Cardiac Physiology
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
heart
2 pump transportation system (blood vessels are delivery route)
mediastinum
middle cavity of thoracic cavity where heart is positioned
pulmonary circulation
consists of blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood to and from the lungs (pumped by right side)
systemic circulation
consists of blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to and from the body tissues (pumped by left side)
upper chambers of the heart
atria
lower chambers of the heart
ventricles
where does the right side of the heart pump blood to?
pulmonary circulation; receives deoxygenated blood from the body —> pumps to the lungs for reoxygenation
where does the left side of the heart pump blood to?
systemic circulation; receives preoxygenated blood —> pumps it to the body
3 membranes enclosing heart
pericardium, epicardium, pericardial cavity
pericardium
outer layer, double-walled, connective tissue sac; protects heart, anchors it to surrounding structures
epicardium
lays directly against the heart
pericardial cavity
space between pericardium and epicardium filled with serous fluid; reduces friction as heart pumps
pericarditis
inflammation of pericardium; roughens membrane surfaces, causing pericardial friction rub heard with stethoscope
cardiac tamponade
excess fluid that leaks into pericardial space, can compress heart’s pumping ability; treated by drawing fluid out of cavity
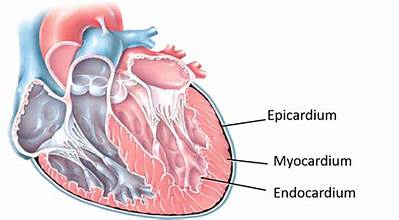
myocardium
cardiac muscle; forms bulk of the heart; arranged around each atria, designed to squeeze blood into ventricles when contracted; arranged in both ventricles, designed to squeeze blood into different circulatory systems
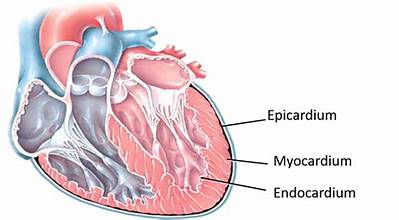
endocardium
connective tissue layer on the inner myocardium surface; lines heart’s chambers and valves, makes up valves that separate the atria from the ventricles
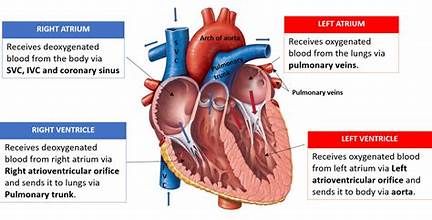
atria
receiving chambers of the heart, separated by interatrial septum, receive blood from venous system and push it inferiorly to the ventricles; thin walls —> minimal contraction to push blood into ventricles
right atria
receives blood from superior and inferior vena cava and coronary sinus; weaker than left atrium, higher oxygen content in blood
left atria
receives blood from pulmonary veins, stronger than right atrium
which atrium is stronger, right or left?
left
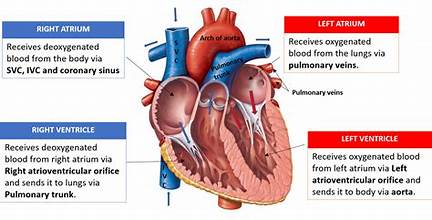
ventricles
discharging chambers; located at apex, separated by interventricular septum; receives blood from atria and pushes it to the lungs (R) or rest of body (L); thick-walled chambers (need to contract forcefully to overcome vascular resistance/friction)
is the left or right ventricle thicker?
left; there is more force counteracting it from the body than the lungs
right ventricle
pushes blood through the pulmonary trunk to the left and right pulmonary arteries
left ventricle
pushes blood through the aorta
do valves open in the opposite direction?
no— valve are one-way
what causes blood to travel one direction in the heart?
4 valves open/close in response to blood pressure on either side preventing backflow
atrioventricular (AV) valves
located between the atria and ventricles; tricuspid and mitral valves
tricuspid valve
between right atrium and ventricle
mitral valve
between left atrium and ventricle
what connects the atrioventricular valves to the ventricular wall?
chordae tendinae (connective tissue strings made of endocardium, anchor cusps of valves to the papillary muscles to keep them from folding backwards after contractions)
semilunar valves (SV)
located between the ventricles and between the major arteries
pulmonary SV valve
between the right ventricle and pullmonary trunk
aortic SV valve
between left ventricle and aorta
what allows arteries to stay closed?
blood pressure in arteries
what is the first heart sound?
closing of AV valves at beginning of ventricular systole
what is the second heart sound?
closing of SL valve at the beginning of ventricular diastole
what does the pause between the lub-dub sounds indicate?
heart relaxation
mitral valve closes slightly ____________ tricuspid
before
aortic valve closes slightly before ___________ valve
pulmonary
heart murmur
abnormal heart sounds heard when blood hits obstructions; indicates valve problems
incompetent/insufficient valve (heart murmur)
fails to close completely, allowing backflow of blood
stenotic valve (heart murmur)
fails to open completely, restricting blood flow through valve
intercalated discs
connect cardiac muscle fibers
desmosomes
prevent adjacent cells from separating during contraction
gap junctions
allow ions to pass quickly from cell to cell
functional syncytium
myocardium behaves as a single coordinated unit
describe cardiac muscle contraction
all or nothing, longer absolute refractory period, longer contraction phase, shorter relaxation cycle; tetanus not possible
energy source for cardiac muscle
more mitochondria, higher O2 dependence, special shuttles in cardiac mitochondria recycle lactic acid and use it for energy
cardiac muscle contracts without __________ input.
neuronal
automaticity
heart contracts rhythmically by its ability to generate its own action potentials (myogenic); rate of rhythm is altered by ANS
autorhythmic cells
initiate and conduct action potentials responsible for contraction of working cells
99% of cardiac muscle cells are ___________.
contractile
pacemaker potential
slow depolarization due to opening of Na+ channels and closing of K+ channels
cardiac muscle action potentials have __________ which is not seen in skeletal muscle contraction
plateau
how long does action potential last in cardiac muscle?
200ms
benefits of longer action potential and contraction in cardiac autorhythmic cells
sustained contraction ensures efficient ejection of blood, longer refractory period prevents tetanic contractions
where are pacemaker cells located?
SA node
________ cells generate action potential faster than any other heart cell
pacemaker
bundle of his
conducts action potential from AV node to interventricular septum, where it splits into left and right bundle branches
function of left and right bundle branches
propagate action potential through interventricular septum to heart apex
purkinje fibers
spread action potentials from apex to left and right ventricles rapidly due to their high proportion of intercalated discs
internodal pathways
conduct action potential from SA node to myocytes in the atria through gap junctions
spread of cardiac excitation is ________ to ensure efficient _________
coordinated/pumping
what must happen before ventricular contraction onset?
atrial excitation and contraction
electrocardiogram (ECG)
measures electrical activity of the heart by measuring voltage differences between regions; composed of all action potentials at given time
p-wave
depolarization (contraction) of atria
QRS complex
depolarization of ventricles
Q wave (QRS complex)
depolarization of the septum
R wave (QRS complex)
depolarization of the anterior wall
S wave (QRS complex)
depolarization of the inferior wall
T wave
repolarization (relaxation of the ventricles)
ectopic focus
abnormal pacemaker that takes over pacing
defective SA node may cause ____________.
ectopic focus
extrasystole
premature contraction; ectopic focus of small region of heart that triggers impulse before SA node can, causing delay in next impulse
pacemakers make up ____% of myocytes
1
99% of myocytes are ____________ cells.
contractile
if AV node takes over, it sets ______________________ at 40-60bpm
junctional rhythm
if AV node is defective, it may cause a ___________
heart block
arrhythmia
irregular heart rhythm; uncoordinated atrial and ventricular contractions
fibrillation
rapid irregular contraction
treatment of fibrillation
defibrillation— interrupts chaotic twitching, giving heart “clean slate” to start regular, normal depolarization
_________ events always follow the electrical events
mechanical
mechanical events always follow the ____________ events
electrical
systole
periods of contraction and emptying of the heart’s chambers; right after QRS complex for ventricles
heart spends _______ time in systole (fraction)
1/3
diastole
periods of relaxation and filling of the heart’s chambers; for atria, occurs during QRS (can’t see it), for ventricles, occurs right after T wave
what ions are moving during repolarization of cardiac pacemaker cell?
Ca2+ channels are inactivated and K+ channels open, allowing K+ efflux
changes in patterns or timing of ______ may reveal diseased or damaged heart/problems with heart’s conduction system
ECG
enlarged R waves may indicate:
enlarged ventricles
elevated/depressed S-T segment indicates:
cardiac ischemia
prolonged Q-T interval reveals:
abnormality that increases risk of ventricular arrhythmias
cardiac cycle
all events associated with blood flow through the heart during one complete heart beat
the cardiac cycle is marked by a succession of ____________ and _____________ changes within the heart’s chambers
pressure/volume
3 phases of the cardiac cycle
ventricular filling (mid-late diastole)
ventricular systole (atrial diastole)
isovolumetric relaxation (early diastole)
describe phase 1 of the cardiac cycle: ventricular filling
blood is returning from circulation, flowing passively from atria through open AV valves into ventricles; aortic and pulmonary valves are closed, atrial systole occurs (P wave), atria contract —> pushing blood up into ventricles; ventricles are in diastole and filled to their maximal volume
describe phase 2 of the cardiac cycle: ventricular systole
atria relax, ventricles begin to contract (QRS complex), ventricular pressure rises rapidly as myocardium begins to contract & close the AV valves; constant blood volume
describe the movement of ions during the plateau phase of contractile cardiac muscle cell AP
slow Ca2+ influx through slow Ca2+ channels, most K+ channels closed (cell is depolarized)
describe phase 2 of the cardiac cycle: isovolumetric relaxation
ventricles relax (T wave), ventricular pressure decreases rapidly, blood flows back into pulmonary valve and aorta, passive filling begins in ventricles (restarts phase 1)
end systolic volume
blood that remains in the ventricles after contraction
muscle tension develops during the ___________ and peaks just after the _________ ends
plateau x 2