Bio Test 3 (A1.1, B1.1, B1.2, C1.1)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
why is carbon the backbone of life?
--> can form 4 single covalent bonds4 e- in valence shell
4 bonds w other elements makes up all 4 macromolecules…
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
monomers <--> polymer transformation
—> monomers join w/ other molecules to form polymers
monomer --> polymer =
condensation(OH+H = H2O)
polymer --> monomer =
hydrolysis(H2O --> OH + H
Monomers, Polymers and Macromolecules
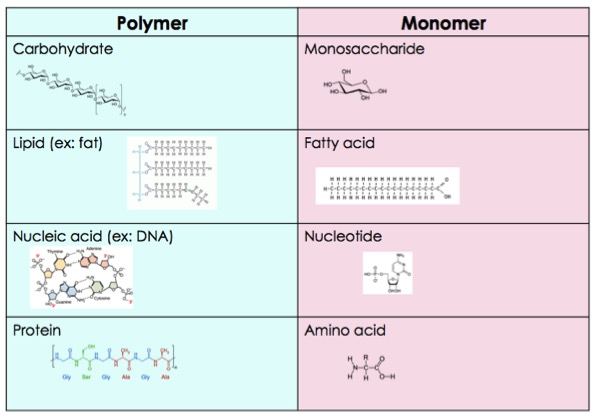
Mono vs Di vs Poly saccharides
Carbs are defined by amt of carbons
has same ratio of h and o as water (2:1)
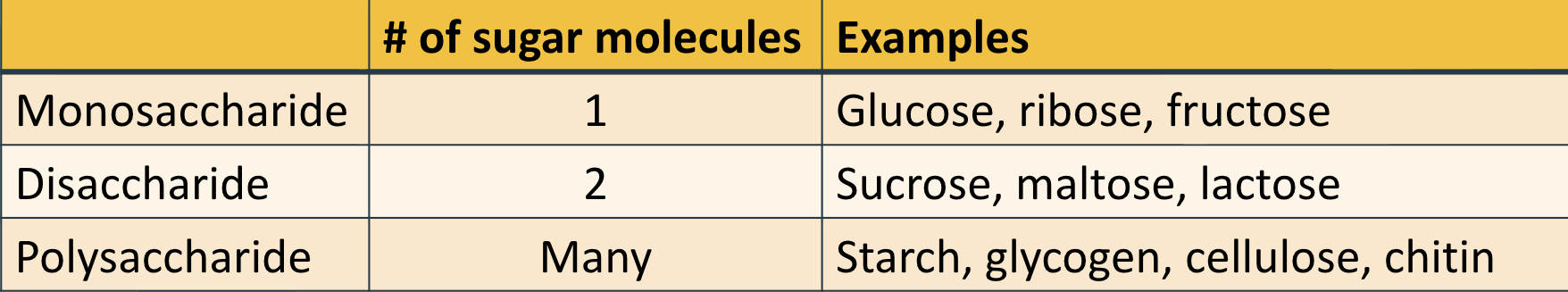
Pentose: ribose vs. deoxyribose
ribose → OH
THE 2nd CARBON FROM THE O IS BONDED TO OXYGEN (OH)
deoxyribose → H
THE 2nd CARBON FROM THE O IS NOT BONDED TO OXYGEN (just H)
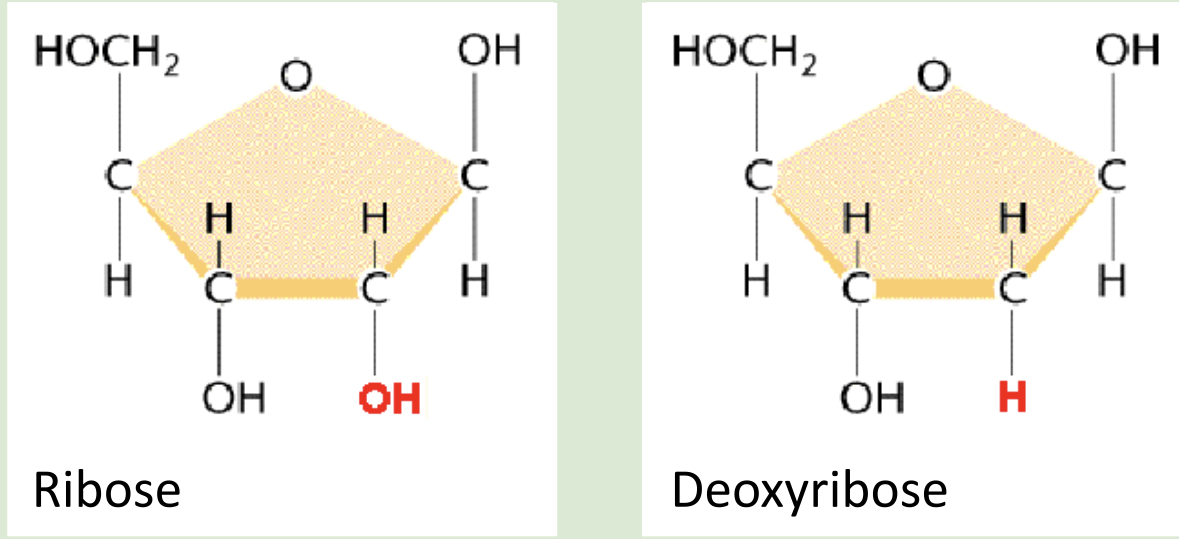
hexose: alpha glucose vs beta glucose
Alpha → H on top
THE 1st CARBON IS BONDED TO H ON TOP
Beta → H on bottom
THE 1st CARBON IS BONDED TO H ON THE BOTTOM
Properties of Glucose
transportability
soluble in water
chemical stability
energy yield
main energy source of respiration
starch composition
starch in plants stores energy
made of 2 polysaccharides
amylose
made of alpha-glucose chain, 1c - 4c bonds (STRAIGHT)
amylopectin
made of alpha-glucose chain, 1c - 4c AND 1c - 6c bonds (BENT) every 20 glucose molecule
glycogen composition & function
polysaccharide, short term energy storage in animals
alpha-glucose chain, 1c - 4c bonds
ALSO has many 1c - 6c branches
is insoluble due to many branches & coiling during polymerization
glucose is stored as glycogen
cellulose composition
polysaccharide, found in cell wall of plants
beta-glucose chain, only 1c - 4c
every other glucose molecule is flipped to have straight bonds
cellulose microfibrils
cellulose molecules group up to form cellulose microfibrils, which are held together by hydrogen bonds
glycoproteins are also known as…
ABO antigens on red blood cells
antigen —> the one present
antibodies —> the ones not recognized
lipids composition & types
have hydrocarbon chains
all are non polar
triglycerides (fats/oils)
steroids
phospholipids
waxes
triglyceride composition & function
1 glycerol
3 fatty acids
(3 OH, 3 reactions can occur)
energy storage (2x more than carbohydrates)
energy stored in bonds of HC chain
insulation for cold climates
fat (triglycerides) is stored in adipose tissue
phospholipids compostion
phosphate, bonded to glycerol, bonded to 2 fatty acids
fats and oils composition
fats and oils are triglycerides
fats
high melting points
solid at room temperature
usually saturated
long term energy storage in animals
oils
low melting points
liquid at room temperature
usually unsaturated
long term energy storage in plants/fish
fatty acid composition
carboxyl (COOH)
hydrocarbon chain
methyl group (CH3)
saturated vs unsaturated fats
saturated —> straight, hydrocarbon chain has single bonds only
unsaturated —> bent, hydrocarbon chain has double bond
steroids composition
4 fused rings = steroid
hydrophobic
can diffuse directly into the bilayer
oestradiol & testosterone = steroid testosterone