Nervous System - grade 12
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
The reflex arc
-Happens in less than a
second - information has
not even travelled to the
brain
.-When it does, the sensation of
pain will become noticeable and you
may scream!
-If you had to wait to feel the pain first - the burn
would be a lot
worse
.
What do the somatic nerves consist of (PNS)
1. To/from skeletal muscle,
bones and skin
2.sensory and motor somatic nerves
What are the divisions the vertebrate nervous system
1. Central Nervous DIVISIONS of the Vertebrate
Nervous System
2. Peripheral Nervous System
(PNS)
What composes the CNS?
1.nerves, brain, spinal cord
2.coordinating centre
What composes the Peripheral Nervous System
(PNS)
1.Somatic Nerves
2.Autonomic Nerves
autonomic nervous system (PNS)
special motor nerves that
control the internal organs
sympathetic nervous system
and parasympathetic nervous system
What do the nervous system cells consist of
Neurons - cells that conduct nerve impulses
(functional unit).
Nerve: is a bundle of many neurons
Glial cells (neuroglial cells):structural
support and metabolism of nerve cells (
do not conduct)
Neuron Anatomy -Diagram
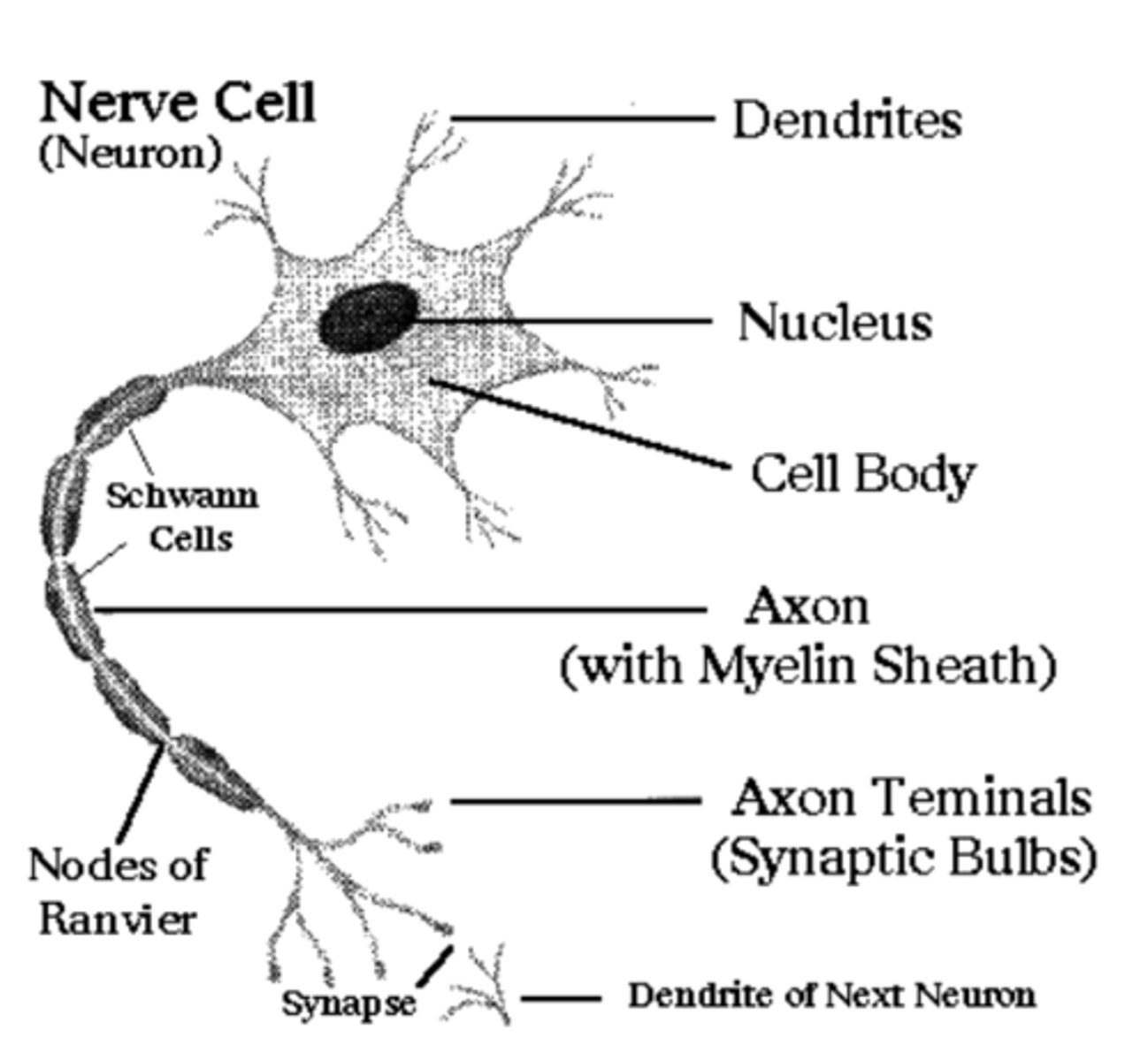
Neuron Anatomy: Cell Body
Nucleus and majority of cytoplasm
Neuron Anatomy: Dendrites
projections of cytoplasm that
carry impulses TOWARD the
cell body
Neuron Anatomy: Axon
extension of cytoplasm that carries
nerve impulses AWAY from the cell body
Neuron Anotomy -Myelin Sheath
Insulated covering (fatty protein)
over the axon of some nerves,
"myelinated" prevents loss of charge
Neuron Anotomy -Schwann cells
type of glial cell that produces myelin sheath
Neuron Anotomy - nodes of Ranvier
regularly occurring gaps between
sections of the myelin sheath
nerve impulses " jump " from one node to another -increases speed of the impulse
axon diameter also effects speed;narrower
= faster.
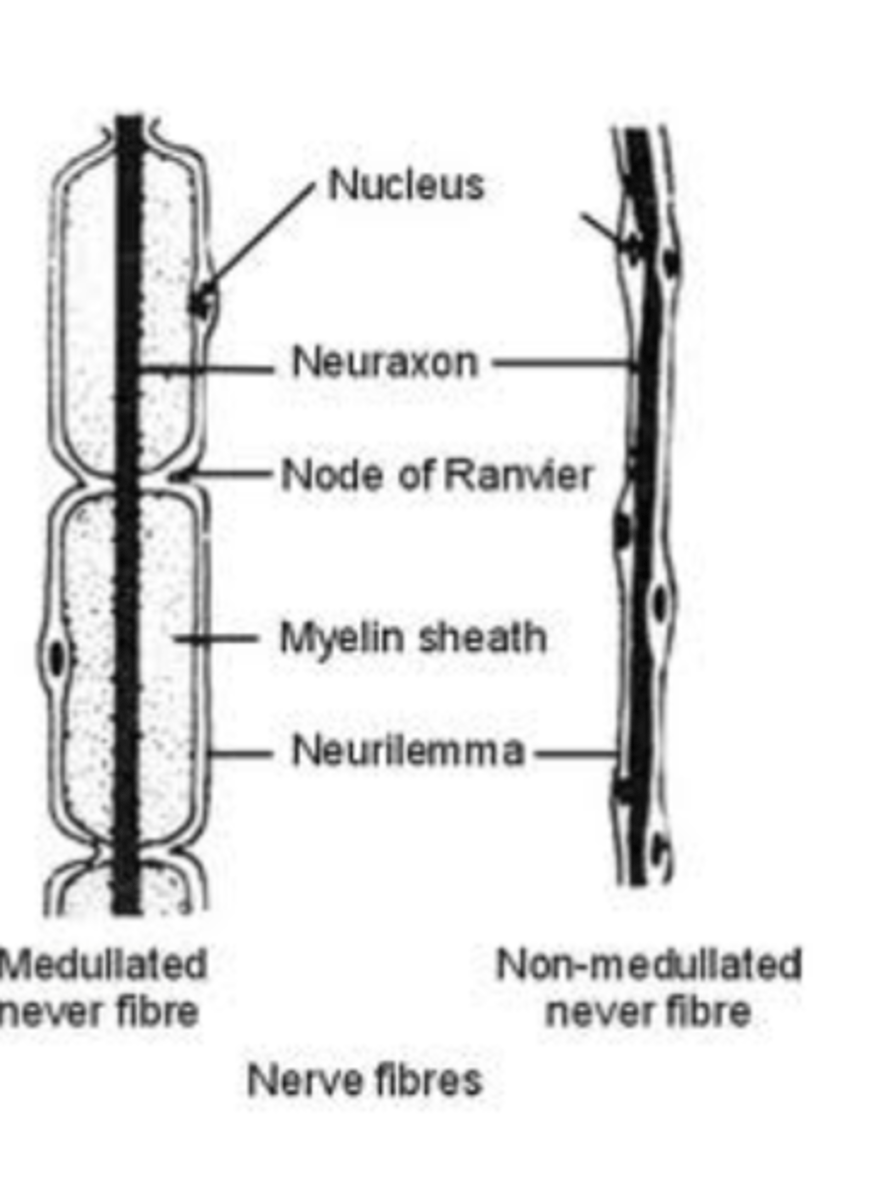
Neuron Anatomy: Neurilema
PNS axons (myelinated or unmyelinated)
have a thin membrane surrounding the axon.
Promotes regeneration of damaged axons
Which nervous system can regenerate
The PNS has greater ability to
regenerate than the CNS (spinal cord injuries).
Neurons without myelin sheath or neurilemma do
not regenerate,damage is permanent
. (“greymatter” in brain and spinal cord; white matter has myelin sheath).
Presence of a growth inhibitor in the CNS. Scientists
are looking for ways around this (stem cells
Types of Neurons: Sensory
Sensory Neurons: (afferent neurons)
carry impulses from sensory receptors to
the CNS
Sensory receptors examples:
photoreceptors in eyes (light),
chemoreceptors in nose and skin
(chemicals),thermoreceptors in skin,
hypothalamus (heat/cold).
Types of Neurons -Ganglion
Ganglia -(singular - ganglion):clusters
of sensory nerve cell bodies located
outside of the CNS.
Types of Neurons - Motor Neurons
(efferent neurons)
carry impulses from the CNS to effectors
(muscles, organs,glands...i.e. Things that
produce a response)
Type of Neurons: Interneron
link neurons within the body (found mostly
in the CNS ).
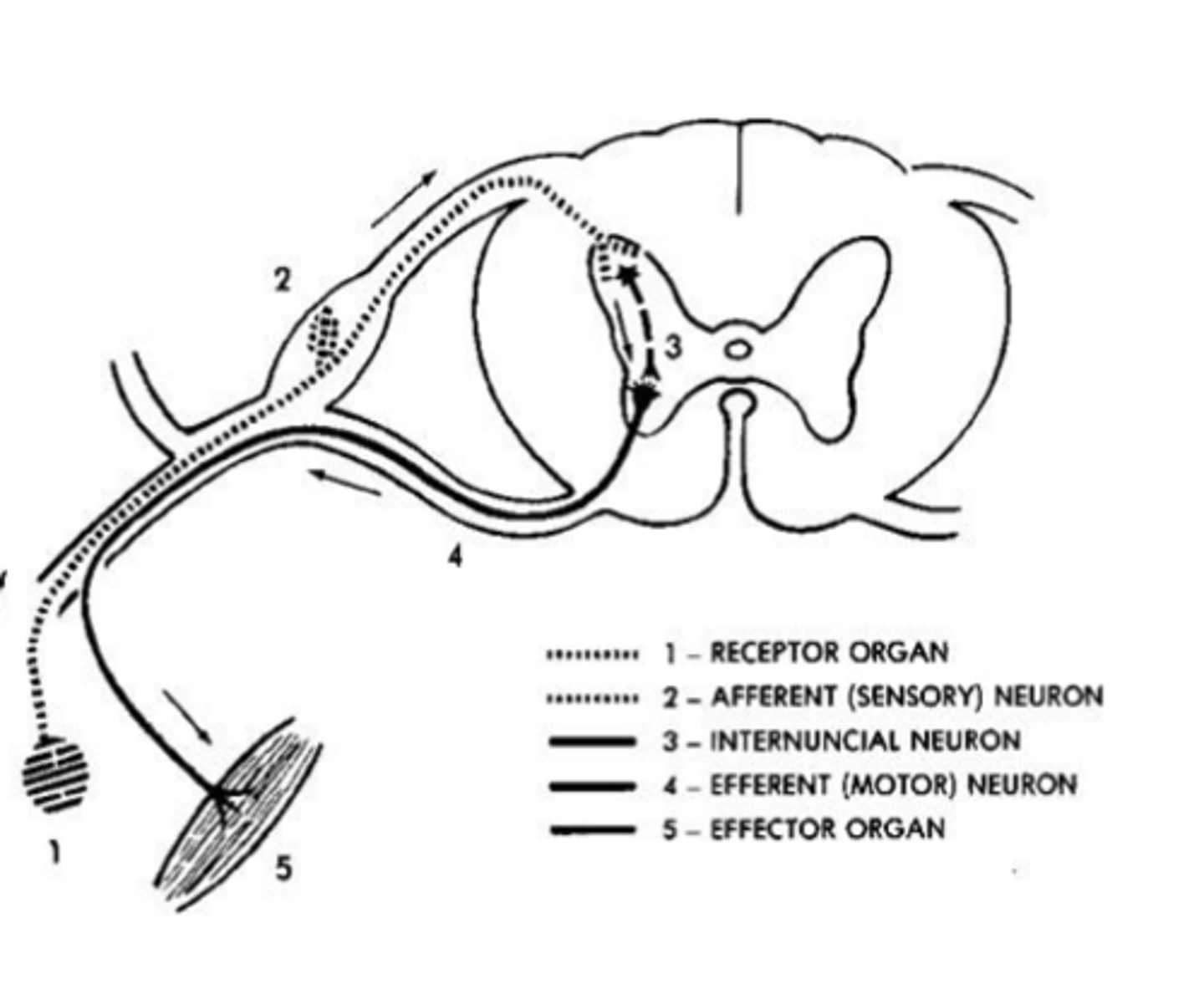
THE REFLEX ARC
-Neural circuit through the spinal cord
that provides a framework for a
reflex action.
-Simplest nerve pathway.
Involuntary,unconscious
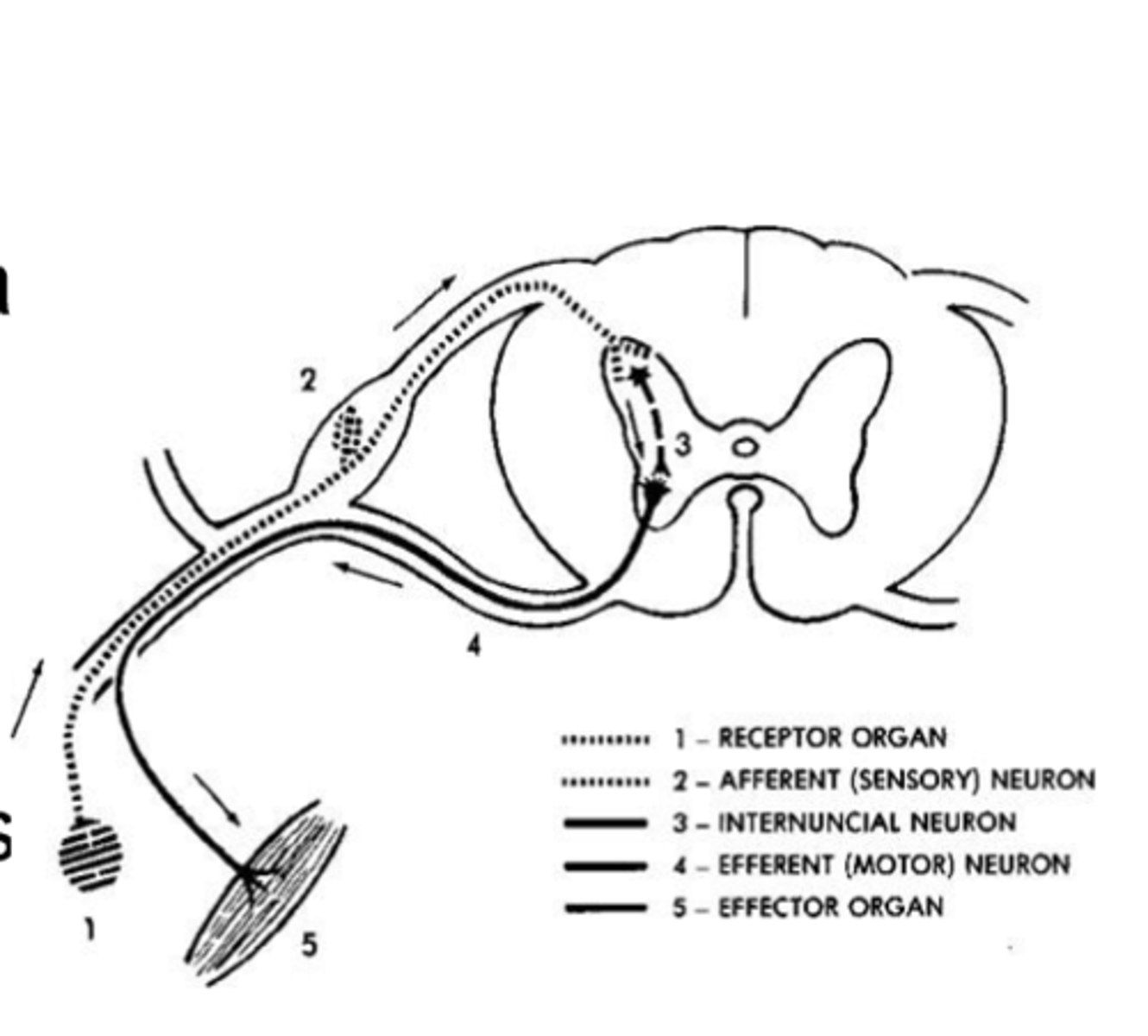
Ex. Accidentally touching a hot
stove
Heat detected by thermoreceptors
in skin
2.nerve impulse carried by a sensory
neuron to the spinal cord
3.interneuron in spinal cord passes the impulse to a
motor neuron
4.motor neuron carries impulse to
muscles in arm /hand
5.causes the muscles to contract
and pull hand away