Revenue from contracts with customers (IFRS 15)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is the definition for revenue?
Income arising in the course of an entity’s ordinary activities
Revenue generally arises from the sale of goods or services to customers
Revenue excludes borrowings and amounts contributed by shareholders and gains
How do we recognise revenue?
Recognise revenue to depict the transfer of goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration that the company receives, or expects to receive, in exchange for these goods or services.
What is the revenue recognition principle?
Recognise revenue in the accounting period when the performance obligation is satisfied.
Dr receivables/cash
Cr revenue (income)
What is the five step model?
Contract with a customer is identified
Performance obligations in the contract are identified
Transaction price is determined
Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract
Recognise revenue when or as a performance obligation is satisfied
What is a contract?
An agreement between two or more parties that creates enforceable rights and obligations.
When should a contract with a customer be accounted for?
Only when:
The parties have approved the contract (written, oral or implied)
Each party’s rights under the contract can be identified
Payment terms can be identified
The contract has commercial substance
Probable that the entity will collect the consideration.
What are performance obligations?
A promise to transfer a distinct good or service to a customer.
How do you identify performance obligations?
You look at the contract and list everything promised to the customer.
Each promise is a seperate performance obligation if it is distinct.
When is a good or service distinct?
If:
The customer could benefit from it on its own or with other readily available resources
It is separately identifiable from other promises in the contract
How to know if a good or service is not distinct?
Significant integration
Major modifications
Highly interconnected
What happens if a promised good or service is not distinct?
It must be combined with other promised goods or services to form a distinct “bundle”. This may mean that all of the goods or services promised in a contract might be treated as a single performance obligation.


What is the transaction price?
The amount of consideration to which an entity expects to be entitled in exchange for transferring promised goods or services to a customer, excluding amounts collected on behalf of third parties.
( how much money the company expects to receive from the customer)
What does the transaction price include?
Fixed amounts- money that is certain
Variable amounts- money that might change e.g. bonuses,refunds,discounts,penalties
TVM (if payment is much earlier or later)
What are the 2 factors that must be considered when determining the transaction price?
Variable consideration & constrained estimates
Significant financing components
What is variable consideration?
Money that is NOT fixed. The final amount depends on something that will happen in the future.
E.g. bonus if a project is finished early, penalty if the delivery is late , refund if customer returns goods
Explain variable consideration.
The transaction price may vary because of items such as discounts, refunds, bonus etc. In these circumstances the amount of the variable consideration should be estimated using either:
The “expected value” method
The “most likely amount” method
The chosen method should be the one that best predicts the amount of the consideration
What is the constraint? (variable consideration)
The constraint is a safety rule. It says:
Only include variable consideration if it is highly probable that you will NOT have to reverse it later.
When do you not include variable consideration?
Uncertainty over a long period of time
Limited experience with similar contracts
Factors outside the entity’s control
Broad range of possible outcomes
In all these cases apply the constraint
When is variable consideration included in the transaction price?
Only when it is highly probable that there will be no significant reversal of revenue.
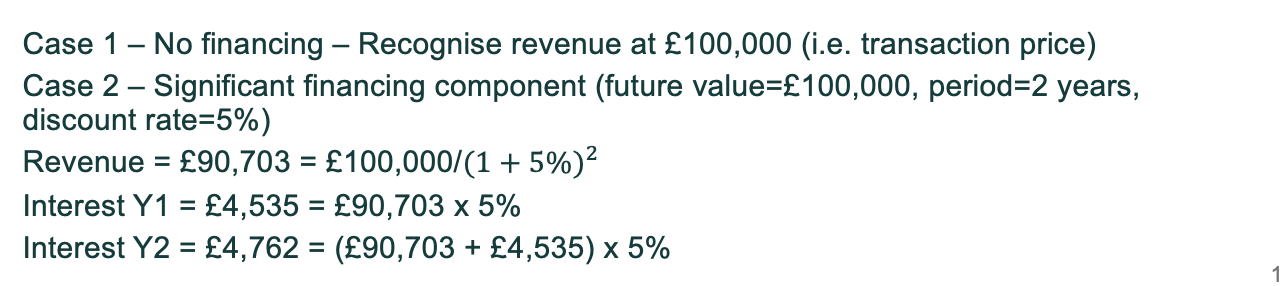
What is the significant financing component?
If the customer pays much earlier or much later than performance adjust for the TVM (interest)
Not required if: Time difference less than or equal to 1 year or the financing benefit provided is considered insignificant to the contract
When is there no adjustment of the significant financing component?
Period between performance and payment is 1 year or less
The financing benefit provided is considered insignificant to the contract

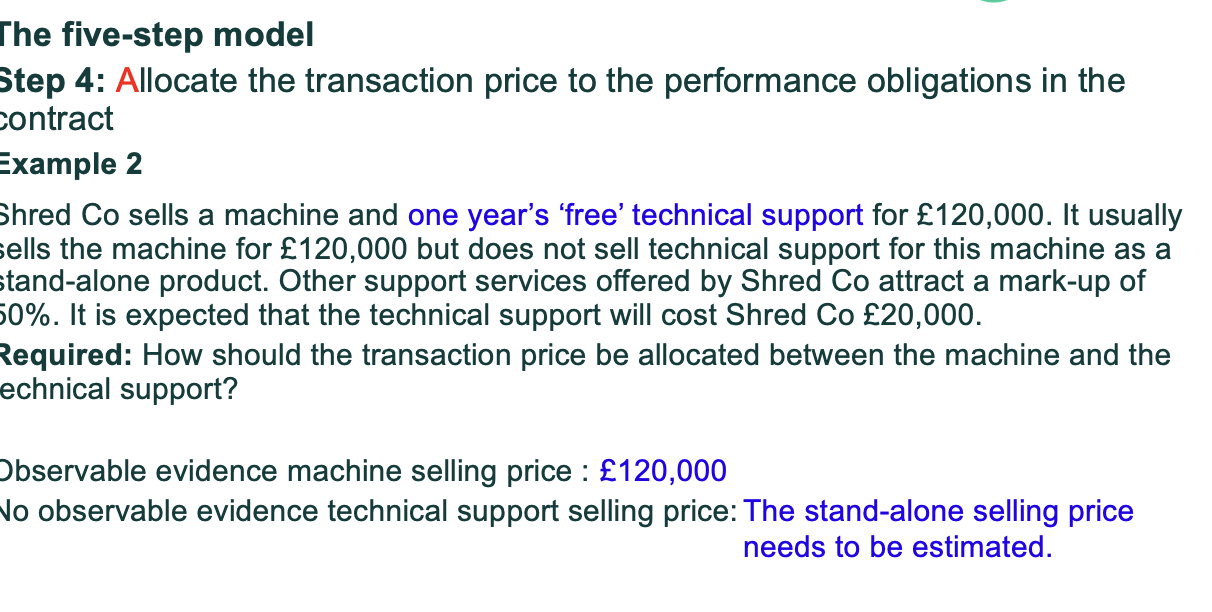
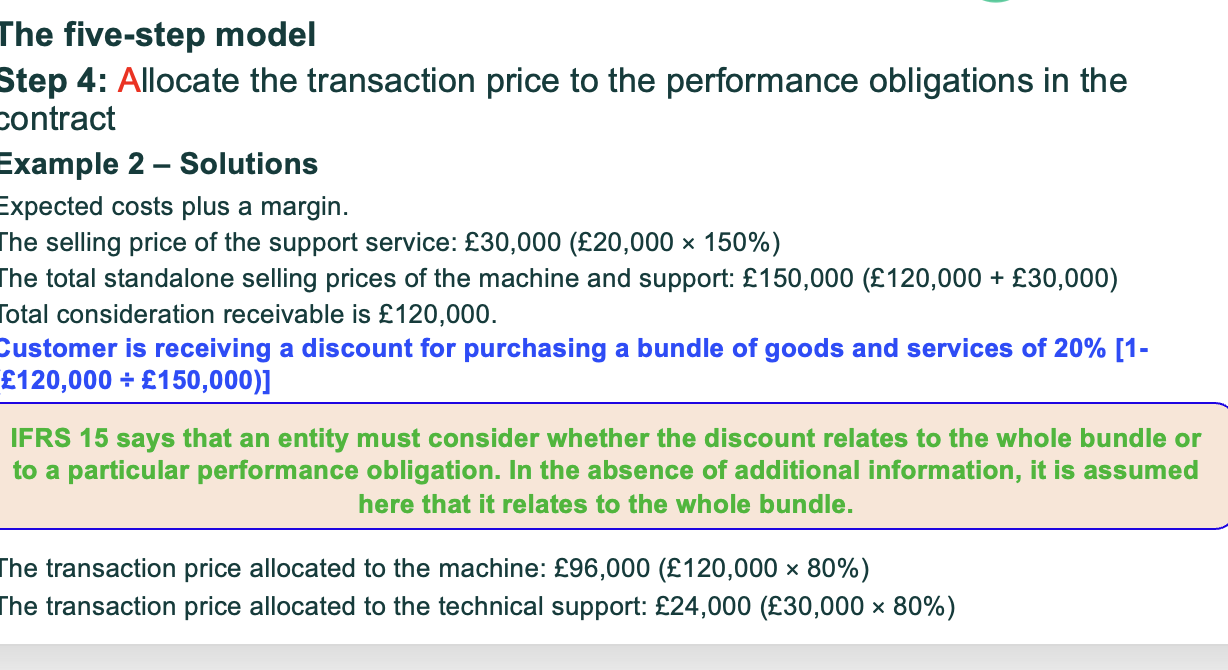
Explain allocating the transaction price to performance obligations?
After you know how much money you expect to receive (transaction price) you must split that amount between each performance obligation in the contract.
What is the basic rule for allocating the transaction price to performance obligations?
Allocate the transaction price based on the relative stand alone selling prices of each performance obligation.
What is a stand alone selling price?
The price at which a good or service is sold seperately to a customer.
What do we do if Standalone selling price is not directly observable?
You must estimate it using one of these methods:
Adjusted market assessment approach- look at market prices for similar goods
Expected cost plus margin approach
Residual approach
What would the journal entry be?

What is step 5 revenue recognition?
Revenue is recognised when (or as) a performance obligation is satisifed by transferring a good or service to the customer.
When is a good or service transferred?
Only when the customer obtains control of that good or service
What are the two ways to recognise revenue?
Overtime- revenue is recognised gradually as the work is done
At a point in time- Revenue is recognised once at a specific moment
How can we identify if the performanc obligation is satisifed over time or at a point in time?
Does the customer receive the asset and consume its beenfits at the same time that entity performs its obligations?
If the entity is creating or enhancing an asset, does the customer obtain control of the asset as it is being created or enhanced?
If the entity is creating an asset does the asset have no alternative use for the entity, the entity have an enforceable right to payment for performance completed to date?
If Yes to these it is satisfied “over time”
For performance obligations satisfied over time how do w measure progress?
Output method- Progress is measured on the basis of direct measurement of the goods and services transferred to date
Input method - Progress is measured on the basis of the entity’s inputs to date relative to the total inputs required to satisfy the performance obligation.