Male Reproductive System
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
what are the 2 essential elements of the male reproductive system?
gonads (testes)
glands/ducts (that constitute accessory structures)
the gonads (testes) are responsible for production of _____________
spermatozoa, the haploid gametes that fertilize the female oocyte
the testis are largely composed of _____________ within which _______ are formed
seminiferous tubules
spermatozoa
once formed, the sperm moves from the tubules into the ______ which serves as a temporary reservoir for sperm
rete testes
describe the formation of sperm and the pathway
spermatozoa are formed in semniferous tubules of testis
sperm moves into rete testes (temporary reservoir for sperm)
sperm passes through efferent ductules into epididymis
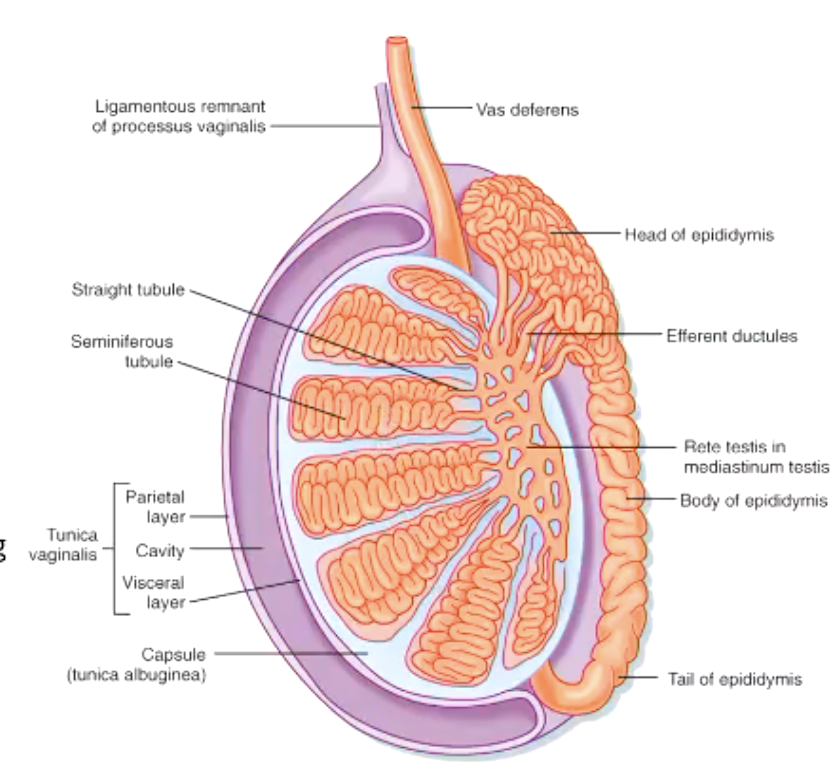
what ducts carry spermatozoa along with glandular secretions?
epididymis
ductus (vas) deferens
ejaculatory duct
urethra
penis
where are the most immature germ cells (spermatogonia) located? mature germ cells (spermatozoa)? what cells are in the spaces between the tubules?
spermatogonia → near periphery of tubule
spermatozoa → near tubule lumen
in spaces between tubules are interstitial cells of Leydig
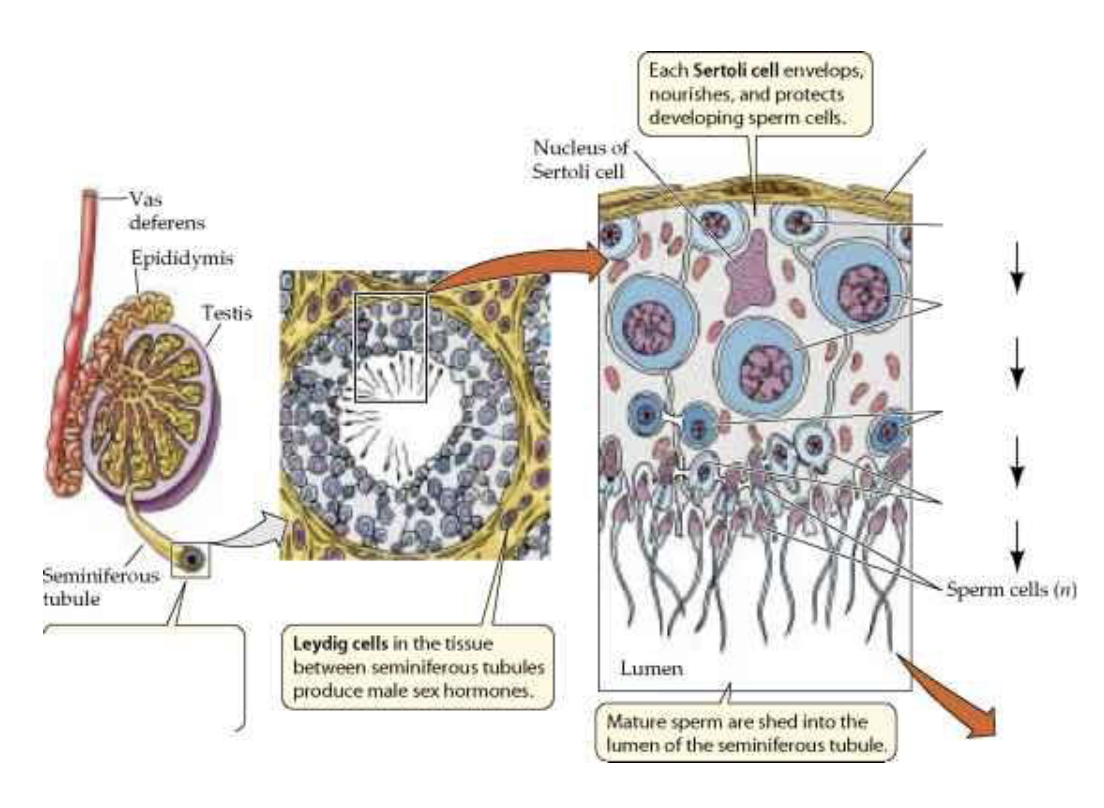
what are the immature sperm germ cells, lie on the basement membrane of the seminiferous tubule?
spermatogonia
how many chromosomes do spermatogonia have?
normal diploid number of chromosomes (22 pairs of autosomal plus one X and one Y chromosome)
describe the process of spermatogenesis starting at spermatogonia
spermatogonia divide mitotically into primary spermatocyte
which enter first meiotic division to become secondary spermatocytes (daughter cells)
secondary spermatocytes enter second meiotic division to become smaller spermatids
spermatids differentiate into functional spermatozoa (spermiogenesis)
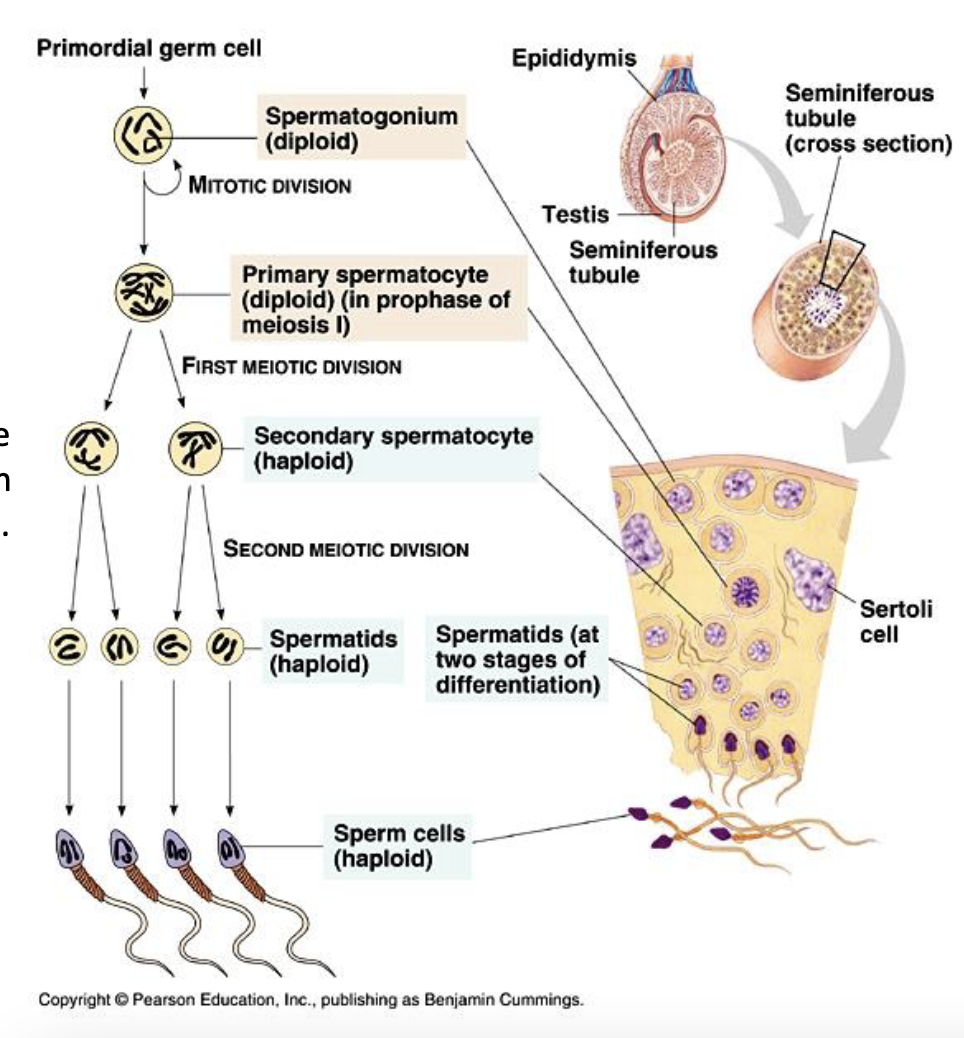
how many chromosomes do secondary spermatocytes have? spermatids?
haploid #
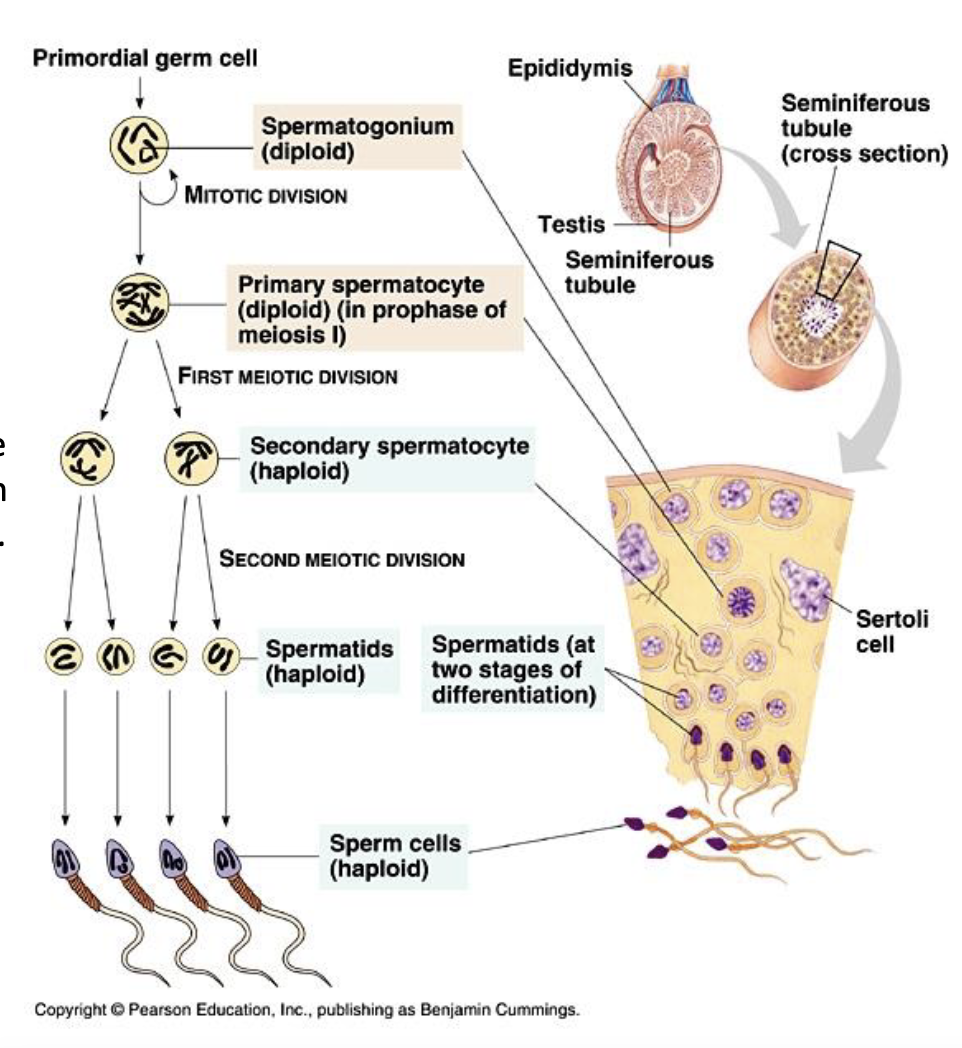
spermiogenesis involves…?
formation of acrosomal cap
condesnsation/elongation of nucleus
formation of flagellum
formation of helical sheath of mitochondria
removal of excess cytoplasm
during spermiogenesis, the acrosomal cap is formed from…?
Golgi apparatus covering the nucleus
during spermiogenesis, the flagellum is formed from…?
centrioles
during spermatogenesis, each primary spermatocyte produces # spermatozoa, # with X and # with Y chromosomes
4
2, 2
as generations of spermatogonia mature, the more advanced cells are displaced towards the …?
lumen of the tubule
the complete process of spermatogenesis takes approximately how long?
74 days, 50 within the seminiferous tubules
in a normal 20 year-old male, about 30 million spermatozoa are produced per day. This number increases/decreases with increasing age
decreases
t/f: spermatogenesis occurs throughout adult life in the male
true
(hormone) binds to receptors on _____ cells and stimulates synthesis of several key proteins necessary for sperm formation and Leydig cell function
FSH
Sertoli
LH (in males, also known as interstitial cell stimulating hormone, ICSH) binds to Leydig cells and stimulates __________ production
testosterone
what feedback control mechanism is involved in inhibiting FSH release?
inhibin (produced by Sertoli cells) inhibits FSH release
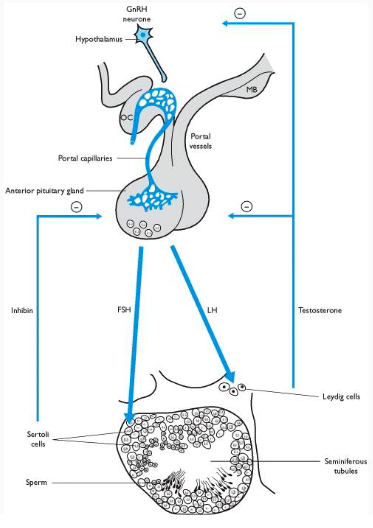
what feedback control mechanism is involved in inhibiting testosterone release?
testosterone inhibition of GnRH from hypothalamus and release of LH
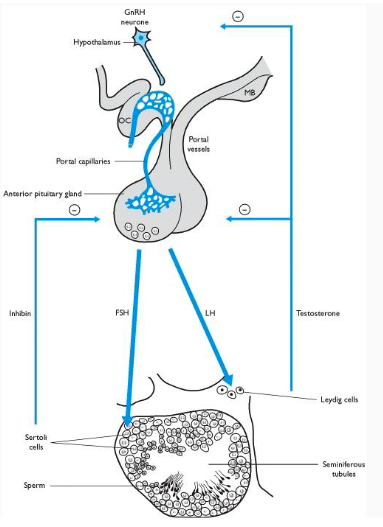
what cells extend from the basal lamina to the lumen of the tubule and surround the germ cells in early stages?
Sertoli cells
FSH stimultes production of what components in Sertoli cells?
androgen binding protein (ABP)
P-450 aromatase
growth factors
inhibins
what is secreted into the lumen –binds to testosterone to maintain high luminal concentration?
androgen-binding protein (ABP)
what does P-450 aromatase do?
convert testosterone to estradiol (testosterone is made by Leydig cells and diffuses into Sertoli)
what do inhibins do?
act on Leydig cells as growth factor and inhibits FSH release
what are some functions of Sertoli cells?
produce ABP, P-450 aromatase, growth factors, inhibins
physical/nutritional support of germ cells
phagocytosis
secrete fructose-rich medium into lumen
blood-testis barrier
what prevents entry of harmful substances from the blood affecting the sperm and also prevents sperm-related proteins to enter circulation and provoke immune response?
blood-testis barrier (established by Sertoli cells)
what cells phagocytose excess cytoplams shed during spermiogenesis and defective sperm?
Sertoli cells
where are Interstitial cells of Leydig located?
between the seminiferous tubules
LH stimulates production of testosterone in what cells?
Interstitial cells of Leydig
t/f: testosterone produced by Leydig cells acts on Sertoli cells, while estrogen, produced by Sertoli cells regulates Leydig cell function
true (example of chemical crosstalk between Leydig and Sertoli cells)
what are some examples of male primary sexual characteristics?
-growth of the male genitalia: viz. penis, scrotum, prostate, seminal vesicles and testes
-acquistion of the ability to produce sperm
what are some examples of male secondary sexual characteristics?
deepened voice, hair distribution, anabolic effects on skeletal muscle growth, thickening of bones, increased red blood cell production, increased libido
primary sexual characteristics depend upon…?
increased androgens at puberty
once formed, sperm move out of the seminiferous tubules into the ________, a temporary reservoir
rete testes
describe the journey of sperm after being formed starting in the semniferous tubules
semniferous tubule → rete testes → efferent ductules → epididymis → vas deferens → ampulla → prostatic urethra (+fluids from seminal vesicles) → bulbous urethra → penile urethra
sperm is propelled through the rete testes and efferent ductules by ___________ into the epididymis
cilia and smooth muscle contractions
the _________ is ~4-5 meters in length- sperm take from 12-26 days to travel its length - during this time, the sperm gains forward motility and undergoes changes in metabolism and shape
epididymis
from the ampulla, sperm receives fluids from the _______ via the ejaculatory ducts and passes into the ________ receiving prostatic secretions
seminal vesicles
prostatic urethra
the prostatic urethra becomes the bulbous urethra and receives input from the _______
bulbo-urethral glands
a typical ejaculate contain ____ ml semen- ~ % is sperm with a small amount of fluid from the epididymis and vas deferens
2-6 ml
10%
90% of the volume of semen comes from acessory glands. how much comes from seminal vesicles? prostate? bulbourethral glands?
seminal vesicles → 70%
prostate → 19%
bulbourethral glands → 1%
fluid from what accessory gland is alkaline (neutralize acidic female reproductive tract, contain fructose for sperm ATP production, semenogelin which helps coagulate semen after ejaculation)?
seminal vesicle
fluid from what accessory gland helps in coagulation and later breaking down the coagulant?
prostate
fluid from what accessory gland is alkaline with mucus that lubricates the urethra?
bulbourethral (Cowper’s) glands
what is the pH of seminal plasma?
7.4
isotonic to plasma, contains multiple electrolytes (Na, K, Ca, Mg, Zn, SO4, PO4, Cl ), sugars, Vit C, B and E, semenogelin , acid phosphatase, and low MW proteins and peptides
what are some of the functions of seminal vesicle fluid being alkaline?
neutralize acidic female reproductive tract
contain fructose for sperm ATP production
semenogelin helps coagulate semen after ejactulation
how is the male sex organs innervated?
testes, epididymis, accessory glands and erectile tissue are all innervated by sympathetic and parasympathetic systems – penis also has afferent and efferent connections to the somatic nervous system
the male sex act involves what 3 processes?
erection
emission
ejaculation
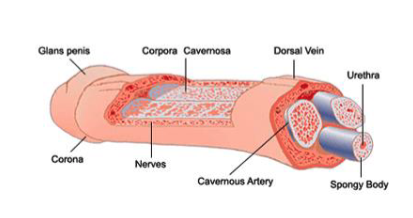
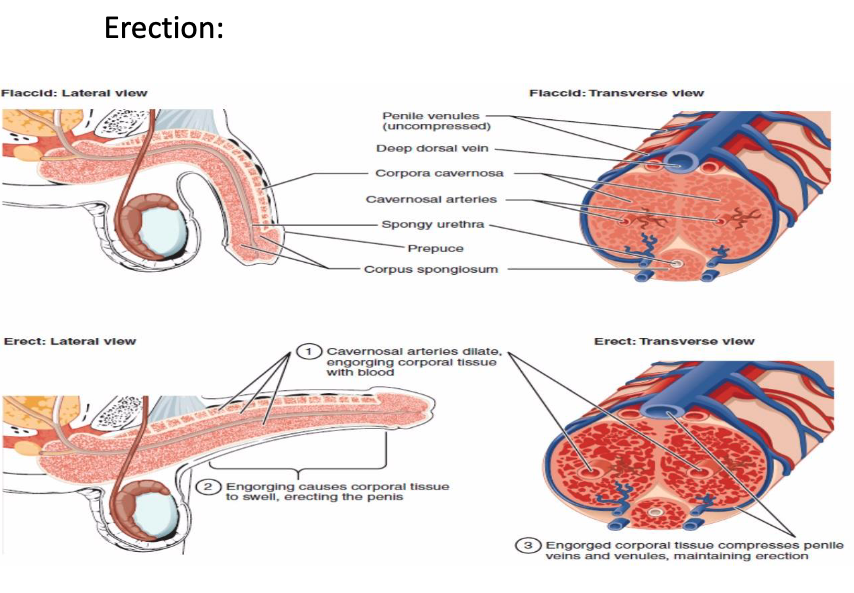
describe the process of erection.
PS stimulation of vessels leading to corpora cavernosa which:
releases acetyl choline → increase NO synthase activity
NO diffuses into vascular smooth muscles which relaxes and increases blood inflow into corpora
increased penile size/rigidity
engorgement compresses penile veins reducing outflow of blood
contraction of ishiocavernosa and bulbospongiosum skeletal muscles that surround copora provide further rigidity
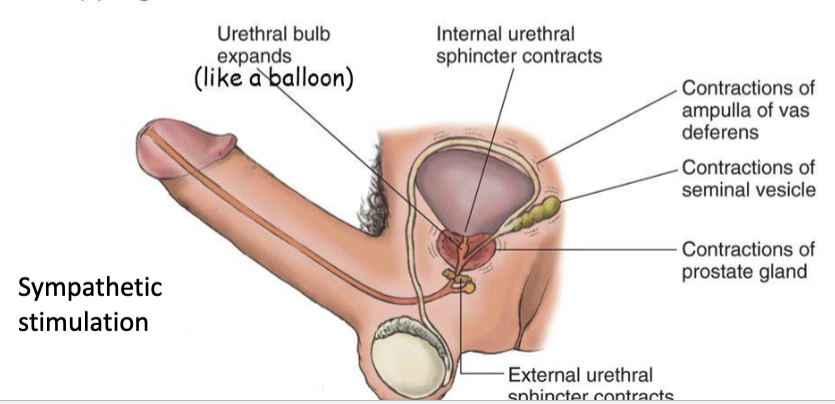
describe the emission phase of ejaculation (phase 1)
contractions in prostate, seminal vesicles, and vas deferens force secretions into urethral bulb
internal and external urethral sphincters close, trapping semen in urethral bulb
is erection stimulated by sympathetic or parasympathetic? what about emission?
erection = parasympathetic
emission = sympathetic
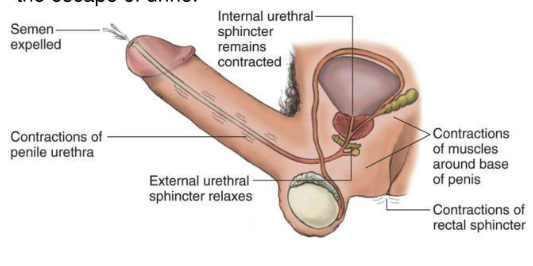
describe the expulsion phase of ejaculation (phase 2)
collected semen expelled out of body by rhythmic contractions of muscles surrounding urethral bulb and urethra
external urethral sphincter relaxes to allow semen out
internal urethral sphincter stays contracted to prevent urine escape
movement of semen into the bulbous urethra (emission) triggers a spinal chord reflex that causes strong rhythmic contractions of what muscles?
perineal muscles
ishio-cavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles
during expulsion phase of ejaculation, efferent signal is carried by somatic motor neurons in which nerve?
pudendal nerve
what is a typical sperm count for ejaculate in fertile male?
40-300 million/mlwha
what is considered low sperm count for ejaculate in fertile male?
<10 million/ml
what are some other factors besides volume and sperm count that can be measured for ejaculat from fertile male?
liquefaction (<15-20 min)
morphology
motility, velocity
pH (7.2-7.8)