myoglobin and hemoglobin
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Write mathematical expression for Kd and relate this parameter to binding affinities
Kd = [L], halfl of the ligand-binding sites are occupied
small Kd value → tight ligand binding
large Kd value → weak ligand binding
![<p>Kd = [L], halfl of the ligand-binding sites are occupied </p><p>small Kd value → tight ligand binding </p><p>large Kd value → weak ligand binding </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c6cc7368-20b3-4901-9174-36502340afe0.png)
Explain why myoglobin is a good O2 storage protein
present in muscles
has high affinity for oxygen, which allows it to bind oxygen tightly and hold it until it’s needed
high affinity because of structure, which lacks the cooperative binding mechanism of hemoglobin, meaning it remains fully started at lower oxygen pressures and only releases oxygen under high demand
O2 binds to heme, F-helix moves
myoglobin is a __
monomer
myoglobin binding curve is ___
hyperbolic
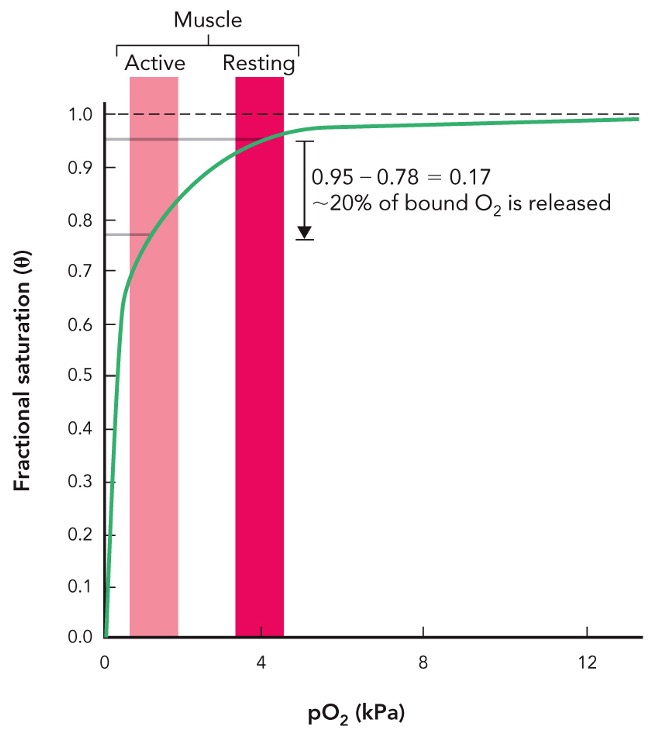
what graph does this represent
myoglobin
Explain why hemoglobin is a good O2 transport protein
cooperative binding, reversible binding, and iron-containing heme groups
as one oxygen molecule binds, the hemoglobin’s shape changes to make it easier to bond more oxygen, ensuring efficient uptake in the lungs
O2 binds to heme, F-helix moves
present in red blood cells
hemoglobin is a ___
tetramer
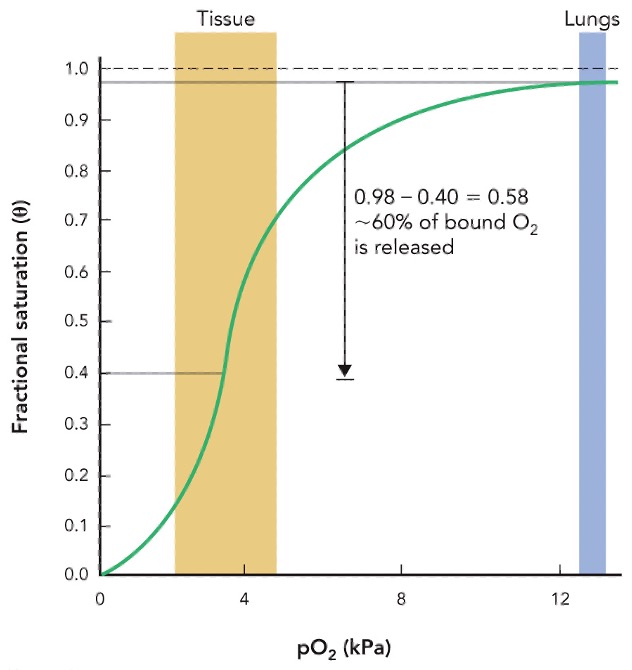
this graph represents
hemoglobin
hemoglobin binding curve is __
sigmoidal
how does pH regulate hemoglobin O2 affinity
pH regulates hemoglobin’s oxgen affinity through the Bohr effect
an increase in pH increases hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen, allowing it to bind more oxygen in the lungs → hydrogen ions form lower pH bind to hemoglobin, causing a conformational change that favors release of oxygen
how does CO2 regulate hemoglobin O2 affinity
bicarbonate can bind to the amino-terminus of each hemoglobin subunit
carbaminohemoglobin favors the T state
when CO2 is bound, another H+ is released which further contributes to the Bohr effect
CO2 is produced in peripheral tissues and need to be released by the lungs; high CO2 production leads to a decrease in local pH
carbonic anhydrase
an enzyme that hydrates CO2 to form bicarbonate and H+
Bohr effect
hemoglobin binds O2 less tightly (higher Kd) at lower pH values
how does BPG regulate hemoglobin O2 affinity
2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) is a side product of glycolysis and acts as a heterotrophic regulator of hemoglobin O2 binding
binds to a positive patch or residues between the B subunits
when BPG is bound, O2 affinity decreases (favors T state)
humans can change BPG levels to tune hemoglobin’s O2 affinity
pO2 is higher at sea level than at high altitude
humans who live near sea level ~ 5 mM BPG in their blood cells
~ 8 mM BPG for living above 4000 m
higher BPG concentration results in more efficient O2 delivery to peripheral tissues
Describe the biochemical mechanisms involved in fetal hemoglobin O2binding
fetuses must acquire O2 from maternal hemoglobin
gene expression of hemoglobin subunits changes during fetal development
fetal hemoglobin has a lower affinity for BPG than adult hemoglobin
therefore, fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for O2 than adult hemoglobin
fetal hemoglobin gene expression stop at ~6 months of age
Describe the biochemical mechanisms involved in sickle cell disease
surface glutamate residue on a B subunits is changed to valine → if both B subunits contain valine, deoxyhemoglobins form polymers based on hydrophobic interactions the aggregate in cells
complexes that contain one B subunit with valine and one B subunit with glutamate do not polymerize
aggregated hemoglobin fibers distort red blood cell morphology → sickle shaped cells cannot easily pass through some vessels and peripheral tissues do not receive sufficient O2
Describe the mechanism of CO poisoning and treating the poisoning
CO binds competitively with O2
exposure can be fatal because O2 cannot be delivered to peripheral tissues and respiratory complexes cannot make ATP
CO binds to the heme irons in hemoglobin and competes with oxygen for binding
CO is rapidly transferred from carboxyhemoglobin to Ngb-H64Q, which is a mutant neurogloibin protein that binds CO 500 times more tightly than does hemoglobin
O2 transport in humans
red blood cells pick ip O2 in the lungs and deliver it to tissues throughout the body
proteins in red blood cells need to bind O2 tightly, but not so tightly that they can’t give it away
how does O2 act as a ligand
the concentration of O2 is expressed as a partial pressure, pO2
instead of using Kd, p50 is the pO2 value in which half of the ligand-binding sites are occupied
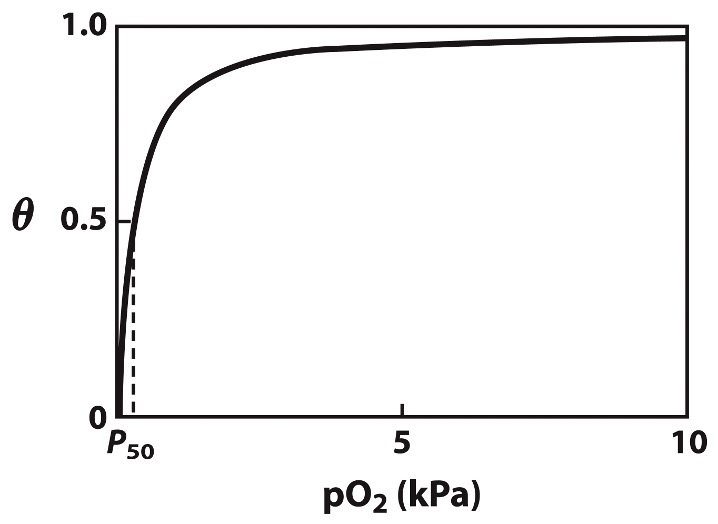
how does O2 bind to heme
the heme iron is Fe2+ (red) in myoglobin/hemoglobin
Fe2+ is slowly oxidized to Fe3+ (brown) in dead cells
Fe2+ in heme has octahedral geometry
four equatorial ligands are provided by the porphyrin
O2 binding causes the protein to move, the F-helix moves by about 1 A which changes the geometry of the heme
when O2 is absent, the heme is puckered or domed; when it is bound, the heme is planar
porphyrin
planar organic structure that contains four pyrrole rings linked by methylene groups
heme
a porphoryin with a coordinating iron ion
proximal histidine residue
one axial ligand
distal histidine residue
one axial ligand is O2 which forms a hydrogen bond
allosteric protein
binding of a ligand to one site affects the binding affinity of a different ligand binding site on the same protein
positive allostery
second ligand binds with higher affinity
negative allostery
second ligand binds with lower affinity
homotropic regulator
affects the binding properties of the protein’s normal ligand
heterotrophic regulator
affects the binding properties of a different ligand
cooperatively
positive homotropic regulation
how is hemoglobin regulated by O2
deoxyhemoglobin (T state) has no cooperatively
oxyhemoglobin (R state) has strong cooperatively
binding of O2 in one subunit makes the subunits more likely to bind O2
tense state (T)
more subunit-subunit interactions lead to more stable quaternary structure
lower affinity for O2
likely to be deoxyhemoglobin
relaxed state (R)
fewer subunit-subunit interactions lead to more flexible quaternary structure
higher affinity for O2
likely to be oxyhemoglobin
concerted model
overall assembly can exist in the T state or the R state
the binding of ligand shifts the equilibrium between these two states
T→ R transition: as oxygen binds, more hemoglobin tetramers are converted from the T state to teh R state, increasing the oxygen affinity of the available binding sites
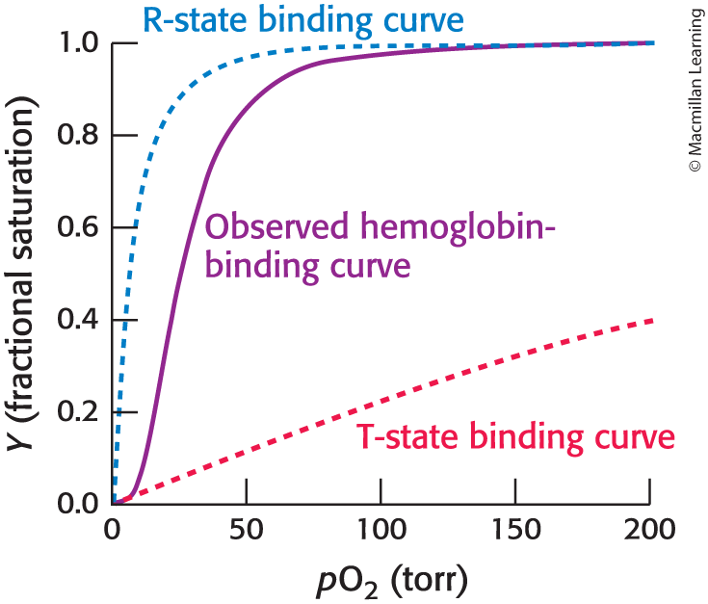
sequential model
the binding of a ligand to one site in an assembly increases the binding affinity of neighboring sites without inducing a full conversation from the T into the R state
why do the model’s not filly account the hemoglobin’s behavior
concerted: the tetramer with three sites occupied by oxygen is almost always in the quaternary structure associated with the R state
sequential: hemoglobin with oxygen bound to only one of four sites remains primarily in the T state
myoglobin and hemoglobin evolution
subunits are structurally very similar
gene duplication events have resulted in multiple global proteins
globin variants can be beneficial or deleterious