Data Management
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ppt, Textbook, Attendance Q's
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
4 Reasons Data Management Matters
AI Systems are only as good at the data they consume
The shift from ‘big data’ to ‘smart data’
Data readiness is the #1 barrier to scaling AI
Good data management is NOT OPTIONAL.
Internal v. External Memory
Internal memory is like the stuff in your brain, short-term.
External memory is like a calendar - essentially a unique way of storing data and suppporting it’s rapid retrieval.
Individual memory systems illustrate some features common to all data management systems. What are they?
There is a storage medium. Data are stored electronically in each case.
There is a structure for storing data. For instance, the address book has labeled spaces for entering pertinent data.
The interface is organized for rapid data entry and retrieval. A calendar is stored in date and time sequence so that the data space for any appointment for a particular day can be found quickly.
The selection of a data management system frequently requires a trade-off decision. In these examples, the trade-off is screen dimensions versus the amount of data that can be seen without scrolling. For example, you will notice the address book sample screen is truncated and will need to be scrolled to see full address details.
Internal memory is __
fast, small, and convenient
External memory is
slower to reference, and not always convenient
TPS
Transaction Processing System - Collect and store data from routine transactions
MIS
Management Information System - Convert data from a TPS into information for planning, controlling and managing an organization
DSS
Decision Support System - Support Managerial decision making by providing models for processing and analyzing data
BI
Business Intelligence- Gather, store, and analyze data to improve decision making
OLAP
Online Analytical Processing - Provide a multidimensional view of data
DM
Data Mining - Use of statistical analysis and artificial intelligence techniques to identify hidden relationships in data
ML
Machine Learning - Using software to make decisions or recommendations traditionally made by humans.
Desirable Attributes of Data
Transportable
Secure
Accurate
Timely
Relevant
Problems with Data Management Systems
Redundancy
Lack of Data Control
Poor Interface
Delays
Lack of Reality
Lack of Data Integration
The Data Deluge
Overwhelming flow of data and information. The volume, velocity, and variety of data make manual curation impossible.
AI tools amplify the good and bad data
External memory extends
Internal memory
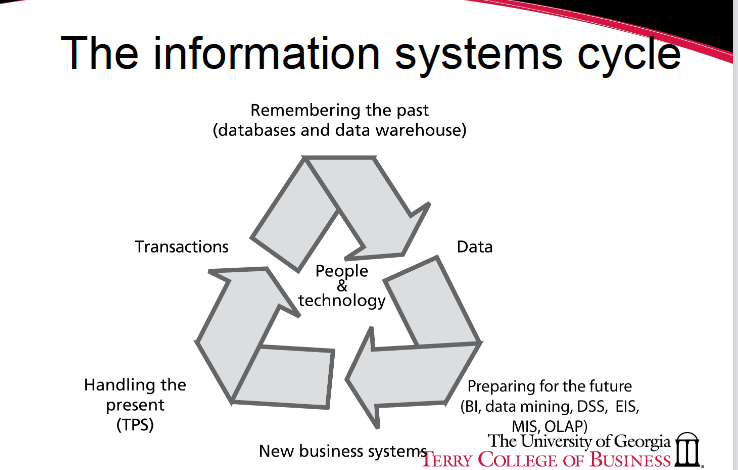
The Information Cycle
The diagram shows a continuous cycle of how organizations use information systems:
Transactions → Handling the present (TPS)
Systems capture day-to-day business activity.Data → Preparing for the future
Collected data is analyzed using tools like BI, data mining, DSS, EIS, MIS, OLAP to support decisions.Remembering the past
Results are stored in databases and data warehouses for long-term use.New business systems
Insights lead to improved or new systems, which generate more transactions.
Components of Organizational Memory
People / Conversations
Tables / Documents
Video / Images / Graphics / Multimedia
Models
Knowledge / Decisions
Specialized memories
Managerial work is
Fragmented
Brief
Frequently Disturbed
High Velocity
Action oriented rather than comtemplative
Two characteristics of Information
Hardness
Richness
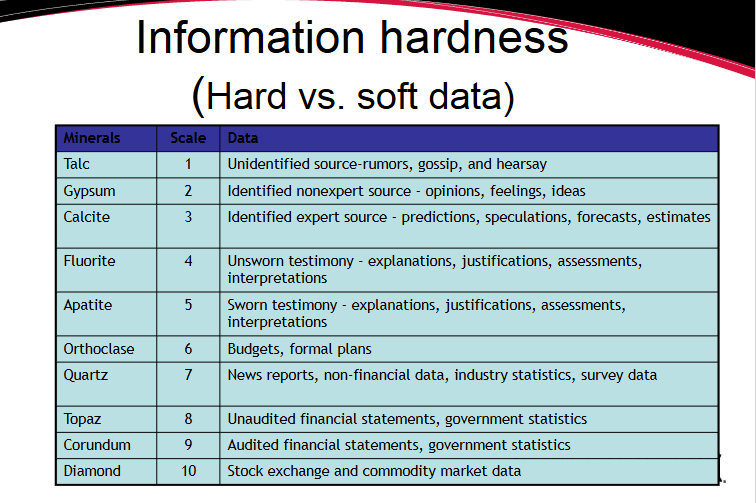
Informatino Hardness
Just know this
What is the biggest barrier to scaling AI systems with organizations?
Data readiness