Week 2: Classification & Phylogeny/cell division, Fungi- Chapters 26, 12, 13, 31
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
analyze this chart
Analyze the Linnaean classification system
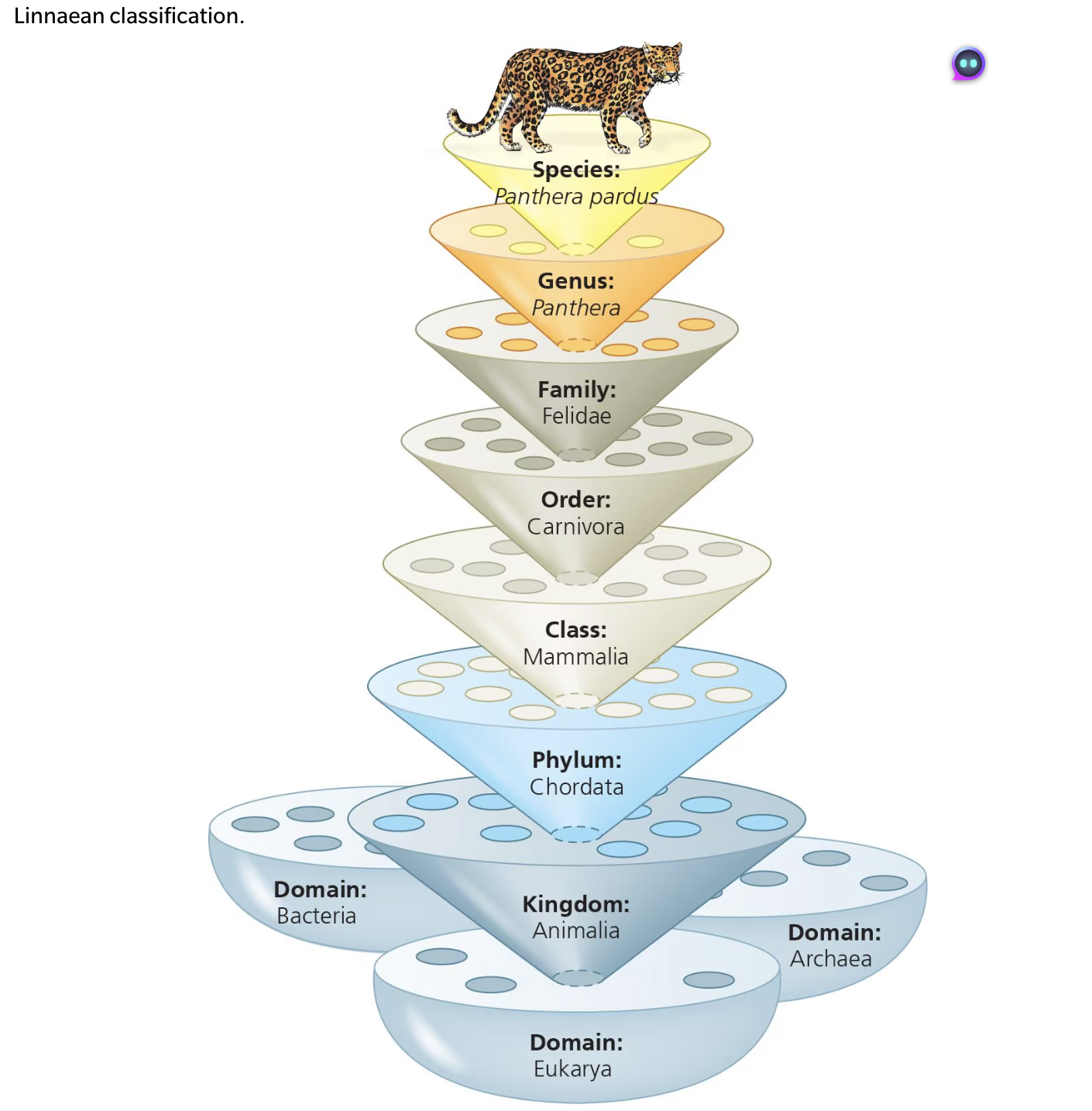
What is hierarchical?
known as the Linnaean classification
grouped from largest to smallest or smallest to largest
What is phylogenetic systematics
it shows cladograms
how to interpret cladograms
how to build cladograms
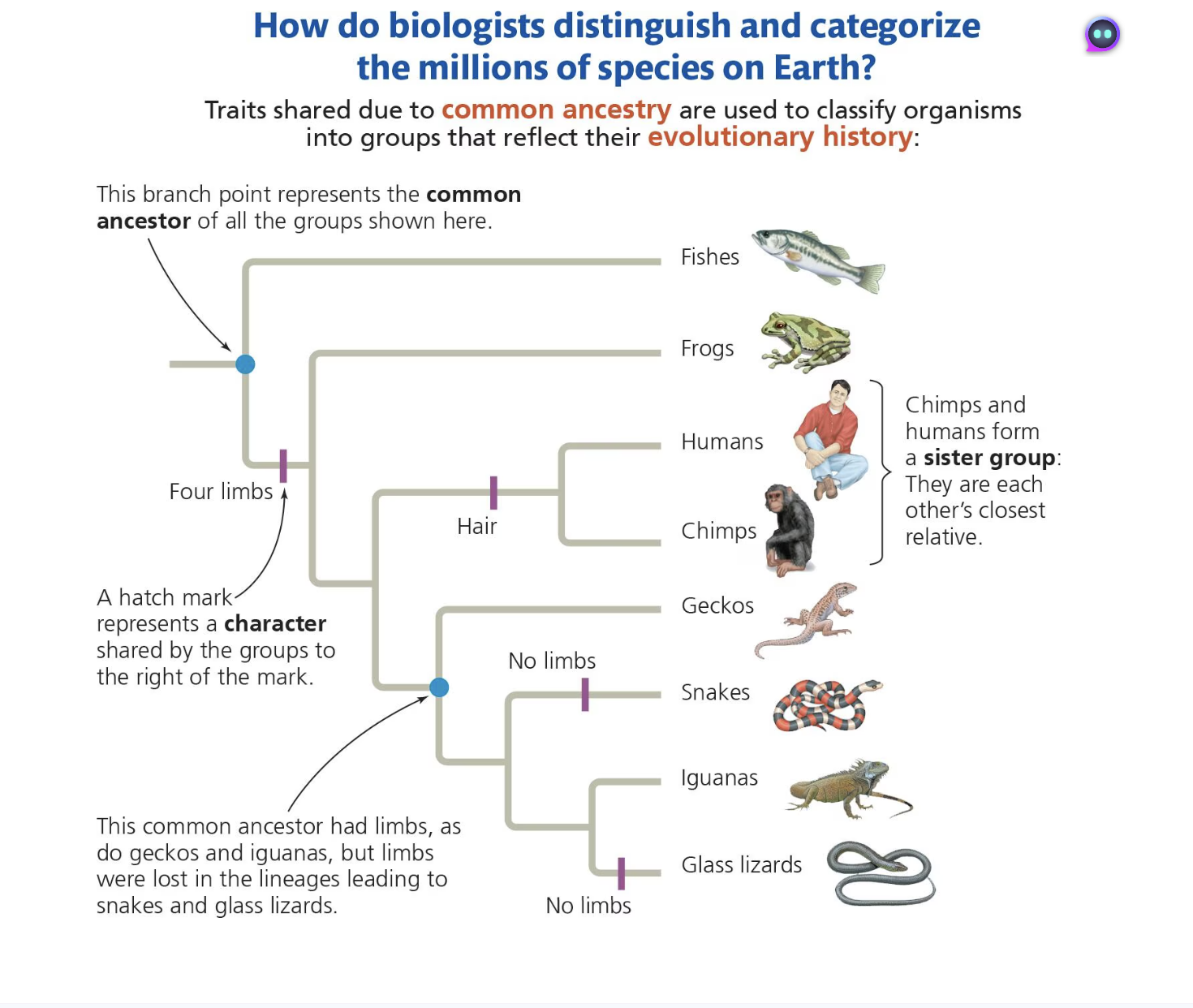
What is a phylogenetic tree
The evolutionary history of a group of organisms can be represented in a branching diagram called a phylogenetic tree
What are the domains of the Linnaean classification system?
Kingdom, Phylum, Class Order, Family, Genus, and Species
Mnemonic: King Phillip Came Over For Good Sleep
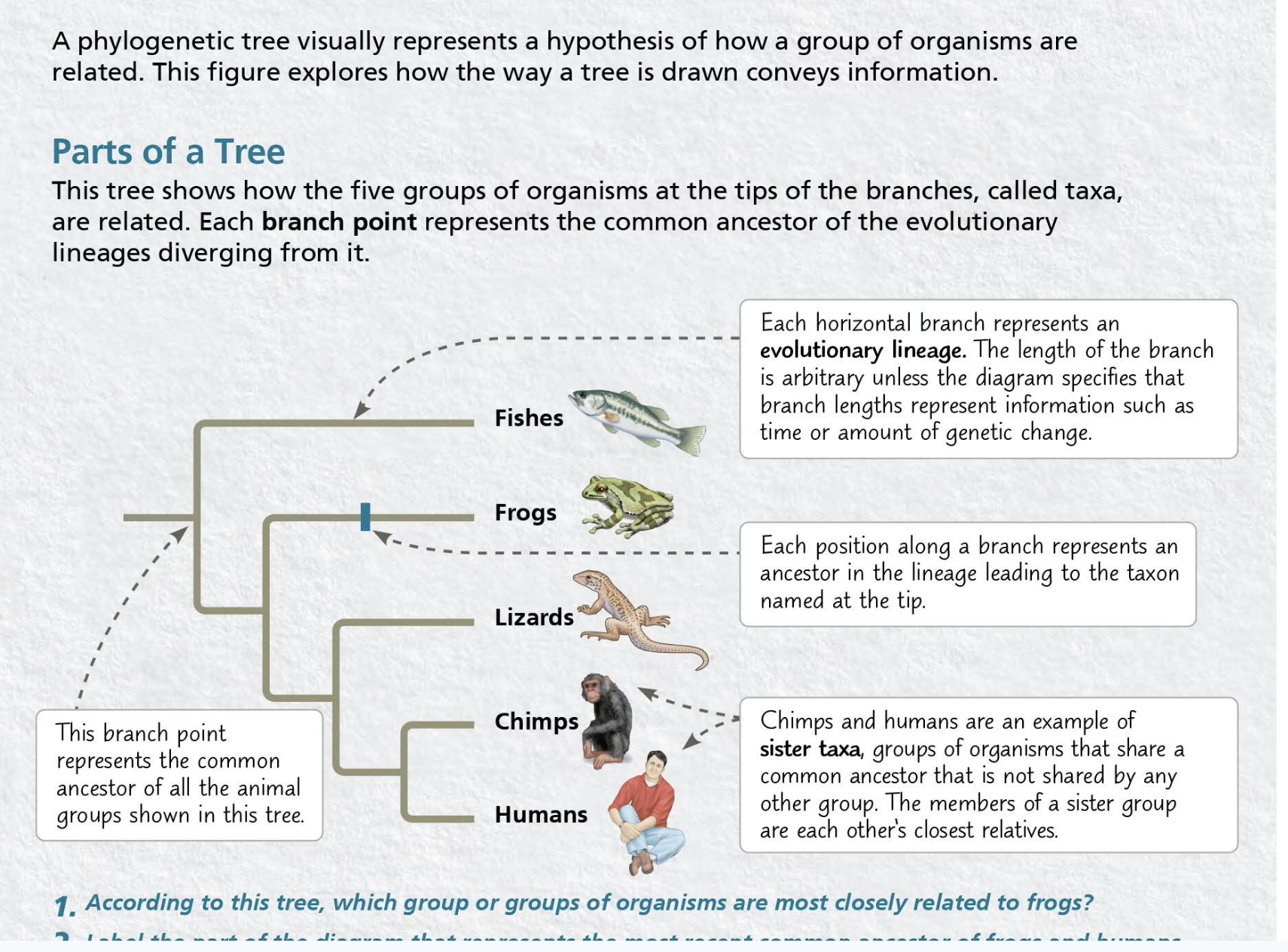
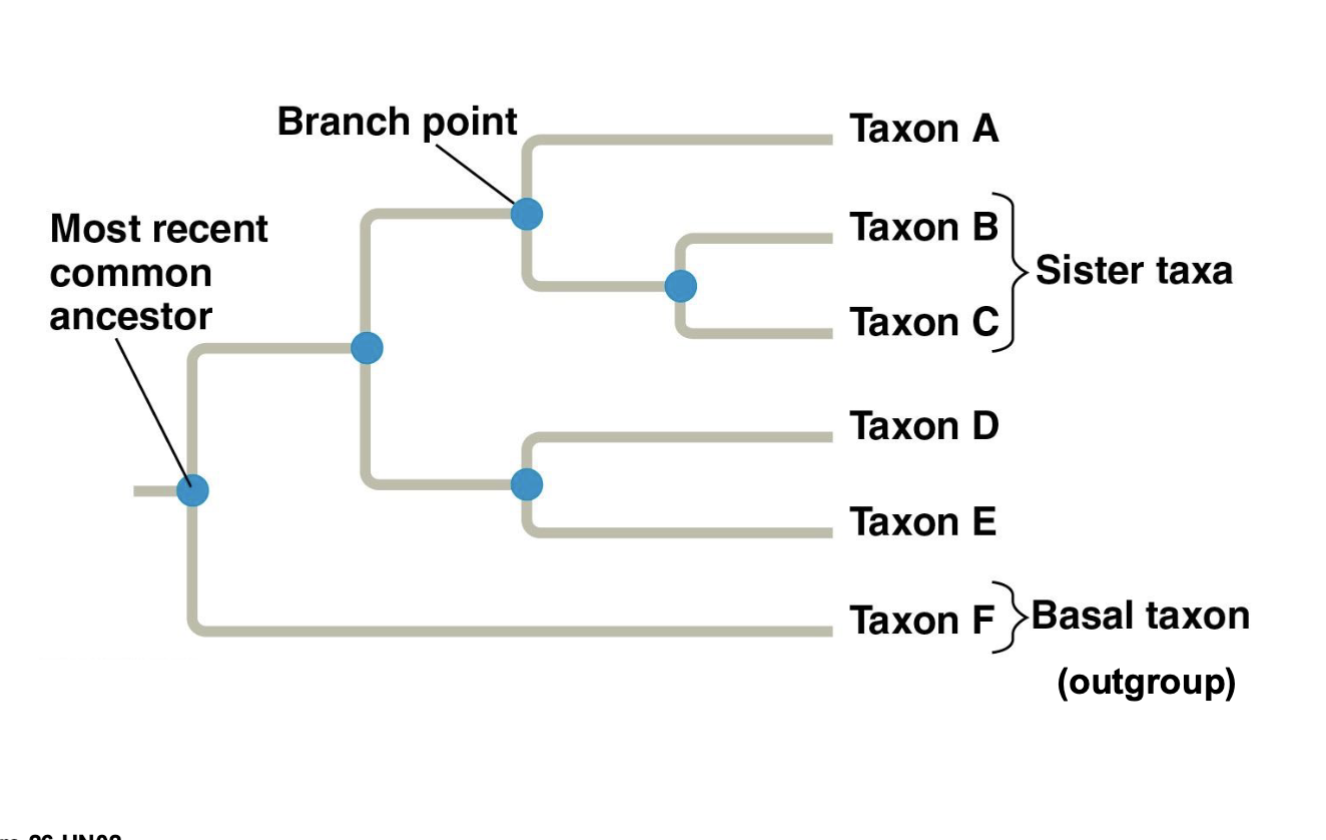
Take a look at what the 1. Branch point 2. evolutionary lineage 3. sister taxa 4. and ancestor looks like on a tree
What are two more alternatives to a regular horizontal phylogenetic tree?
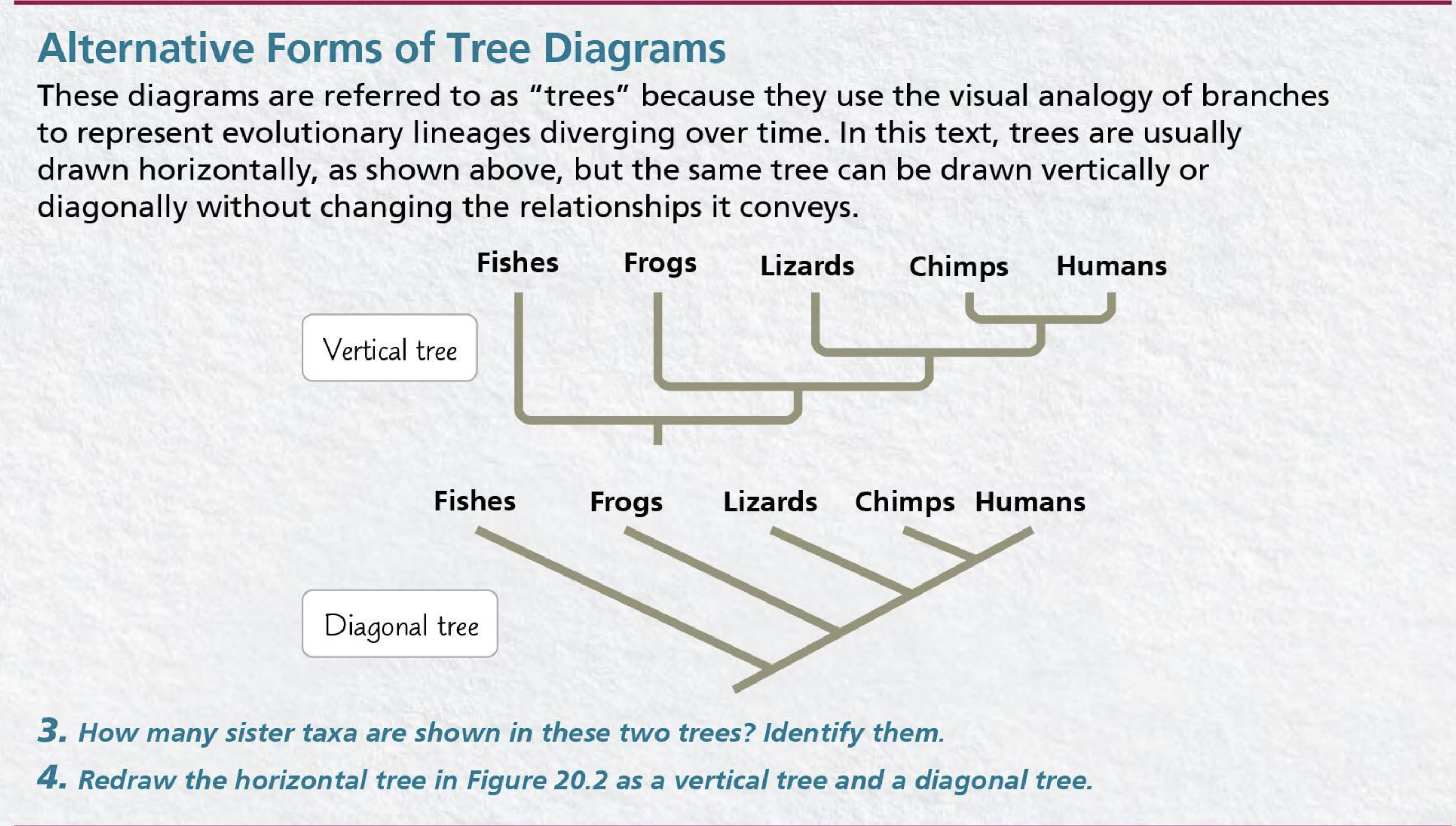
vertical and diagonal
What is autotropic?
“self feeding”
photosynthesis
chemosynthesis
What is heterotropic?
“feed on others”
intracellular digestion
extracellular/ external digestion and/or absorption
Do Bacterias have a true nucleus? Do they have big or small prokaryotic cells?
What is the cell wall made up of?
No true nucleus
Small prokaryotic cells
cell wall is made up of Peptidoglycan
Do Archaea have small or big prokaryotic cells? Do its cell walls contain peptidoglycan? Are archaea “Extremophiles”? Describe what Extremophiles mean
They have small prokaryotic cells
Its cell walls do not contain peptidoglycan
They are extremophiles, meaning they can tolerate heat, high salt, etc
Are protists eukaryotic or prokaryotic? Are they often single-celled? Are protists heterotropic or autotropic? Name some examples of protists.
They are eukaryotic
they are often single celled
they can be heterotropic, autotropic,or both
Amoeba, algae, plasmodium
Are plants Eukaryotic? Are they Multicellular? How do they consume nutrients and in what organelle does it occur in? What is the plant cell wall made up of?
Plants are eukaryotic
Plants are multicellular
They are photosynthetic, and it occurs in the chloroplasts
the cell wall is made up of cellulose
Are fungi eukaryotic or prokaryotic? Are they multicellular or single celled? What is the cell wall of fungi made up of? Are fungi heterotropic or autoptropic?
Fungi are eukaryotic
They are multicellular
the cell wall is made up of chitin
they are heterotropic because they cannot make their own food
Are animals eukaryotic or prokaryotic? Are they multicellular? Do they have cell walls? Are they heterotropic or autotropic?
They are eukaryotic
they are multicellular
they do not have cell walls
they are heterotropic
Remember that:
While the Linnean system may distinguish
groups, it does not indicate different groups’
evolutionary relationships to one another
– E.g., how are birds and reptiles related?
analyze this tree
What is Homology?
similarity due to shared ancestry
What is Analogy?
Similarity dude to convergence (Similar adaptations to similar environments; not shared ancestry
What is a clade?
It means “branch”
What does bifurcating mean?
it means that the groups of organisms are derived from a common ancestor by bifurcating (the branches splits two way)
What is apomorphy? what is synapomorphic?
Each two way splitting branch (bifurcating) is based upon the acquisition of a new unique character — a new trait is apomorphy
Shared derived traits
what does maximum parsimony mean?
the branch pattern that
can be created with the fewest required steps is
most likely the most correct
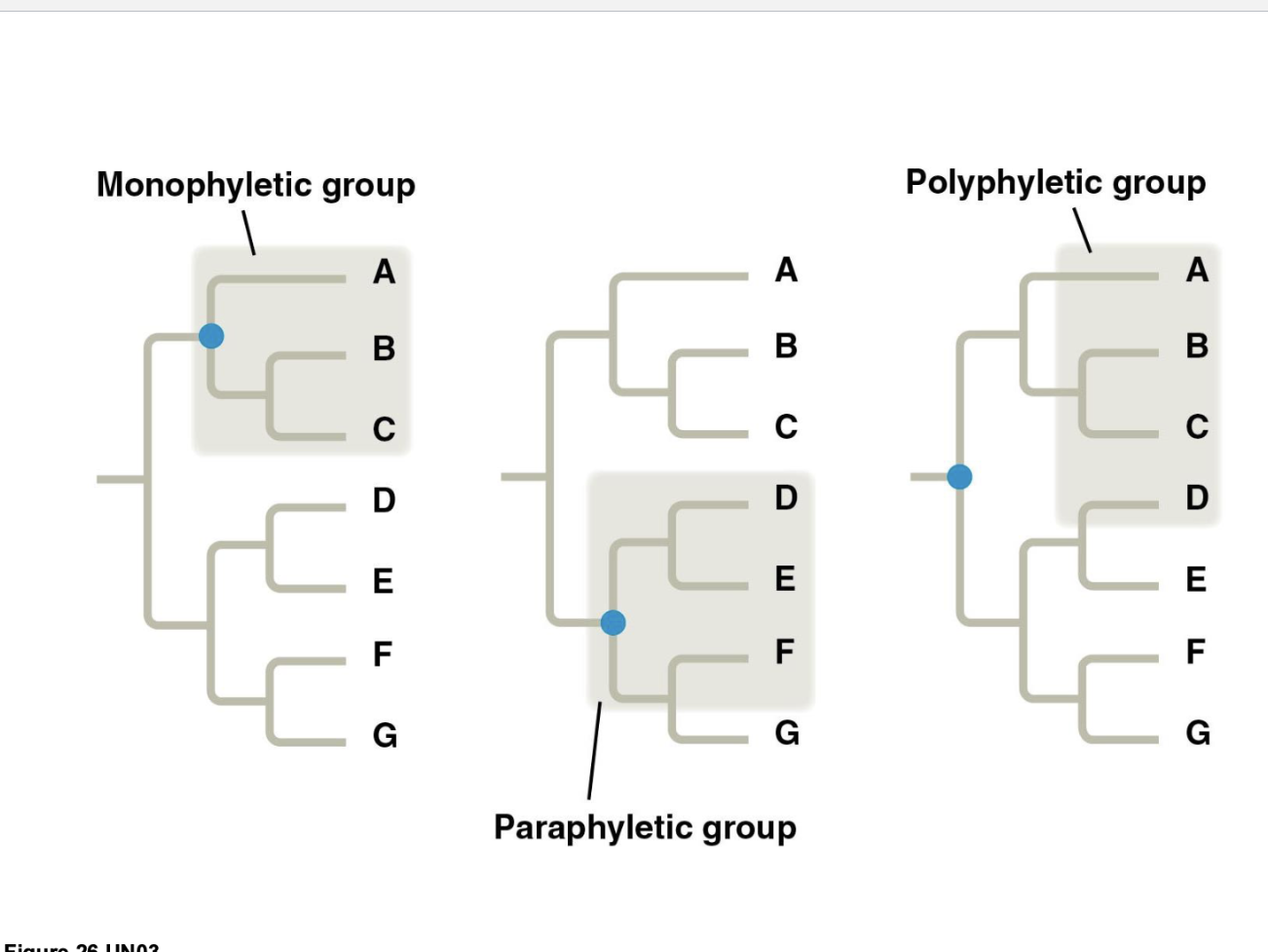
what is monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic group?
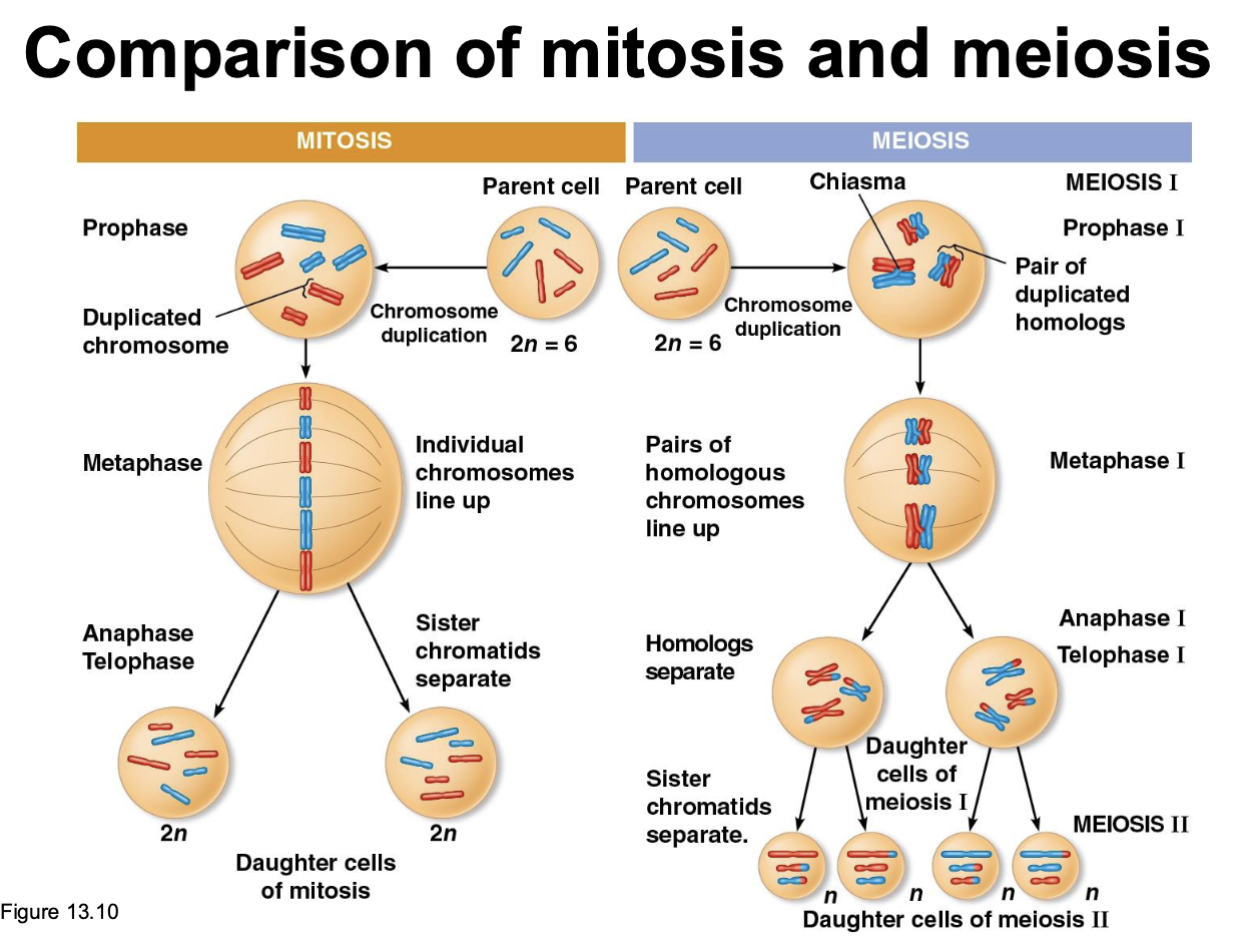
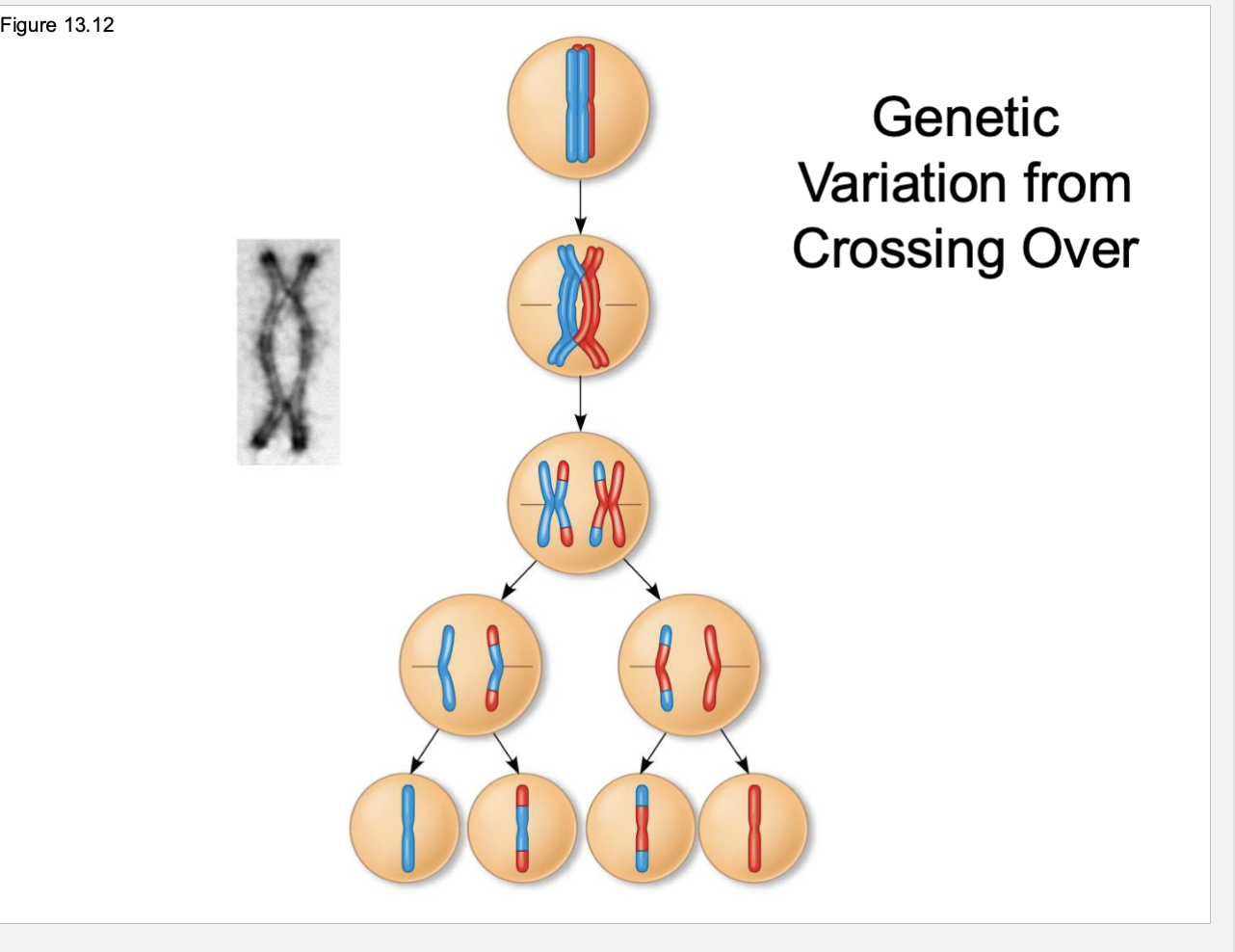
What happens in meiosis 1 & 2
Meiosis 1: Homologous paired chromosomes separate (diploid—→haploid)
Meiosis 2: sister chromatids separate (duplicated—→unduplicated)
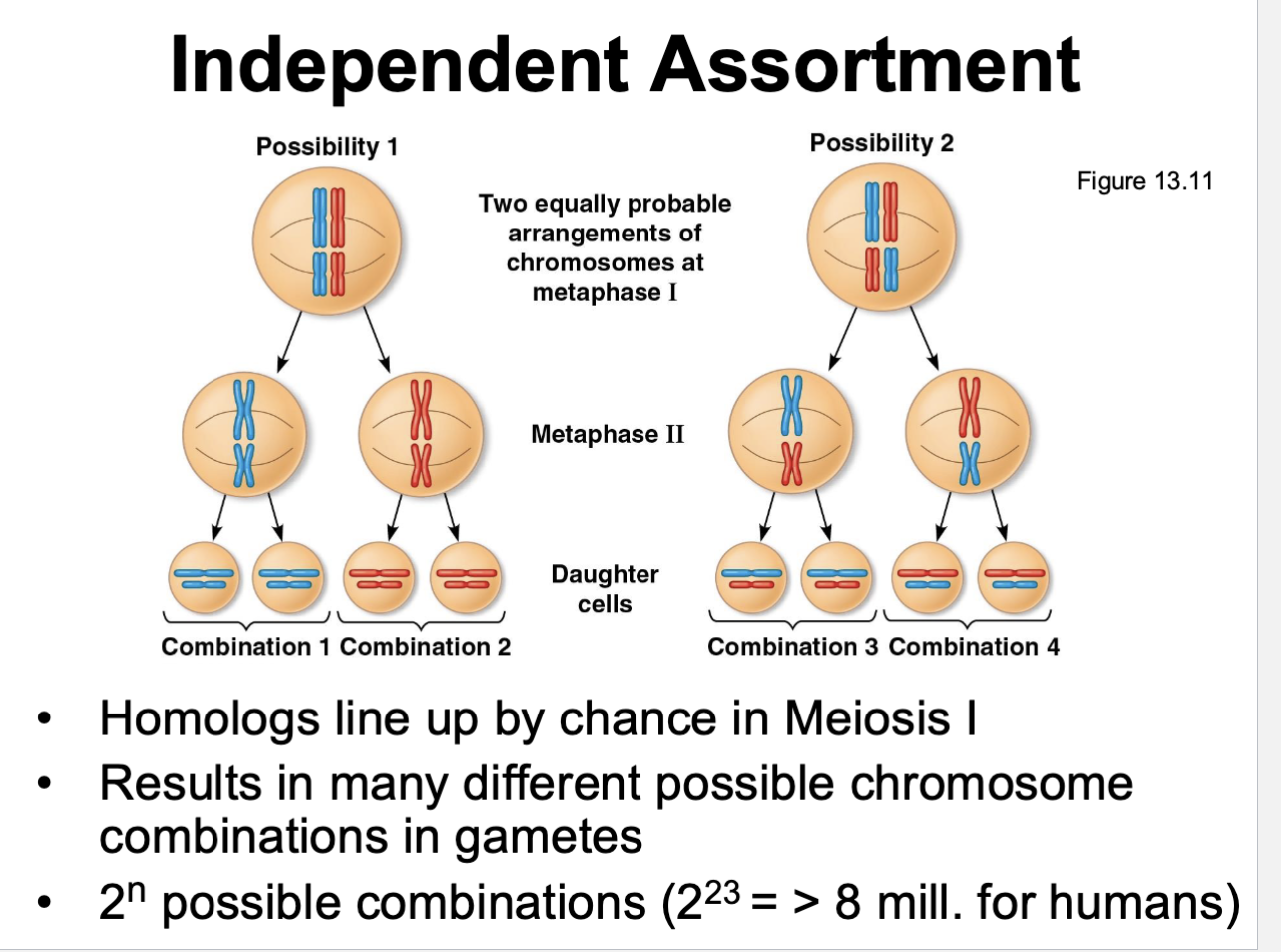
Name three variation methods of sexual reproduction
independent chromosome assortment
crossing over
fertilization

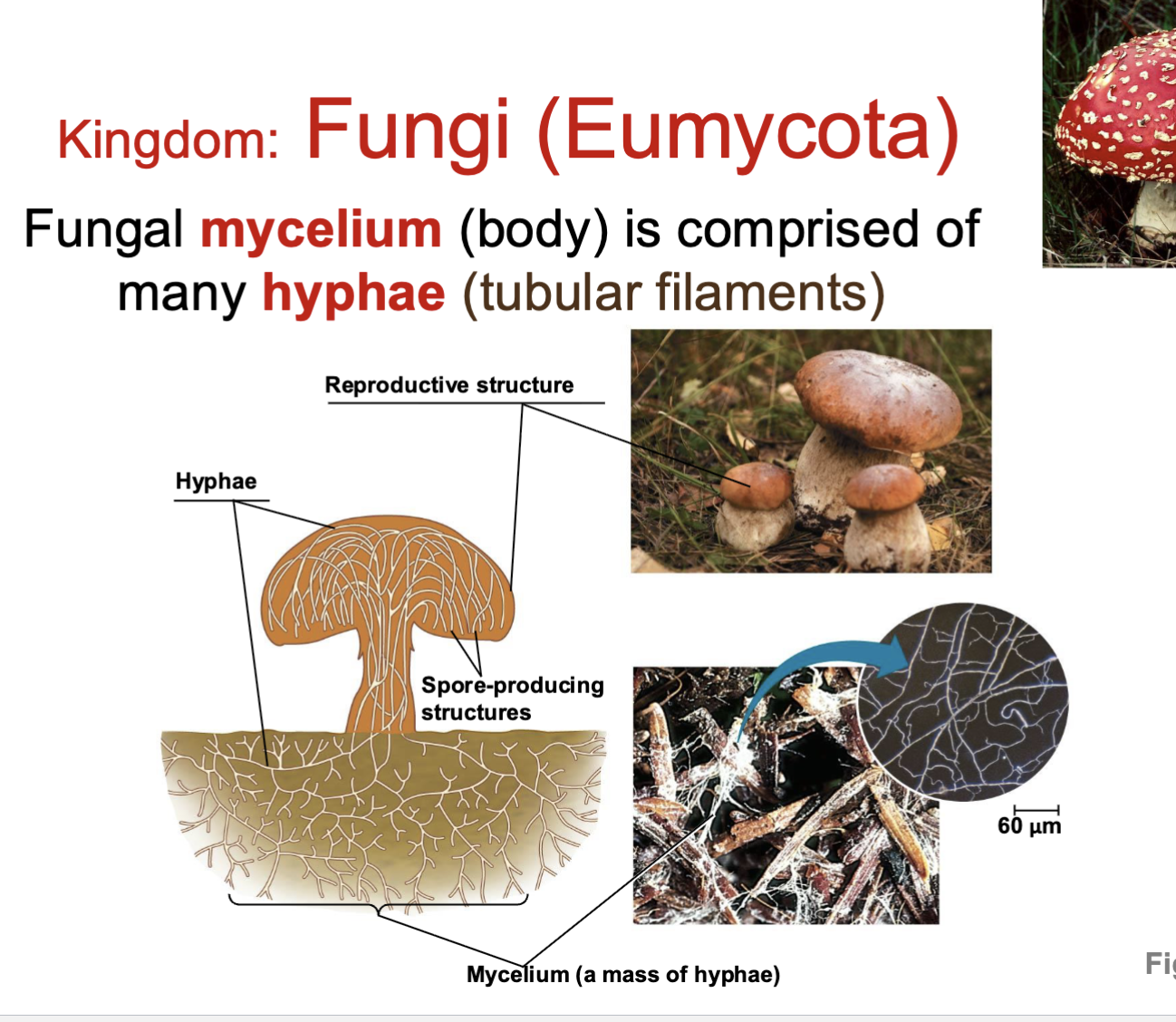
Are Fungi eukaryotic? Are Fungi multicellular? What is fungi wall made up of? Are they autotropic or heterotropic? Do they spend most of their life in haploid or diploid?
Fungi’s are eukaryotic
they are multicellular (only yeast are unicellular)
Fungi wall are made up of Chitin
They are heterotropic
and they spend their life mostly in the haploid stage
what makes up the Fungi’s Mycellium?
A mass of hyphae
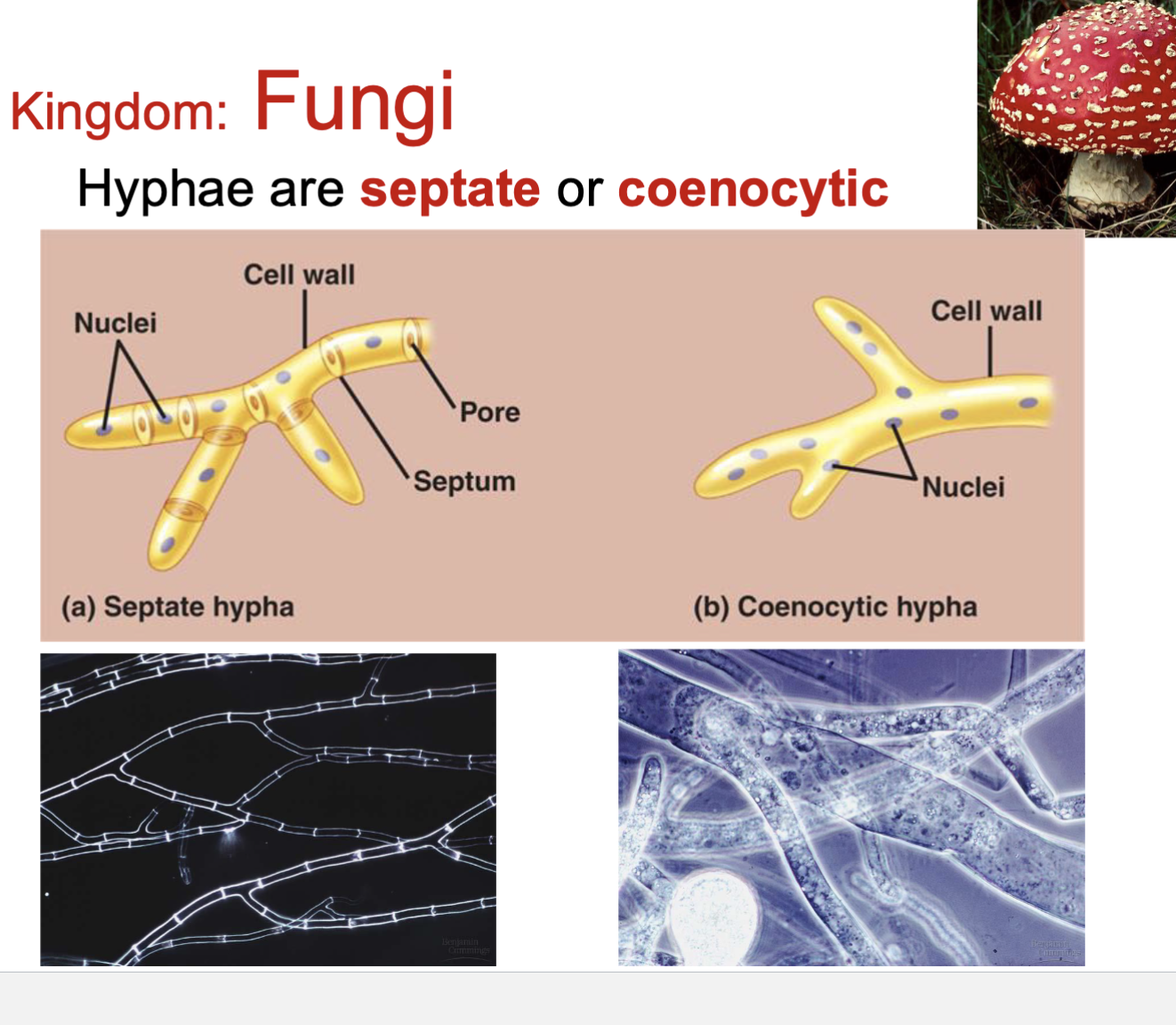
What are the two types of hyphae?
Septate
coenocytic
How are fungi heterotropic?
They secrete exoenzymes for external digestion
absorb nutrients from environment
they store fuel as glycogen (like animals)
They are major decomposers
many are parasitic
many are mutualistic symbionts- meaning they live with a host
some are predatory
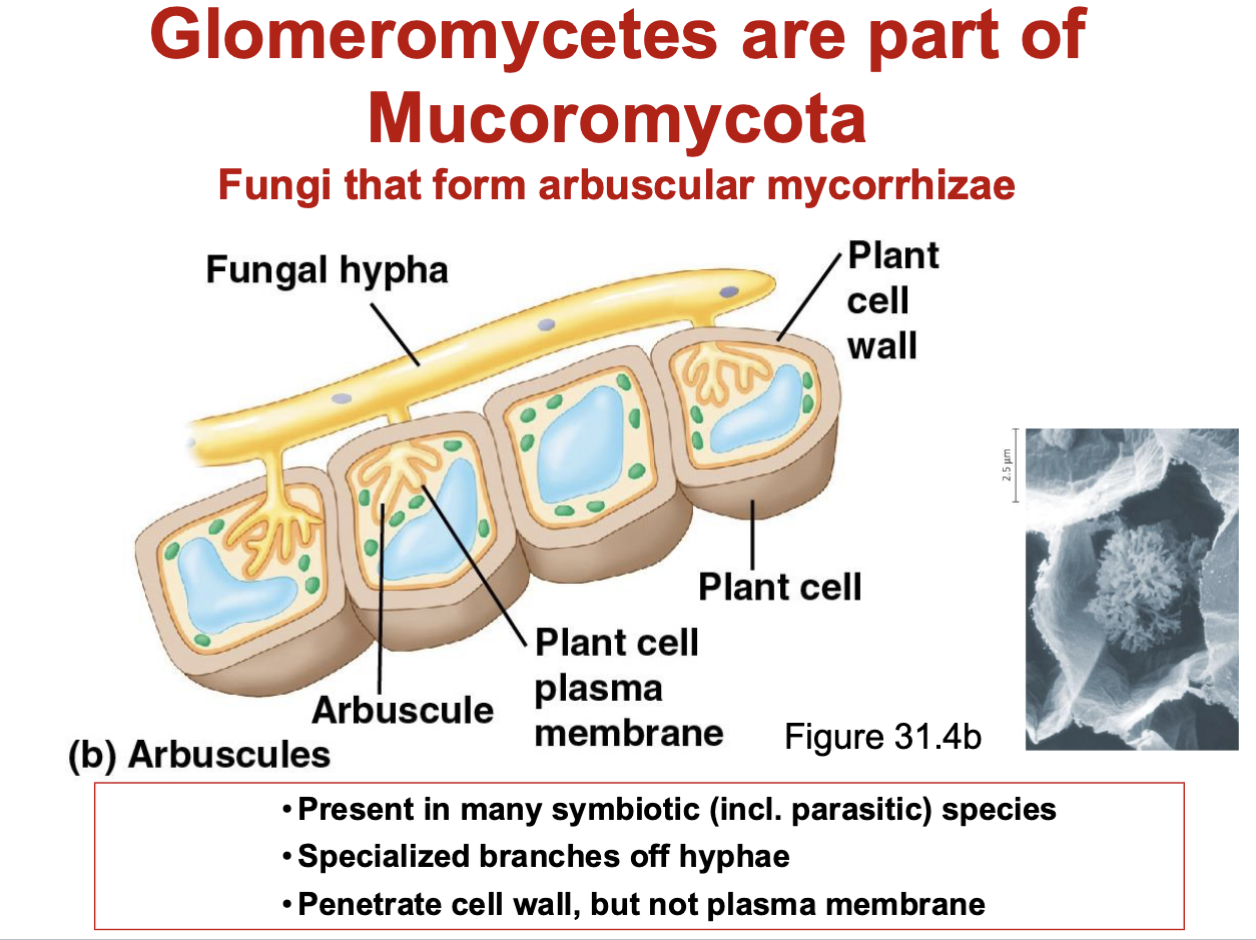
How does it look when the fungi absorbs nutrients from the host?
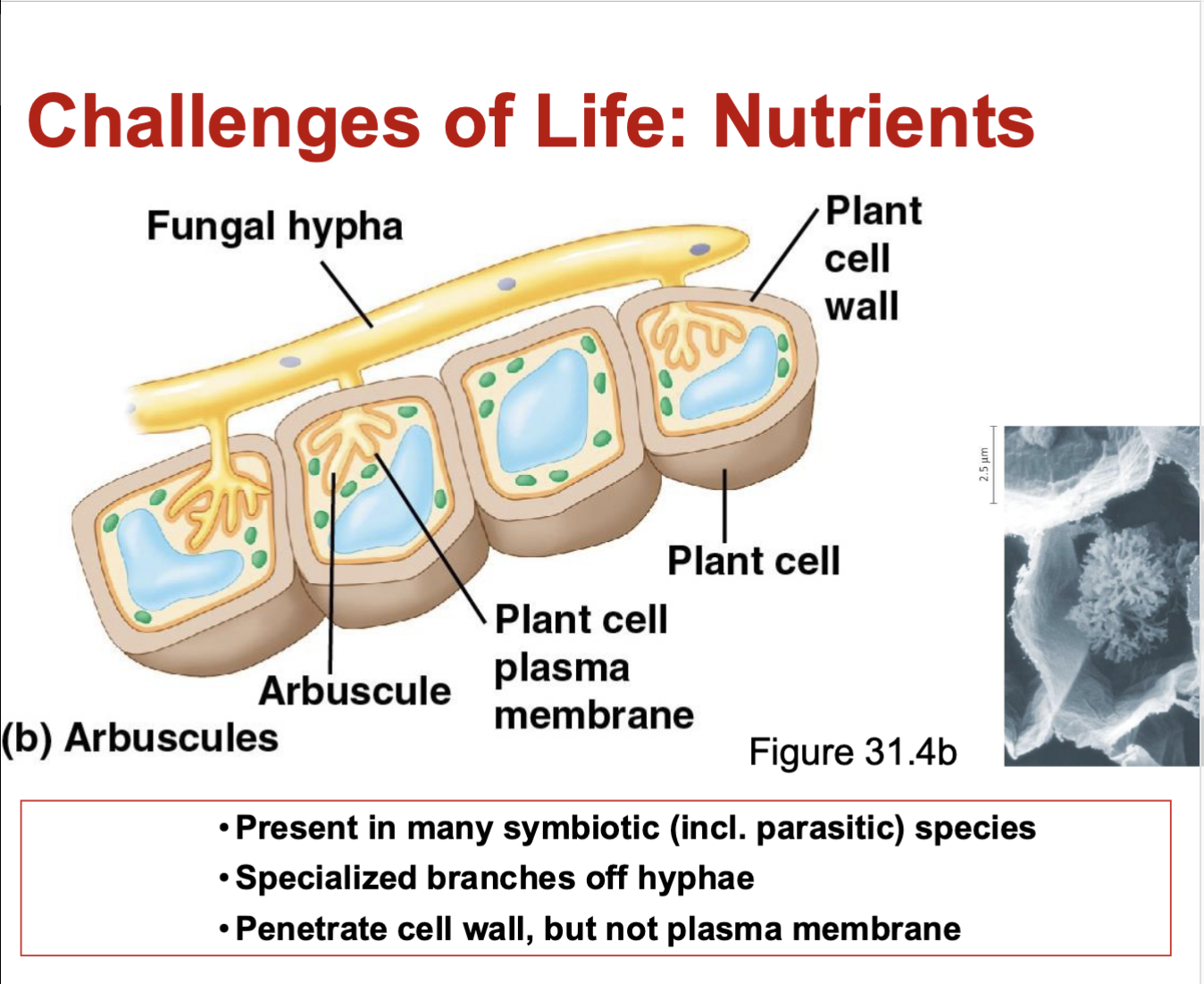
The “arbuscule” will kind of attach itself to the plasma membrane but it will not break through, and then it absorbs nutrients.
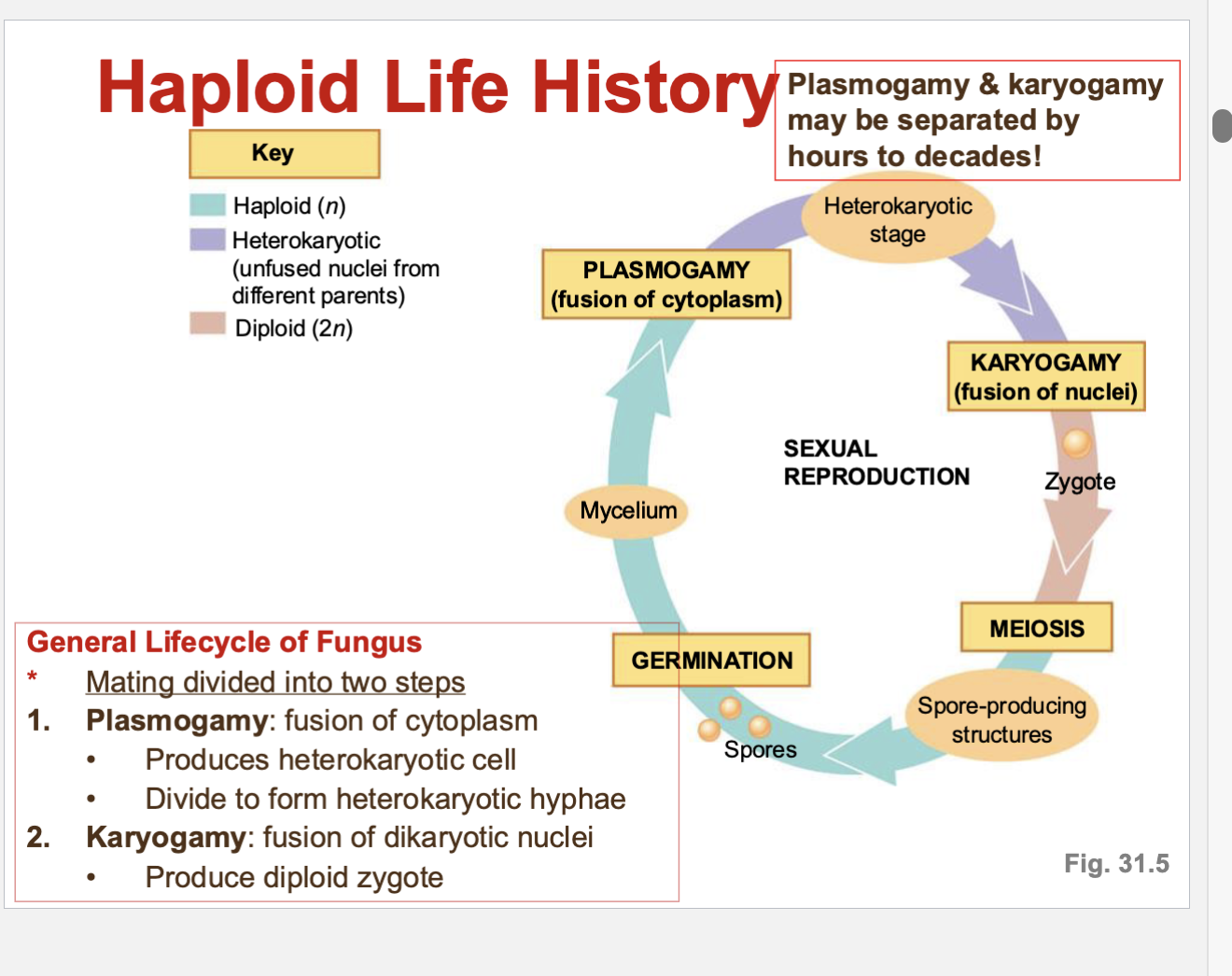
What is the general lifecycle of fungus? And how do the haploid hyphae mate with another haploid hyphae?
They mate with haploid hyphae from another mycelium
the hyphae could be same species but different mating type
they are prevented from mating with its own hyphae
they are attracted by pheromones
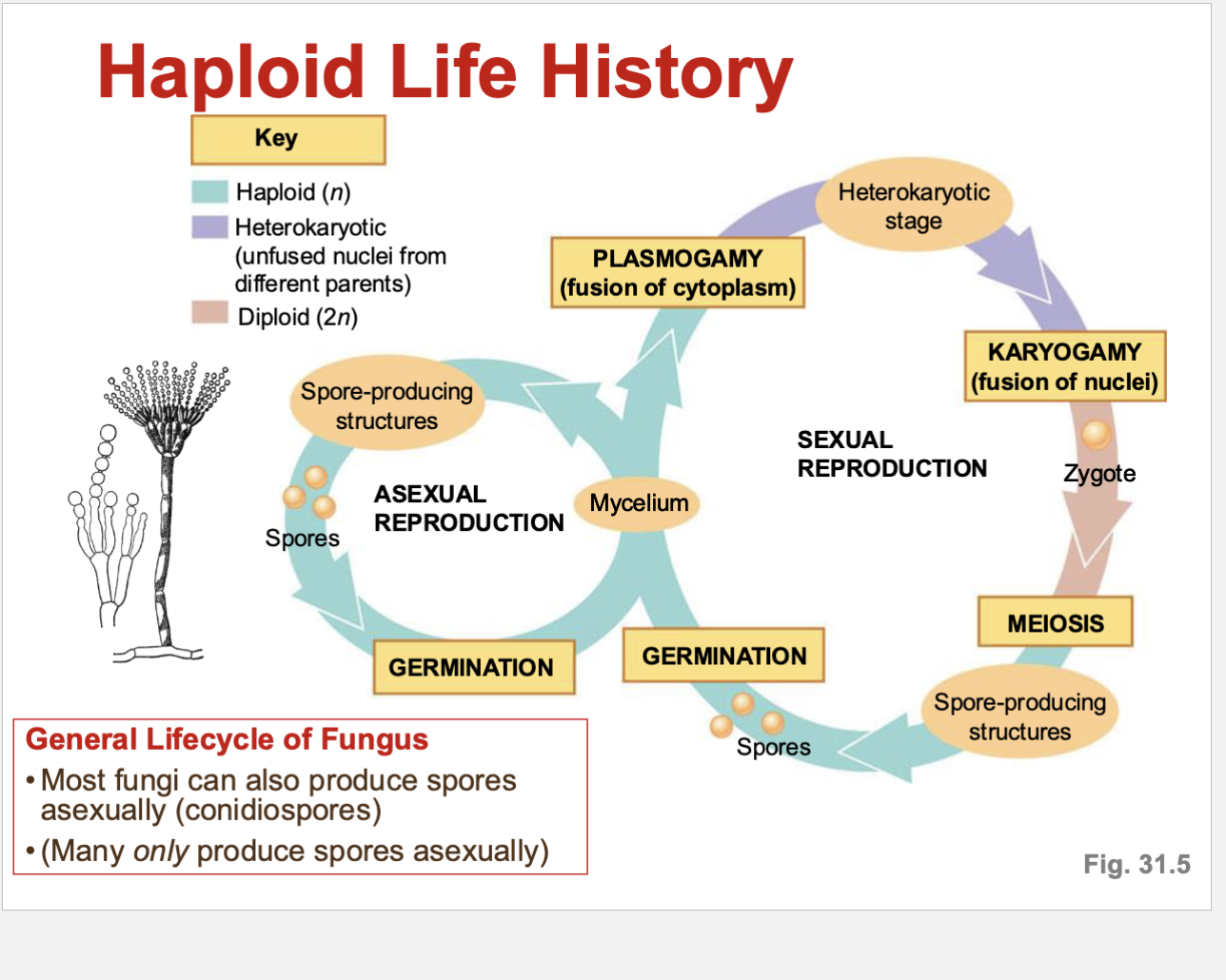
Can fungus reproduce asexually too?
yes
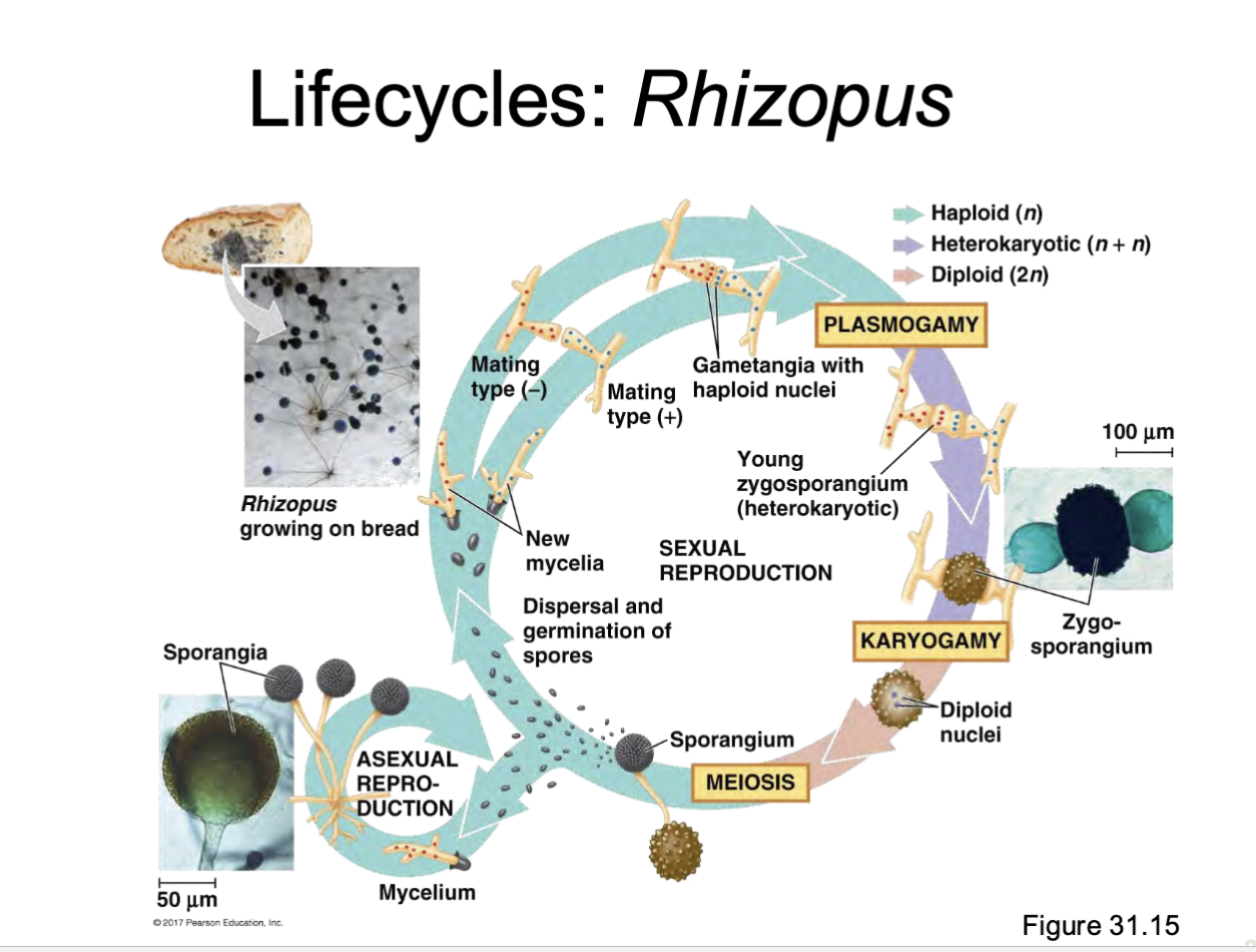
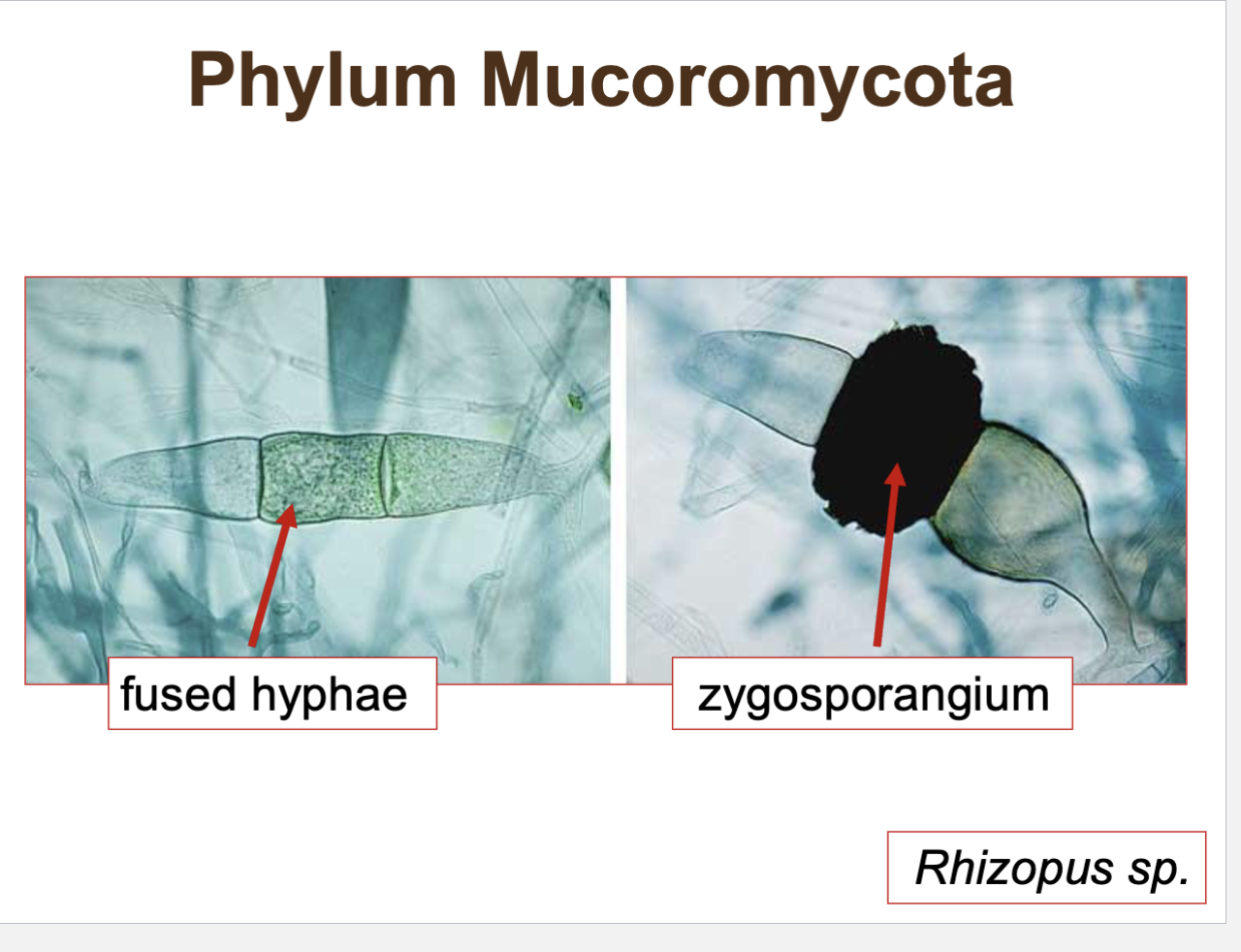
Phylum Mucoromycota (Rhizopus)
a common mold we see in food such as bread and strawberries
an example we will be looking at is Rhizopus
What is Mycorrhizae?
When a symbiotic relationship between fungi and plant roots, where the fungi extend the plant's root system into the soil to access water and nutrients, while the plant provides the fungi with sugars from photosynthesis
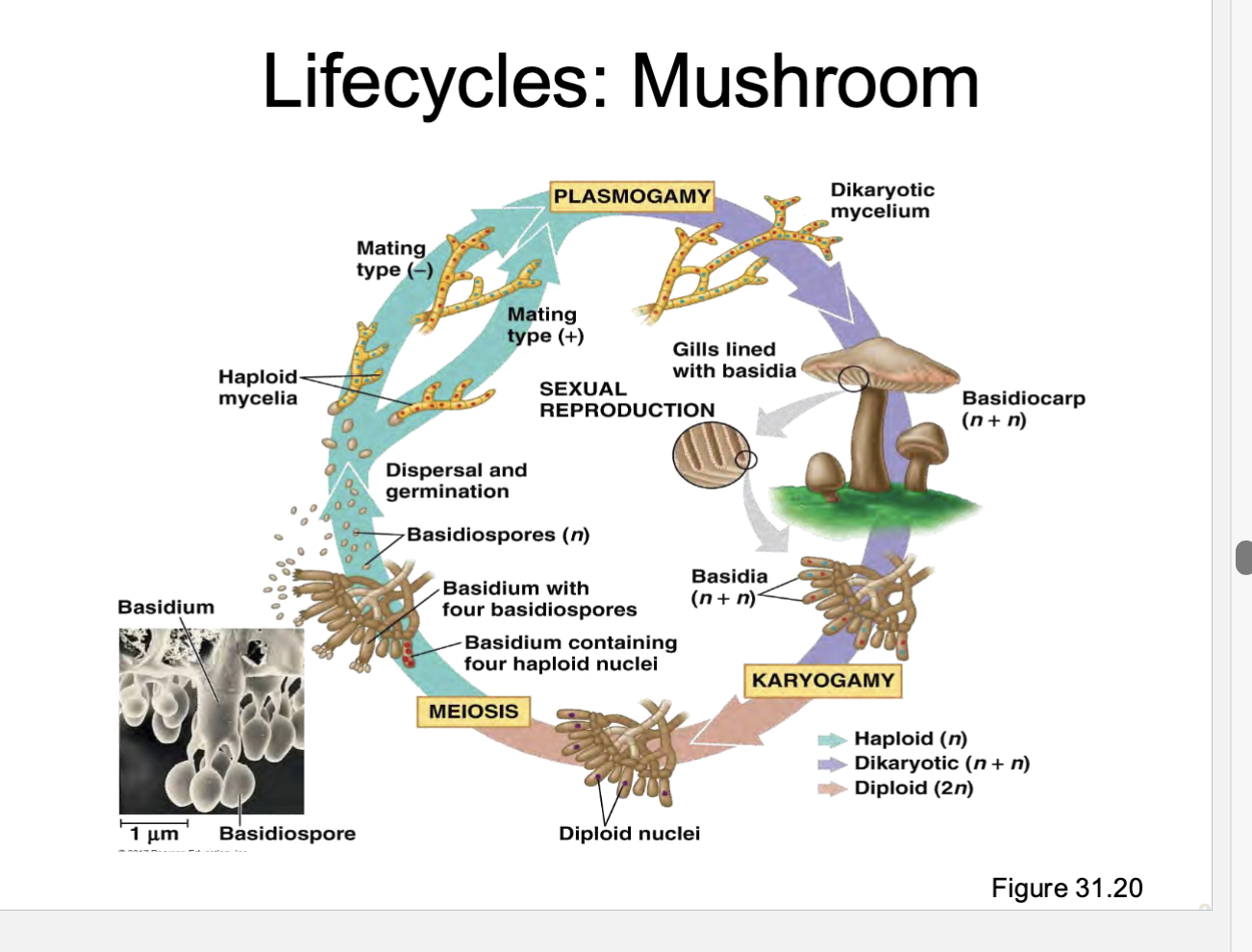
Phylum Basidiomycota (club fungi)
they have fruiting bodies
ex. mushrooms/shelf fungus
Describe the lifecycle of mushroom
Phylum Ascomycota (Sac fungi)
ex. yeast
single celled ascomycetes
includes baker’s and brewers yeasts
What are other symbiotic relationships other than mycorrhizae? what are the differences between lichen and mycorrhizae?
lichens
important pioneer species on cleared rock and soil
The main difference is that lichens are a partnership between a fungus and an alga or cyanobacterium, while mycorrhizae are a partnership between a fungus and a plant root