chemistry definitions syllabus/textbook
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
lattice energy
energy released when one mole of an ionic compound is formed from gaseous ions, under standard conditions
electron affinity
energy change associated with addition of electron to gaseous atom or ion
entropy
measure of the disorder or randomness of a system or surroundings
gibbs free energy
energy of a system that is available to do work at a constant temp and pressure
standard electrode potential
voltage produced by a half cell compared with a standard hydrogen electrode under standard conditions
standard cell potential
potential difference of voltage between 2 half cells under standard conditions
standard hydrogen electrode
half cell consisting of inert platinum electrode immersed in 1M HCl with hydrogen gas at 1atm, bubbling through the solution. used as the standard of a cell potential of zero.
enthalpy change of hydration
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions dissolves in enough water to form a dilute solution
enthalpy change of solution
energy absorbed or released when 1 mole of an ionic solid dissolves in enough water to form a dilute solution
enthalpy change of atomisation
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions is formed from its element under standard conditions
conjugate pair
an acid and base on each side of an equilibrium equation that are related to each other by difference of a proton
buffer solution
solution that minimises changes in pH when moderate amounts of acid or base are added.
common ion effect
reduction in solubility of a dissolved salt by adding a compound that has an ion in common with the dissolved salt, leading to precipitation
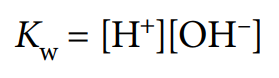
ionic product of water, Kw
equilibrium constant for ionisation of water
partition coefficient
ratio of concentrations of a solute in two different immiscible solvents when an equilibrium has been established
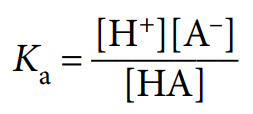
acid dissociation constant, Ka
equilibrium constant for a weak acid
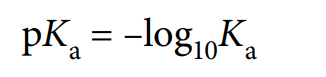
pKa
values of Ka expressed as a logarithm to base 10
pH
hydrogen ion concentration expressed as a logarithm to base 10
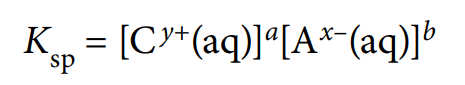
solubility product, Ksp
equilibrium expression showing product of concentrations of each ion in a saturated solution of a sparingly soluble salt at 298K, raised to the power of the relative concentrations
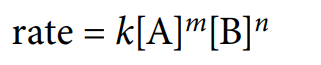
rate equation
equation showing relationship between rate constant and concentrations of those reactions that affect the rate of reaction.
order of reaction
power that the concentration of a reactant is raised in the rate equation.
concentration does not affect rate
zero order
rate is directly proportional to reaction concentration
first order
rate directly proportional to square of reactant concentration
second order
half life
time taken for amount/concentration of limiting reactant to decrease to half its initial value
rate constant
proportionality constant in the rate equation
rate determining step
slowest step in a reaction mechanism
transition element
a d block element that forms one or more stable ions with an incomplete d subshell
degenerate orbitals
atomic orbitals at the same energy level
complex ion/complex
central transition metal ion surrounded by ligands
coordination number
number of coordinate bonds formed by ligands to the central transition metal ion in a complex
ligand
molecule or ion with one or more lone pairs of electrons available to donate to a transition metal ion
stability constant, Kstab
equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex ion in a solvent from its constituent ions
heterogenous catalyst
type of catalyst in a different phase from reactions eg iron in Haber process
homogenous catalyst
type of catalyst in same phase as reactions eg sulfuric acid in formation of ester
racemic mixture
mixture with equal amounts of optical isomer
optical activity
effect of an optical isomers interaction with plane polarized light
polymer
long chain molecule made of many repeating units
polyester
polymers whose monomers are bonded to each other via ester link
stationary phase
immobile phase in chromatography that the mobile phase passes over or through
mobile phase
solvent in chromatography process which moves through the column or over paper
retention time
time taken for component in a mixture to travel through the column in GLC or HPLC
retention factor, Rf value
ratio of the distance a component has travelled compared with distance travelled by the solvent front during paper chromatography
TMS, tetramethylsilane
inert volatile liquid used as a reference in NMR, given a chemical shift of zero