NURS205 Midterm
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
what is med surg nursing?
looking after people who have had surgery and help them go home, acute care typically, any nursing setting, diverse pt population
what is critical thinking?
process used to examine and analyze patient issues at point of care.
identifying a change in patient status and taking into account the context and concerns of the patient and deciding what to do about it
what is evidence-informed practice?
continuous interactive process involving the explicit, conscientious and judicious consideration of best available evidence to provide care
improves patient outcomes
best possible evidence: systematic or integrative reviews
translate to clinical practice guidelines
what is a clinical practice guideline?
single conclusion about state of science based on summaries of the literature
ex. registered nurses association of ontario
what should you consider during clinical decision making?
your clinical expertise, patient’s preferences or values and what the evidence tells you; research, clinical findings
what does clinical expertise entail?
clinical state, setting & circumstance
patient preferences and actions
health care resources
research evidence
what is the nursing process?
way of thinking that nurses use
what nurses do when planning and providing care
problem solving approach
basic framework that uses unique combination of knowledge, skills, and caring that makes the art & science of nursing
what are the 5 parts of the nursing process?
assessment
diagnosis
planning: outcomes and interventions
implementation
evaluation
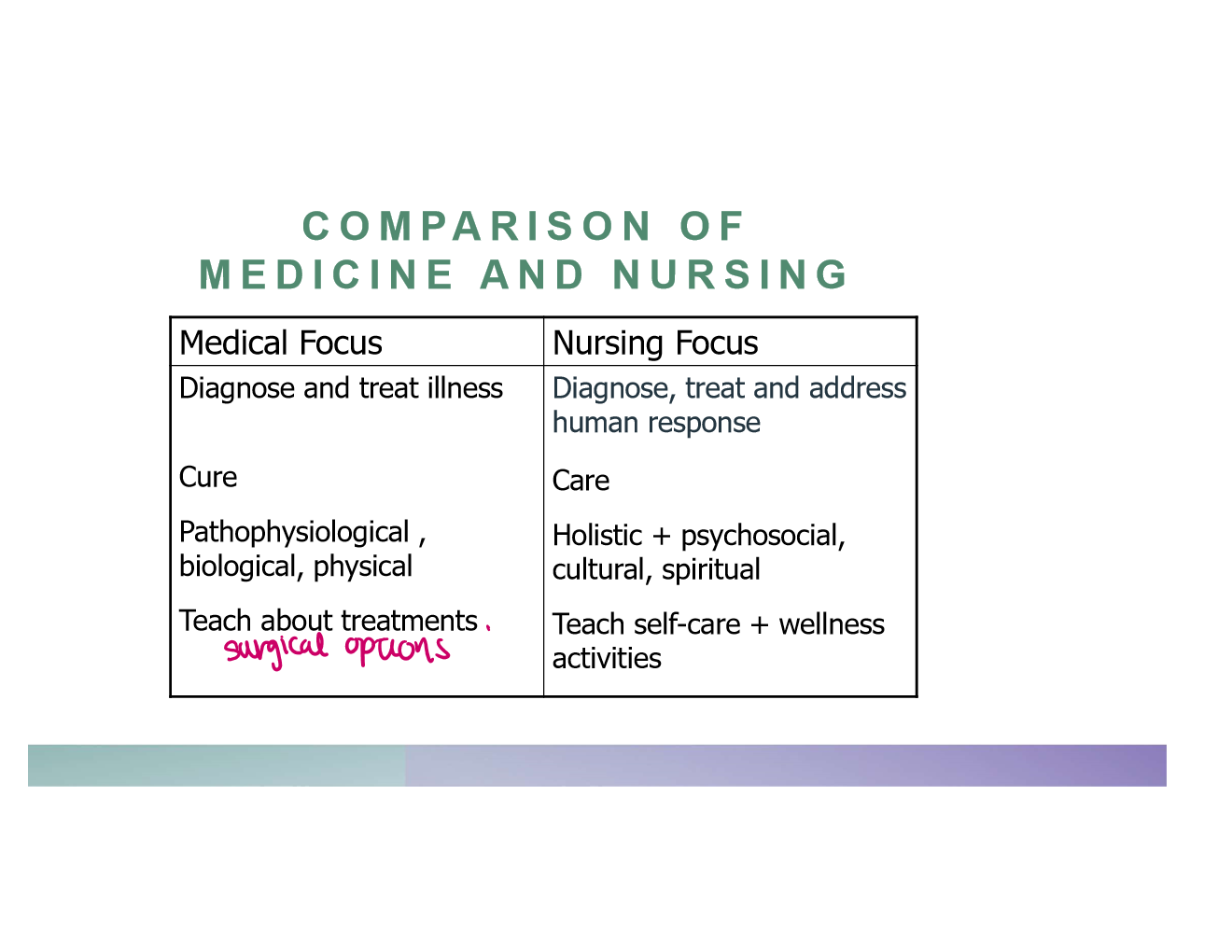
what are the comparisons between medicine and nursing?
what are human responses?
reactions to events or stressors like disease, injury, or life changes
can be actual or potential health problems
what are the 4 types of human responses?
biological
psychological
social
spiritual
what does phase 1 of assessment include?
systematic gathering of relevant and important data on patient’s present health status
uses date to identify health problems, plan nursing care, evaluate patient outcomes
how do we collect data
interview
observation
physical examination
collateral information; patient chart, other nurses or HCPs
how do we validate data?
ensure assessment is complete, accurate and factual before making a diagnosis
eliminate own biases and misconceptions of data
avoid jumping to faulty conclusions about data
what does diagnosis include?
sorting, clustering analyzing data to identify patient’s present health status
writing precise statement to describe patient status and contributing factors
prioritize the diagnoses
decide which diagnoses will respond to nursing care and which must be referred to another healthcare professional
what is the format for writing diagnostic statements?
problem (p) related to/caused by etiology as evidenced by/resulting in signs & symptoms
ex. pain related to surgical incision as evidenced by swelling, pt immobility
how do we plan outcomes?
identify goals that are patient-centered and mutually set if feasible
important to identify short and long-term goals
smart criteria
how do we plan interventions?
identify independent and dependent nursing interventions to accomplish the desired patient outcomes
being specific with who, what, where, when and how
what should you consider when choosing an intervention
desired patient outcomes, rationale, feasibility of successfully implementing the intervention
what do we incorporate into clinical decision making?
research, clinical expertise, preferences, other available resources
what does implementation include?
communicating the plan of care to other members and carry out interventions
recording the care given & the client’s responses
what does evaluation include?
what were the outcomes of pt care? evaluating long term and short term goals, if the interventions worked, do the plan of care need to be continued or revised and evaluation data becomes new assessment data
what are the two types of documentation?
charting by inclusion (narrative); assessments, interventions, outcomes in progress notes in chronological order
charting by exception (focused): completed when assessments, interventions or outcomes vary from established norms or standards of care
why do we use focus charting?
focus on patient/client concern or behavior
change in patient condition
significant treatment event
what does DARP stand for
D - data
A - analysis and action
R - Response
P - Plan
what is SOAPier charting?
S - subjective
O - objective
A: assessment
P: plan
I: implementation
E: Evaluation
R; Revision
what is clinical reasoning?
collecting cues
weighing evidence
using intuition
recognizing patterns
selecting from alternatives
what are cues?
physiologic or psychosocial changes
how do we communicate your concerns?
s - situation
b - background
a - assessment
r - recommendations
what is homeostasis?
set point that the body is trying to balance itself to
range that the body allows us to stay in equilibrium for adaptive responses
maintain composition and volume of body
how much % of the adult body weight is water content?
60
what are the body fluid compartments?
ecf and icf
where is extracellular fluid found?
between clls in the interstitial and lymph
where is intracellular fluid found?
located within cells
1L of water weight weighs __kg
1
what are electrolytes?
substances whose molecules dissociate into ions when placed into water
what are examples of cations
sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium
what are examples of anions?
biocarbonate, chloride, phsophorus
what are the major electrolytes in the ecf and icf?
ecf: sodium and calcium
icf: potassium and phosphorus
what are the mechanisms for controlling fluid and electrolyte movement?
diffusion, facilitated difficusion, active transport, osmosis, hydrostatic pressure, oncotic pressure
what is diffusion
movement of molecules from high to low concentrationw
what is facilitated diffusion?
movement of molecules from high to low concentration without enery but using specific carrier molecules to accelerate diffusion
what is active transport?
moelcules move against concentration gradient from high to low which requires external energy
what is osmosis?
movement of water between two compartments by a membrane permeable to water but not to solute from low solute to high solute and requires no energy
what is osmotic pressure?
amount of pressure required to stop osmotic flow of water
determined by concentration of solutes in solution
what is osmolality?
measure of osmotic force that is the concentration of molecules per weight of water - measure for evaluating concentration of urine, body fluids and plasma
what is the major colloid in the vascular system that contributes to toal osmotic pressure?
albumin
what is the role of albumin?
keep vascular fluid in vascular space
what is a hypotonic fluid?
fluid where solute is less concentrated than the cells they are in
what is a hypertonic fluid?
fluid where solute is more concentrated than the cells they are in
normally ecf and icf are ______ to one another
isotonic
what is hydrostatic pressure?
force within fluid compartment
pushes water out of vascular system at capillary level
what causes edema?
plasma leading to interstitial fluid shift
an elevation of venoushydrostatic presure
what are the type of fluid spacings
first spacing (normal distribution of fluid ICF and ECF
second spacing (abnormal accumulation of interstitial fluid) - edema
third spacing (third space syndrome): fluid accumulation in part of body where not easily exchanged with ecf (ascites, burns, pleural effusions, bowel obstructions
what is sodium content
135-145mmol/L
what is normal potassium content
3.5-5.0mmol/L
what is normal chloride content
95-105mmol/L
what is normal bicarbonate content
21-28 mmol/L
urea nitrogen content
2.5-6.4 mmol/L
creatine content
71-106 umol/L
what does insensible loss mean?
nonmeasurable
what does hypovalemia mean?
ecf volume deficit
what is hypervolemia
ec volume xcess
who are at risk for hypovolemia and why
children (greater bsa, immature kidneys, higher metaolic rate and immature endocrine system)
elderly (chronic medical conditions, decreasedd thirstand mobility, medication effects)
what type of solution is isotonic
0.9 sodium chloride and lactated ringers
what type of iv solution is hypotonic
0.45 sodium chloride
what type of solution is hypertonic
3% sodium chloride
normal saline changes icf volume true or false
false
dextrose moves into icf true or false
true
does dextrose provide electrolytes
no
what can dextrose be used for
replace water losses
what are the 3 categories of cbc?
leukocytes, erythocytes and platelets
what is heamtocrit
percentage of rbc in volume of whole blood
what is hemoglobin
protein/iron compound on red blood cells that bind with xygen
what is hemoglobin volume
female: 7.4-9.9 mmol/L or 12-16 g/dL
male: 8.7-11.2 mmol/L (14-16 g/dL)
hat is normal hemtocrit
female 0.35-0.47 volume
male: 0.42 -0.52
is osmolality affected in hypervolemia?
no b/c fluid and solutes are gained in equal proportion
who is at risk for hypervolemia?
pt with impaired renal or elderly patient
what are some interventions for hypervolemia?
treating primary cause with diuretics or fluid restriction or sodium intake
measure intake and output
measure daily weights
good skin care
elevation of edematous extremities
monitor patient
what level is sodium at for hyponatremia?
<135 mmol/L
severe: <125mmol/L
what can we give for severe symptoms of hypernatremia?
3% NaCl to cause water to hift out of the cells
why must we be careful giving 3% nacl solution?
fluid can rush out and cells can die, must do it at rate of 100ml/hr
depletion of cells
overwhlem the pt with fluid volume - must give through IV and central line infusion preferred
what is the numbers for hypernatremia?
>145mmol/L
lifethreatening >155mmol/L
death: >180mmol/L
hypernatremia causes hyperosmolality - true or false
true b/c hyperosmolality causes shift water out of cells, causing celular dehydration
what are the interventions for hypernatrium
oral flui replacement
receieve salt-free solution like dextrose to return serum levels to normal
but careful becasuse too much fluid can cause cerebral edema
hypokalemia occurs when…
levels below 3.5 mmol/L
what is the primary route for potassium loss
kidneys
what are the clinical manifestations of low potassium
cardiac issues, fatigue, muscle weakness, leg cramps, nausea vomiting
ileus
soft flaby muscles
paresthesias, decreased reflexes
weeak irregular pulse
rate of adminstration of kcl should not exceed ____ to prevent hyperkalemia
10-20mmol/hour
can you administer potassim throughIV push or bolus?
no
what is the max amount of potassium given in 24 hours?
200mEq/L
how do we increase elimination of potassium
diuretics
dialysis
ion-exchange resins like kayexalate
increase fluid intake
how do we force potassium from ecf to icf?
iv insulin with glucose to prevent hypoglycemia
iv sodium bicarbonate
blood pressure is equal to what
cardiac output x stroke volume times heart rate
what are baroreceptors
specialized nerve cells in carotidsinus and aortic arch that relay info
what are the sns receptors responsible for
a1: vasoconstriction
a2: vasoconstriction
B1: increase contracitility, hr, conduction and renin
B2: dilate bronchial passages
how does the raas system lead to vasoconstriction?
juxtaglomerular apparatus release renin
renin converts angiotensin —> angiotensin 1
angiotensin 1 goes to lungs wehere ACE makes angiotensin ii leading to vasoconstriction and secrete aldosterone to retain sodium and water
what is stage 1 hypertension
SBP 140-150 or DBP 90-99 mmHg
what is stage 2 hypertension
SBP 160mmHg or DBP 100mmHg
what are some lifestyle modifications for hypertension?
dash diet
weight reduction
alcohol consumption - nomore than 2 drinks/week
30-60min physical activity 4-7x week
avoid tobacco
stress management