Eukaryotic Diversity: Unicellular to Multicellular Organisms
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Eukaryotic microbes
Extremely diverse organisms with specialized structures.
Protozoa
Unicellular, animal-like, heterotrophic eukaryotes.
Helminths
Parasitic worms, often affecting humans.
Fungi
Eukaryotic organisms, including molds and yeasts.
Algae
Plant-like protists, can be unicellular or multicellular.
Lichens
Symbiotic relationship between fungi and algae.
Protists
Eukaryotes that are not plants, animals, or fungi.
Plankton
Microorganisms drifting in water, moved by currents.
Zooplankton
Motile, non-photosynthetic plankton.
Phytoplankton
Photosynthetic microorganisms in aquatic environments.
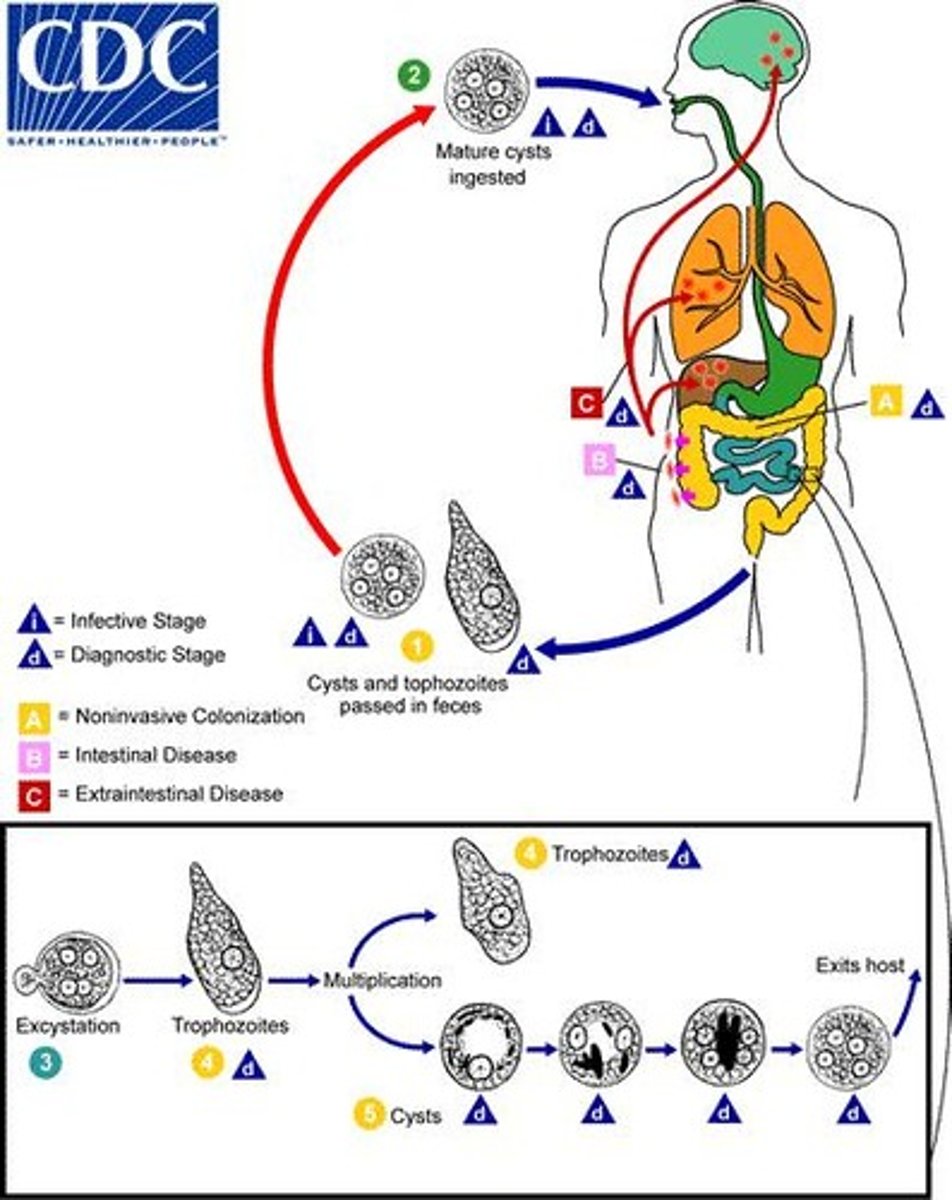
Trophozoites
Feeding and growth stage of protozoa.
Cysts
Encapsulated stage for protection in harsh environments.
Asexual reproduction
Reproduction without gamete fusion, e.g., binary fission.
Sexual reproduction
Involves fusion of haploid gametes, syngamy.
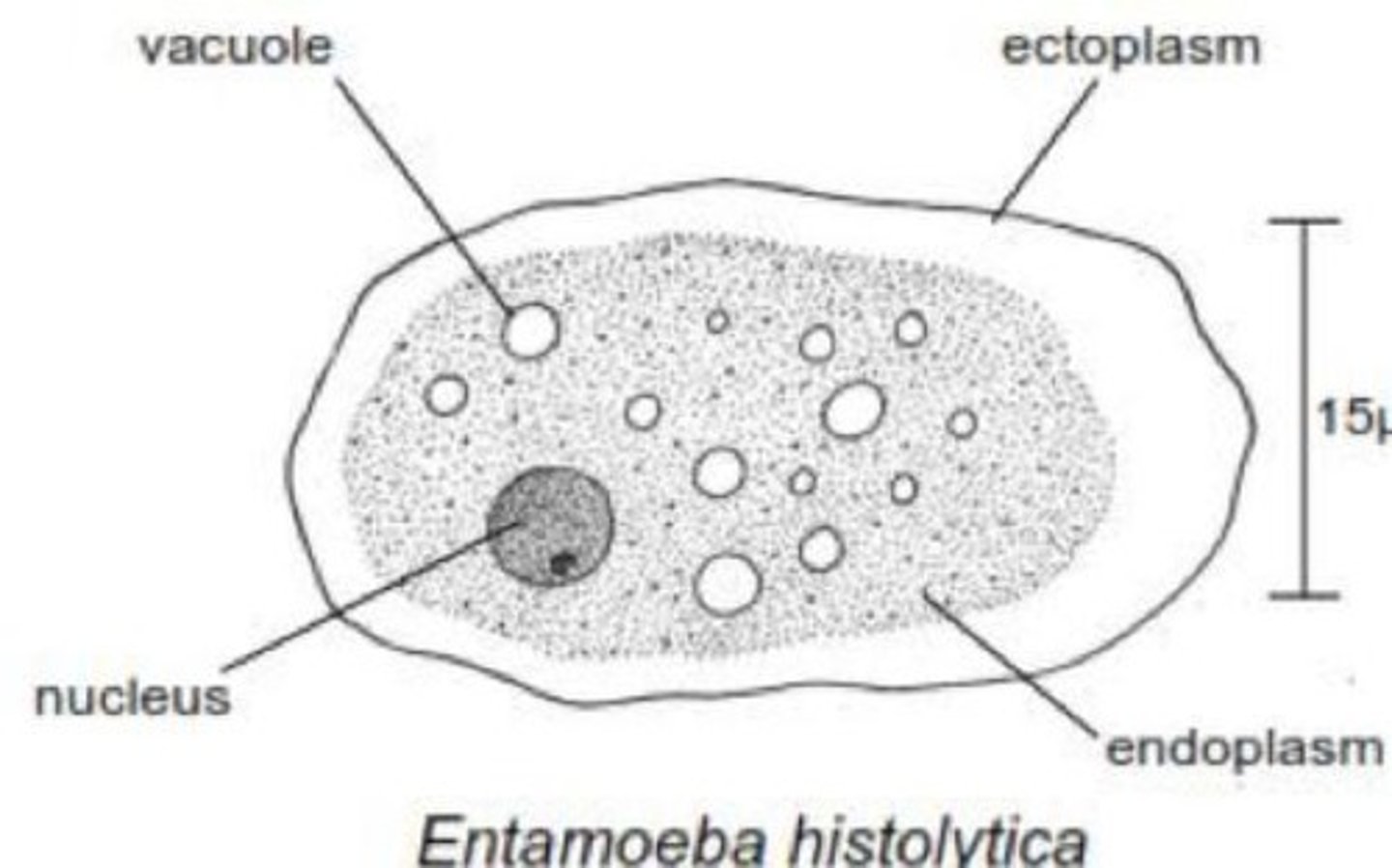
Plasmalemma
Membrane surrounding protozoan cells.
Pellicle
Protein bands providing rigidity to protozoan membranes.
Cytostome
Structure for nutrient uptake in protozoa.
Holozoic protists
Take in whole food particles.
Saprozoic protists
Absorb smaller nutrient molecules.
Cytoproct
Exocytosis structure for waste removal.
Flagella
Whip-like structures for protozoan locomotion.
Cilia
Hair-like structures for movement and feeding.
Pseudopodia
Cytoplasmic extensions for attachment and movement.
Contractile vacuoles
Regulate osmotic pressure in protozoa.
Kinetoplastid DNA
DNA bundles associated with flagella in some protozoa.
Hydrogenosomes
Organelles producing ATP without oxygen.
Polyphyletic
Groups derived from multiple ancestral sources.
Amoebozoa
Group of protists with amoeba-like movement.
Entamoeba histolytica
Causative agent of amoebic dysentery.
Naegleria fowleri
Agent of amoebic meningoencephalitis.
Acanthamoeba spp.
Causes keratitis in contact lens users.
Cellular slime molds
Aggregate into mobile slugs to reproduce.
Plasmodial slime molds
Large cells with multiple nuclei, form stalks.
Dictyostelium discoideum
Example of cellular slime mold.
Fuligo septica
Example of plasmodial slime mold.
Excavata
Group with a depression on cell surface.
Chromalveolata
Group characterized by plastids containing pigments.
Apicomplexans
Intracellular parasites with an apical complex.
Ciliates
Organisms using cilia for movement and feeding.
Oomycetes
Water molds resembling fungi, with cellulose walls.
Plasmodium spp.
Genus causing malaria, infects multiple hosts.
Cryptosporidium parvum
Contaminates water, causes intestinal symptoms.
Babesia microti
Transmitted by ticks, causes babesiosis.

Toxoplasma gondii
Causes toxoplasmosis, transmitted via cat feces.
Balantidium coli
Only pathogenic ciliate affecting humans.
Paramecium
Commonly studied ciliate in laboratories.
Conjugation
Reproductive process in ciliates.
Fornicata
Excavata group lacking mitochondria, possessing flagella.
Giardia lamblia
Causes giardiasis, spread via contaminated water.
Parabasalia
Endosymbionts in termites, modified mitochondria present.
Trichomonas vaginalis
Causes trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted infection.
Euglenozoa
Includes photo and non-photosynthetic organisms.
Trypanosoma
Genus causing African sleeping sickness and Chagas disease.
Helminths
Multicellular parasites with complex life cycles.
Nematoda
Phylum of roundworms, includes many parasites.
Platyhelminthes
Phylum of flatworms, includes flukes and tapeworms.
Monoecious
Organisms with both male and female reproductive organs.
Dioecious
Organisms with distinct male or female sexes.
Ascaris lumbricoides
Largest roundworm infecting humans.
Enterobius vermicularis
Commonly known as pinworm, infects humans.
Toxocara spp.
Common in dogs and cats, can infect humans.
Schizogeny
Asexual reproduction process in Apicomplexans.
Helminths
Parasitic worms including tapeworms and flukes.
Cestodes
Segmented flatworms known as tapeworms.
Trematodes
Nonsegmented flatworms with oral suckers.
Proglottid
Segment of a tapeworm containing reproductive structures.
Scolex
Head region of a tapeworm with suckers/hooks.
Taenia spp.
Beef and pork tapeworms from contaminated meat.
Mycoses
Illnesses caused by fungal infections.
Hyphae
Filamentous structures forming the body of molds.
Mycelium
Mass of hyphae forming the main body of fungi.
Septate hyphae
Hyphae with walls separating individual cells.
Coenocytic hyphae
Hyphae without walls between cells.
Pseudohyphae
Budding yeast cells that resemble hyphae.
Chitin
Polysaccharide in fungal cell walls.
Ergosterol
Sterol found in fungal cell membranes.
Dimorphic fungi
Fungi that can exist as yeast or mold.
Ascomycota
Fungal phylum including pathogens and food producers.
Ascospores
Sexual spores produced by Ascomycota.
Conidia
Asexual spores produced by Ascomycota.
Candida albicans
Yeast causing opportunistic infections like thrush.
Basidiomycota
Fungal phylum producing basidiospores.
Amanita phalloides
Poisonous mushroom known as the death cap.
Microsporidia
Unicellular parasites lacking mitochondria.
Zygomycota
Fungal phylum with coenocytic hyphae.
Zygospores
Sexual spores formed by Zygomycota.
Dinoflagellates
Algae with two flagella and cellulose armor.
Stramenopiles
Algae group including diatoms and brown algae.
Diatoms
Algae with silica frustules, major oxygen producers.
Red algae
Algae with agar or carrageenan in cell walls.
Prototheca spp.
Algae causing rare skin infections.
Lichens
Symbiotic association of fungi and algae.
Crustose lichen
Flat, crust-like lichen morphology.
Foliose lichen
Leafy, lobed lichen morphology.
Fruticose lichen
Shrub-like, branching lichen morphology.