
a mutation involving the addition or loss of nucleotides; every codon beyond the insertion or deletion is effected
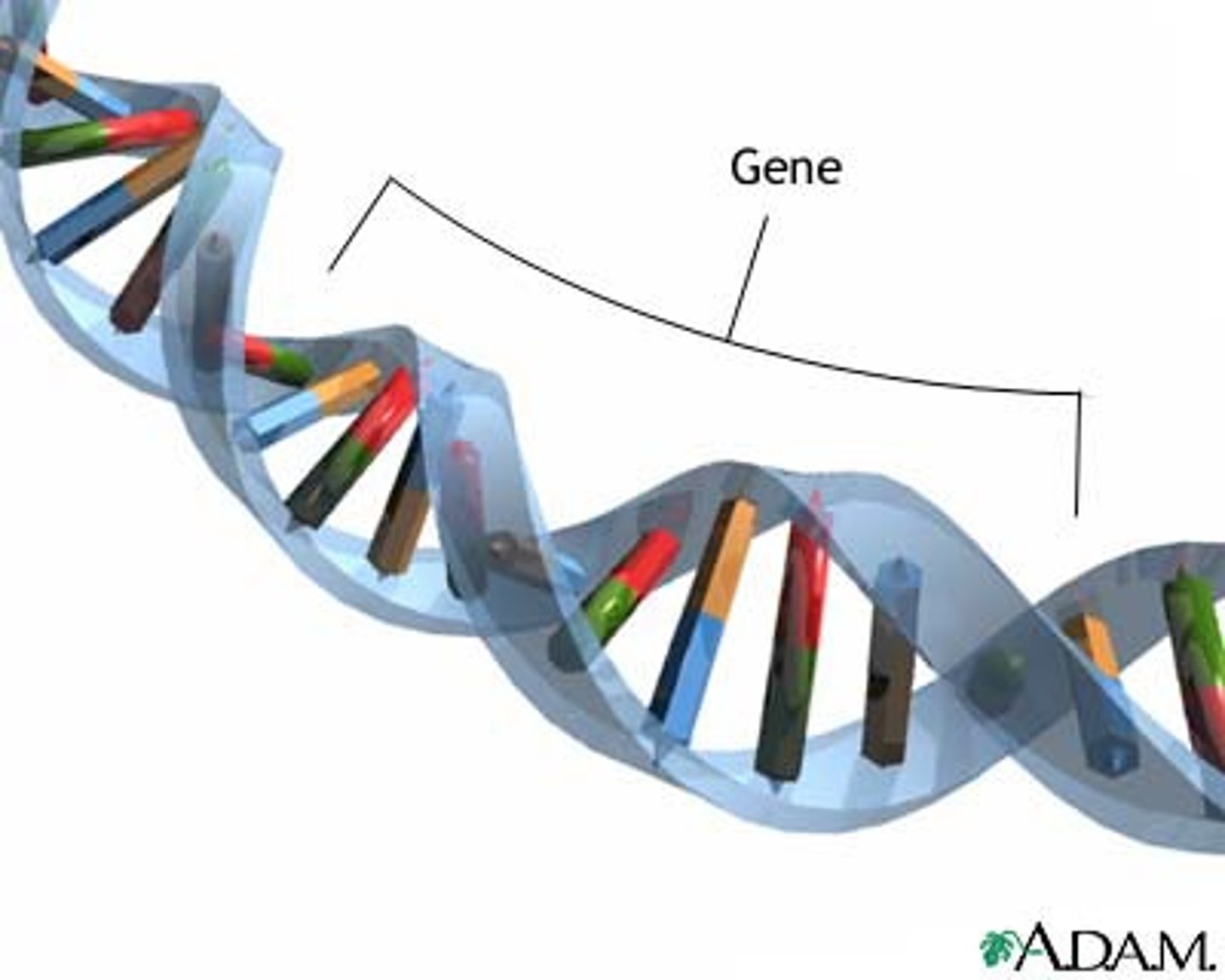
gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait (protein)
RNA
A single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along genetic messages ( 3 types)
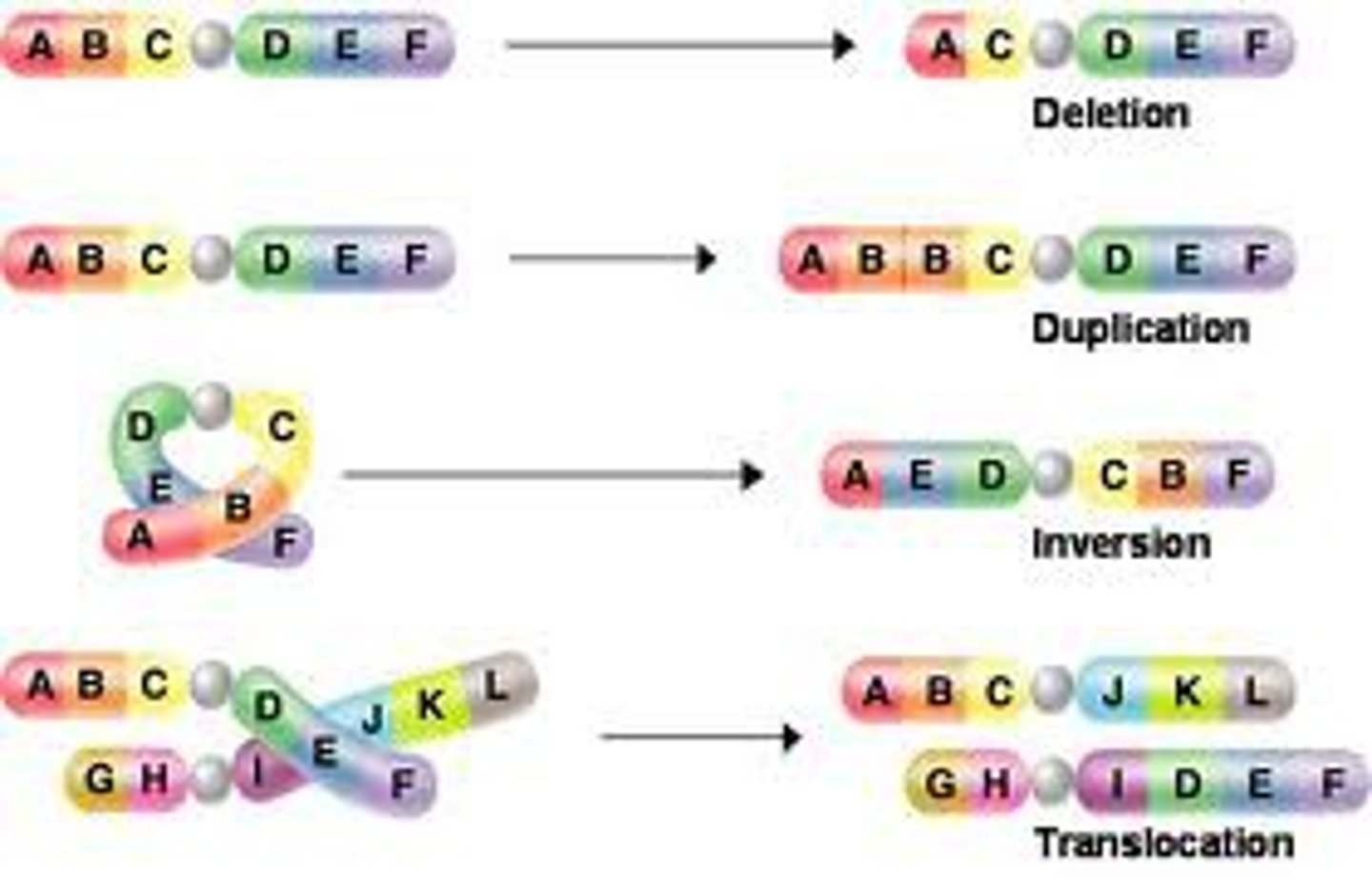
chromosomal mutation
A change in the chromosome structure, resulting in new gene combinations.
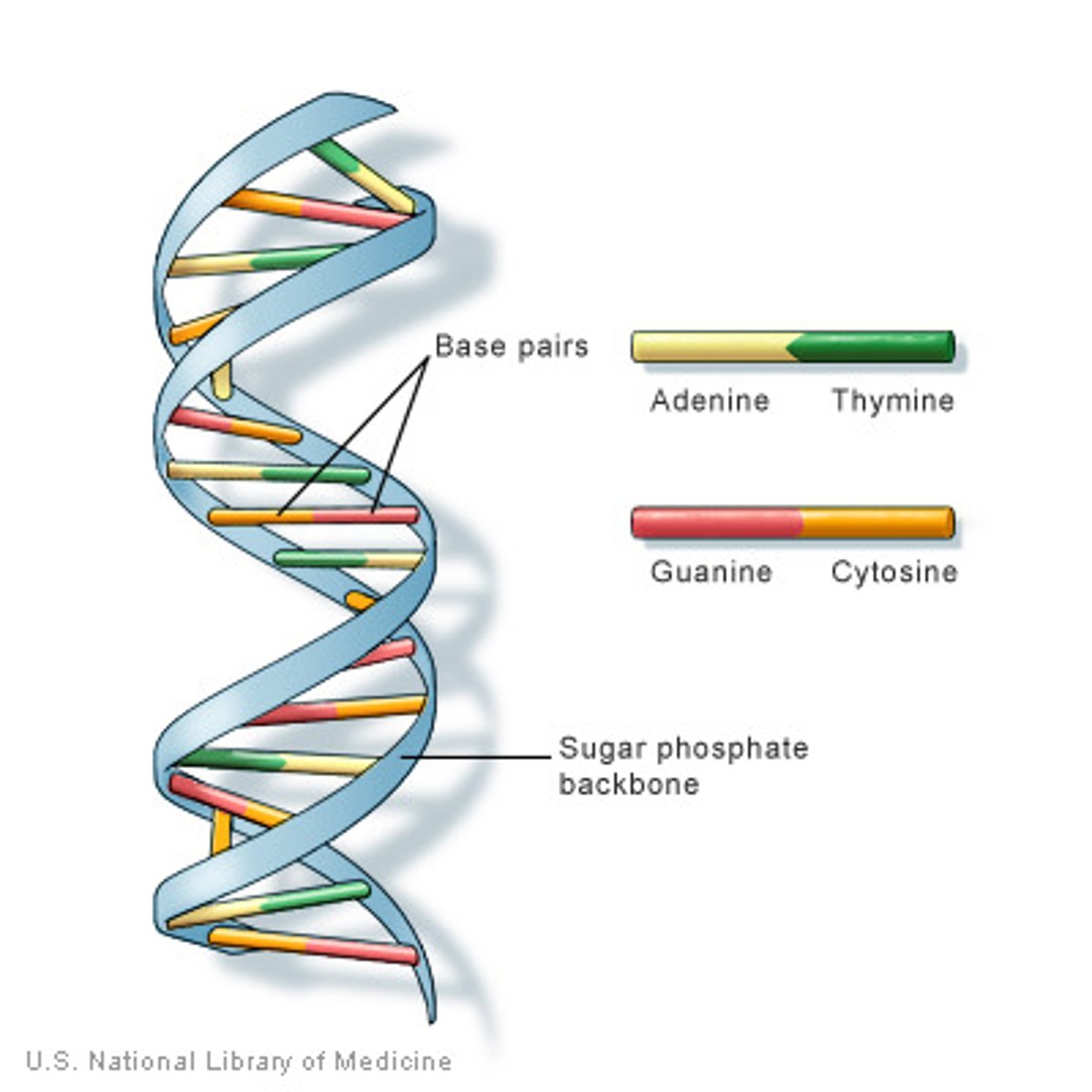
Chargaff's Rule
Because of base pairing rule:
A-T & G-C
%A must equal %T and,
% G must equal % C
when looking at a DNA molecule

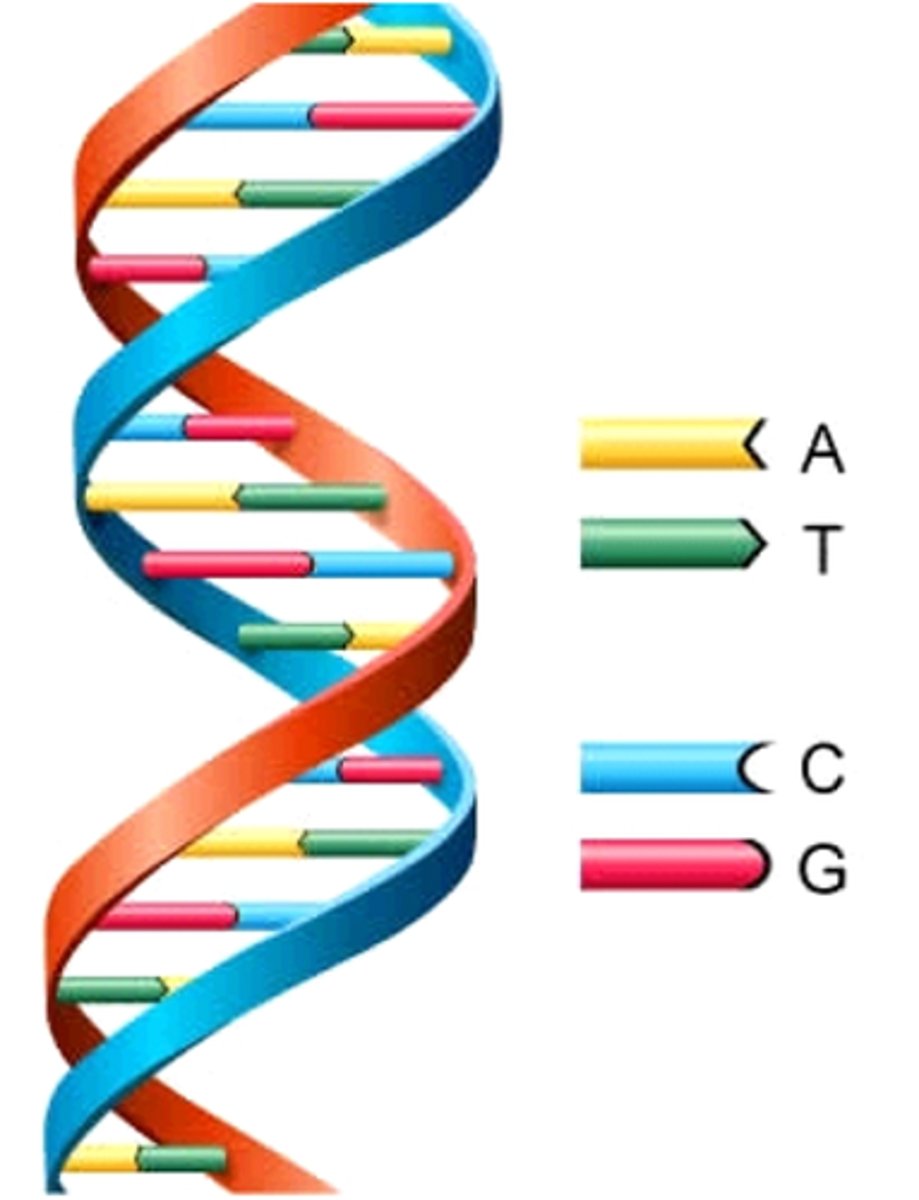
double helix
two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; structure of DNA

DNA Fingerprinting
a technique that uses gel electrophoresis to analyze a person's unique pattern of DNA
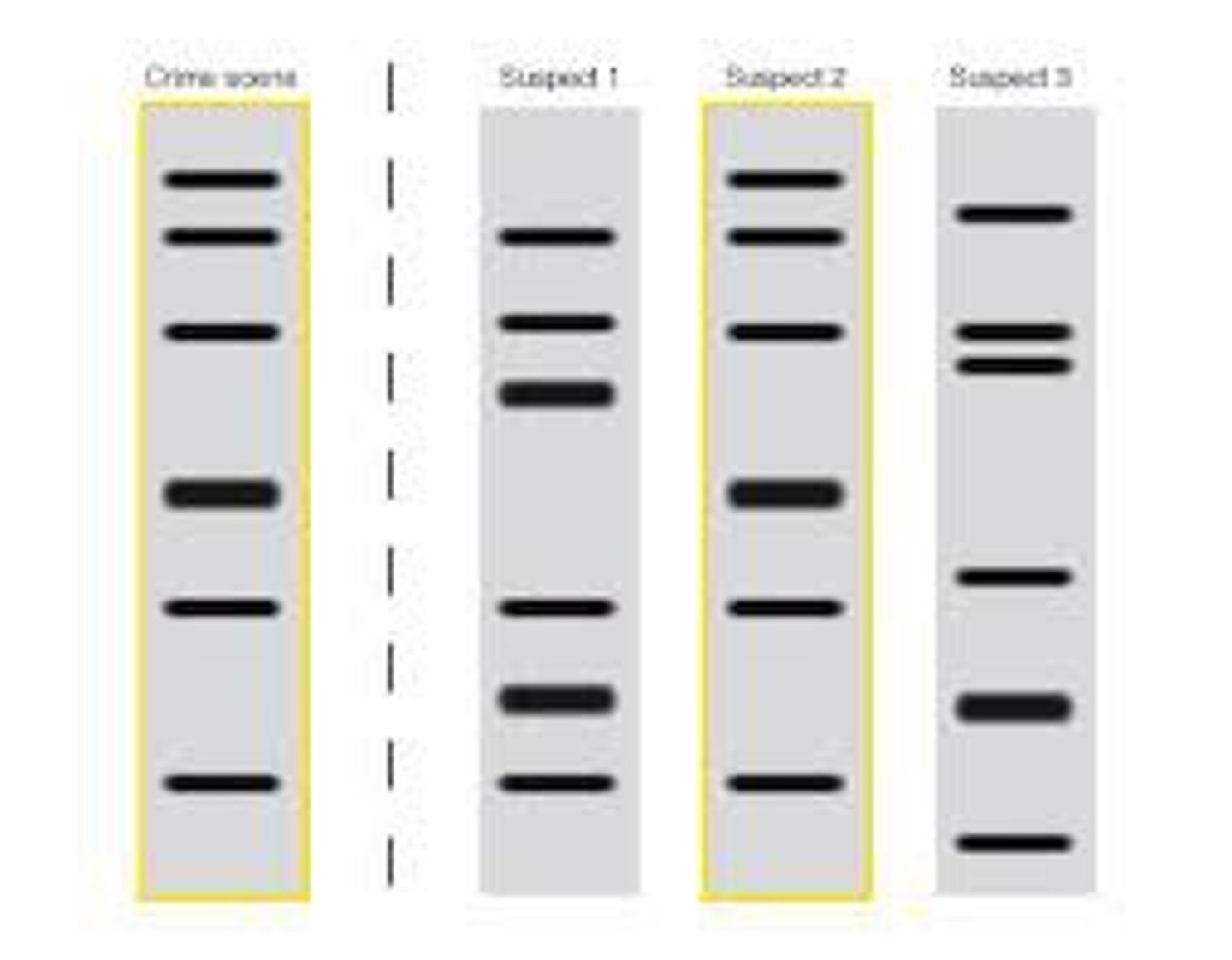
gel electrophoresis
method of separating various lengths of DNA strands by applying an electrical current to a gel

ribosome
a cell organelle composed of rRNA and protein; the site of protein synthesis (protein factory)
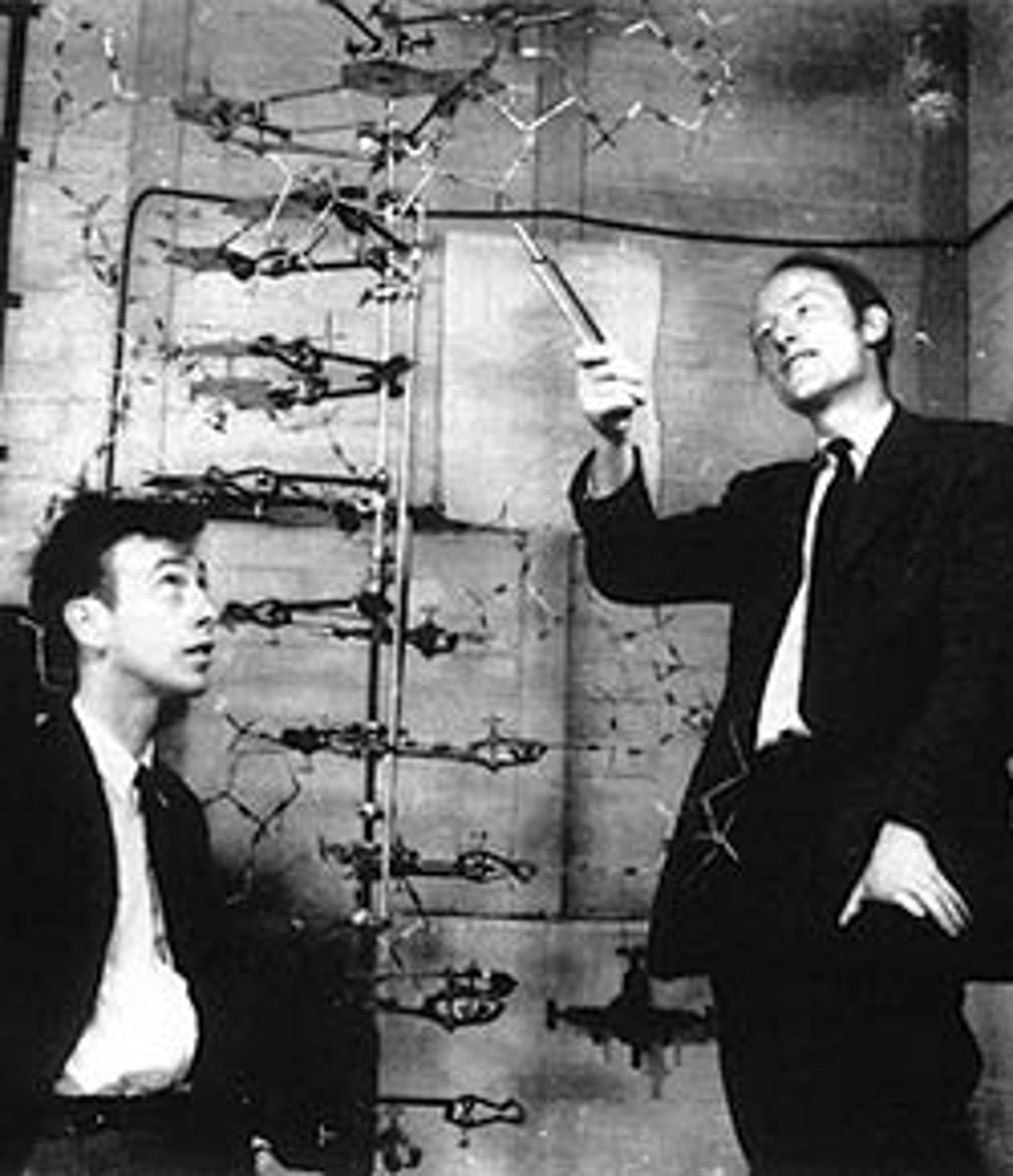
Watson & Crick
credited with discovery of the shape of DNA known as Double Helix, resulting in noble prize in 1953

Rosalind Franklin & Maurice Wilkins
used X-ray crystallography to gather data that led to the discovery of DNA's double helix structure

start codon
specific codon (AUG) that signals to the ribosome that the translation commences at that point, amino acid methionine, Met

stop codon
In mRNA, one of three triplets (UAG, UAA, UGA) that signal gene translation to stop.

base pairs
bases on opposite sides of the DNA strand that pair up A-T, C-G (A-U, G-C in RNA)
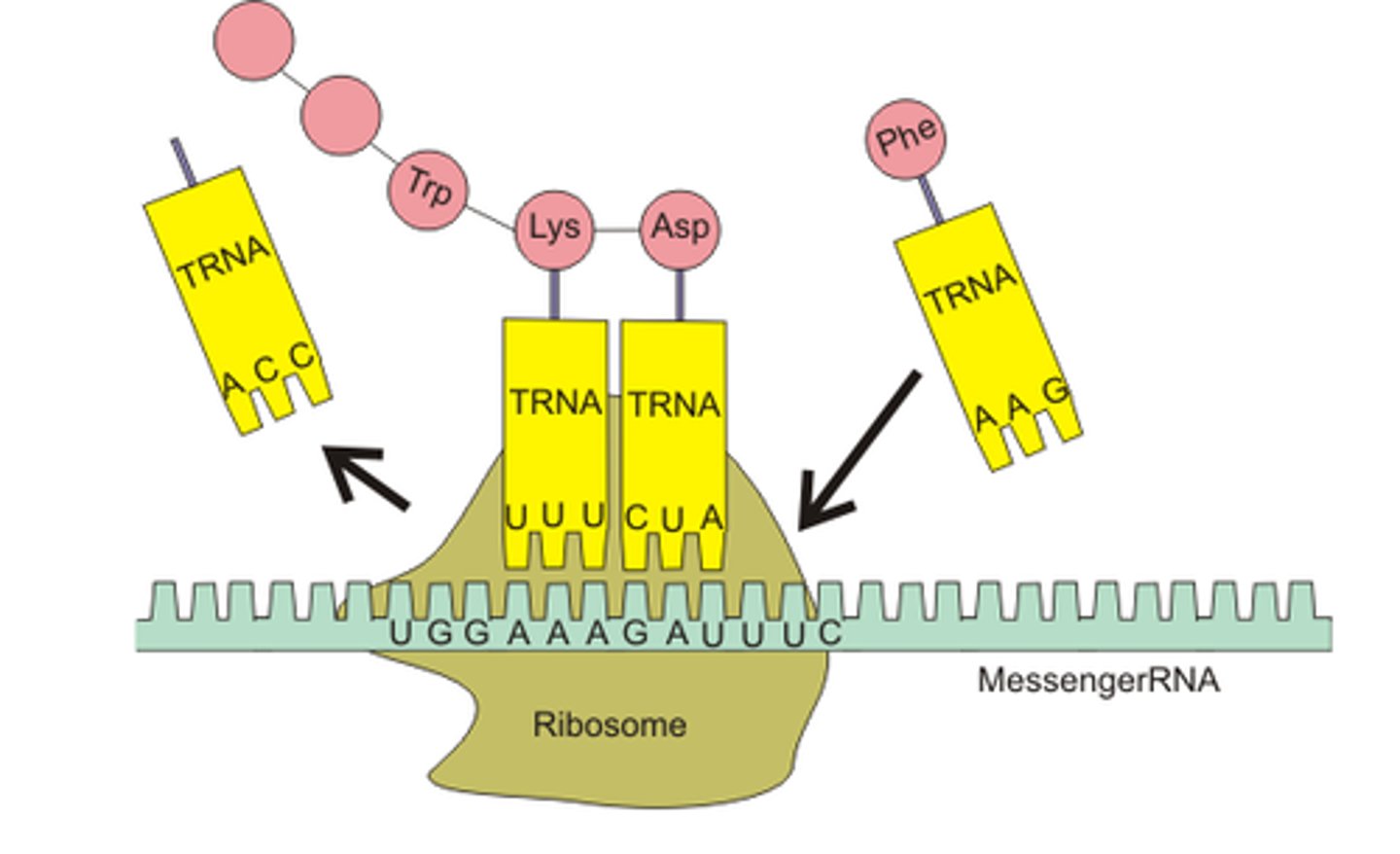
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
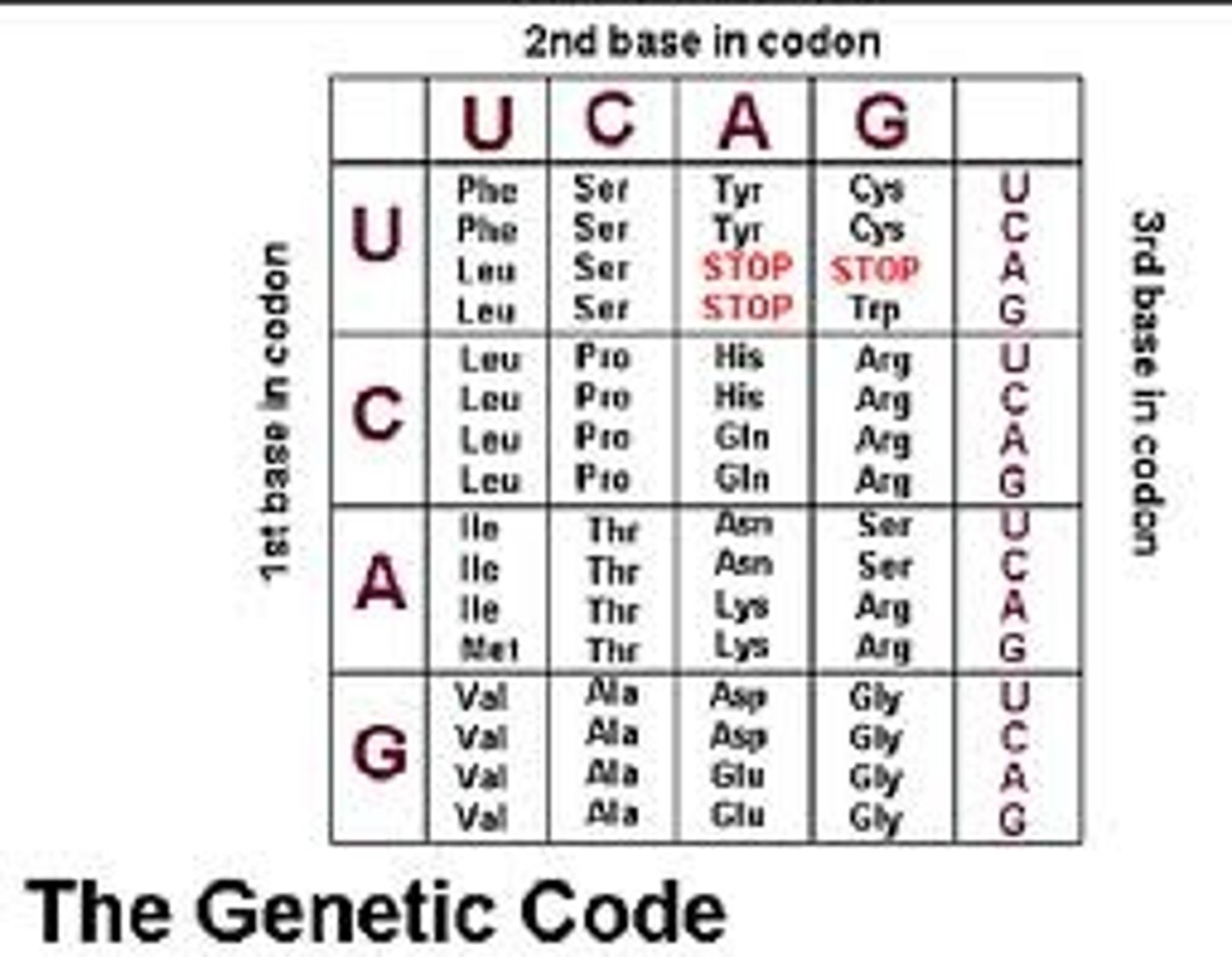
codon chart
shows which codon codes for a specific amino acid
-start with the left
-go to the top
-end with the right
(example: codon UGG = amino acid Trp)
peptide bond
Bonds that connect amino acids, during TRANSLATION of protein synthesis, forms a polypeptide (protein)