Linear Algebra Def.
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
The Pivot of a row in a matrix is…
The leftmost nonzero entry in that row.
A matrix is in row echelon form if…
(1) all rows consisting only of zero are at the bottom
(2) the pivot of each nonzero row is in the column to the right of the pivot in the row above it
A matrix is in reduced row echelon form if
(1) the matrix is in echelon form
(2) the pivot in each nonzero row is 1
(3) each pivot is the only nonzero entry in the column
A system of linear equations is called consistent if it has at least one solution.
If the system has no solutions, it is called
Inconsistent
Let C be the coecient matrix for a consistent system of linear equations in
variables x1, . . . , xn.
(1) We say that xi is a basic variable for the system if. . .
(2) We say that xi is a free variable for the system if. . .
(1) We say that xi is a basic variable for the system if the ith column of rref(C)
has a pivot.
(2) We say that xi is a free variable of the system if the ith column of rref(C)
does not have a pivot.
A linear combination of vectors v1, v2 … , vn in Rm is the vector of the form
…
where c1, c2, … cn are scalars called coefficients of the linear combination
vector w = c1v1 + c2v2 + … + cnvn
The span of vectos v1, v2, … ,vn in Rm is the set
…
That is span(v1, v2, …, vn) is the set of all linear combinations of vectors v1, v2,… , vn
span(v1, … ,vn) = {c1v1 + c2v2 + … + cnvn | c1, c2, …, cn element of R }
A set of vectors {v1,v2,…,vn} in Rm is linearly dependent if
…
otherwise the vectors are called linearly independent
if atleast one of the vectors is a linear combination of the others. That is, for at least…
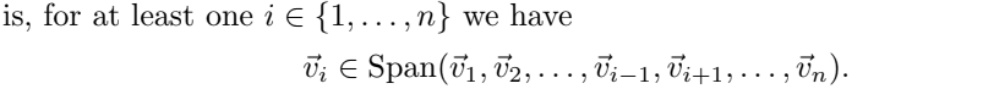
A vector space (over real numbers) in any set of vectors in R^n that satisfies all of the following properties
(1) v is non empty
(2) v is closed under addition
(3) v is closed under scalar multiplication
Let V be a vector subspace of Rn. A spanning set (also known as a generating set) for V is…
any subset B of V so that v = span(B)
A subset B of a vector space V is called a basis if…
(1) B is a spanning set for V
(2) B is linearly independent
Let V be a nonzero vector subspace of R^n. Then, the dimension of V, denoted as dim(V) is…
equal to the size of any basis for V
The standard basis of Rn is the set e := {e1, e2,…, en} where ei is…
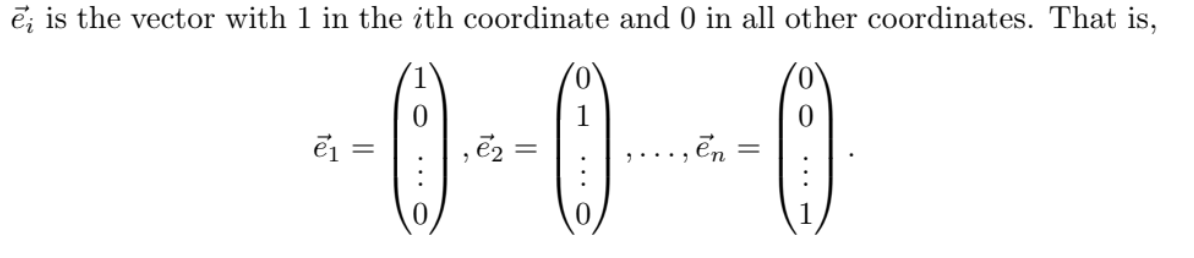
Let A be an mxn matrix with column vectors A = (v1,v2,…,vn). Then for a vector x in Rn , the matrix-vector product of A and x is the vector in R^m defined by…
Ax := x1v1 + x2v2 + … + xnvn
Let A be an mxn matrix. Then, the matrix transformation associated to A is the function…
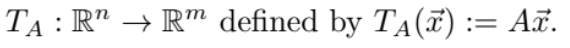
A function F: Rn → Rm is called Linear if it satisfies the following two properties for all vectors v,w element of Rn and scalars c element R
(1) F(U + V) = F(U) + F(V)
(2) F(cU) = cF(U)
Let F: Rn → Rm be a linear transformation. Then, the defining matrix of F is the m x n matrix M satisfying…
F(x) = Mx
A function f: X → Y is called one - to - one (or injective) if the following property holds…
for every y ∈ Y , there is at most one input x ∈ X so that f(x) = y. We often use the arrow f : X ,→ Y to indicate when a function is injective.
A function f : X → Y is called onto (or surjective) if the following property holds:
for every y ∈ Y , there is at least one input x ∈ X so that f(x) = y. We often use the arrow
f : X → Y to indicate when a function is surjective.
A function f : X → Y is called bijective if. . .
it is both injective and surjective
Let V be a subspace of Rn and W a subspace of Rm. An isomorphism between V and W is
. . .
If an isomorphism exists between two vector spaces, we say these spaces are isomorphic, and we write V ~= W.
any linear bijective map F : V → W.
Let F: Rn → Rm be a linear transformation
(1) The kernel F is the subset ker(F ) (= R^n defined by…
(2) The image of F is the subset im(F) (= R^m defined by …

Let F: Rn → Rm be a linear tranformation.
(1) The rank of F is…
(2) The nullity of F is…
(1) The rank of F is the dimension of im(F)
(2) The nullity of F is the dimension of ker(F)
Let A be an mxn matrix with column vectors A = (v1,v2,…vn).
(1) The column space of A is the subspace of Rm given by…
(2) The null space of A is the subspace of Rn given by…

Let A be a matrix.
(1) The nullity of A is…
(2) The rank of A is…
(1) The nullity of A is the dimension of nul(A) and is denoted by nullity(A)
(2) The rank of A is dimension of col(A) and is denoted by rank(A)
A system of linear equations is called homogenous if…
the constant coefficients are all equal to zero
Let A = (v1,v2,…,vn) and B = (w1,w2,…,wn) be m x n matrices and c element of R be a scalar.
(1) The sum of A and B is the mxn matrix given by…
(2) The scalar product of A with c is the mxn matrix given by…
(1) The sum of A and B is the mxn matrix given by A + B := (v1+w1,v2+w2,…,vn+wn)
(2) The scalar product of A with c is the mxn matrix given by cA := (c1v1,…,cnvn)
Let A be an m x k matrix and B = (b1,b2,…,bn) be a k x m matrix. Then the matrix product of A and B is the m x n matrix…
B = (Ab1, …, Abn)
The identity matrix In is…
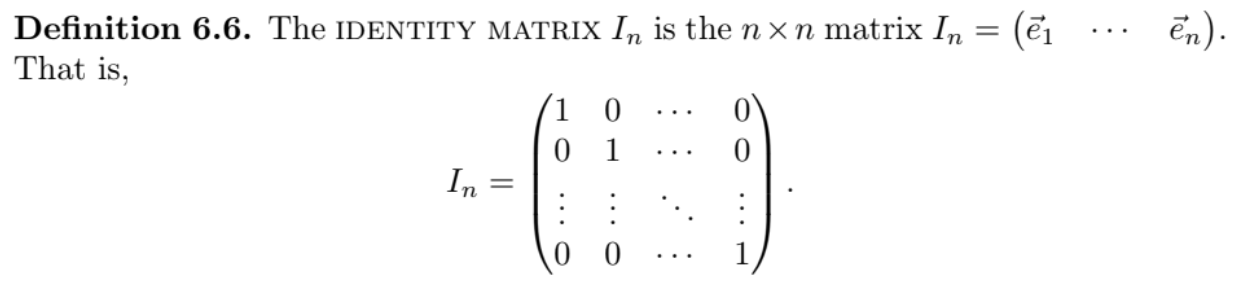
Let A be an n x n matrix. Then the inverse of A, if it exists is
is the matrix B so that AB = BA = In. In this case, we write B = A-1
An n x n matrix is called elementary if…
it can be obtained by performing exactly one row operation to the identity matrix.
The unit square is the subset of R2 given by…
S := {α1e1 + α2e2 : 0 ≤α1,α2 ≤1}.
An ordered basis {b1, b2} for R2 is called positively oriented if…
we can rotate b1 counterclockwise to reach b2 without crossing line spanned by b2
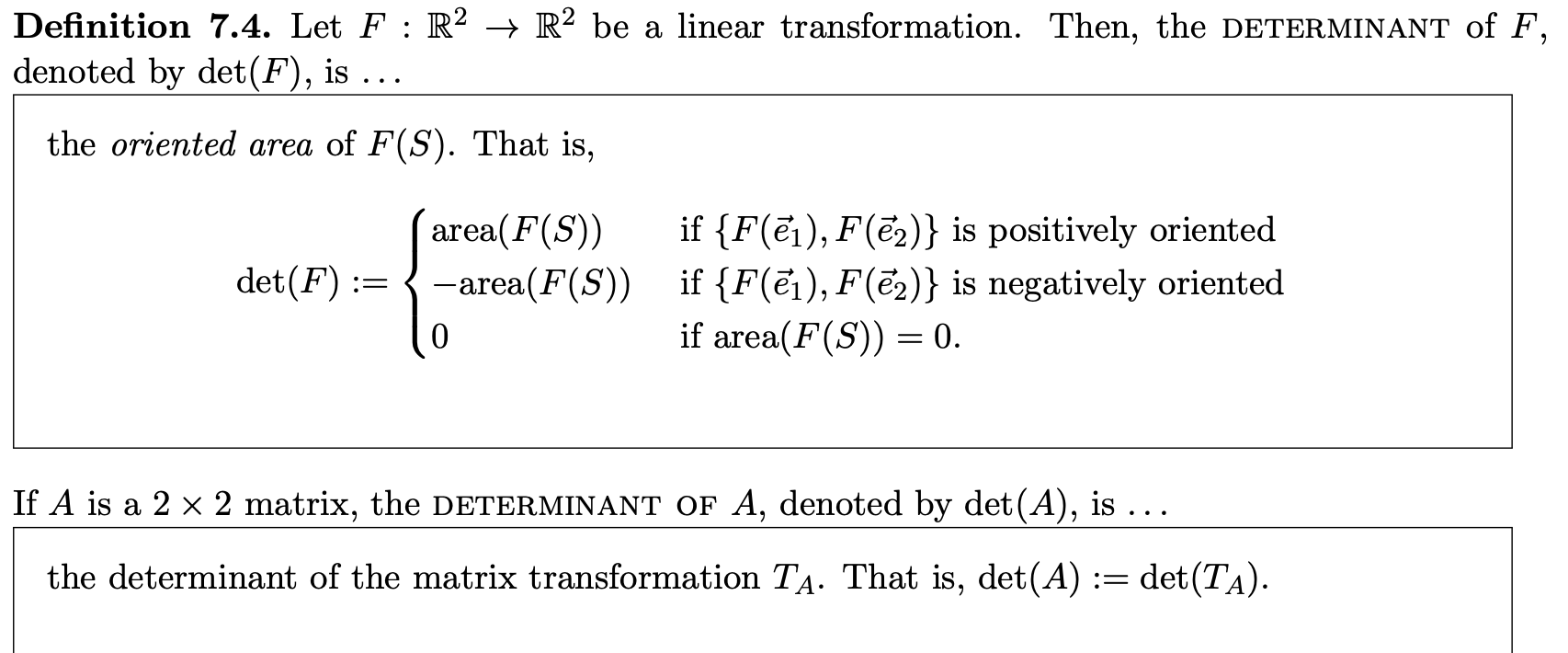
Let F: R2 → R2 be a linear transformation. Then, the determinant of F, denoted by det(F), is…
If A is a 2×2 matrix, the determinant of A, denoted by det(A) is…
The unit cube is the subset of R3 given by…
C := {α1e1 + α2e2 + α3e3 : 0 ≤ α1,α2,α3 ≤1}.
For an n x n matrix A = (Aij), the ij-minor of A is…
the (n-1) x (n-1) matrix Aij with the ith row and jth column deleted
Let A be the n x n matrix with ij-entry equal to aij. We define the determinant of A by the following cofactor expansion formula:
det(A) := a11 det(A11)−a12 det(A12) +···+ (−1)n+1a1n det(A1n).
Let A be an n x n matrix. A non-zero vector v is an eigenvector of A if
…
The scalar λ is called an eigenvalue
there is a real number scalar lambda such that Av = λV
Let A be an n × n matrix with eigenvalue λ.
(1) The λ-eigenspace of A is the vector subspace of Rn defined by…
(2) The geometric multiplicity of λ is…
(1) Eλ := Nul(A - λIn)
(2) the dimension of the λ-eigenspace Eλ
For an n x n A, the characteristic polynomial of A is…
Xa(x) = det(A-XIn)

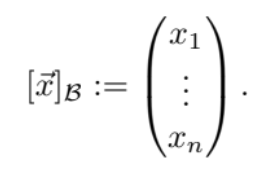
Let C and B be bases for a vector space V. Then, the change of basis matrix
MC←B is the matrix satisfying
…
for every vector x in V
MC←B[x]B = [x]C
Let F : Rn → Rn be a linear transformation, and B be any basis for Rn. Then,
the defining matrix of F with respect to the basis B is the matrix M so that
…
We use the notation M = MF,B
[F(x)]B = M[x]B
Two n x n matrices B and C are called similar if they represent the same function, but in possibly different bases. That is…
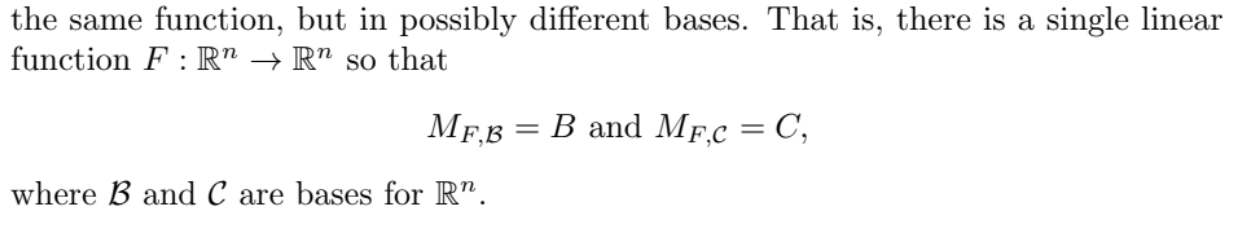
An n x n matrix D is called diagonal if
…
in this case we write D = diag(d1,d2,…,dn)
the only nonzero entries in the matrix appear on the diagonal.
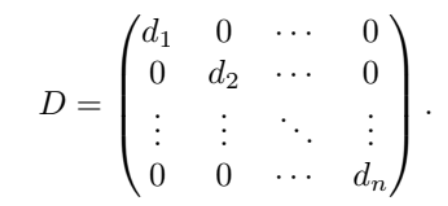
An n x n matrix is called diagonalizable if…
it is similar to a diagonal matrix.
Suppose that A is an n x n diagonalizable matrix with eigenvalues λ1,…,λn and corresponding linearly independent eigenvectors v1,v2,…,vn.
We call the equality. . .
the eigendecomposition of the matrix A. By diagonalization theorem, we know that…
(1) A = CDC-1
(2) C = [v1,v2,…,vn] and D = diag(λ1,…,λn)
The dot product of u and v is the scalar
u * v = u1v1 + u2v2 +…+ unvn
Let u and v be vectors in Rn
(1) The norm of a vector u in Rn is…
(2) The distance between vectors u and v is…
(3) We say that u and v are orthogonal if…
(1) ||u|| := sqrt(u * u)
(2) d(u,v) := ||u-v||
(3) u * v = 0
A basis B = {v1,v2,…,vn} is orthogonal if
…
An basis B is orthonormal if it’s orthogonal and…
(1) vi * vj = 0 for every i not equal to j
(2) ||vj|| = 1 for every vj in B
We call an n x n matrix Q orthogonal if
…
Equivalently, Q is called orthogonal if QT = Q-1
its column vectors form and orthonormal basis for Rn
For vectors x,y in Rn, the orthogonal projection of x onto y is…
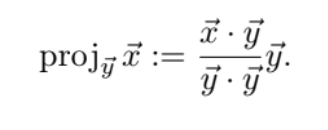
An n x n matrix A is called orthogonally diagonalizable if…
there exists an orthogonal matrix Q and a diagonal matrix D such that QTAQ = D
Suppose that A is an n x n symmetric matrix with eigenvalues λ1,…,λn and orthonormal basis of eigenvectors {v1,v2,…,vn}. We call the equality
…
a spectral decomposition of A, where…
(1) A = QDQT
(2) D = diag(λ1,…,λn), and Q = (v1,v2,…,vn)
Let A be an m x n matrix and {v1,v2,…,vn} be an orthonormal basis for Rn of eigenvectors for ATA, as above. The singular values of A are…
{std}i := ||Avi||