307 (Exam 2) Nurs 307 ch 23: Musculoskeletal System
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
what are the functions of the musculoskeletal system?
1. support
2. movement
3. protect
4. produce: rbc, abc, platlets in bone marrow
5 reservoir for essental minerals
fibrous bands from one bone to another that strengthen the joint and prevent unwanted movement
ligament
enclosed fluid filled sac that serves as a cushion
Bursa
Skeletal
Voluntary control
Connected by TENDON to bone
muscle
ROM of the TMJ?
protraction
retraction
open
close
side to side
additionally assess this area for popping and clicking
TMJ
ROM of neck?
flexion, extension, hyper extension, lateral flexion, rotation, shoulder shrug=elevation & depression
ROM of shoulder
flexion, extension, hyperextension, internal rotation, external rotation, abduction, adduction, CIRCUMDUCTION
ROM of elbows
flexion, extension
ROM of the wrists
flexion, extension, hyperextension, radial deviation, ulnar deviation, rotation
ROM of fingers
flexion, extension, abduction, adduction
ROM of the hips
flexion, extension, (hyperextension), abduction, internal rotation, external rotation
ROM of the knees
flexion, extension
ROM of the ankles
plantar flexion, dorsiflexion, inversion, eversion, rotation
ROM of the toes
flexion, extension
ROM of the spine
flexion, extension, hyperextension, lateral flexion, rotation
What Joint has
Bones united by interjacent fibrous tissue or cartilage and do not move. (sutures in skull)?
Fibrous joints
This joint is separated by fibrous cartilage and are SLIGHTLY movable (VERTEBRAE)
Cartilaginous joints
Freely moveable joint separated by one another and enclosed in a cavity lined with synovial membrane that secrets fluid
synovial joints
- articulation of mandible and temporal bone
- can feel it depression anterior to trigs of ear
- permits jaw function of speaking and chewing
TMJ
Hip is an articulation between __________ and _______
acetabulum, head of femur
it permits wide range of motion on many axes
ball and socket
this structure gives more stability for weight bearing function
hip
knee joint is an articulation of which three bones?
femur, tibia, and patella
hinge joint, largest joint in body, permitting flexion and extension of lower leg on a single plane
knee
which synovial membrane is the largest in the body
knee
Two wedge-shape cartilages that cushion tibia and femur
medial and lateral menisci
lateral view shows vertebral column having found curves, a double-S shape
spine
Factors that allow spine to absorb shock
balance or compensatory nature of curves, together with intervertebral disks
Each disk center is composed of soft, semifluid, mucoid material
Nucleus pulposus
- Accounts for 40-50% of body weight
-are under voluntary conscious control
-attached to bone with a tendon
muscles
Flexion?
bending limb at joint
Extension?
straightening limb at a joint
Abduction?
moving limb away from joint
Adduction
moving limb toward joint
pronation
turning forearm so palm is down
Supination?
turning forearm so palm is up
Circumduction
moving arm in circle around shoulder
inversion?
moving sole of foot inward at the ankle
Eversion?
moving sole of foot outward at the ankle
Rotation
moving head around a central axis
protraction?
moving (jaw) forward and parallel to the ground
Retraction?
moving jaw back and parallel to the ground
elevation
raising body part
depression
lowering body part
With history questions of the MUSCLES: ask about location of _____ or ______
pain, cramping
With muscle characteristics: Ask whether the person has any _____ in his or her muscles
weakness
with aging adults, you want to ask about this during subjective HISTORY qustions
new onset weakness
Recommendation for DEXA screening for ______ages ______ and older
females, 65
Ask specific functional assessment of these ADLs
bathing, toileting, dressing, grooming, eating, mobility, communicating
Purpose of of a musculoskeletal examination is to assess function for ______ and _______
ADLs and screen for abnormalities
when prepping for physical examination, Take an orderly approach by:
head to toe, proximal to distal, midline outward
note _____ and ___ of EVERY JOINT
size and contour
inspect skin and tissues over joints for _____,______, and any_______, or ______
color, swelling, masses or deformities
palpate each joint including
-
-
-
-
skin temp
muscles
bony articulation
area of joint capsules
While palpating, notice any:
-
-
-
-
*which signals inflammation
heat
tenderness
swelling
mases
joint fluid is usually????
not palpable
Ask for _____ voluntary ROM, while stabilizing the body area _____ to that being moved
active and proximal
If you see a limitation, gently use ______ rom
passive
Audible and palpable crunching or grating that accompanies movement b/c the articular surfaces in the joints are roughened
Crepitation
true or false: crack, which is heard as a tendon or ligament slipping over the bone during motion as you do a knee bend is the same as crepitation?
false
5/5 muscle strength is
normal
3/5 muscle strength is
movement against gravity ONLY
When asking person to move jaw forward and laterally against your resistance and to open mouth against your resistance, tests which cranial nerve
Cranial never V (trigeminal nerve)
Inspect _____ of head and neck( (c-spine)
alignment
If person can maintain (cervical) flexion against full resistance, this tests for CRANIAL NERVE?
CN XI (SPINAL NERVE)
What movement also test CN XI, SPINAL ACCESSORY NERVE
shoulder shrug
Inspect size and contour of elbow in which two positions?
flexed and extended
palpate elbow flexed about ___ degrees and relaxed
70
acute flexion of wrists for 1 minute produces numbness and burning if positive
Phalen test
What is the most common motion dysfunction found in hip disease?
limitation of abduction of hip while supine
note symmetric levels of
-
-
-
in the hips
iliac crests
gluteal folds
equally sized buttocks
Smooth even gait reflects
-
-
equal leg lengths
functional hip motion
while inspecting the knee check lower leg for:
-
-
-
alignment
knee shape
contour
If swellings observed in the knee, test for ________ and ______ to distinguish soft tissue swelling or increased fluid injoint
Bulge sign
Ballottement of patella
perform ______ to assess for any limitation or prescreens of pain in the knee
ROM
Examining well-worn shoes help asses areas of
wear and accommodation
when assessing muscle strength in ankle/foot, ask the client to maintain ________ and ______ against your resistence
plantar and dorsiflexion
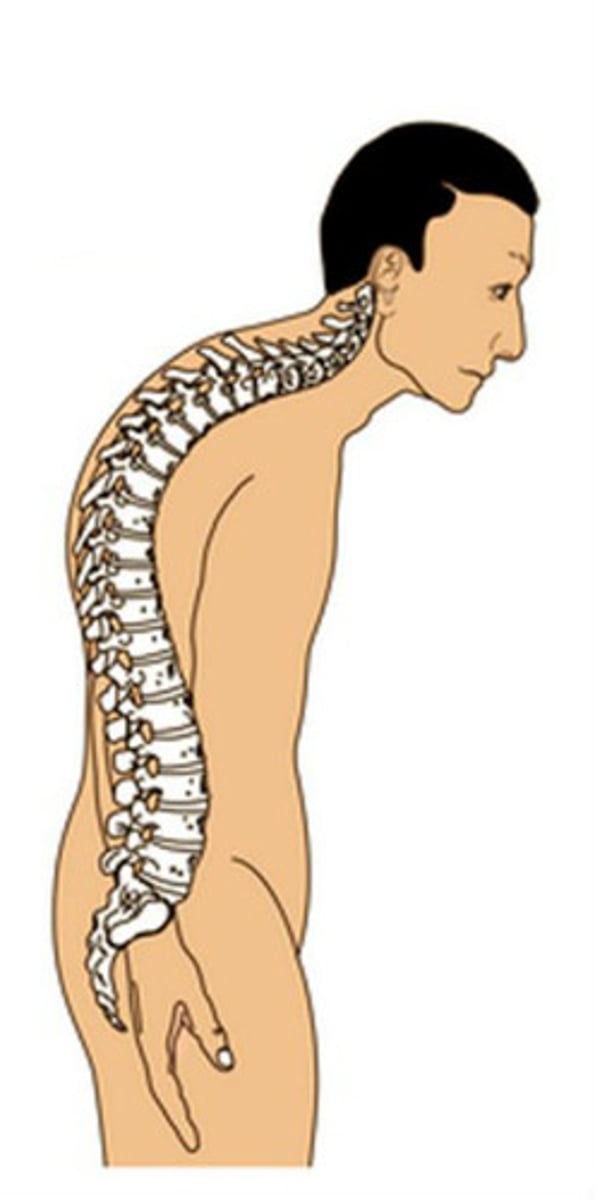
This spinal condition has ENHANCED THORACIC CURVE, usually seen in aging people
Kyphosis
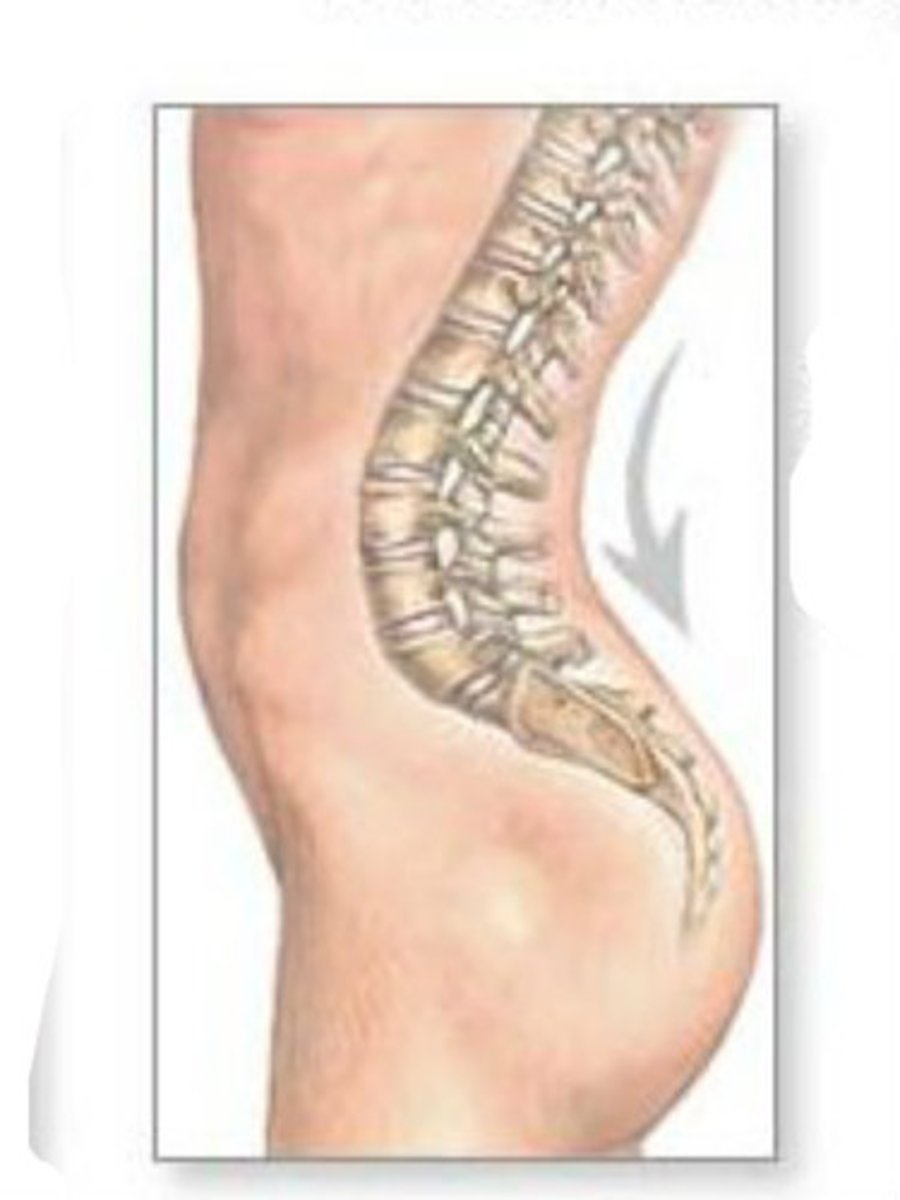
This spinal curve has a PRONOUNCED LUMAR CURVE, normally seen in obese and pregnant people
lordosis
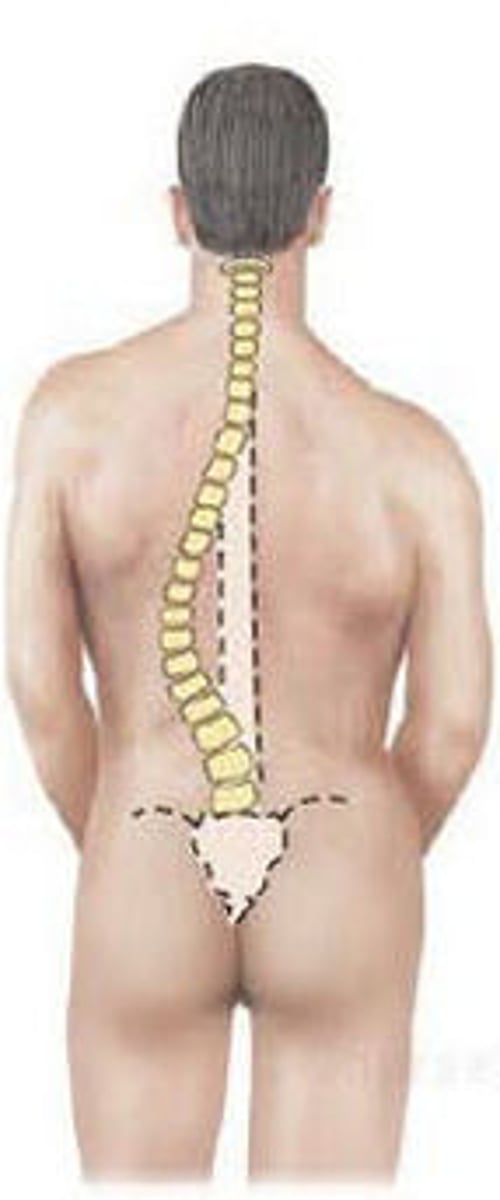
scoliosis
lateral curvature of the spine
kyphosis
curvature of the thoracic spine
lordosis
anterior curvature in the lumbar spine
back(spine) should have ______ curve
single convex C-shaped
While stabilizing pelvis with your hands, check ROM
lateral. bending of ______ degrees
Hyperextension of _____ degrees
Twisting shoulders one side and the other: rotation of _____ degrees
35, 30, 30
Higher Bone mineral density (BMD) =
denser bone
Low BMD indicates
predictor of hip and vertebral fractures
Earlier peak and rapid decline of BMD assoiciated with increase fx affects _______
Caucasian women
pay attention to _______ in adolescences and adults
spinal posture
Which condition of the spine will affect pregnant women leading to increased back strain
lordosis
after age _____, resorption (breakdown,osteoclasts) occurs more rapidly than desposition (new bone formed, osteoblasts)
40
Systemic inflammatory disease of joints surrounding CT
Rheumatoid arthritis
non inflammatory, localized disorder, normally caused by OVERUSE
osteoarthritis
rate of resorption(breakdown) is greater than deposition(bone formation)
osteoporosis
loss of muscle mass
atrophy
Anterior dislocation (95% is exhibited as a hollow where it would normally look rounded
Dislocated shoulder
swelling from excess fluid in the joint capsule
Joint effusion
"hunched" position and limit of abductin of arm
torn rotator cuff
redness, heat, soft, boggy, or FLUCTUANT FULLNESS to palpation and limited ROM
gouty arthritis
curvature of the spine
scoliosis