module 8 rigid object rotations
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
s =
r∆θ, where r is the radius, ∆θ is angular displacement, and s is the translational displacement
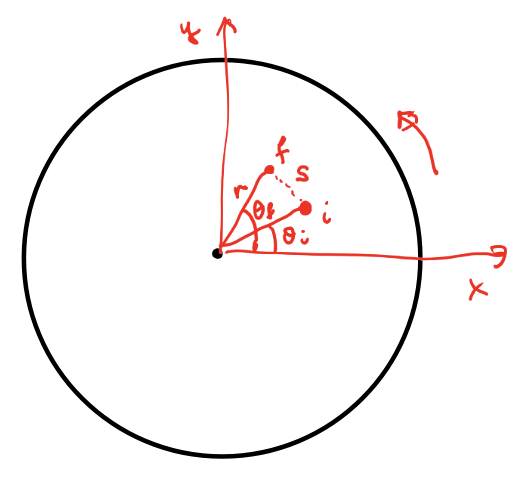
average angular speed
ωavg = ∆θ/∆t , in units of sec-1
angular acceleration
α , in units of sec-2
angular velocity vector points
in direction of cross product (curl fingers in direction of rotation
x, v, and a for translational motion correspond to
theta, omega, and alpha for rotation = same kinematics equations
Vp moving along s =
rω
rotational radial acceleration =
rω2
rotational tangential acceleration =
rα
total rotational acceleration =
√(rα)² + (rω²)²
moment of inertia
I = Σ (i) (miri²) ; plays role of mass
rotational kinetic energy
½ Iω²
integral for moment of inertia
∫r²dm , where dm is usually density * dV
moment of inertia for a rigid rod about its centre
I = ML²/12
moment of inertia for a solid cylinder about its axis that makes sense
I = ½ MR²
parallel axis theorem
moment of inertia around a parallel axis = Icm + MD² -
D is distance to the axis
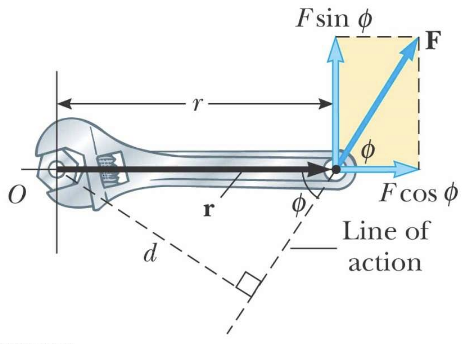
torque
τ (tau), analogue of force
τ =
rFsinφ = r x f (cross product) = Fd (d is perpendicular to the line of action)
net torque on a cylinder
T2R2 - T1R1
torque (second law application) =
Iα
rotational work =
τ • Δθ
rotational power =
rotational work/time or τ • ω
net work done by torque =
change in rotational KE
acceleration of a rolling object
Rα
kinetic energy of a rolling object
½ Icm ω² + ½ mvcm²
object rolling down an incline vcm =
√2gh/1 + k ; where k is involved in I = kmR²