432 Exam 2
1/258
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
259 Terms
Between L and D amino acids, which is only found in proteins?
L amino acids
What amino acid is Ala?
Alanine
What amino acid is Arg?
Arginine
What amino acid is Asn?
Asparagine
What amino acid is Asp?
Aspartic acid
What amino acid is Cys?
Cysteine
What amino acid is Gln?
Glutamine
What amino acid is Glu?
Glutamic acid
What amino acid is Gly?
Glycine
What amino acid is His?
Histidine
What amino acid is Ile?
Isoleucine
What amino acid is Leu?
Leucine
What amino acid is Lys?
Lysine
What amino acid is Met?
Methionine
What amino acid is Phe?
Phenylalanine
What amino acid is Pro?
Proline
What amino acid is Ser?
Serine
What amino acid is Thr?
Threonine
What amino acid is Trp?
Tryptophan
What amino acid is Tyr?
Tyrosine
What amino acid is Val?
Valine
What amino acid is Asx?
Asparagine or aspartic acid
What amino acid is Glx?
Glutamine or glutamic acid
How is proline an exception to the typical amino acid structure?
It has a secondary amino group (not a second amino group); Nitrogen is bonded to both the alpha carbon and the side chain
What are the aromatic amino acids?
Phe, Tyr, Trp
What amino acids have aliphatic hydroxyl groups?
Ser, Thr
What amino acids have aliphatic side chains?
Val, Leu, Ile, Met
Which amino acid has cyclic structure?
Proline
Which amino acid has an indole?
Tryptophan
Which amino acids contain carboxamide
Asn, Gln
What is the difference between asparagine and glutamine?
Glutamine’s side chain is one methylene longer
Which amino acid can form disulfide bonds?
Cys
Between cys and ser, which is more reactive and why
Cys; -SH is more reactive than -OH
Which amino acids are basic?
Lys, Arg, His
What unique property does histidine have?
At physiological pH, it can bind or release protons
What amino acids have carboxylate side chains?
Asp and Glu
Is glycine chiral?
No, has 2 hydrogens
What amino acids contain sulfur?
Methionine and cysteine
Why does proline significantly affect protein structure?
Its ring structure makes it more conformationally restricted
Are amino acids containing hydroxyl groups hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Hydrophilic
Which amino acid contains a guanidinium in its side chain?
Arginine
Which amino acid contains imidazole in its side chain?
Histidine
Under physiological pH, do amino acids with carboxylates have a positive or negative charge?
Negative charge
What is the most basic amino acid?
Arginine
Under physiological pH, do basic amino acids have positive or negative charge?
Positive charge
Which amino acids are acidic?
Asp, Glu
Which amino acids are essential?
Val, Leu, Ile, Phe, Trp, Met, Thr, Lys, His
Why is cysteine conditionally essential?
It is synthesized from methionine
Which amino acid is cysteine synthesized from?
Methionine
Why is arginine conditionally essential?
It’s formed in the urea cycle and is essential for growing children
Why is tyrosine conditionally essential?
It’s essential for phenylketonuria patients
Under low pH, what ionization state are amino acids in?
Cation (both groups protonated)
Under high pH, what ionization state are amino acids in?
Anion (both groups deprotonated)
Under neutral pH, what ionization state are amino acids in?
Neutral (zwitterion)
How do you calculate the isoelectric point (pI) of an amino acid?
Identify all ionizable groups and assign pKas
Protonate each ionizable group and calculate the net charge
Move up in pH to the first ionizable group’s pKa and deprotonate it; subtract 1 from the net charge
Repeat until each group is deprotonated; this determines the pH at which each charged form of the molecule occurs
Identify which form has a net charge of 0
Average the pKa on either side of the neutral form to get pI
What is the isoelectric point (pI) of an amino acid?
The pH at which the charge of the molecule is 0
What is the basic structure of an amino acid?
Side chain, Hydrogen, primary amino group, and carboxyl group; all bonded to a chiral alpha carbon
What are the classifications of amino acid chains based on increasing length?
Peptide, polypeptide, and protein
How many amino acids long are peptides?
<10 amino acids
How many amino acids long are polypeptides?
10-50 amino acids
How many amino acids long are proteins?
>50 amino acids
What are the classifications of proteins based on shape?
Globular and fibrous
What protein shape class do enzymes, antibodies, transporters, and receptors fall under?
Globular proteins
What protein shape class do collagen, keratin, and elastin fall under?
Fibrous proteins
What is primary protein structure?
The amino acid sequence
What is secondary protein structure and its classes?
The folding of the primary structure
α helices
β sheets or strands
β turns or reverse turns
What molecule is lost when joining 2 amino acids?
Water
Between separate amino acids and amino acids joined by a peptide bond, which is more thermodynamically stable and what does this mean?
Separate amino acids; Energy is needed to form peptide bonds
In what direction are amino acid sequences written/read?
Amino to carboxyl terminal residue (N to C)
What determines the 3D structure of proteins?
The amino acid sequence
Why are polypeptide chains flexible yet conformationally restricted?
The peptide bond has partial double bond character due to resonance that prevents it from rotating freely
Why are peptide bonds strong?
Resonance gives peptide bonds partial double bond character which decreases their length, increasing the amount of energy it takes to break
Which conformation of peptide bonds is favored and why?
Trans conformation decreases steric repulsion between side chains
Why can proline exist in equal amounts of cis and trans isomers?
Its cyclic ring already has high steric repulsion, decreasing the difference in energy between the cis and trans conformations
Are protein helices right or left handed?
Right handed
What intermolecular force maintains the structure of helices?
Hydrogen bonding
How many residues apart does H-bonding occur in helices?
4 residues apart
What is an α helical coiled coil?
Two helices wind around one another to form a superhelix
What function do superhelices serve?
Form stiff bundles of fibers and used in proteins that span biological membranes
How are superhelices held together?
Van der Wal forces between Leucine separated by 7 residues
How is a single strand of a collagen triple helix stabilized?
Steric repulsion of the pyrrolidine rings of the proline and hydroxyproline residues
What is the structure of collagen (triple helix)?
Each strand is h-bonded to the other two strands. Every 3rd residue is glycine because there is no space in the center of the helix. Pyrrolidine rings are on the outside.
Describe the structure of a β strand
Almost fully extended with the side chains of adjacent amino acids point in opposite directions
How are antiparallel β sheets held together?
H-bonds between single NH and CO groups
How are antiparallel β sheets held together?
2 H-bonds between each NH and CO group
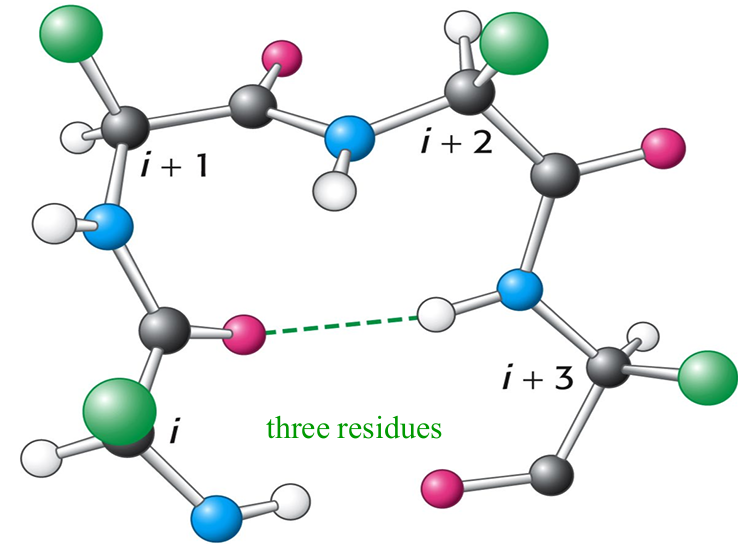
How are β turns stabilized?
The CO group of residue i of the polypeptide chain is hydrogen
bonded to the NH group of residue i+3
What kind of amino acids are α helices made of?
Small aliphatic amino acids
What kind of amino acids are β sheets or strands made of?
Aromatic amino acids
What kind of amino acids are β turns or reverse turns made of?
Glycine and proline
Describe the properties of a peptide bond
Resistance to hydrolysis
Partial double bond character
Has an H-bond donor and acceptor
Neutral
What is native conformation?
When a protein can have many arrangements in space but only uses 1
What is a domain?
A stable unit of a 3* structure; The unit of protein folding
What are the components of a tertiary protein structure?
3D non-repetitive folding
Domains and lobes
What are the components of a quaternary protein structure?
1+ polypeptides
Subunits
Explain the advantage of having separate domains on a protein
Efficient folding
Larger folded proteins
Flexibility and motion
Union of new functions
What is a homodimer?
A protein consisting of 2 identical polypeptide chains
What is a heterodimer?
A protein consisting of 2 different polypeptide chains
What are the forces governing quaternary subunit association?
Ionic interactions
Hydrophobic interactions
2* structure
What is the only information required to specify the native conformation of a protein?
The sequence of its amino acid residues
What function does β-mercaptoethanol serve in denaturation?
Break or reduce disulfide bonds