GE - STS NUCLEAR ENERGY SUMMATIVE
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Nucleons
particles found in the nucleus of an atom
o neutrons
o protons
Atomic Number (Z)
number of protons in the nucleus
Mass Number (A)
sum of the number of protons and neutrons
Isotopes
atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers
Nuclide
each unique atom
There are two main types of isotopes
stable and
unstable (radioactive)
254
There are _______ known stable isotopes
radioisotopes
All artificial (lab-made) isotopes are unstable and therefore radioactive; scientists call them _______.
unstable
Some elements can only exist in an _______ form (for example, uranium)
hydrogen
is the only element whose isotopes have unique names: deuterium for hydrogen with one neutron and tritium for hydrogen with two neutrons
radioactive decay
This is called _______since the original nucleus is "decaying" into a more stable one.
Radioactivity
– the spontaneous decomposition of a nucleus forming a different nucleus and producing one or more additional particles
Nuclear Equation
shows the radioactive decomposition of an element
Nuclear Forces
strong nuclear force holds neutrons and protons together to form a nucleus (counters electromagnetic repulsion).
Weak nuclear force
operates within individual nucleons and gives rise to some kinds of radioactivity.
Alpha particle production
Beta Particle production
TYPES OF RADIOACTIVE DECAY
Alpha particle
helium nucleus
Beta particle
electron
ALPHA-PARTICLE PRODUCTION
From what production is this example:
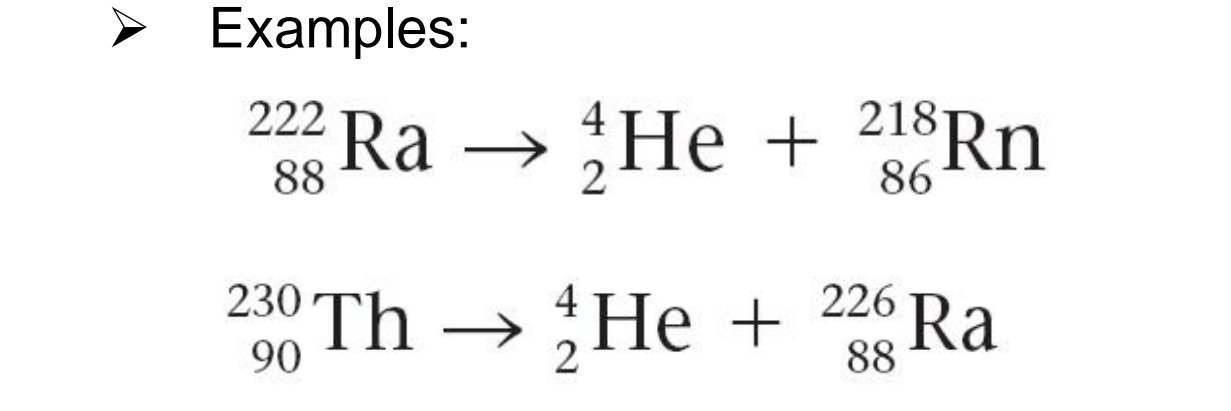
Alpha particle production
Net effect is a loss of 4 in mass number and a loss of 2 in atomic number.
BETA-PARTICLE PRODUCTION
Net effect is to change a neutron to a proton.
BETA-PARTICLE PRODUCTION
From what production is this example:
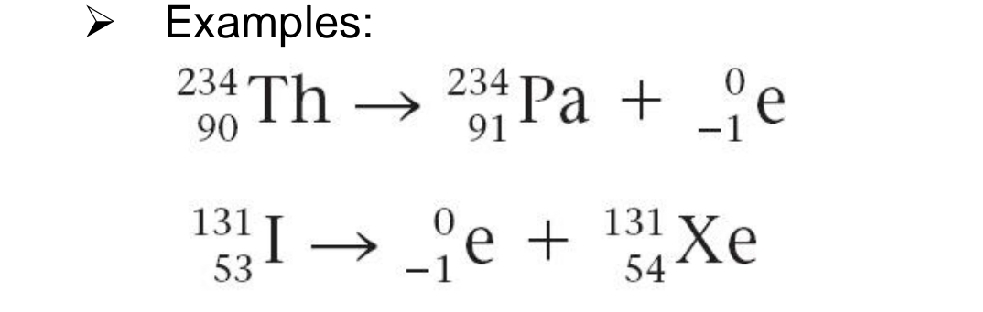
half-life, 50%
_______ is the amount of time it takes for half of the atoms in a sample of a radioactive substance to decay. During each half-life, the substance loses _____ of its remaining radioactive atoms, transforming them into a more stable form, often a different element or isotope.
Exist in an insoluble form
Exist in a form such that it presents no or minimal
chemical toxicity
Have relatively low neutron, beta and gamma
radiation emissions
Be stable at high temperatures
Have a long enough half-life (at least 15 to 100
years)
Have a high-power density
To be suitable for space missions, a radioisotope must meet all of the following criteria:
plutonium-238, 88 years
The only radioisotope that has consistently met the basic criteria is _____, which has a half-life of ______
Aircraft and space emissions
operate through a combination of advanced engineering, physics, computer systems, and human planning.
Nuclear-powered submarines
Nuclear-powered Deep Sea Technologies
HOW IS IT POSSIBLE FOR DEEP-SEA TECHNOLOGIES TO OPERATE?
CARBON DATING
HOW DO WE KNOW THE ”AGES” OF THE CARCASS/REMAINS?
Carbon-14
a naturally occurring isotope produced in the atmosphere, undergoes beta decay with a halflife of about 5,730 years
is a radioactive isotope of carbon, created naturally in the atmosphere
organic materials (like bone or wood)
Scientists measure the amount of carbon-14 in __________to determine the age of archaeological and geological samples.
decay (beta)
When an organism dies, it no longer takes in carbon. The carbon-14 it contains starts to ______
phosphorus- 32 and strontium-89
RADIOTHERAPY FOR CANCER TREATMENT
Beta-minus emitting isotopes, such as _______and ______ are used in radiotherapy to target cancer cells.
These isotopes emit beta particles (electrons) that can damage and destroy cancerous tissue with minimal impact on surrounding healthy tissue.
Radionuclide therapy (RNT) - lutetium-177 or yttrium-90
is attached to a molecule and ingested. Once inside the body, this molecule travels to the cancer cells.
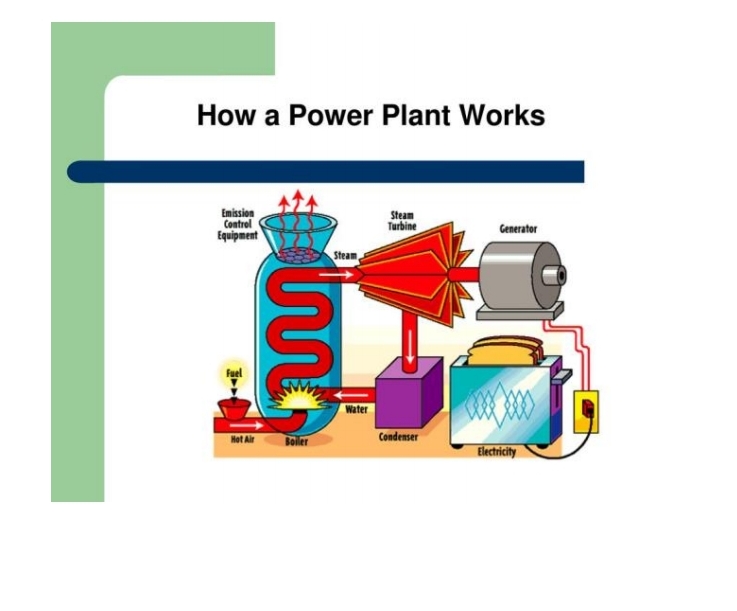
PROCESS OF HOW A POWER PLANT WORKS
involves converting the energy stored in fuels into electrical energy through combustion or nuclear reactions, which then drives turbines connected to generators.
FISSION AND FUSION
NUCLEAR ENERGY CAN BE OBTAINED IN TWO WAYS
FISSION
➢ Splitting atoms
➢ Get energy if the nucleus is big.
➢ The smaller ones are more stable.
➢ What we do in nuclear reactors.
FUSION
➢ Joining atoms
➢ Get energy if the nuclei are small.
➢ The larger one is more stable.
➢ This is how the sun works
Nuclear fission
is the process of splitting a nucleus into two nuclei with smaller masses.
A very heavy nucleus splits into more stable
nuclei of intermediate mass.
a large nucleus is bombarded with a small
particle.
Chain Reaction
➢ when a critical mass of uranium undergoes fission.
➢ releasing a large amount of heat and energy that produces an atomic explosion.
➢ _________is an ongoing series of fission reactions. Billions of reactions occur each second in a chain reaction.
Nuclear power plants
➢ fission is used to produce energy.
➢ control rods in the reactor absorb neutrons to slow and control the chain reactions of fission
Manhattan project
➢ The __________ not only helped bring an end to World War II, but it also advanced the knowledge of the atomic age and determined how future wars would be fought.
➢ This was a project to develop the first atomic bomb during World War II.
➢ The project involved roughly 600,000 people and cost more than $2 billion, yet it remained top secret throughout WWII.
➢ ____________was a code name to keep the project concealed.
➢ Project research and productions sites took place all across the United States.
Albert Einstein
In 1939, _________wrote a letter to President Franklin Roosevelt warning that Germany was secretly trying to develop an atomic bomb and urged U.S to do likewise.
Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
This EINSTEIN’S LETTER led to the establishment of the Manhattan Project, the U.S. program that eventually developed the atomic bombs dropped on __________________.
J. ROBERT OPPENHEIMER
He eagerly joined the project at Lawrence's Radiation Laboratory at Berkeley.
➢ In June 1942 he was appointed the scientific director of the Project.
➢ He managed over 3,000 people and is often referred as the “father” of the atomic bomb
ENRICO FERMI
➢ Born in Italy, Fermi created a nuclear fission chain reaction, which was critical to creating the atomic bomb.
➢ In 1944, he joined the Manhattan Project and was the overseer of the scientists.
➢ The uranium “Little Boy” bomb was dropped on Hiroshima on August 6, 1945.
➢ The plutonium “Fat Man” bomb was dropped on Nagasaki on August 9, 1945.
WHAT ARE THE TWO BOMBS CREATED
It was finally decided to use the atomic bomb in the war and two more atomic bombs were created by the project.
atomic bomb
President Harry Truman’s decision to drop the _______ is one of the most controversial issues in American History
It helped bring an end to World War II.
nuclear fission
So, atomic bombs are a kind of nuclear bomb that only utilize _______
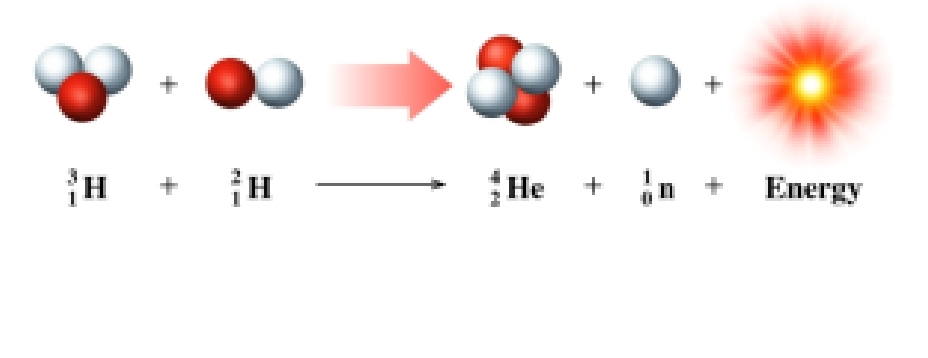
Fusion
➢ Light-mass nuclei combine to form a heavier, more stable nucleus.
➢ More energetic than fission reactions
➢ Source of energy for the H-bomb
➢ Origin of the elements
➢small nuclei form a larger nuclide, release energy
NUCLEAR FUSION
➢ occurs at extremely high temperatures (100 000 000°C).
➢ combines small nuclei into larger nuclei.
➢ releases large amounts of energy.
➢ occurs continuously in the sun and stars.
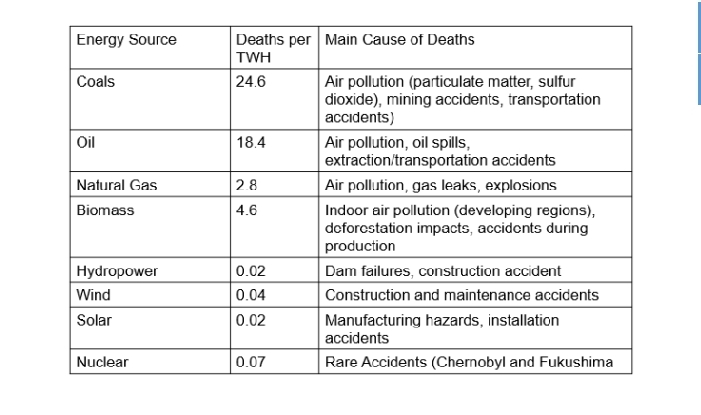
deaths per terawatt-hour (TWh) of energy produced
The number of deaths caused by different energy sources for electricity generation is often expressed in terms of _______________
Familiarize lng na uy🫰