Exam 3: Introduction to Natural Products
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Herbal medicine
Use of roots, stems, leaves, flowers, or seeds of plants to improve health, prevent disease, and treat illnesss
Pharmacognosy
Study of medicinal drugs obtained from plants or other natural sources
Phytotherapy
Study of the use of extracts of natural origin as medicines or health-promoting agents
Dietary supplements
• Vitamins, minerals, herbs and amino acids
• Supplement the diet by increasing intake of concentrates, metabolites, constituents or extracts
• Other terms to describe: nutraceuticals, natural supplements, herbs, botanicals or phytochemicals
Complementary medicine
Natural products used in addition to conventional medicine
Alternative medicine
Use of natural products to replace conventional medicine
DIETARY SUPPLEMENT HEALTH AND EDUCATION ACT OF 1994 (DSHEA)
Defined “dietary supplements” as vitamins, minerals, herbs, botanicals, fatty acids, and amino acids as long as they are prescribed in dosage forms, such as capsules, tablets, liquids, gels or powder
Dietary supplements are used orally to supplement the ________ by increasing dietary intake of ________________, _______________, _______________, and ________________
- diet
- concentrates
- metabolites
- constituents
- extracts
DSHEA allows the FDA to regulate dietary supplements under what act?
the Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition
What does the DSHEA exclude dietary supplements from?
strict purity and potency standards applied to prescription and nonprescription drugs
T/F: Clinical trials are required to prove safety and efficacy of dietary supplements
FALSE
they are not required
Who is responsible for the product's safety and efficacy?
the manufacturer
What must happen for a dietary supplement to be taken off the market?
FDA must prove that a dietary supplement is unsafe
Dietary supplement ingredients sold in the US prior to October 15, 1994 were not required to do what?
manufacturers were not required to submit product for review for safety by FDA
For new ingredient dietary supplements, manufacturers must...
- Notify FDA 75 days in advance of its intent to market the new product
- Provide FDA with evidence that its safe in humans when used as directed
Nutritional Labeling and Education Act (NLEA) of 1990
Allowed for limited health label claims for food and health food supplement for seven categories (no other food or food supplements were allowed to include any disease label)
The 7 categories in the NLEA of 1990 and their diseases
– Calcium- osteoporosis
– Sodium- hypertension
– Saturated fat and cholesterol- heart disease
– Dietary fat- cancer
– Fiber-containing grain products- cancer
– Fruits, vegetables- cancer
– Fiber containing grain products, fruits, vegetables- heart disease
Problems With Health Food Supplement Industry: Many herbals continued to be sold in health food stores and the _____________________ was sometimes on the label
indication
Herbal products had to be sold with no....
information about indication on label
What would happen if the indication appeared on the label?
product was confiscated by the FDA as an unapproved drug
Good Manufacturing Final Rule (cGMP) passed by Congress in 2007
- What does it require?
- Dietary supplements must be manufactured without what?
- What must they do?
- What must be evaluated?
Requires manufacturers of dietary supplements to assume responsibility for premarket product safety
- Dietary supplements must be manufactured without adulterants or impurities
- Must be labeled accurately
- Raw materials must be evaluated by the manufacturer
FDA is responsible for regulating the claims found on........
packaging, package inserts, and promotional materials distributed at the point-of-sale
What must plant-based dietary supplements indicate?
the plant's scientific name and specific plant part used on the label
Combo of DS can be labeled as....
proprietary blend
- Ingredients listed (not the quantity in order) by predominance and total weight
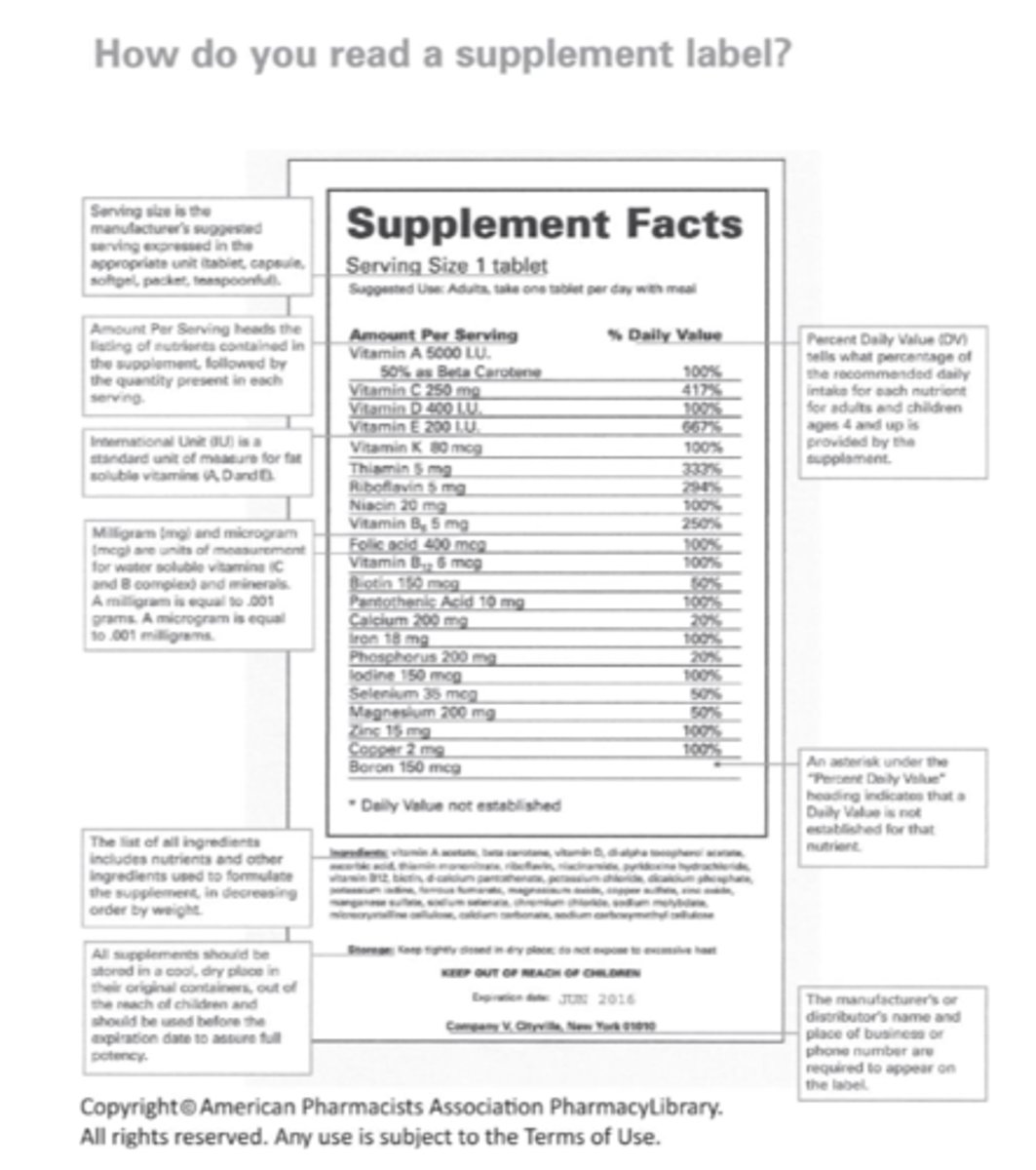
Labeling Requirements For Supplements (8)
- Product name
- Net quantity of contents
- Serving size (dose)
- Ingredients list
- Supplements fact box
- Directions
- Name and address of manufacturer
- Allows "structure and function claims"
- Plant name and part use (if botanical)
"How do you read a supplement label?" diagram
The 3 types of dietary supplement claims
- Health claims
- Nutrient content claims
- Structure-function claims
What must be included in the structure-function claims?
the disclaimer, "This statement has not been evaluated by the FDA. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent disease."
- must notify FDA within 30 days of these claims
Health Claims
- What do they require?
- What does it describe?
- Example:
- requires FDA approval
- describes relationship between a food, food component, or dietary supplement ingredient and resulting reduction in risk of a disease or health-related condition
- Ex: "daily ingestion of 25g of soy reduces risk of CHD"
Nutrient Claims
- What do they require?
- What does it describe?
- Example:
- requires FDA approval
- describes the relative amount of a nutrient or DS in a product
- Ex: "very low sodium"- product must have 35 mg or less of sodium per reference amount
T/F: Dietary supplements can be labeled as drugs for treatment, prevention, or diagnosis of a disease
FALSE
cannot be
DSHEA allows _______________ and ____________ claims on dietary supplements
structure and function
- how supplement affects the structure and function of the body without specifying a disease state
- Ex: prevent cholesterol buildup; promotes regularity
- Cannot use: prevents heart disease; prevents colon cancer
DS and Nonprescription Consumer Protection Act of 2006
Manufacturers, packers and distributors of DS must report serious adverse events based on information from the public
DS and Nonprescription Consumer Protection Act of 2006 serious adverse events include: (7)
- Death
- Life-threatening situation
- Hospitalization
- Persistent or significant disability or incapacity
- Birth defect
- AE that requires medical or surgical intervention to prevent serious outcomes
- Consumers can report AE to FDA MedWatch
Misbranding: Manufacturers are not allowed to make claims that product will....
diagnose, cure, mitigate, treat, or prevent disease
Misbranding occurs when the manufacturer fails to... (3)
- follow labeling requirements
- include name or place of manufacturer, packer, or distributer on label
- include accurate statements regarding quantity of the contents
Adulteration occurs when
- When used as suggested, can cause a significant or unreasonable risk of illness or injury
- Is new entity and lacks evidence to ensure safety of use
- Has been declared an imminent hazard by the DHHS secretary
- Contains a dietary ingredient in an amount that makes the product poisonous or harmful
- Are intentional or nonintentional, ex: pollution from the envrion. contaminates soil that plant grows in. manufacturer substitutes a different DS for an ingredient that is in short supply or too expensive
Quality Assurance Programs
- Voluntary or involuntary
- manufacturers pay to have their products what?
- How many batches at a time?
- Is safety and efficacy guaranteed?
- Indicates whether the DS product content match the...
- voluntary
- manufacturers pay to have their products tested
- only single batches tested at a time, safety and efficacy not guaranteed
- indicate whether the DS product contents match the label contents

When counseling on DS, respect each person's ___________ and __________ to create a trusting, nonjudgmental relationship with pt
beliefs and values
Explain the risks vs. benefits
- Not enough evidence or evidence is conflicting regarding the use of the product
- Potential to cause adverse effects
- Educate the patient on the time frame to see benefit and what side effects to looks for
- When counseling, advise them to purchase products with a ________________.
- Avoid giving to ______________, taking while _______________ or ______________
- Inform providers of all ______________, especially for interactions
- seal of quality
- children
- pregnant or breastfeeding
- DS taking
Multivitamins are essential in providing....
good health and are necessary for many life functions
T/F: Everyone needs a multivitamin dietary supplement
FALSE
not everyone
Nutritional supplements should be ________________ to a balanced diet
adjuncts
NIH has concluded there is insufficient evidence to support routine use of MVMMs for.....
primary prevention of chronic disease
What was the Dietary Reference Intakes (ORIs) established by?
the National Academies of Science, Engineering and Medicine
Dietary Reference Intakes (ORIs)
Nutrient reference standards
- Set of reference standards
- Values vary based of stage (age) and sex
- Development after an assessment of nutrient in take in health people
Terms for Reference Standards: Recommended dietary allowance (RDA)
Average daily level of intake sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of nearly all (97%-98%) healthy people
Terms for Reference Standards: Adequate Intake (AI)
Established when evidence is insufficient to develop an RDA and is set at a level assumed to ensure nutritional adequacy
Terms for Reference Standards: Tolerable upper intake level (UI)
Maximum amount of daily vitamins and minerals that can besafely take without risk of an overdose or serious side effects
Terms for Reference Standards: Chronic disease risk reduction intake
New reference standard - related to amount which reduces risk of chronic disease
- has only been established for sodium
Types of water soluble vitamins (10)
• B vitamins
• Folic acid
• Thiamine
• Riboflavin
• Niacin
• Pantothenic acid
• Biotin
• Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
• vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin)
• Vitamin C
Types of fat soluble vitamins (4)
• Vitamin A
• Vitamin D
• Vitamin E
• Vitamin K
Calcium
- most abundant mineral in the body
- 99% is stored in the skeleton as calcium-hydroxyapatite
What is the function of calcium? (6)
- Acetylcholine synthesis
- Enzyme activation
- Cell membrane permeability
- Muscle contraction/relaxation
- Clotting cascade
- Nerve transmission
Calcium is absorbed by both ______________ and ______________ across intestinal mucosa
- active transport and passive diffusion
Sources of calcium
- dairy products
- clams
- oysters
- sardines
- turnip
- mustard greens
Recommendations for intake of calcium is based on _________________, not _________________
- elemental calcium
- calcium salt
Calcium carbonate (40% elemental calcium)
• Must be taken with food to enhance absorption
• Individuals with low levels of stomach acid have low absorption
• Inexpensive
Calcium citrate (21% elemental calcium)
May be taken with or without food
Absorption of calcium is highest in doses ≤ ________
≤ 500 mg
For example, 1,250 mg of calcium carbonate contains how many mg of elemental calcium (40%)?
1250/100 = X/40 = 500 mg
or
1250 x 0.4= 500 mg
How many mg of calcium citrate (21%) =1000 mg of elemental calcium?
1000 mg/21% = x/100% = 4761.9 mg
Calcium for groups at risk for inadequate intake: (6)
- Postmenopausal women due to age-related bone loss
- Lactose intolerant or allergy to cow's milk
- Individuals who avoid dairy products
- Vegans
- Pregnancy/Lactation
- Same as nonpregnant or nonlactating
Age and recommended Intake (elemental)
0 to <6 months (adequate):
6-12 months (adequate):
1-3 years (RDA):
4-8 years:
9-18 years:
19-50 years:
51-70 years:
>70 years:
0 to <6 months (adequate): 200
6-12 months (adequate): 260
1-3 years (RDA): 700
4-8 years: 1000
9-18 years: 1300
19-50 years: 1000
51-70 years: women: 1200, men: 1000
>70 years: 1200
Calcium toxicity (5)
• Bloating, gasconstipation (carbonate) when taken in doses >500mg
• Hypercalcemia
• Renal stones → renal damage
• CV disease in high doses
Calcium drug interactions
• Fluoroquinolones, tetracycline, and dolutegravir
• Chelation calcium and reduces absorption
• Levothyroxine- interferes with calcium absorption
Vitamin D
a fat-soluble vitamin that is primarily responsible for the maintenance of calcium and phosphorus homeostasis, which is important for bone health
Cholecalciferol (vitamin D3)
Naturally occurring; synthesized in skin on exposureUV light (sunlight)
Ergocalciferol (vitamin D2)
- Food additive
- Is slightly structurally different from vitamin D3
What do both forms of Vitamin D undergo for activation?
hydroxylation
- Liver: vitamin D 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D]
- Kidney: vitamin D1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D] = calcitriol
Calcitriol- is it inactive or active?
is physiologically active
What can cause Vitamin D deficiency?
Either liver or kidney disease can cause vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D functions (5)
- Bone and mineral homeostasis
- Serum calcium homeostasis
- Parathyroid activity
- Modulation of cell growth
- Immune function
What can Vitamin D deficiency (hypocalcemia) lead to? (5)
- Rickets
- Osteoporosis
- Cancer
- Broad spectrum sunscreen
- Long term use of anticonvulsants (phenytoin, phenobarbital)
What is Vitamin D measured in?
What is the conversion?
- mcg and IU
- 1 mcg=40 IU
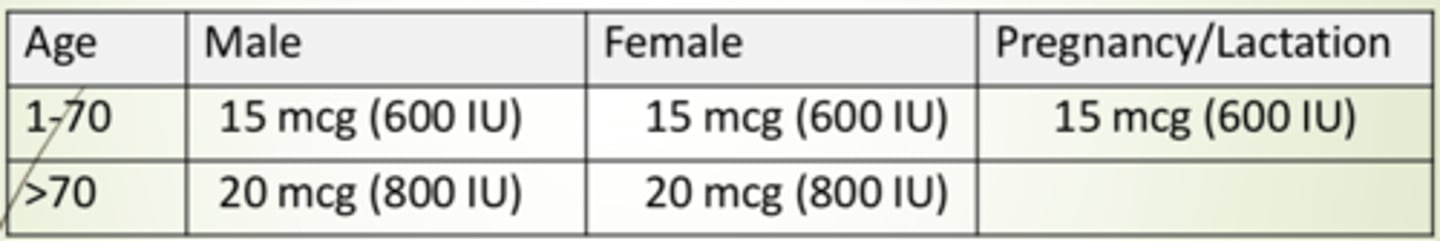
Recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for Vitamin D in males and females from ages 1-70 and >70
Male and female age 1-70: 15 mcg (600 IU)
Male and female age >70: 20 mcg (800 IU)
Pregnancy/Lactation: 15 mcg (600 IU)
Groups at increased risk of vitamin D deficiency (7)
• Breastfed infants
• Older adults
• People with limited sun exposure
• People with dark skin
• People with fat malabsorption
• Chronic renal failure
• Liver disease
Sources of Vitamin D (4)
- Milk
- Fatty fish
- Egg yolk
- Sun exposure
What can Vitamin D lead to? (toxicities) (5)
- Anorexia
- Hypercalcemia
- Soft tissue calcification
- Kidney stones
- Renal failure
Normal serum 25 (OH)D vitamin D value
30-125 nmol/L (12-50 ng/mL)
Calcium/Vitamin D - Questionable Benefit: Meta-analysis found that calcium, vitamin D, and combined calcium/vitamin D supplements failed to...
improve the risks for hip and other fractures among community-dwelling older adults
- suggest that it does not protect against CVD
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
water-soluble vitamin required for the biosynthesis of collagen, L-carnitine, certain neurotransmitters, and is involved in protein metabolism
Functions of Vitamin C (5)
- Antioxidant
- Collagen formation
- Wound healing
- Bone health
- Iron absorption
Sources of Vitamin C (6)
- Green and red peppers
- Broccoli
- Spinach
- Tomatoes
- Strawberries
- Citrus fruit
Persons at risk for deficiency of Vitamin C (4)
some individuals are unable to synthesize vitamin C
- Smokers and passive smoker - due to oxidative stress
- Infants fed with artificial formulas
- Individuals with limited food variety
- Malabsorption
What does Vitamin C deficiency result in? With less than what amount/day?
results in scurvy with < 10 mg/day
Signs and symptoms of Vitamin C deficiency (6)
- Fatigue
- Malaise/depression
- Inflammation/bleeding of the gums
- Loss of teeth
- Connective tissue disorders
- Iron deficiency anemia
What can happen with toxicity with an excess amount of vitamin c? (4)
- diarrhea
- nausea
- cramps
- kidney stones
Vitamin C and colds: Doses up to ___________________________ seem to prevent colds in general population
3 g/day do not seem to prevent
- RCT do not show a consistent effect of vitamin C on the duration or severity of cold symptoms
Vitamin C may prevent colds in individuals undergoing....
extreme exercise and in cold environments
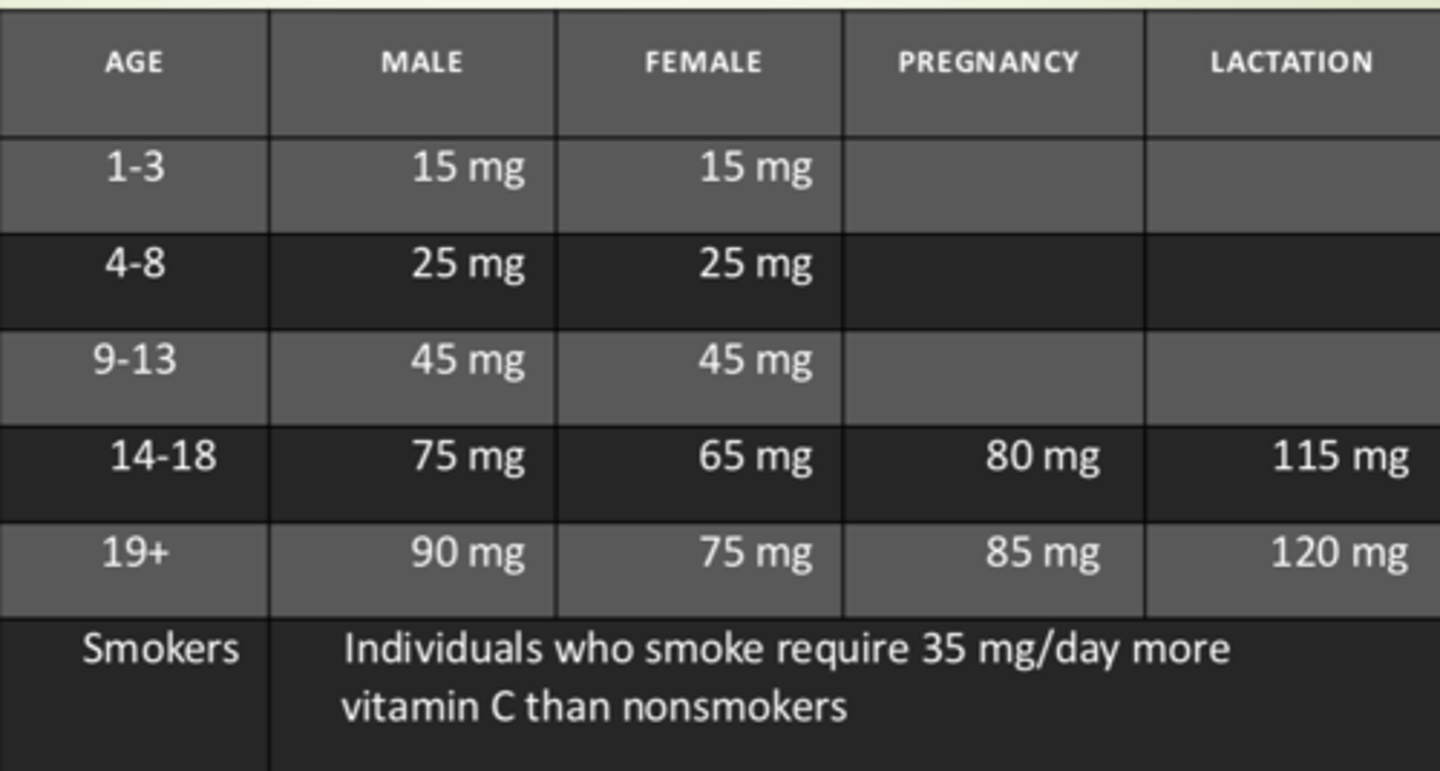
Recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for Vitamin C
- Males and females ages 1-3: 15 mg
- Males and females ages 4-8: 25 mg
- Males and females ages 9-13: 45 mg
- Males ages 14-18: 75 mg
- Females ages 14-18: 65 mg
- Pregnancy in ages 14-18: 80 mg
- Lactaction in ages 14-18: 115 mg
- Males ages 19+: 90 mg
- Females ages 19+: 75 mg
- Pregnancy ages 19+: 85 mg
- Lactaction ages 19+: 120 mg
Vitamin E
- an essential fat-soluble vitamin
- known as tocopherols andtocotrienols
- generally safe when used orally or topically and appropriately even at doses exceeding RDA; adverse effects more likely to occur with higher doses
Vitamin E functions (4)
- Antioxidant
- Protects cell membranes from oxidative damage
- Enhances immune response
- Regulates protein kinase C activation
- Regulates platelet aggregation by inhibiting platelet cyclooxygenase activity and decreases prostaglandin production
Vitamin E supplements are derived from plant oils containing _________________, which is believed to be the active form.
- d-alpha-tocopherol
- naturally occurring d-alpha-tocopherol has the highest biological activity
What are synthetic vitamin E supplements a mixture of?
Synthetic vitamin E supplements are a mixture of d-alpha-tocopherol and l-alpha-tocopherol (inactive forms)
Sources of vitamin E
- Corn, cottonseed, and peanut oil
- Almonds, hazelnuts, sunflower seeds, walnuts, and margarine
- Whole grains
- Spinach, lettuce, onions, blackberries, apples, and pears
Susceptible groups to Vitamin E deficiency
- pts with malabsorption syndromes
- premature infants due to inadequate body stores, impaired absorption, reduced transport capacity in blood due to low LDL levels
- patients on TPN
Vitamin E deficiency is characterized by....
progressive neurological syndrome
- Gait disturbances
- Absent or altered reflexes
- Limb weakness
- Sensory loss in arms and legs
- Improved neurological function with vitamin E therapy
Doses of Vitamin E
The tolerable upper intake level (UL) in healthy people is 1000 mg daily
- Equivalent to 1100 IU of synthetic vitamin E (all-rac-alpha-tocopherol
- Equivalent to 1500 IU of natural vitamin E (RRR-alpha- tocopherol)