PHARM 115 NIOSH and USP 800 Lecture 20
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
NIOSH (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) List of Hazardous Drugs
- all drugs on list considered hazardous
- 3 groups and also any drug with safe handling guidelines from manufacturer
- need to be labeled as hazardous
- solid intact medications may not pose a risk (except if they are altered); do not use in automated counting machines
group 1 (NIOSH drugs)
antineoplastic drugs
Group 2 (NIOSH drugs)
non-antineoplastic drugs that meet one or more of the NIOSH criteria for a hazardous drugs
Group 3 (NIOSH drugs)
drugs that primarily pose a reproductive risk to men and women who are actively trying to conceive and women who are pregnant or breast feeding
hazardous drugs include
cancer chemotherapy meds, antivirals, hormones, bioengineered drugs, others
six characteristics associated with hazardous drugs
- carcinogenicity
- teratogenicity (or other developmental toxicity)
- reproductive toxicity
- organ toxicity at low doses
- genotoxicity
- new drugs with structure and toxicity profiles similar to existing hazardous drugs
reproductive and developmental toxicity
- adverse effects observed in animal testing at doses near, at, or below the maximum recommended human dose (highly relevant)
- adverse effects observed in animal testing at doses many times the maximum recommended human dose (not considered NIOSH evaluation)
Hazardous drugs at individual organizations
- facility specific
- evaluate any new drugs entering the facility, add to list as needed
OSHA (occupational safety and hazard administration) standard
- requires employers to develop a hazard communication program specific to their facility
- identify all hazardous chemicals that employees may come into contact with
- make list of hazardous drugs available to employees
resources for evaluating a drug's hazard potential
- safety date sheets
- drug package insert
- international agency for research on cancer
- drugbank
- dailymed
- special health warnings from manufacturers, FDA, professional organizations
- medical and healthcare journal reports
- other facilities' evidence-based recommendations
NIOSH risk factor assessment
- Level of toxicity
- Manner in which the drug enters the body (dermal, mucosal, inhalation, injection, ingestion)
- Manipulation of the drugs (freq of manipulation and exposure controls (PPE, PECs, etc))
drugs on NIOSH list that must follow USP 800 reqs
- any HD (hazardous drug) API (active pharmaceutical ingredient)
drugs on NIOSH list that don't have to follow all the containment reqs of USP 800 IF an assessment of risk is performed and implemented
final dosage forms of compounded HD preparations and conventionally manufactured HD products, including antineoplastic dosage forms that do not req any further manipulation other than counting or repackaging (unless required by the manufacturer)
assessment of risk of USP 800 HD in healthcare settings
- type of hazardous drug
- dosage form
- risk of exposure
- packaging
- manipulation
- must document alternative containment strategies for specific dosage forms
- must review every 12 months and document review
examples of alternative containment strategies for specific dosage forms
- packaging drug inside a powder hood
- special area for storage with labeling
- wearing gloves when counting or packaging drugs
- separate counting trays and spatulas, decontaminating after use
- placing HD containers in sealed plastic bag
What is a potential exposure to receiving hazardous drugs?
- contact with drug residue on containers, work surfaces, etc
What is a potential exposure to dispensing hazardous drugs?
- counting or repackaging tablets and capsules
What is a potential exposure to compounding and other manipulations of hazardous drugs?
- crushing or splitting tablets, opening capsules, pouring liquids, weighing, mixing, reconstituting powders, withdrawing injectable liquids, residue on PPE or other garments
What are some other ways of potential exposure to hazardous drugs?
administration, pt care, spills, transport, waste
USP 800
- designated areas for receipt, unpackaging, storage, compounding
- hazardous drugs must be unpacked in neutral or negative pressure areas (must wear PPE; spill kit)
- don't store on floor, areas prone to items falling
- storage requirements for anti-neoplastic drugs used in compounding, any HD API: externally ventilated room, negative pressure room, at least 12 air changes per hour, designated refrigerator r products requiring refrigeration
containment secondary engineering control (C-SEC) requirements for hazardous drugs
- externally vented
- physically separated from other preparation areas
- appropriate air changes per hour (ACPH) (12 ACPH for non-sterile or 30 ACPH for sterile in cleanroom suite; 12 ACPH for sterile in unclassified C-SCA (containment segregated compounding area)
- negative pressure
- sink and eye wash station
containment primary engineering controls (C-PEC)
- sterile: externally vented (class II BSC or CACI)
- non-sterile: externally vented or redundant HEPA filter (BSC, CACI, or CVE- containment ventilated enclosure)
supplemental engineering controls
closed system drug transfer devices (CSTDs)
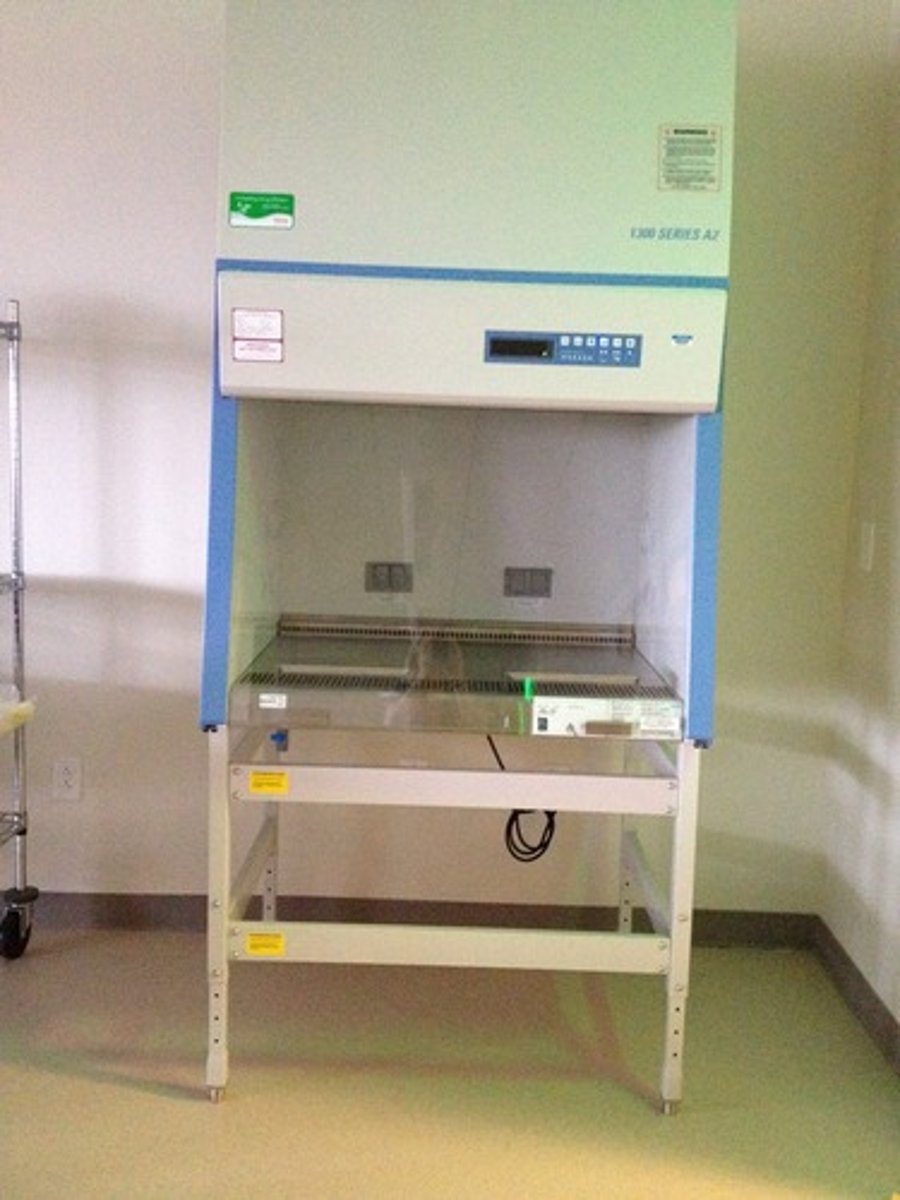
biological safety cabinet
bsc

compounding aseptic containment isolator
CACI

closed system drug transfer device
CSTD
- critical not only to the safety of employees who administer HDs, but also to those who compound HDs
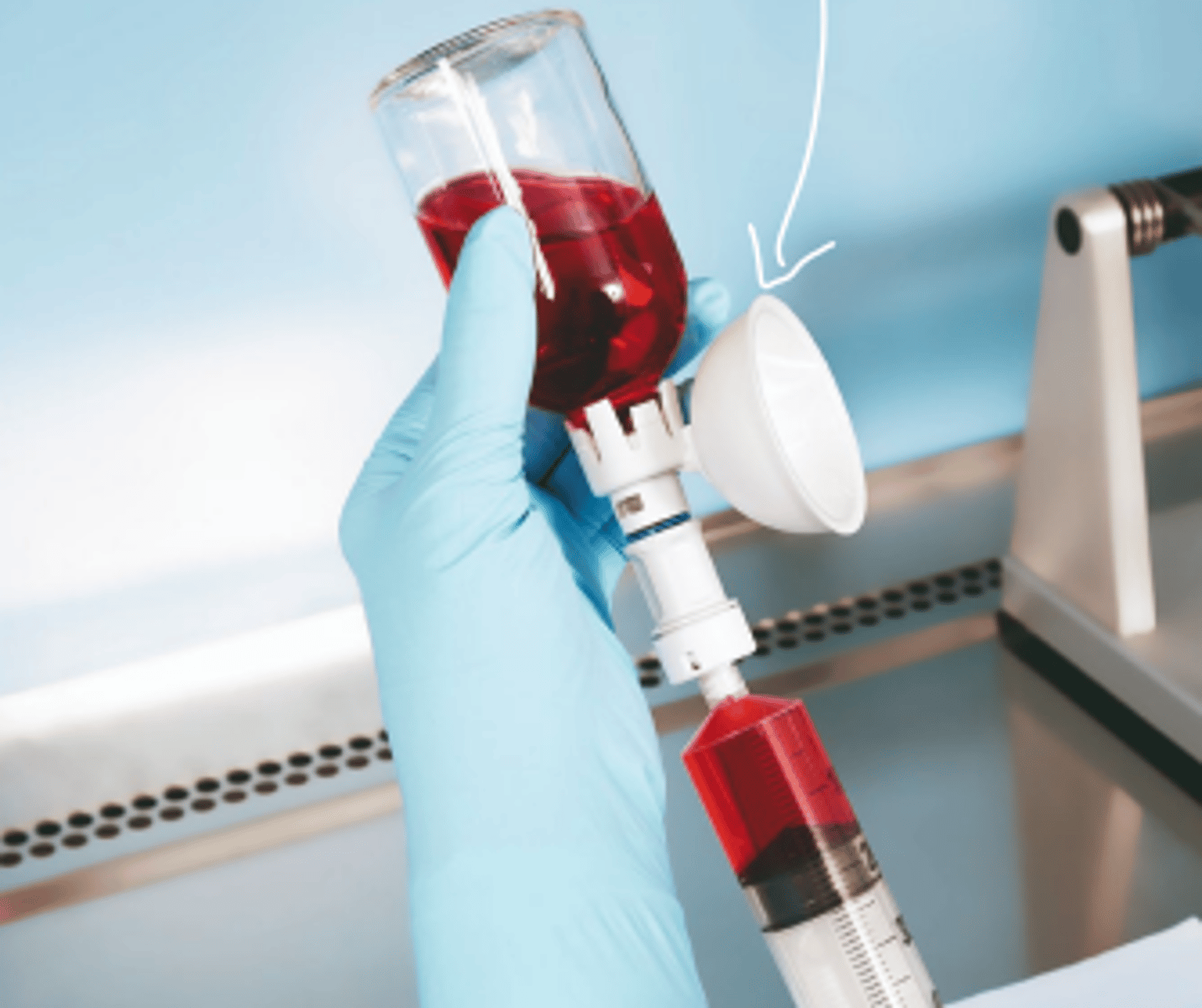
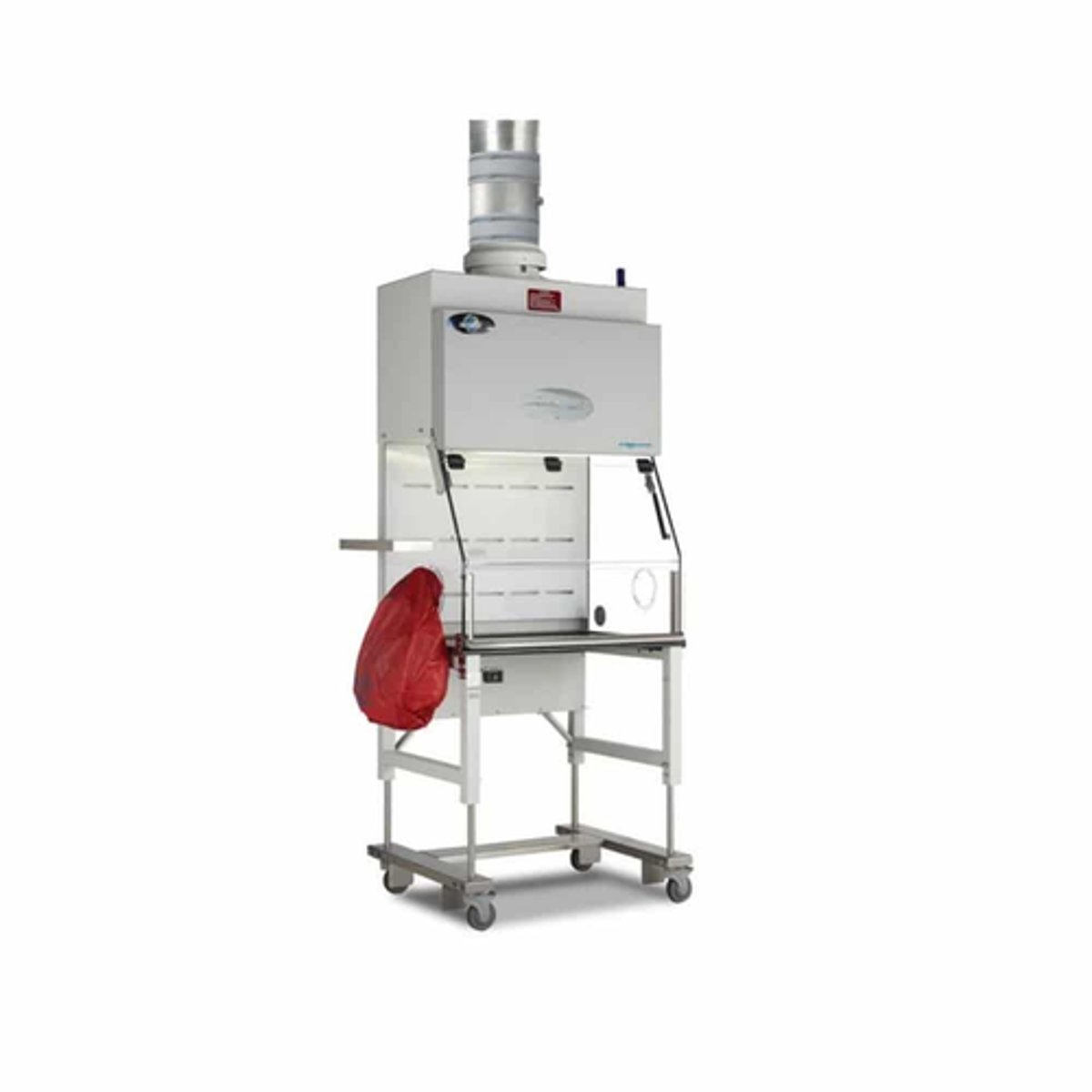
containment ventilated enclosure
CVE
- powder containment hood

- gowns
- head cover
- hair cover
- shoe covers
- 2 pairs chemotherapy gloves
- eye and face protection, if risk of spills or splashing
- respiratory protection, if risk of inhalation
- sleeve covers if deemed necessary
USP 800 PPE
What is required when compounding sterile and non-sterile hazardous drugs?
USP 800 PPE gowns
- must be closed in the back, long-sleeved, cuffed disposable, impermeable to HDs
- change per mfr recommendations or every 2-3 hours
- do not wear outside HD area
USP 800 PPE additional consideration for shoe covers
- 2nd pair of shoe covers in SEC area
USP 800 PPE chemotherapy gloves
- two pairs of chemotherapy drugs
- outer gloves must be sterile when sterile compounding
- wash hands after removing gloves
eye and face protection
- goggles and full mask or face-full respirator
- if risk of spills or splashing
respiratory protection
- if risk of inhalation
- fit-test, NIOSH-certified N95 respirator
- full-face piece respiratory for gases, vapors, or liquid splashes
deactivating
renders compound inert or inactive
decontaminating
inactivating, neutralizing, or physically removing HD residue from non-disposable surfaces
cleaning
removal of contaminants
disinfection
inhibiting or destroying microorganisms
- spills
- designated person to oversee compliance
- hazard communication program
- personnel training
- environmental quality control
- receiving potentially damages items
- transport
- administering
- medical surveillance
List some other considerations of USP 800