Ch.5 Pt. 1 Viruses, Prions, and Viral Diseases
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Virion
- extracellular state of a virus
- only capable of infecting a host cell
- consists of >/= 1 molecule of DNA OR RNA enclosed in a coat of protein at min. (nucleocapsid)
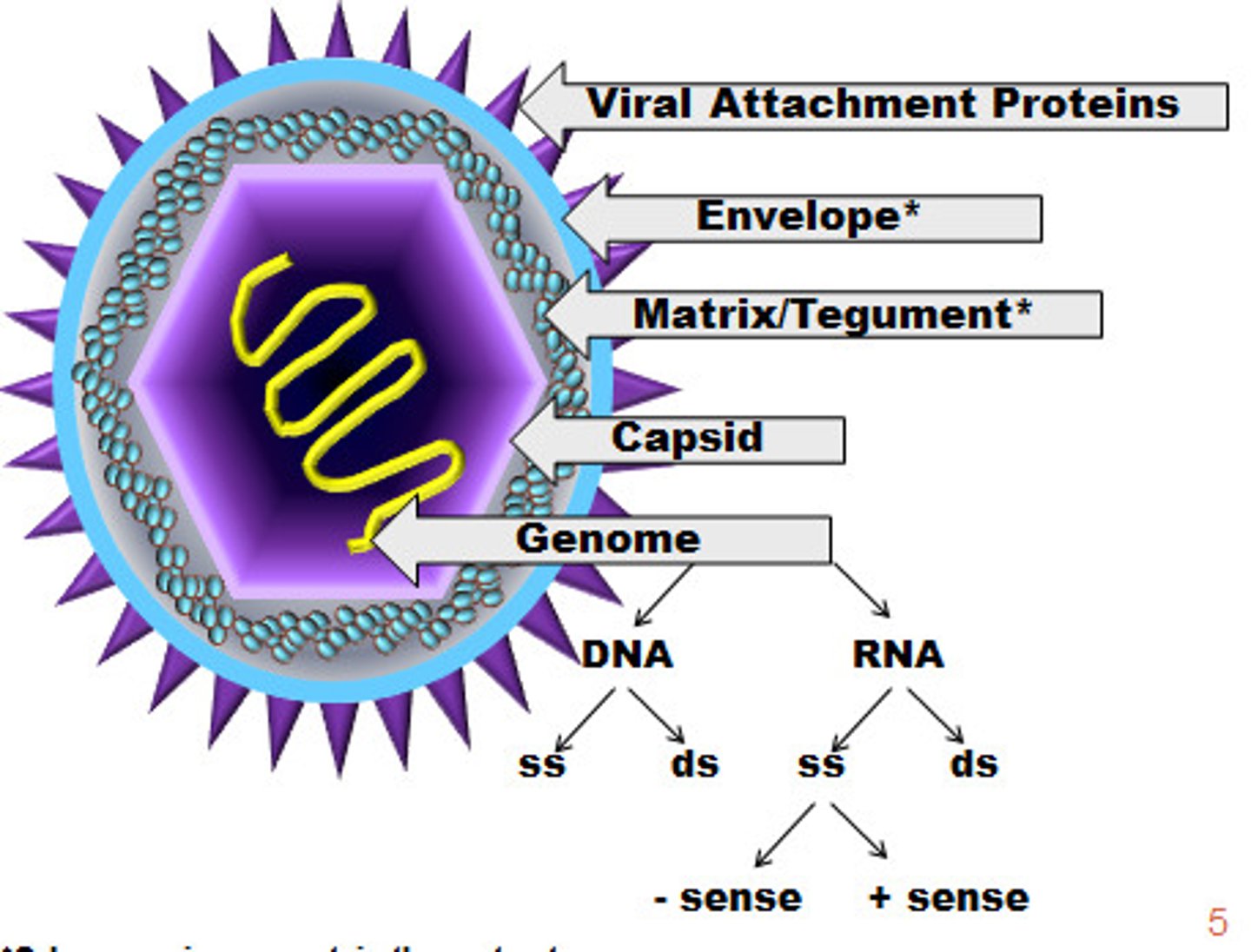
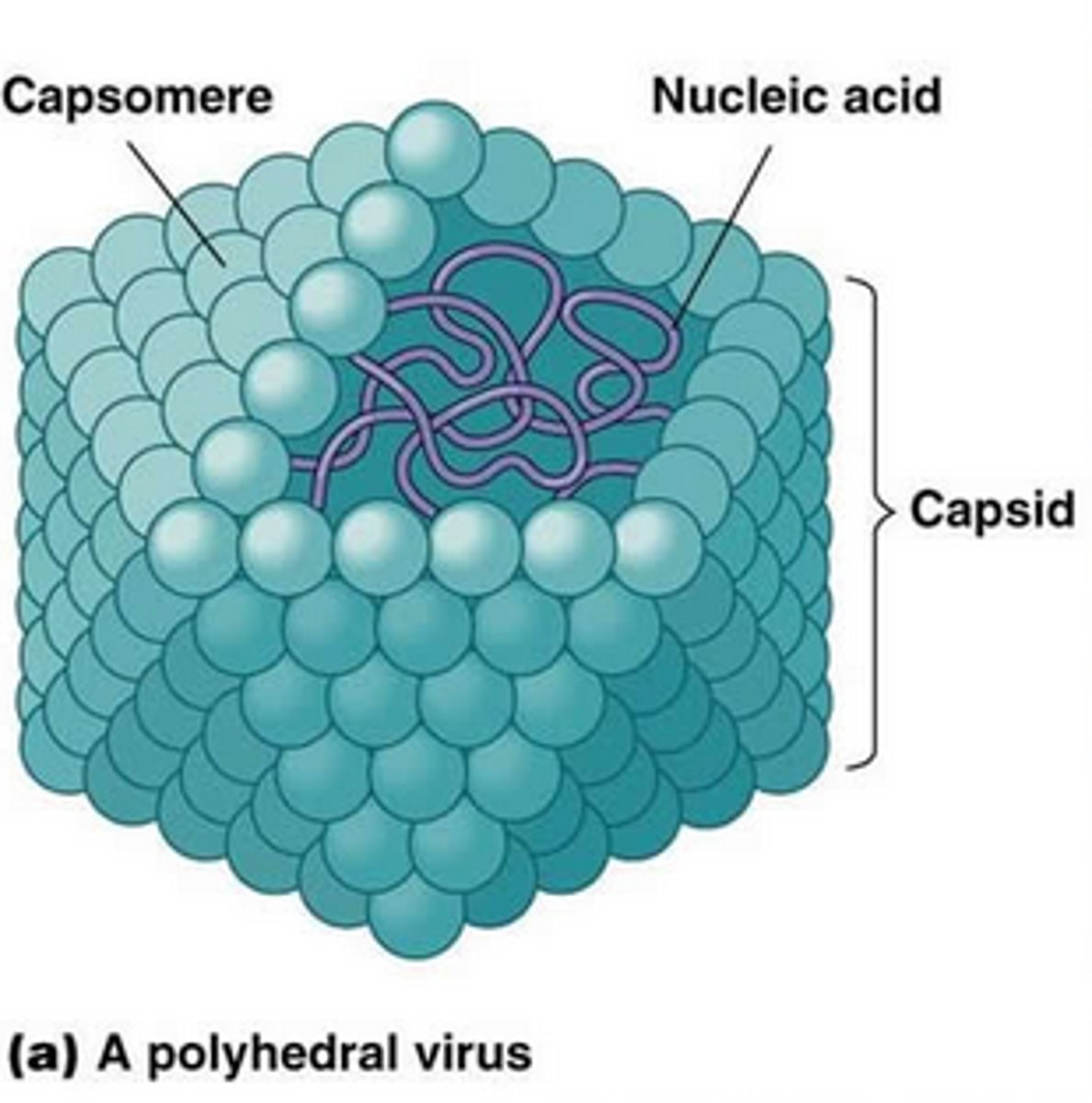
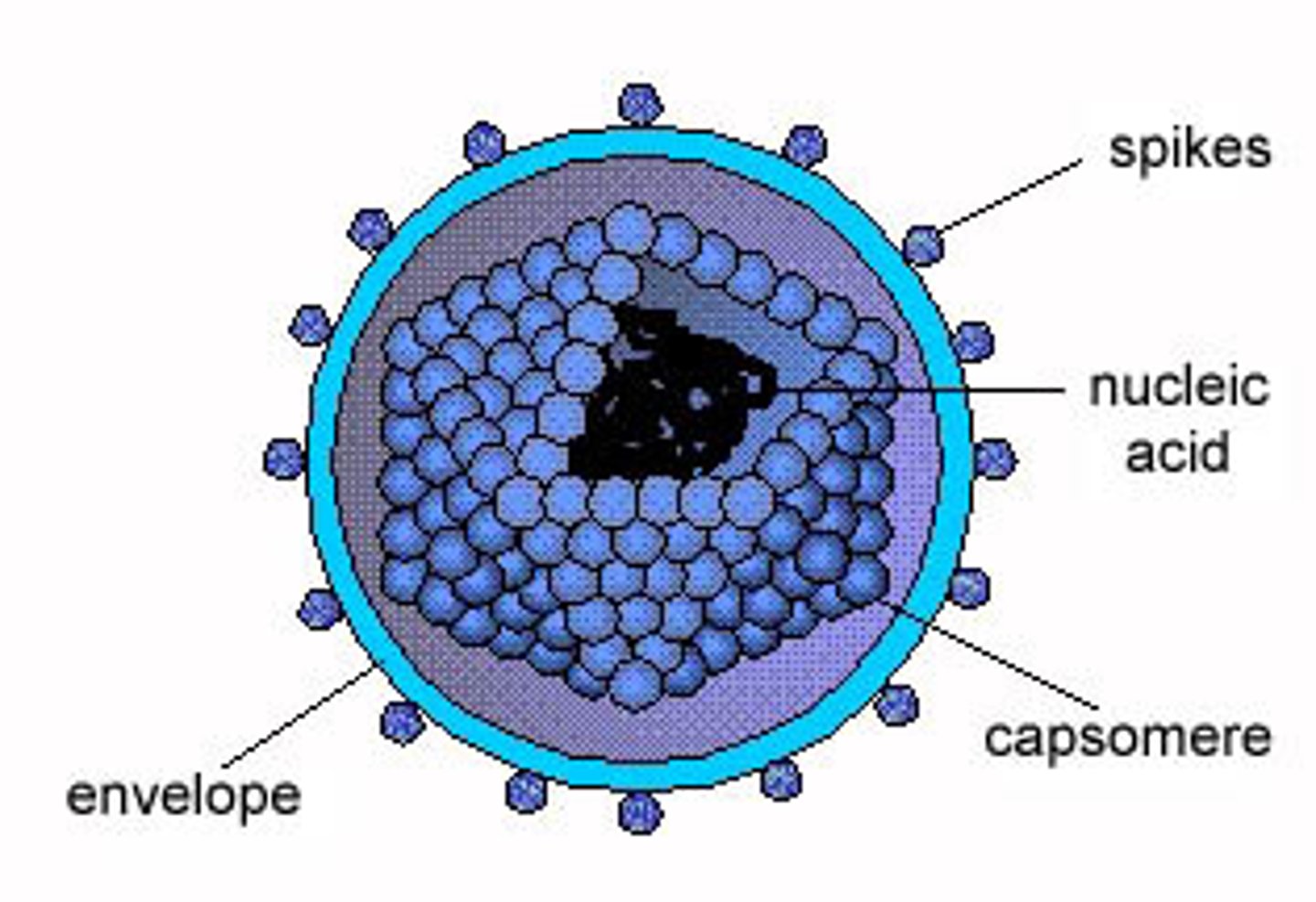
Capsid
a protein coat made up of capsomeres
Nucleocapsid
- nucleic acid (DNA or DNA) surrounded by a protein coat (capsid)
- all viruses have this
Capsomere
protein subunit that makes up the capsid
Spike
- viral proteins that are responsible for host cell specificity (host range)
- they attach a virion to the host cell for infection
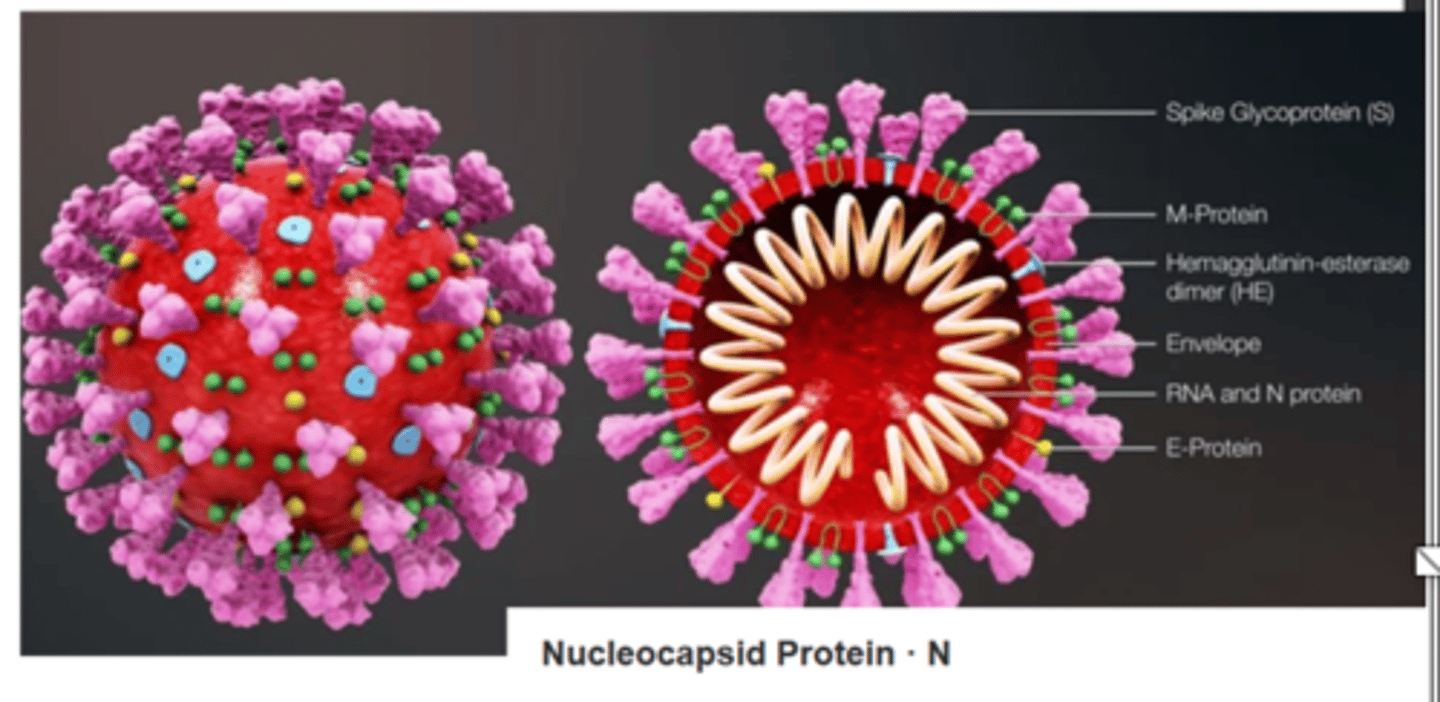
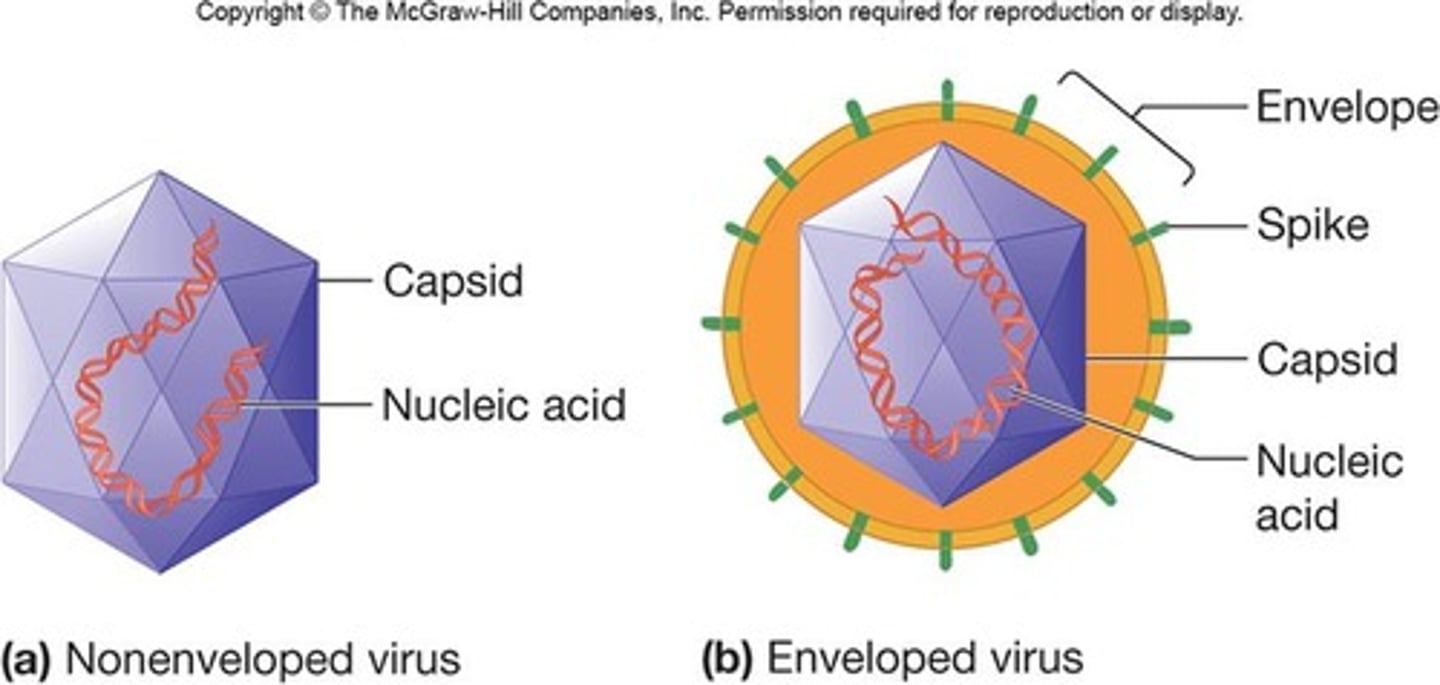
Envelope
- enveloped viruses: virion HAS envelope
- nonenveloped viruses: virion LACKS envelope
Lytic phages (virulent phages)
can ONLY do the lytic cycle
Lysogenic phages (temperate phages)
can do both lytic and lysogenic cycles
Steps in lytic cycle of T4 bacteriohages
attachment > penetration > biosynthesis > maturation > release
Lysogen
a bacterial cell containing a prophage
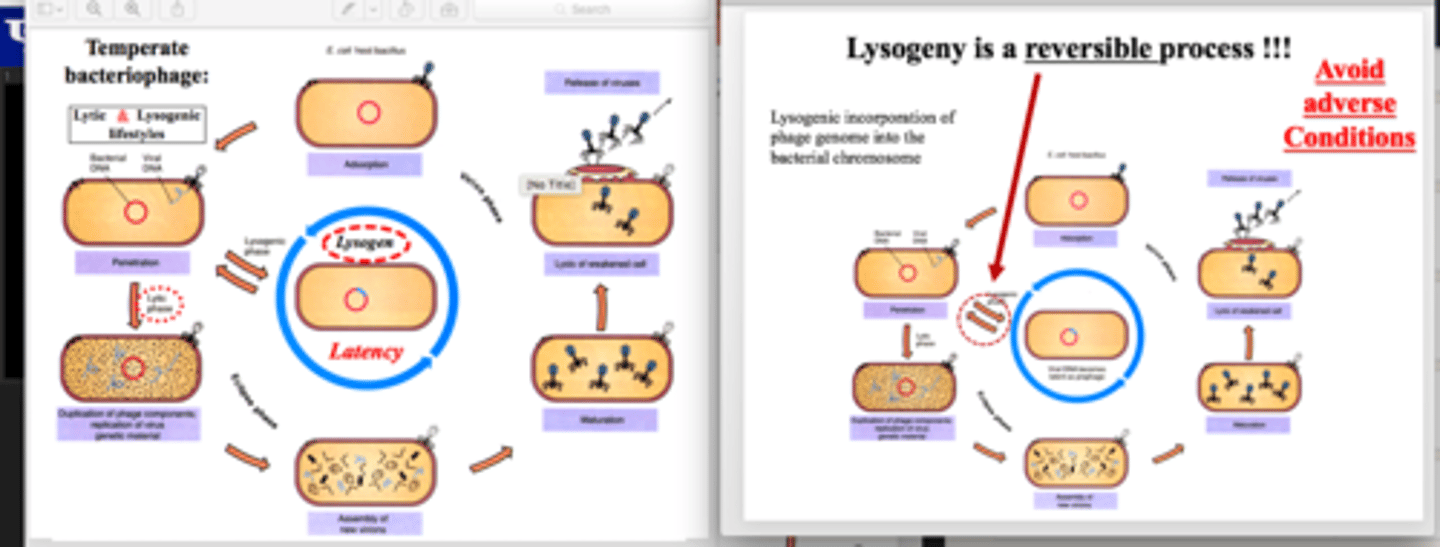
Done by many temperate phages by integration of their genome into the host chromosome in a relationship called...
Lysogeny
Prophage
Phage DNA integrated within a bacterial chromosome
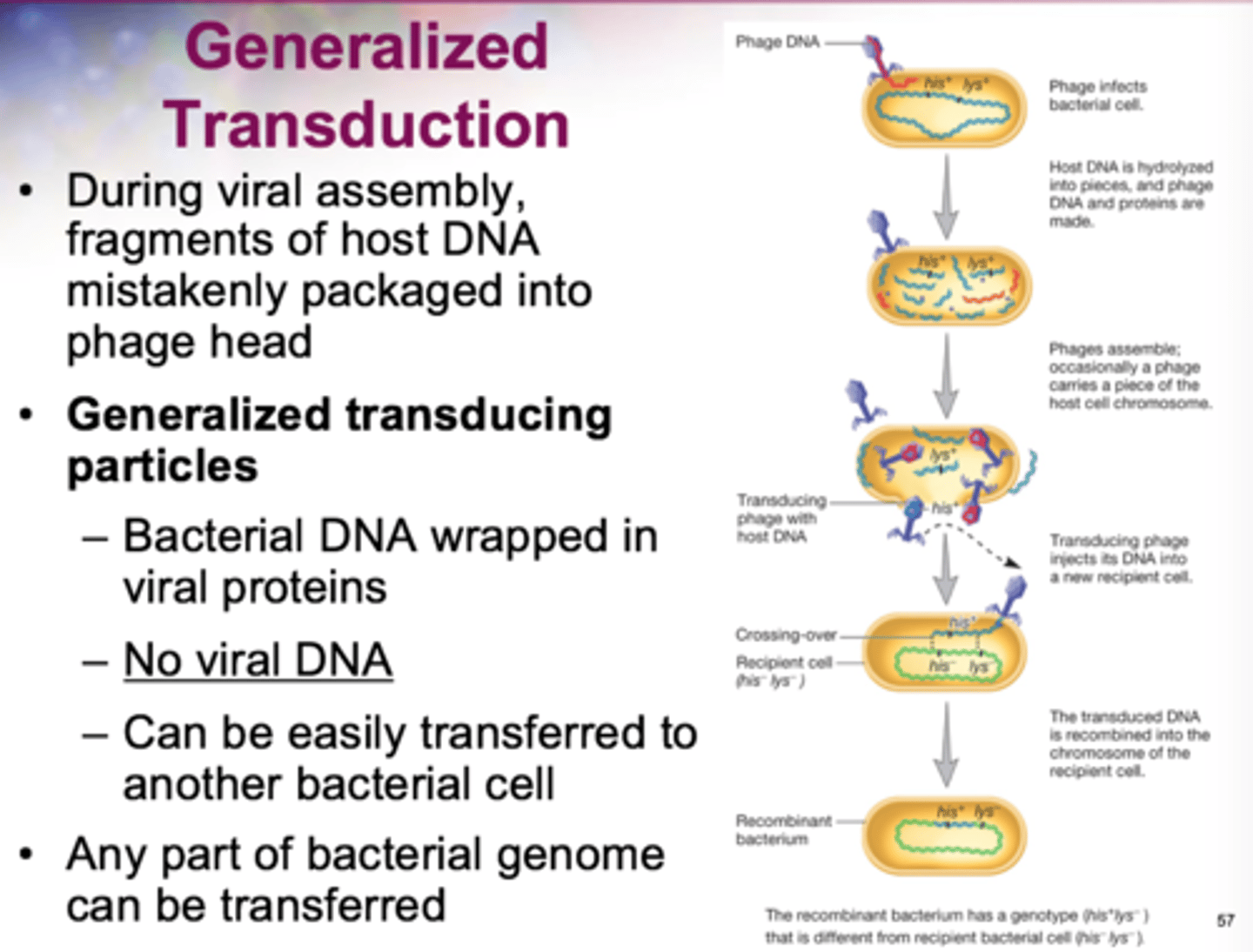
Generalized transduction
associated with the lytic cycle
Lysogenic conversion
when the presence of a propahge causes a phenotypic change for the lysogen, the infected bacterial cell gains new abilities/characteristics from the new genes on the prophage
Attachment
viruses attach to cell membrane
Penetration
- by endocytosis or membrane fusion
- uncoating by viral or host enzymes
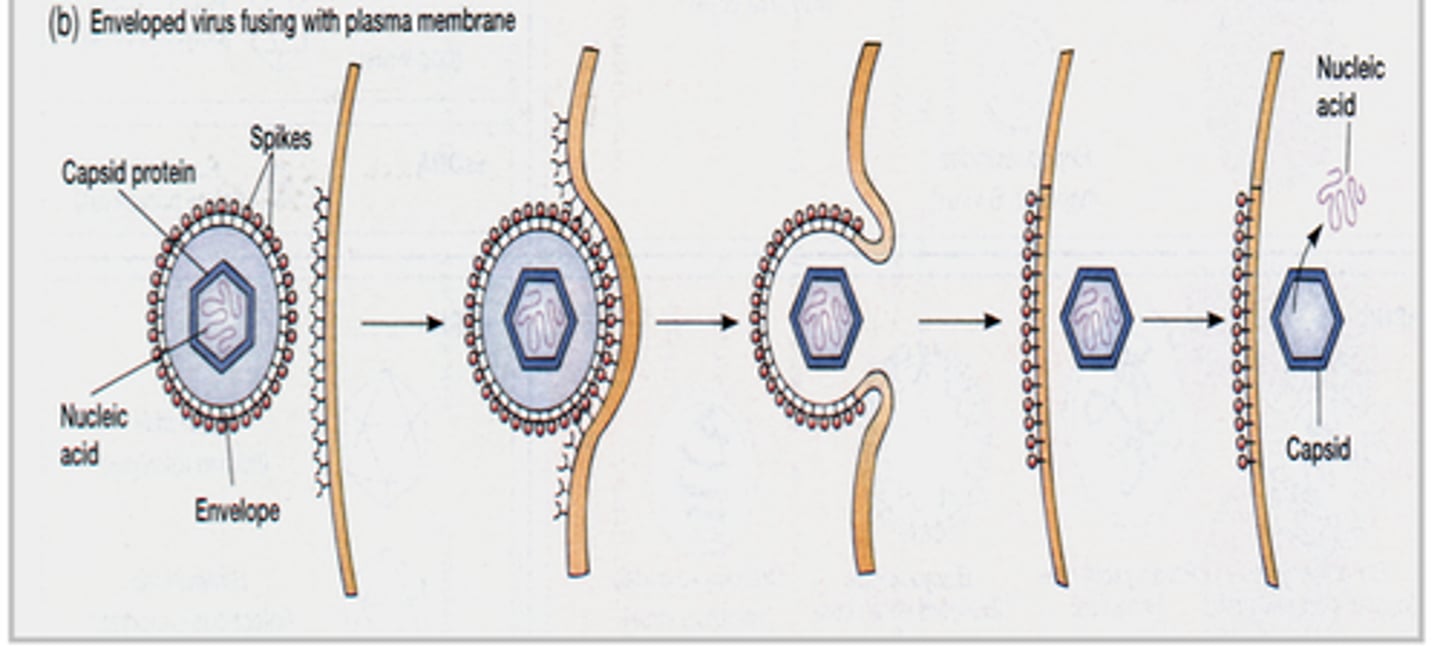
Animal virus penetration by membrane fusion
Fusion occurs btwn the viral envelope and the host cell plasma membrane to release nucleocapsid into the cytoplasm, thus penetration and uncoating both occur at the same time.
- Does not need an additional step
Animal virus penetration by endocytosis
- membrane fusion used for uncoating
- sometimes the envelope of virus can fuse w/ the membrane of the endosome after endocytosis, then the nucleocapsid is released into the cytoplasm (can be stimulated by low pH of endosome)
Uncoating
process of getting the viral genetic info into the cytosol since it will often be in an endosome initially
Biosynthesis
production of nucleic acid and proteins
Maturation
nucleic acid and capsid proteins assemble
Release
by budding (enveloped viruses, most common) or rupture
Most common penetration for animal viruses...
endocytosis + membrane fusion
Most common penetration for bacteriophages
direct penetration (phage DNA injected into host cell)
7 classes of the Baltimore system
1. dsDNA viruses
2. ssDNA viruses
3. dsRNA virsues
4. (+) sense ssRNA viruses
5. (-) sense ssRNA viruses
6. RNA reverse transcribing viruses
7. DNA reverse transcribing viruses
dsDNA examples
- papillomaviridae
- adenoviridae
- hepadnaviridae
- poxviridae
- herpesviridae
+ssRNA examples
- Picornaviridae
- Flaviviridae
- Coronaviridae
-ssRNA examples
- Rhabdoviridae
- Filoviridae
- Orthomyxoviridae
ssRNA retrovrisues examples
- retroviridae
Oncogene
cancer-causing gene
Transformation
activated oncogenes transform normal cells into cancerous cells
Transformed cell
transformed into cancerous cells
Acute viral infections
Virus makes the person acutely ill, and is subsequently cleared from the body by the immune system.
Acute infection examples
- the flu
- colds
Persistent viral infections
Slow production of virions over time; disease processes ocurs over a long time period; often is fatal.
Persistant viral infections examples
- Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (measles virus)
- HIV (AIDS)
Latent viral infections
- virus remains in asymptomatic host cell for long periods
- no virions produced during this phase
- then virus is activated and begins production of new virions
Latent viral infections examples
- cold sores
- shingles
- herpesviruses
DNA viral families
- Papillomaviridae (NE)
- Adenoviridae (NE)
- Hepadnaviridae (E)
- Poxviridae (E)
- Herpesviridae (E)
Papillomaviridae
Nucleic Acid: dsDNA
Enveloped? NE
Examples: Papillomavirus HPV, cervical cancer + warts
Adenoviridae
Nucleic Acid: dsDNA
Enveloped? NE
Examples: respiratory infections in humans (common cold)
Hepadnaviridae
Nucleic Acid: dsDNA
Enveloped? E
Examples: Hep B virus
Herpesviridae
Nucleic Acid: dsDNA
Enveloped? E
Examples: Varicellovirus (HHV-3, Varicella-Zoster virus, causes chickenpox + shingles), many can cause latent viral infections
+ ssRNA viral families
- Picornaviridae
- Flavivirdae
- Coronaviridae
Picornaviridae
Nucleic Acid: + strand
Enveloped? NE
Examples: Rhinovirus (most common cause of the common cold)
Coronaviridae
Nucleic Acid: + strand
Enveloped? E
Examples: Coronavirus: cause respiratory infections (common cold, SARS, MERS, COVID-19
Other RNA viral families
- Orthomyxoviridae
- Retroviridae
Orthomyxoviridae
Nucleic Acid: -ssRNA, multiple strands
Enveloped? E
Examples: Influenzavirus
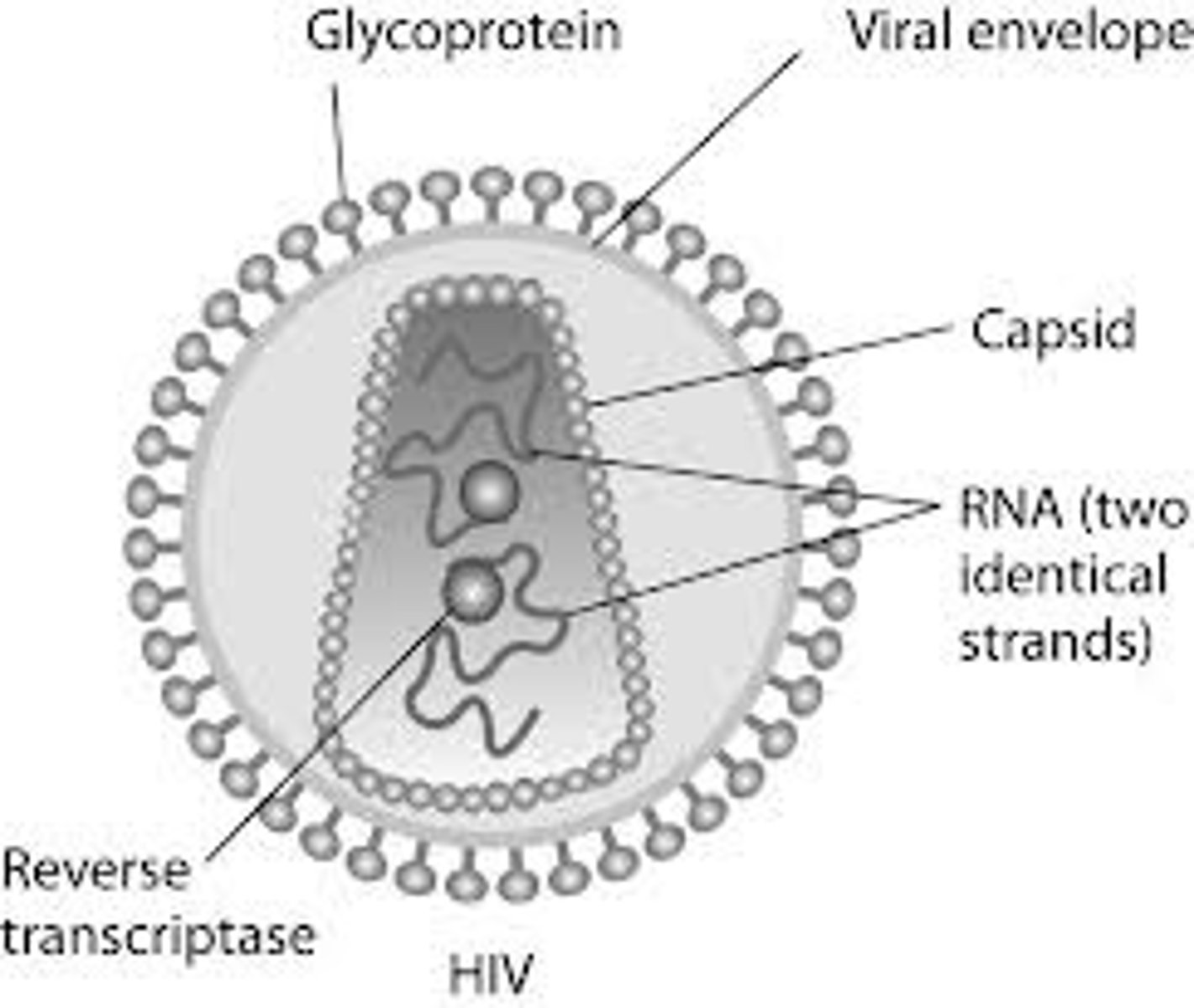
Retroviridae
Nucleic Acid: +ssRNA in virion, dsDNA made in host cell
Enveloped? E
Examples: Lentivirus (HIV)