Lecture 7: Cartilage tissue
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
What type of connective tissue is cartilage?
A specialized type of connective tissue.
What is the composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in cartilage?
High concentrations of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and proteoglycans.
Does cartilage have a vascular supply?***
No, cartilage is avascular.
How do nutrients reach cartilage cells?
By diffusion from the surrounding perichondrium (connective tissue).
Does cartilage have innervation?
No, cartilage has no innervation.
What framework does cartilage provide in the body?
It forms the framework for soft tissues such as the respiratory tract, ears, and nose.
What role does cartilage play within joints?
Provides cushioning and sliding regions with high resiliency and a smooth, lubricated surface.
How does cartilage facilitate bone movements?
Its high resiliency and smooth, lubricated surface allow easy movement of bones.
What developmental role does cartilage serve in long bones?
It guides development of long bones before and after birth as a cartilaginous model in the fetus and infants.
Why does cartilage function as a shock absorber?
Because of its high content of bound water.
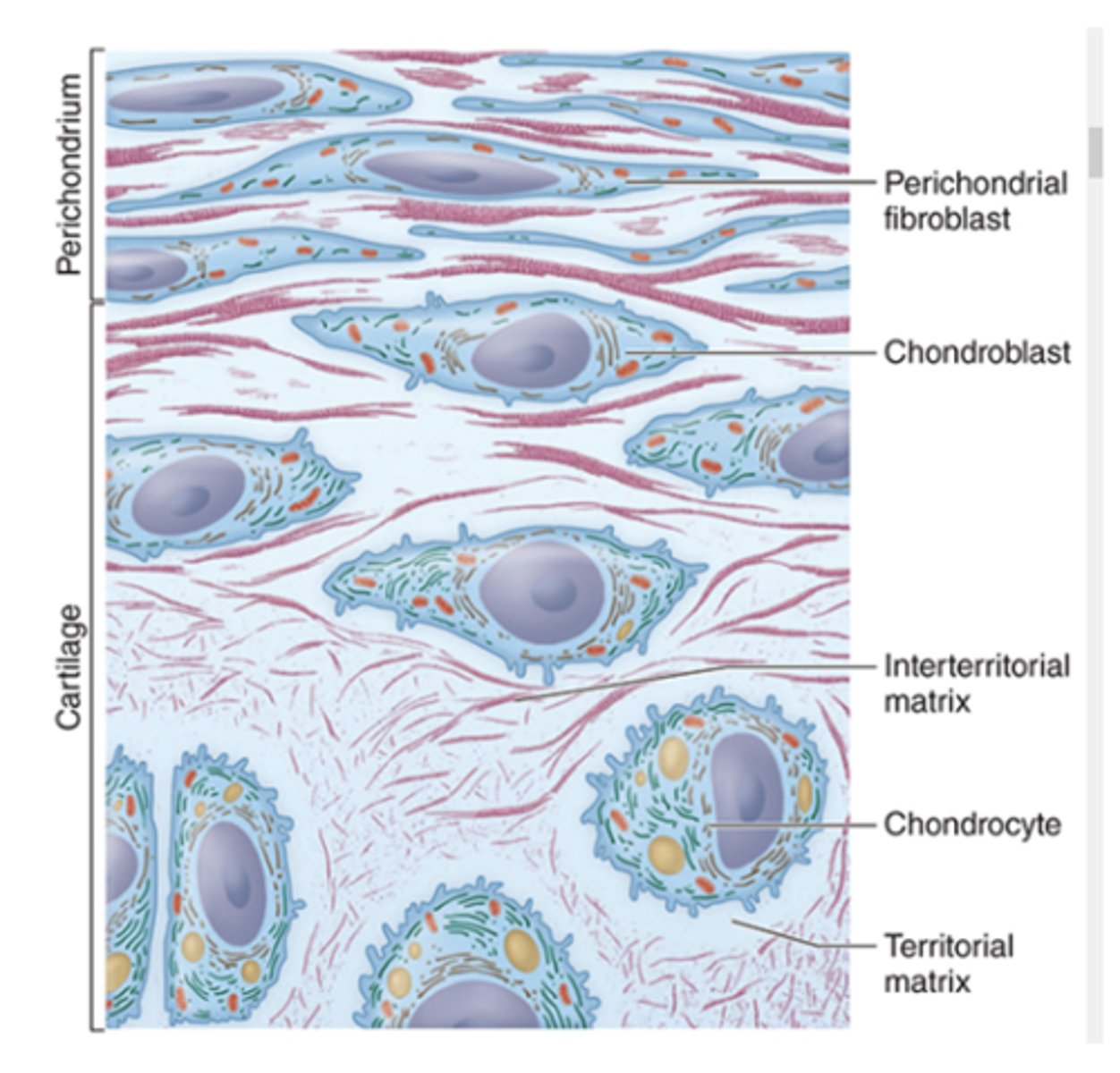
What surrounds cartilage and provides support?
The perichondrium (dense irregular connective tissue).
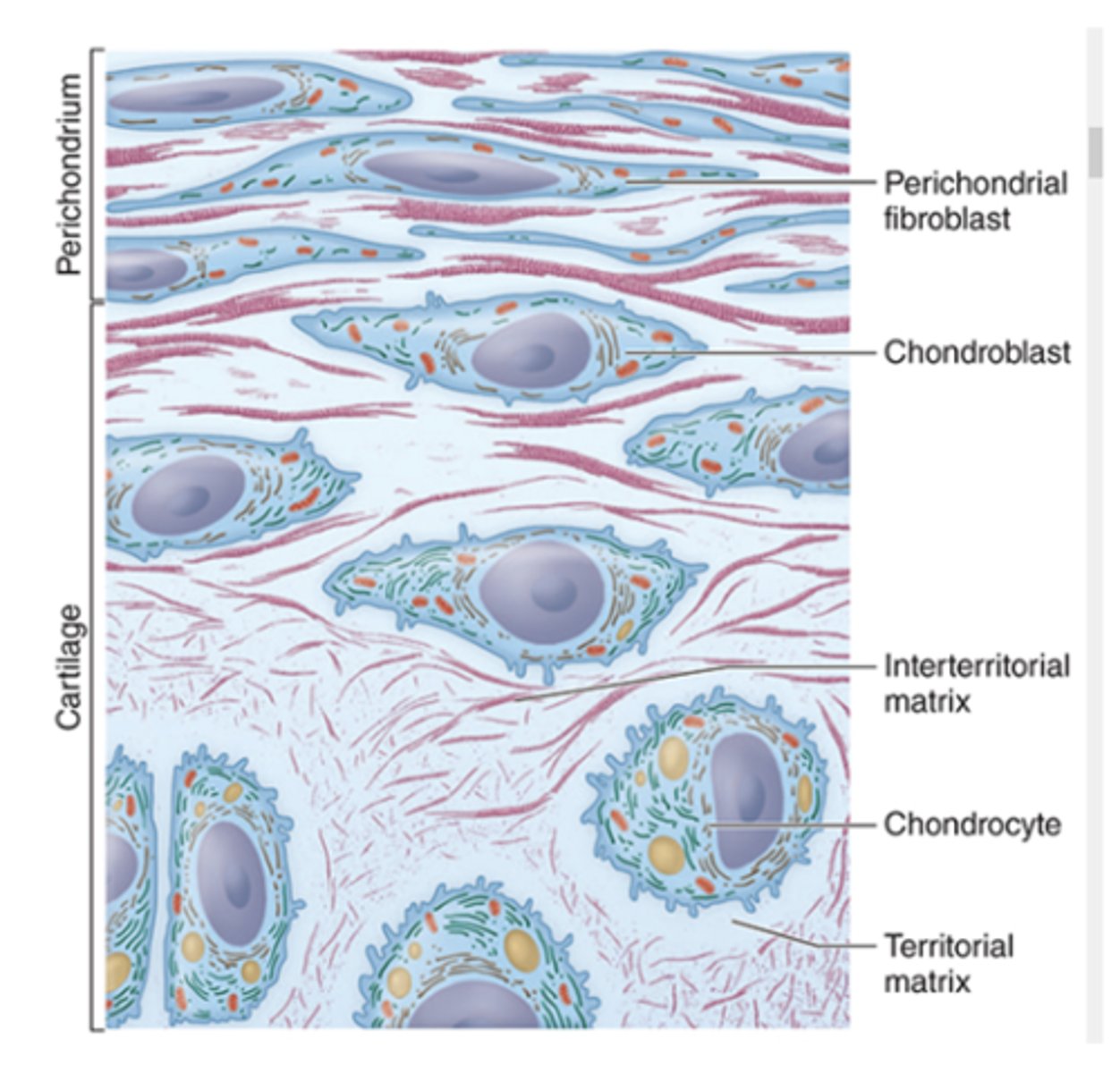
What percentage of cartilage is made up of extracellular matrix (ECM)?
More than 95% of the tissue.
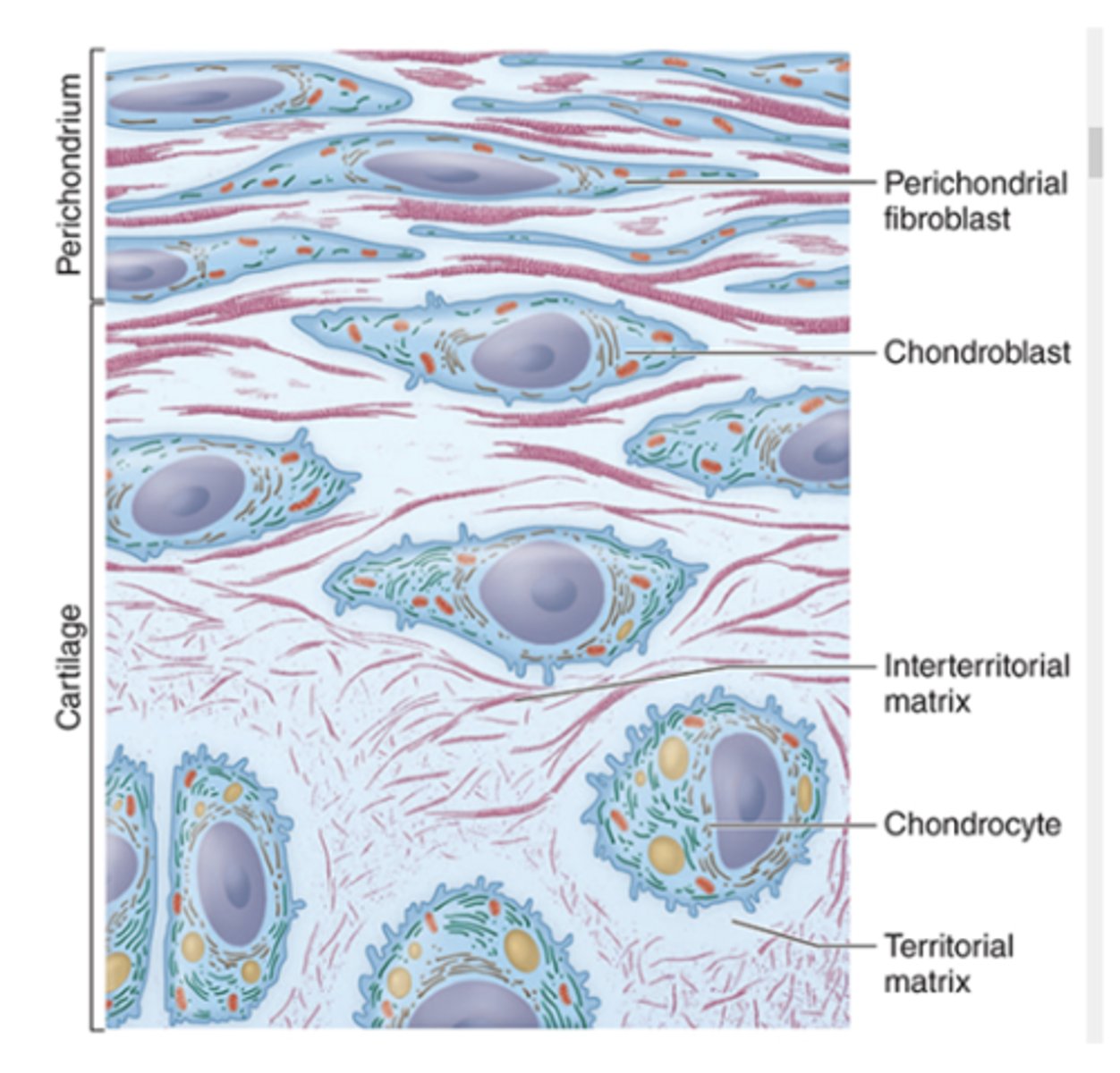
What is the primary collagen type in cartilage ECM?***
Type II collagen.
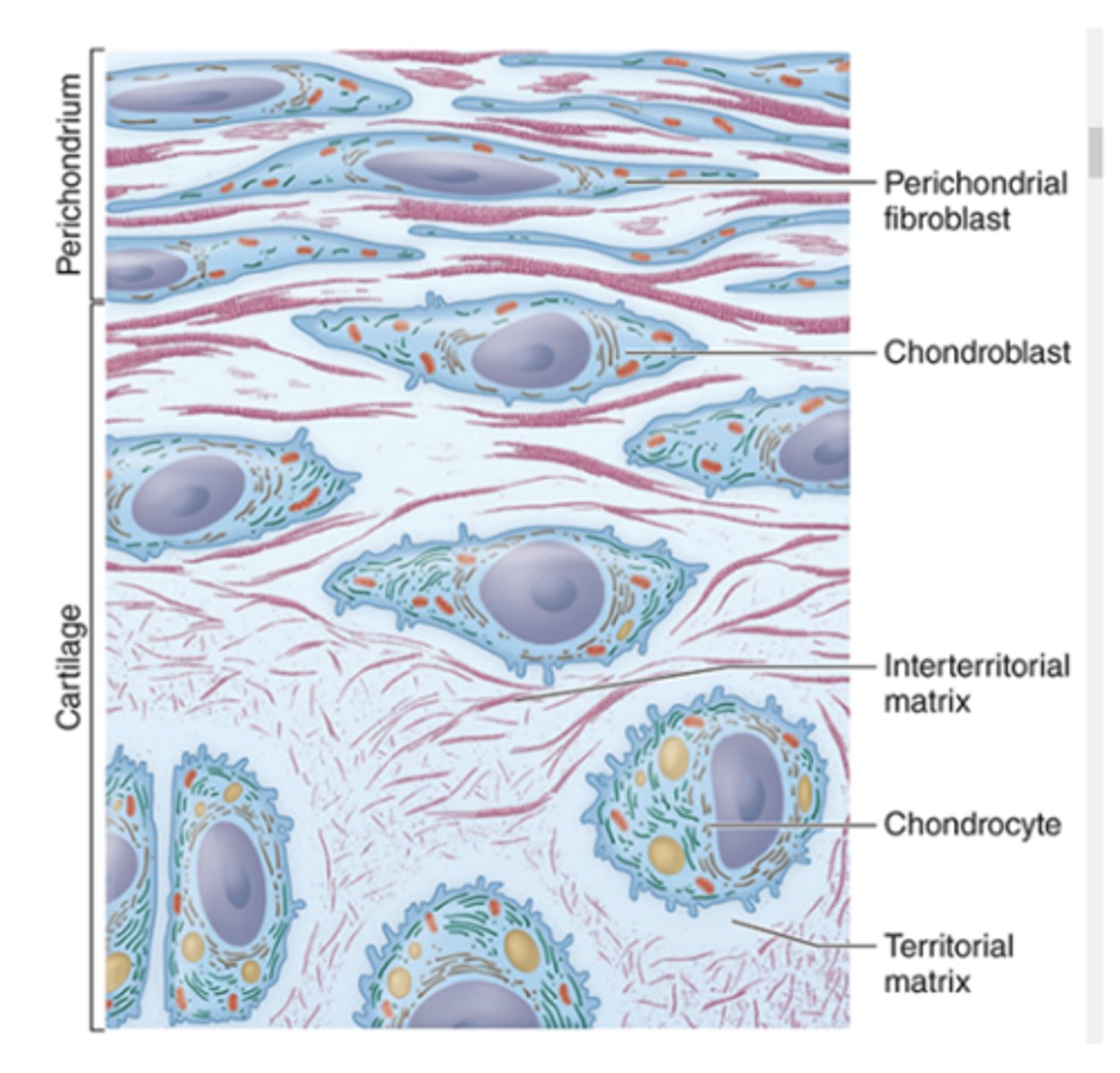
What glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are found in cartilage ECM? (2)
Hyaluronan and sulfated GAGs.
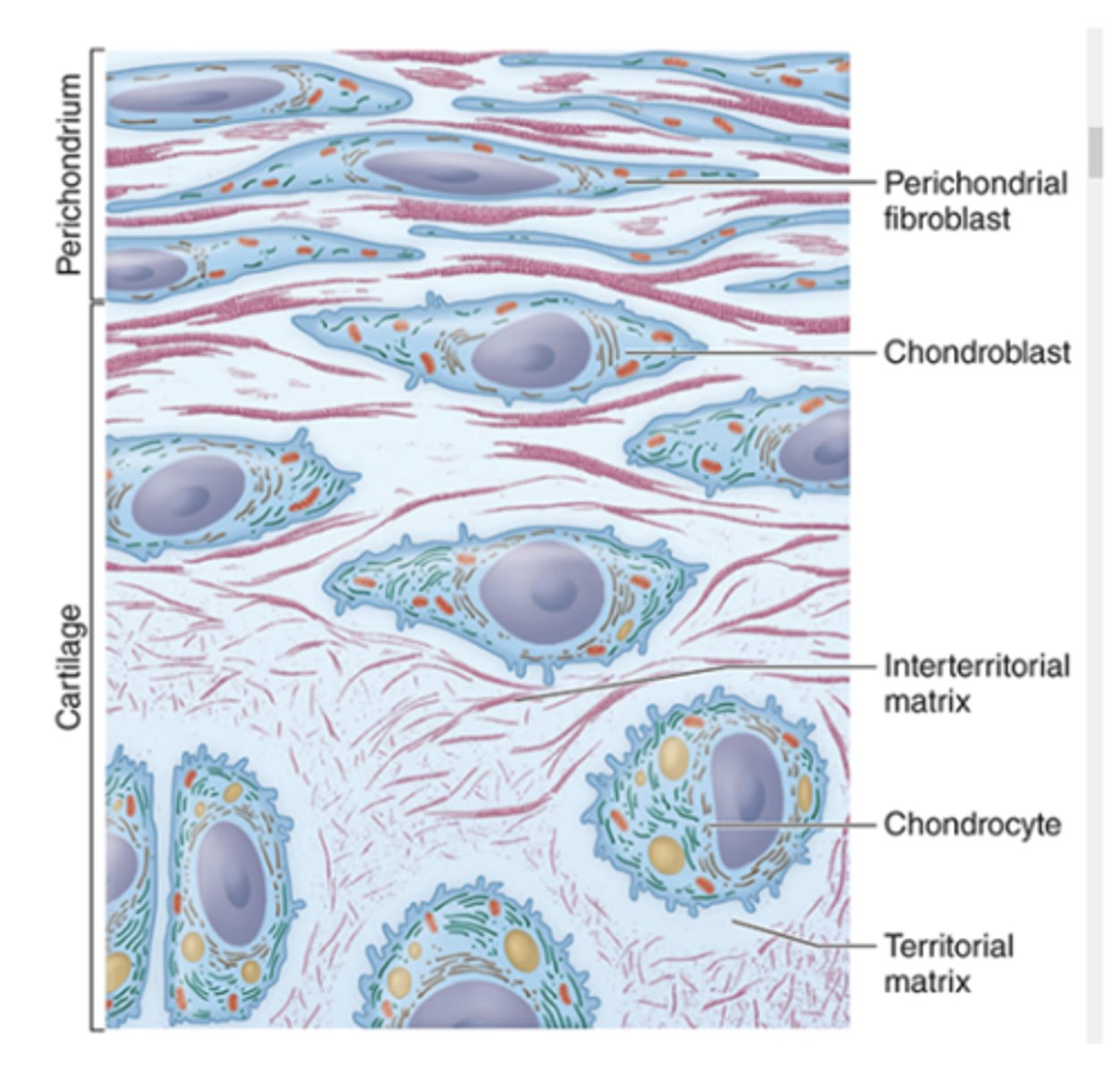
What cells are found in cartilage, and what are their functions? (2)
1. Chondroblasts: synthesize ECM components
2. Chondrocytes: synthesize and maintain ECM components (within lacunae)
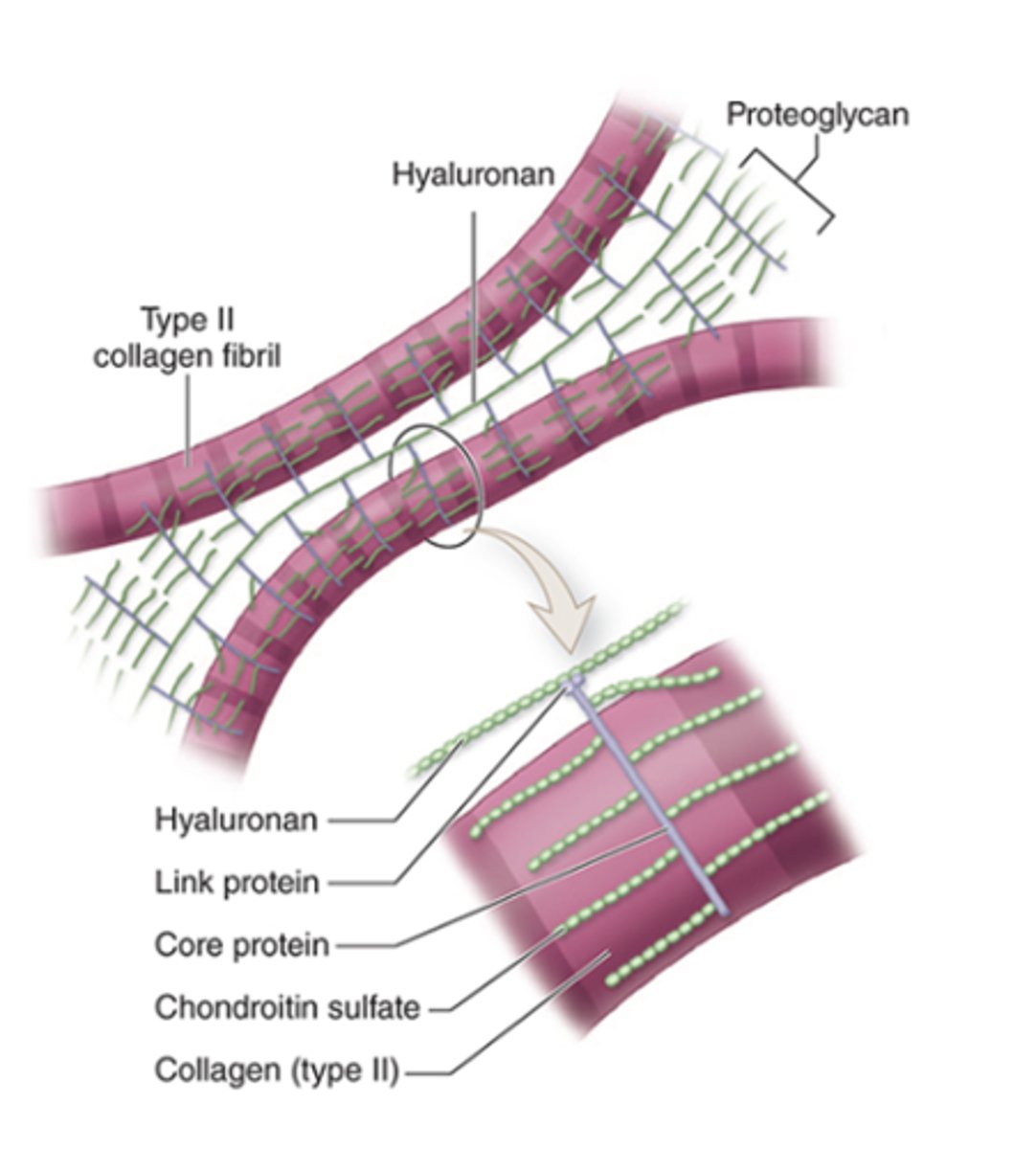
What type of collagen fibrils are found in the ECM of cartilage?***
•Type II collagen fibrils
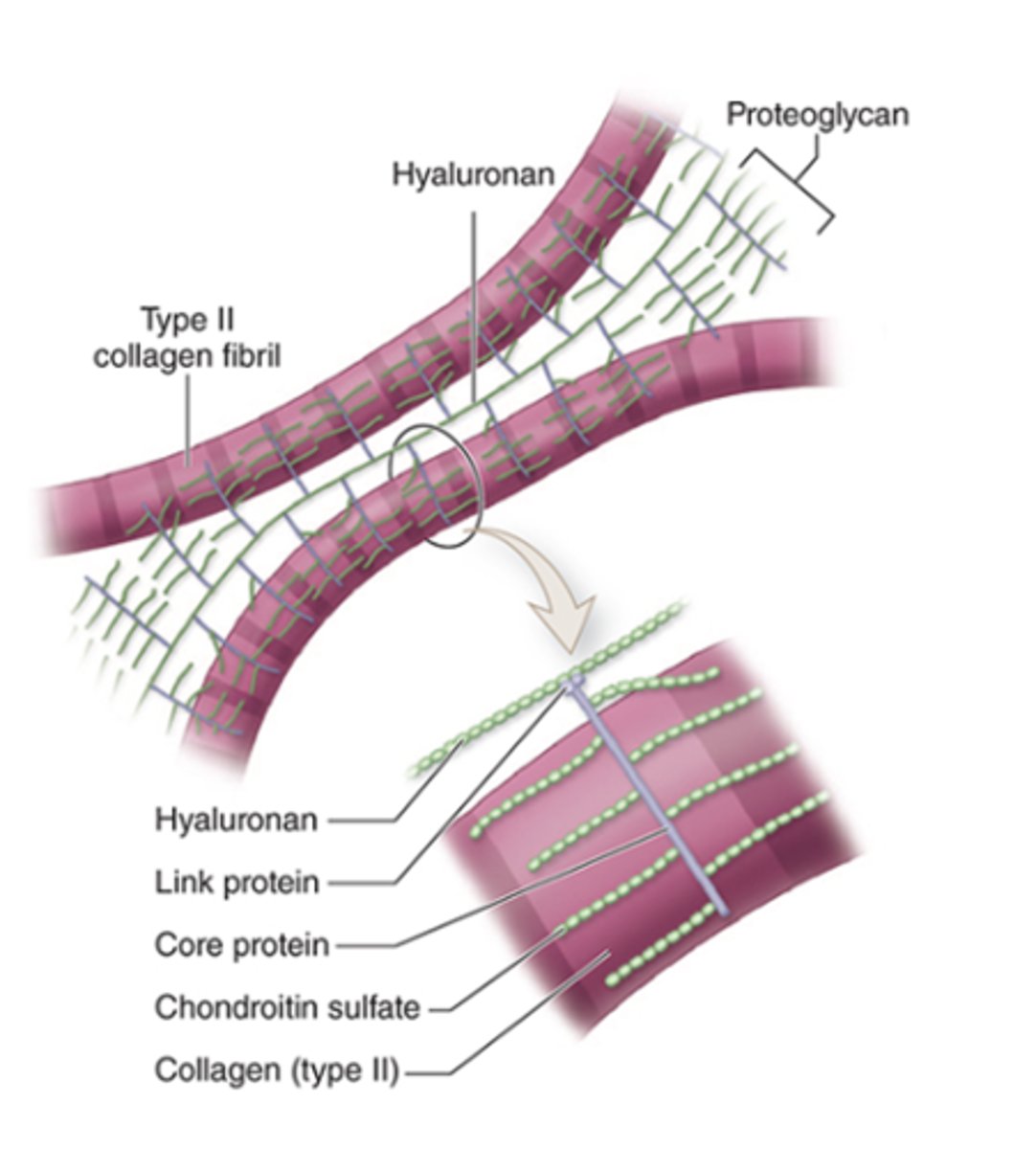
What glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are present in the cartilage ECM?*** (2)
1. Hyaluronan
2. Sulfated GAGs: chondroitin sulfate
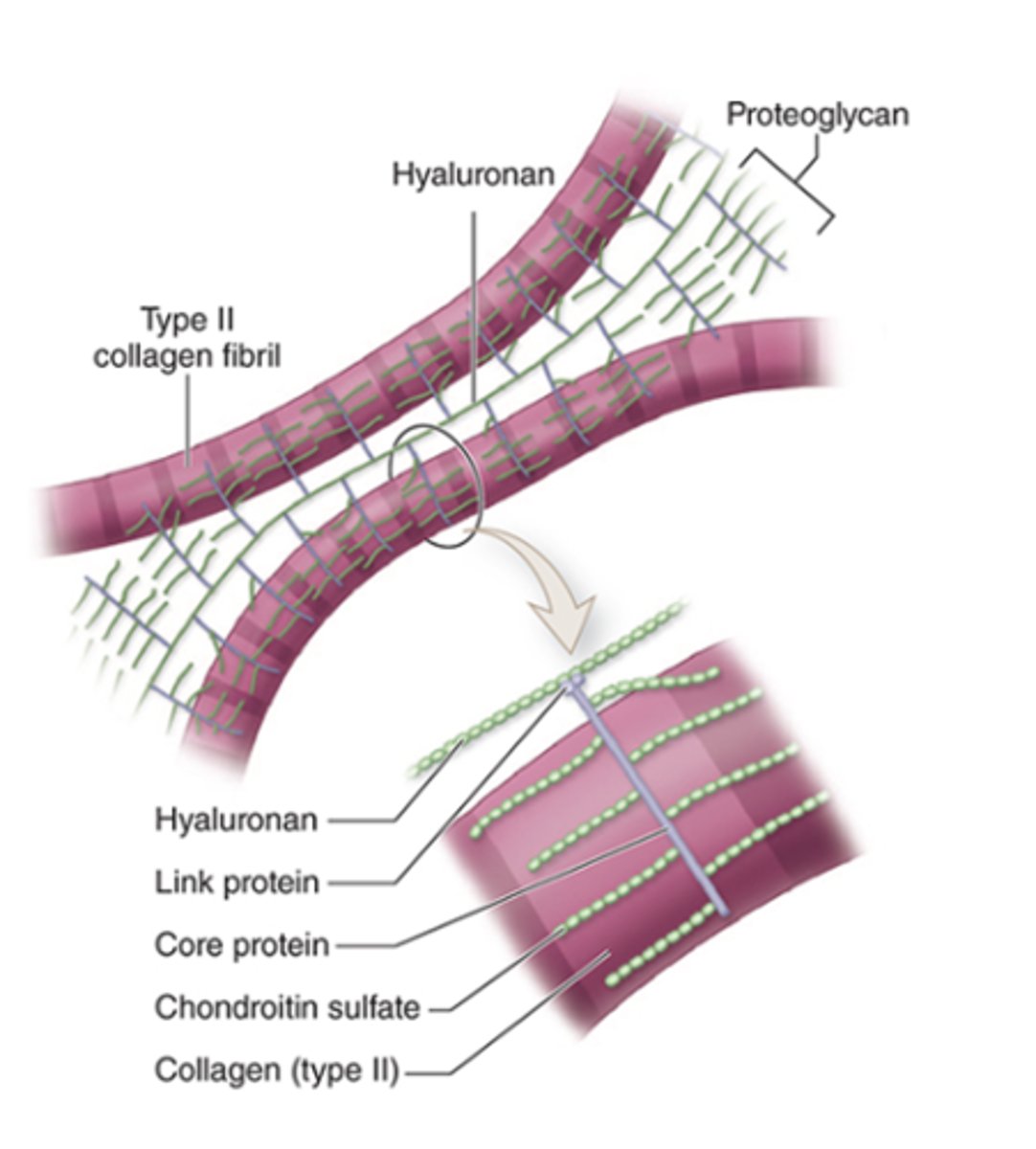
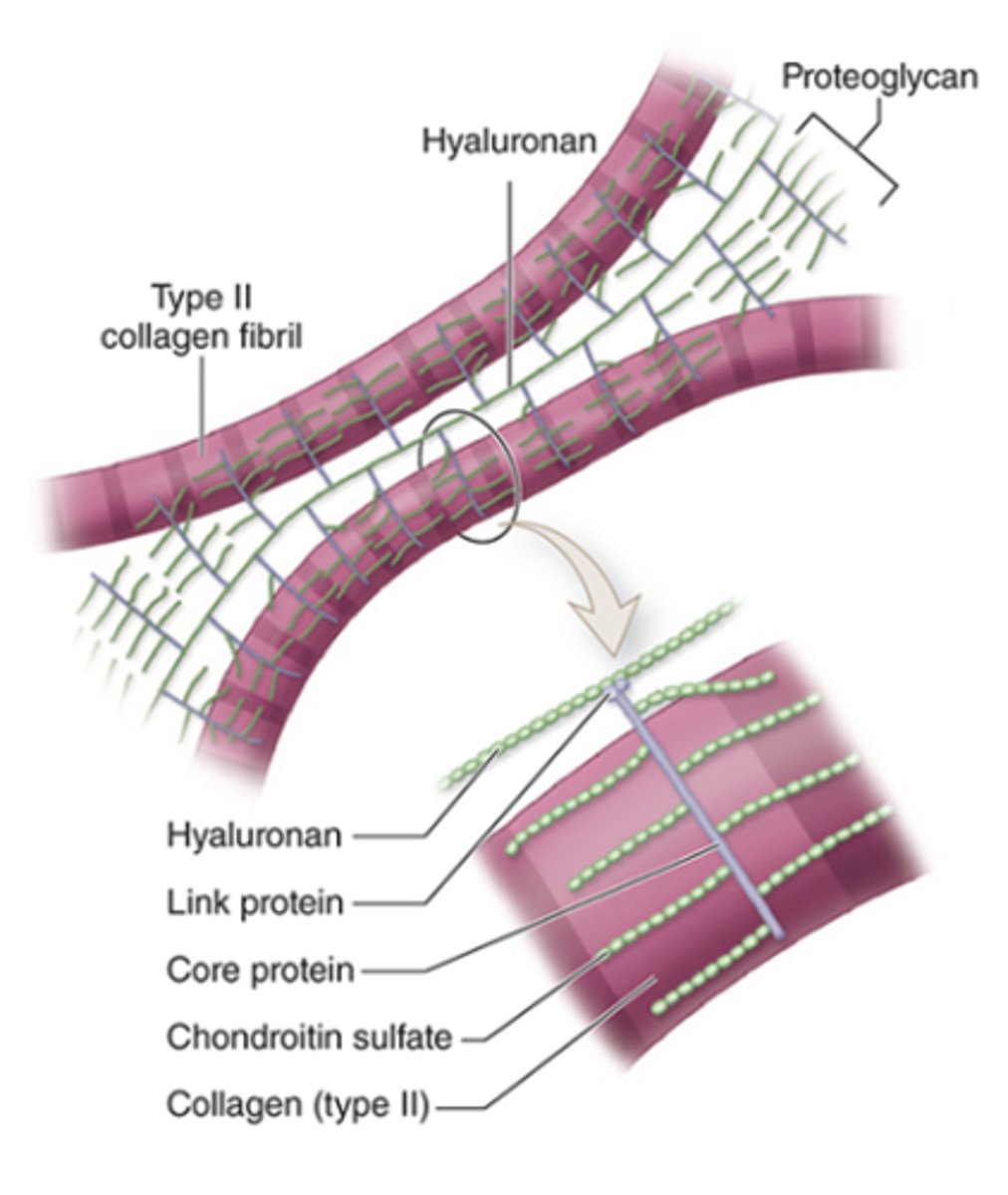
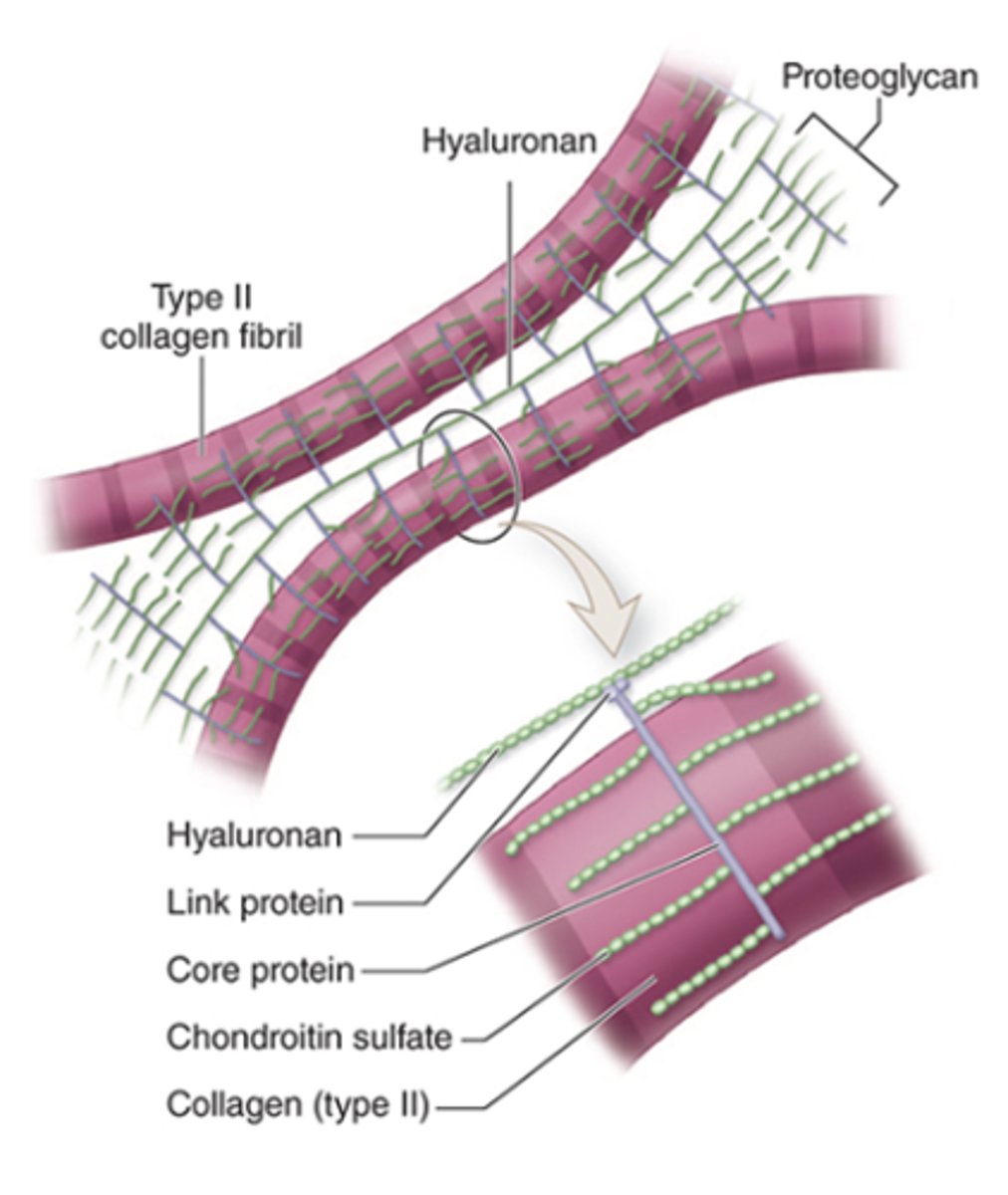
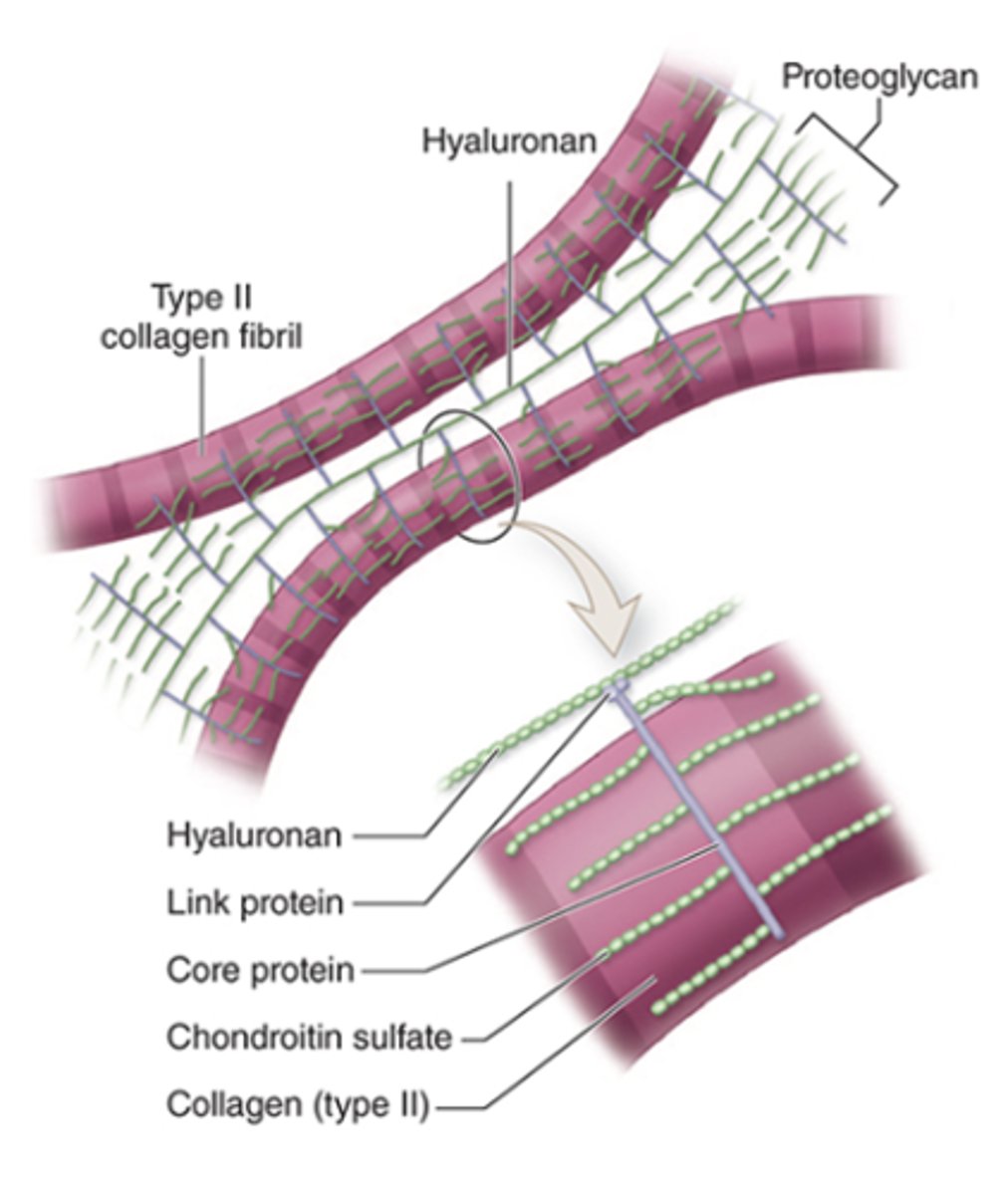
What is the basic structure of proteoglycans in cartilage ECM?
•Core protein and side chains of chondroitin sulfate
•Link proteins attach them to hyaluronan
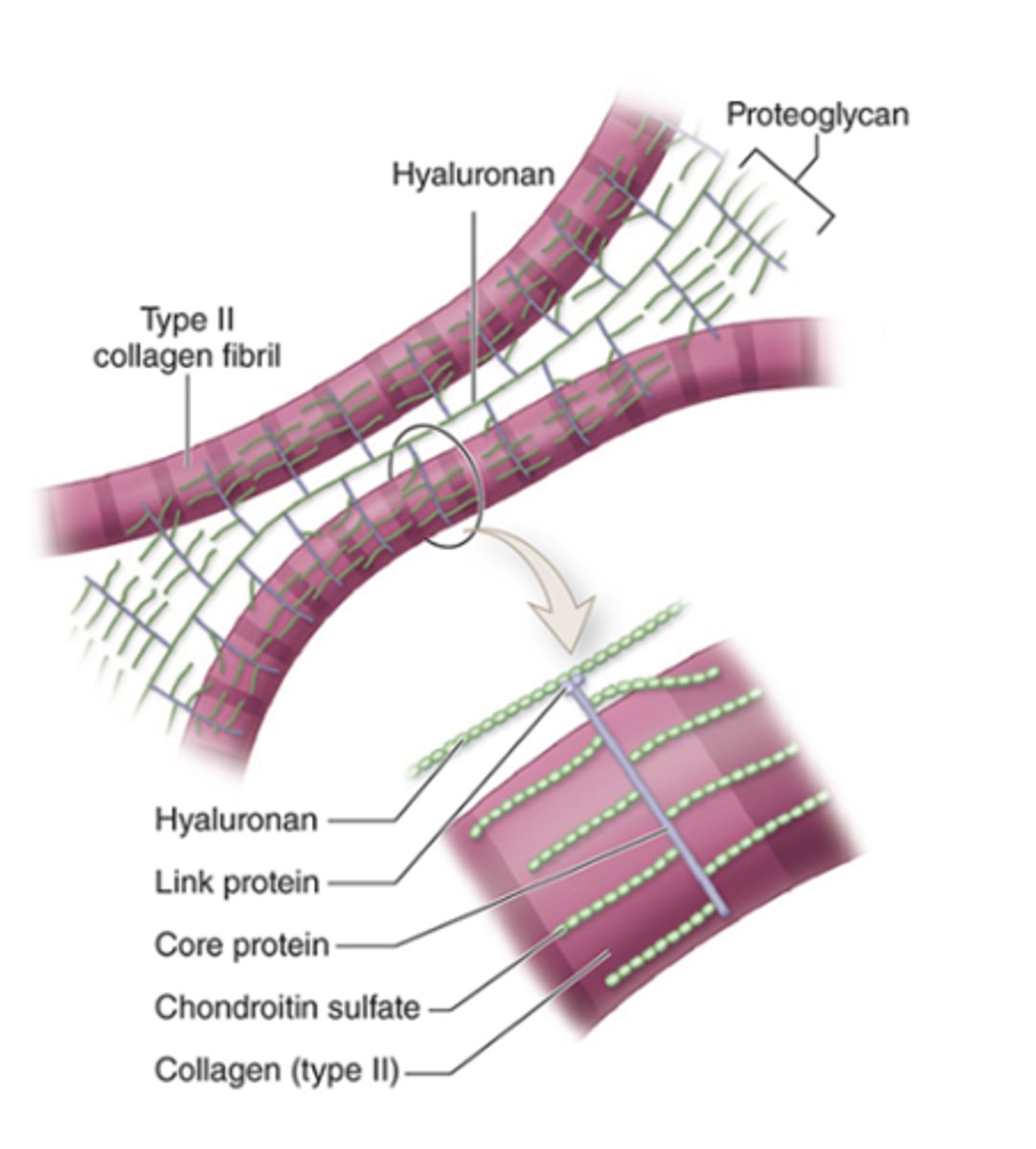
How are Type II collagen and proteoglycan components held together in the ECM?
bound by electrostatic bonds
What are the three types of cartilage based on variations in the ECM?
1. Hyaline cartilage
2. Elastic cartilage
3. Fibrocartilage
What type of connective tissue makes up the perichondrium?
Dense connective tissue.
What is the main function of the perichondrium?
Surrounds cartilage, provides an interface between cartilage and other tissues, and supplies vascular support.
Does the perichondrium contain nerves?
Yes, it has a small neural component.
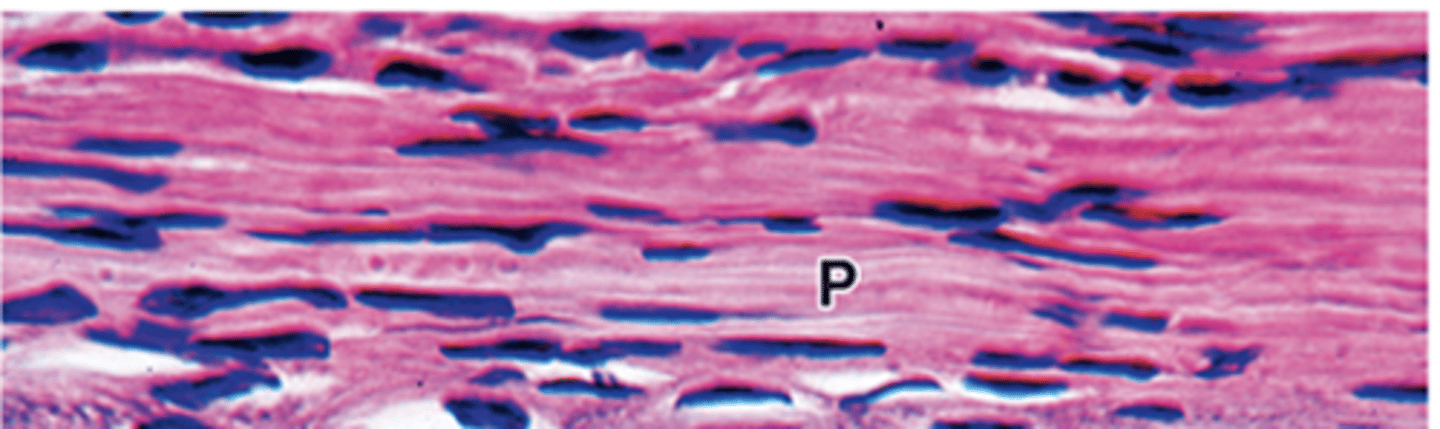
Which types of cartilage lack a perichondrium? (3)
1. Articular cartilage (hyaline)
2. Epiphyseal cartilage (hyaline)
3. Fibrocartilage
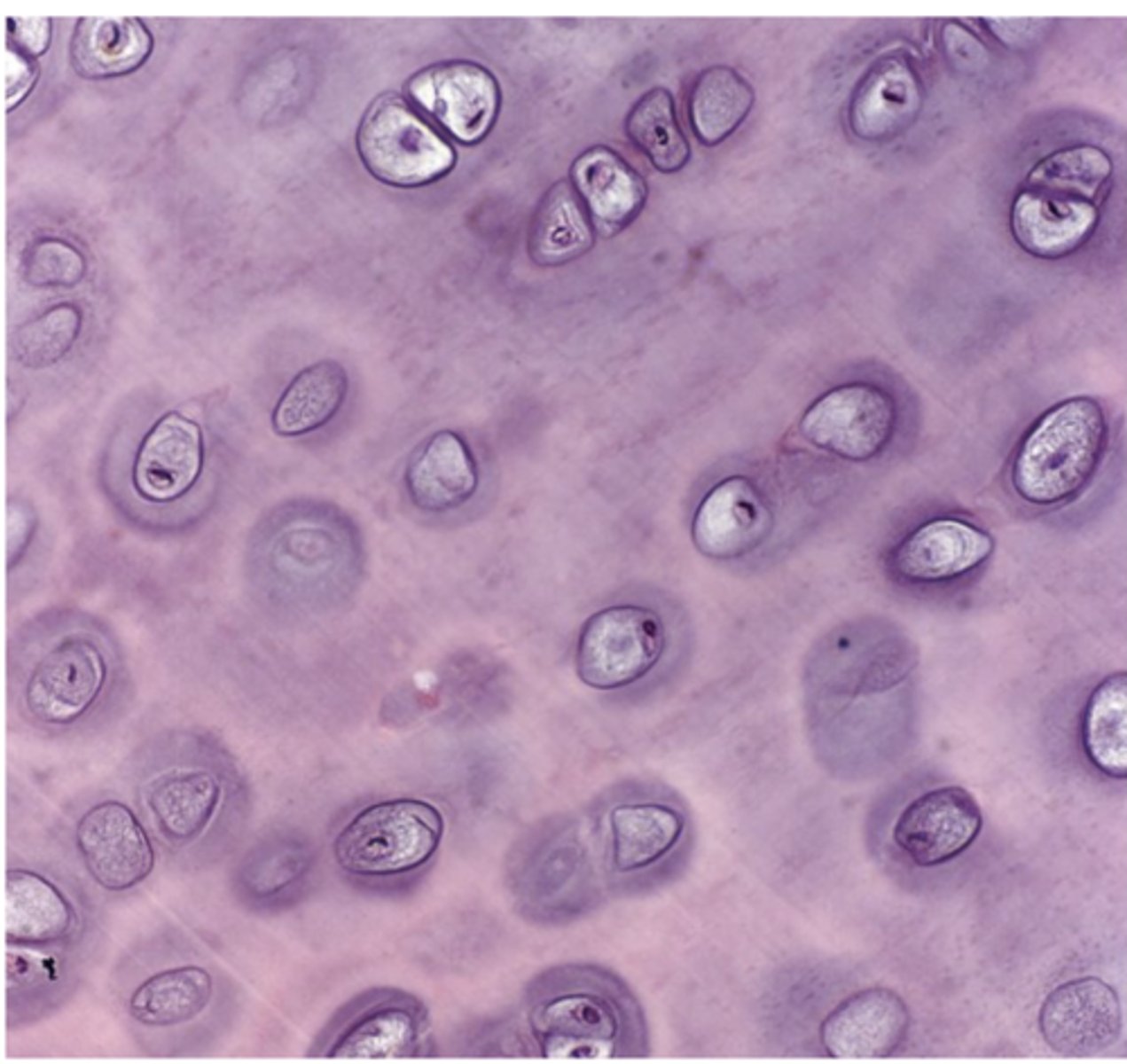
What does "hyalos" mean in hyaline cartilage?
Glass
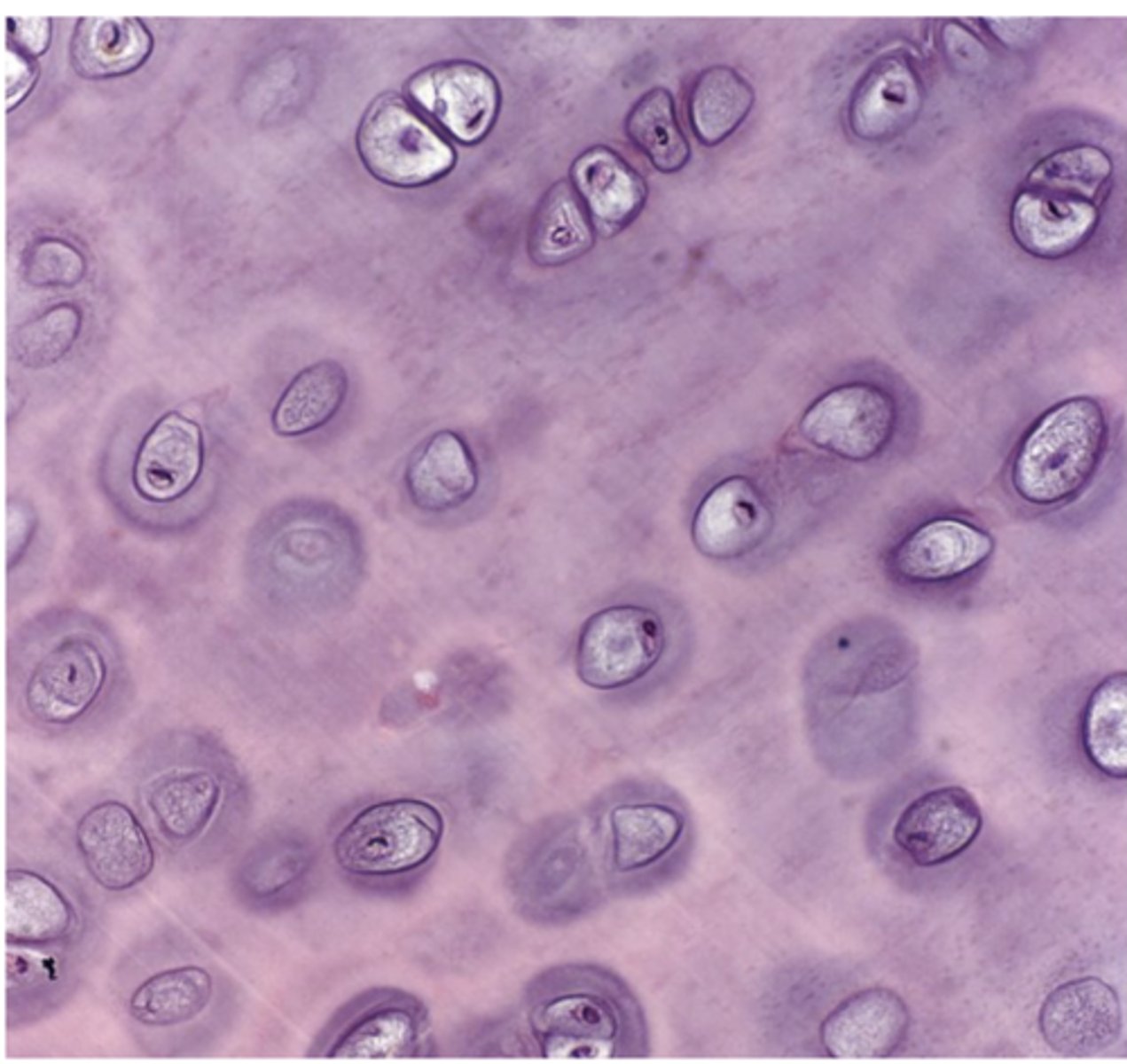
Which type of cartilage is the most common in the body? ***
Hyaline cartilage
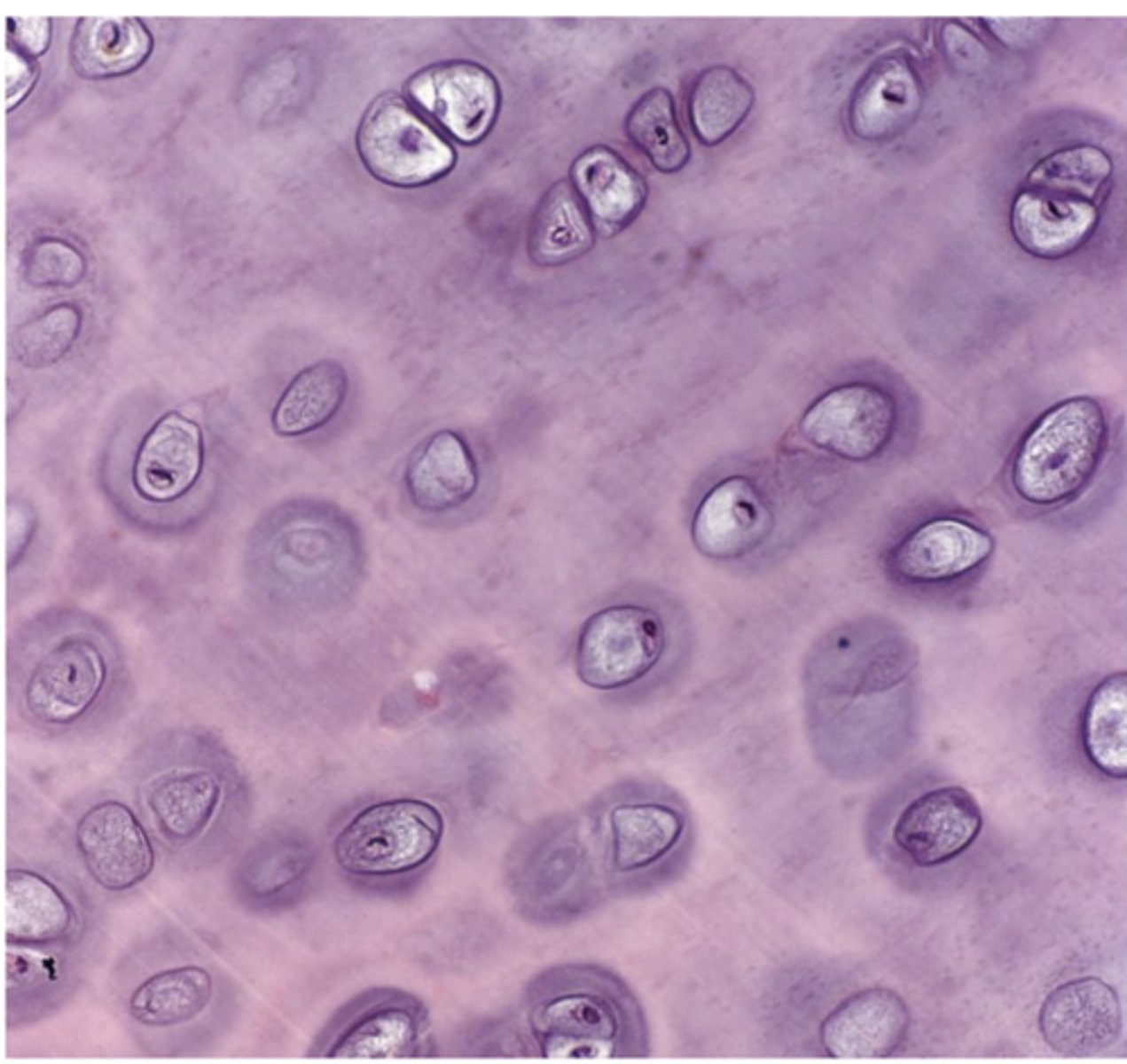
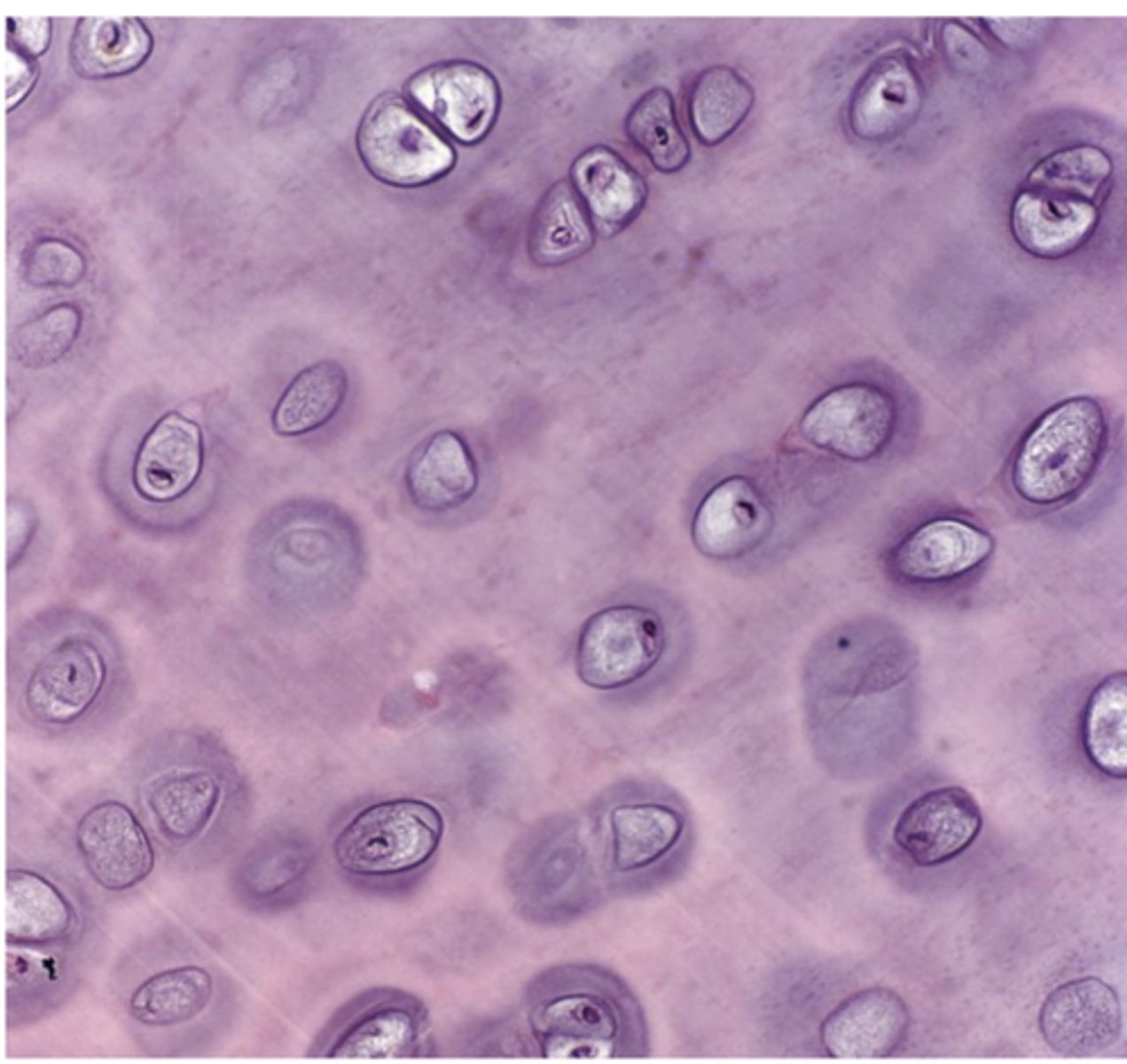
How does hyaline cartilage appear under the microscope
Homogeneous and semitransparent.
Where is hyaline cartilage commonly found? (5)
1. Articular surfaces of diarthroses
2. Walls of respiratory passages
3. Ventral ends of ribs
4. Epiphyseal plates
5. Temporary fetal skeleton
What percentage of hyaline cartilage ECM is collagen?
About 40%.
What forms the hydrated gel in hyaline cartilage ECM?
Proteoglycans and structural glycoproteins.
What is the main type of collagen in hyaline cartilage?
Type II collagen (often barely discernible).
Why does hyaline cartilage stain basophilic?
Due to the high content of proteoglycans.
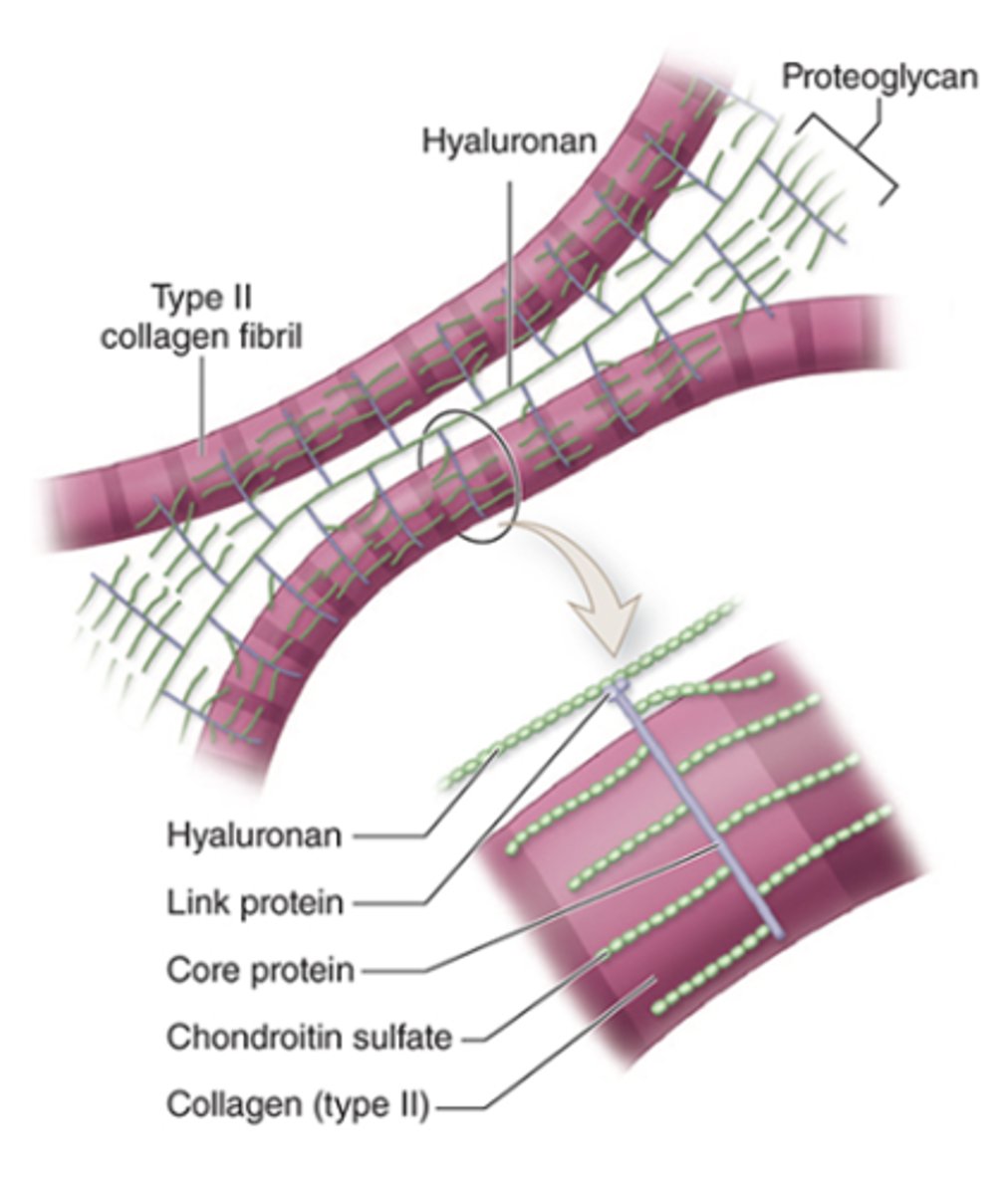
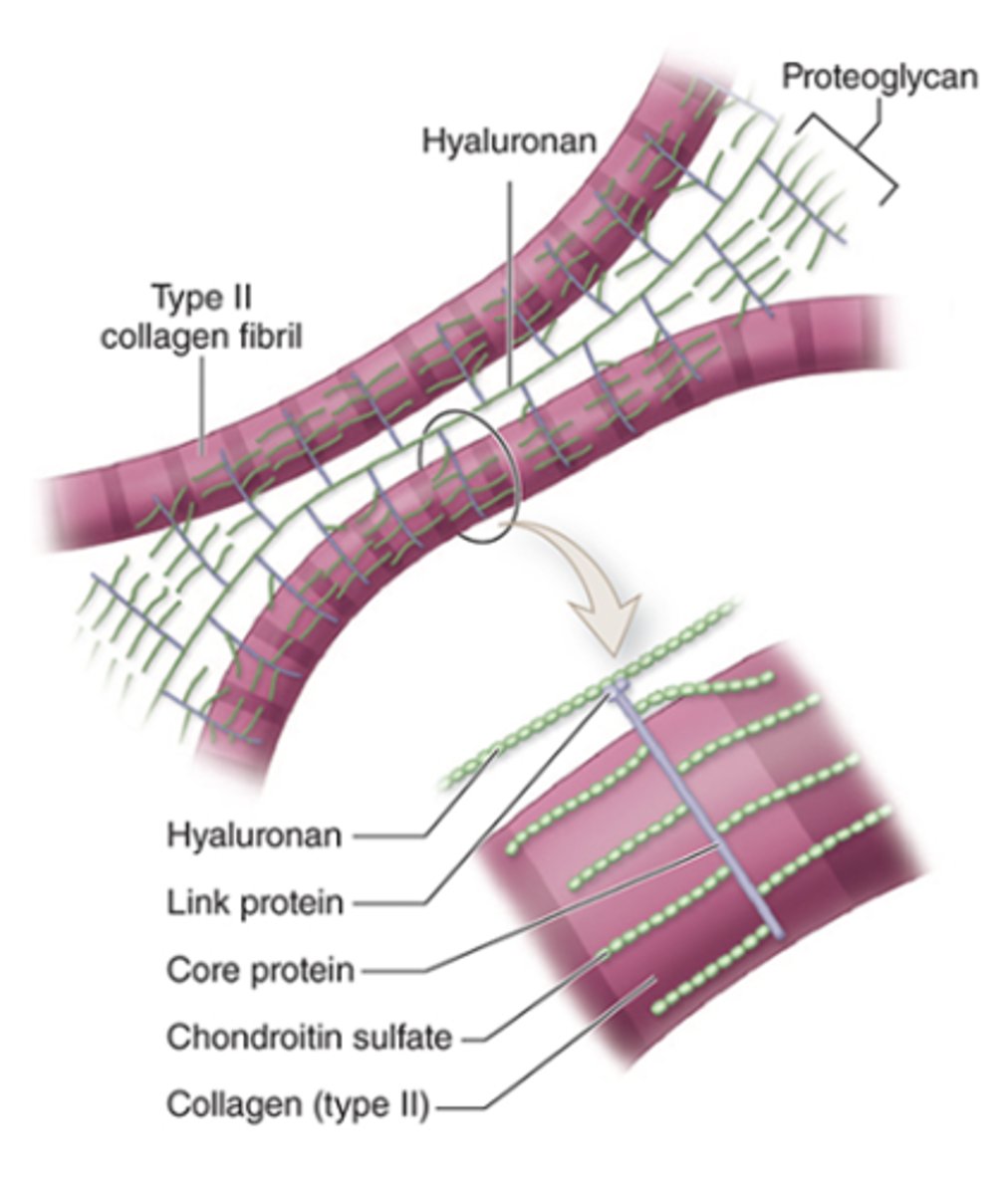
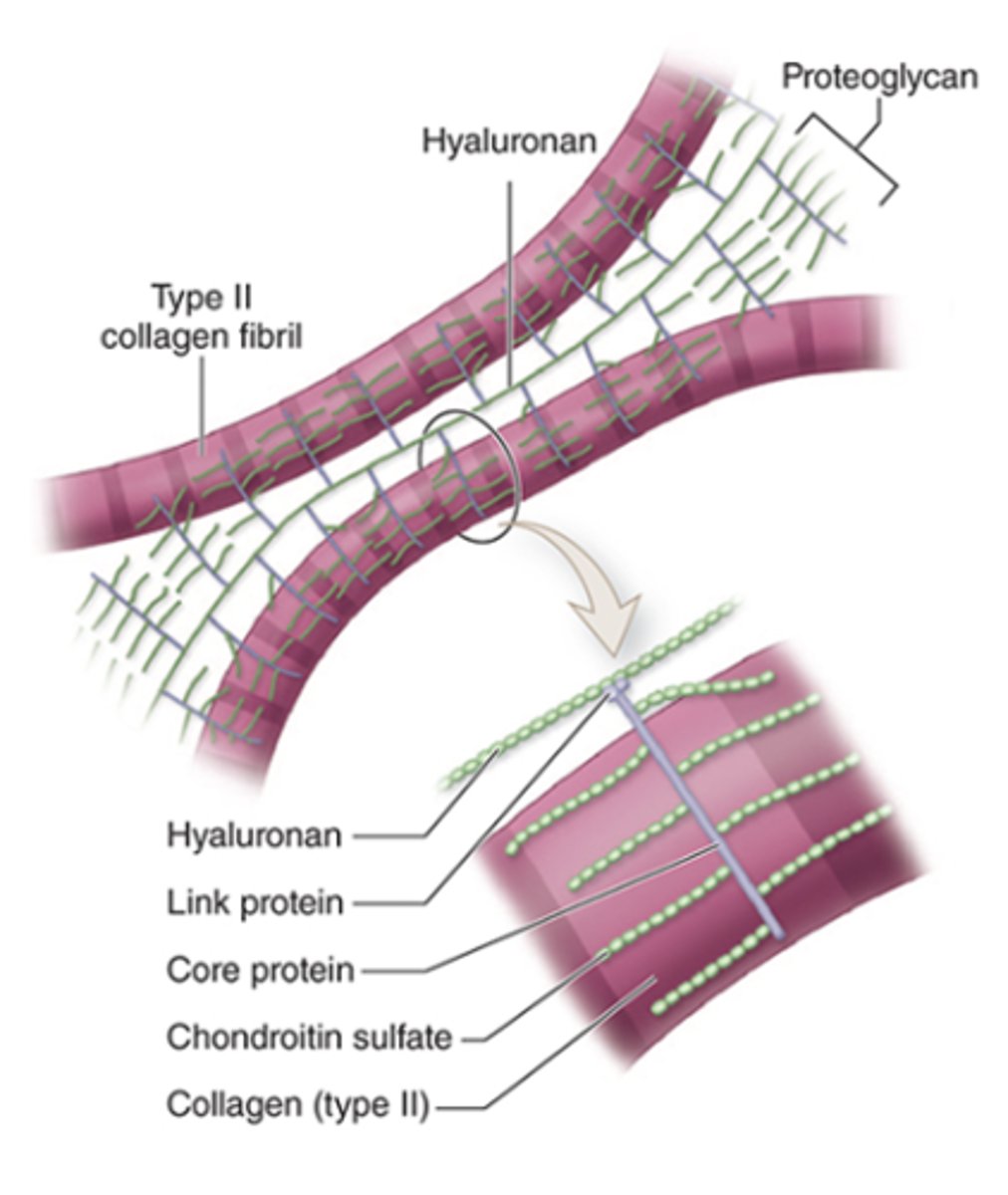
What is aggrecan and what is its structure?
A proteoglycan with side chains of chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate, covalently bound to long polymers of hyaluronan.
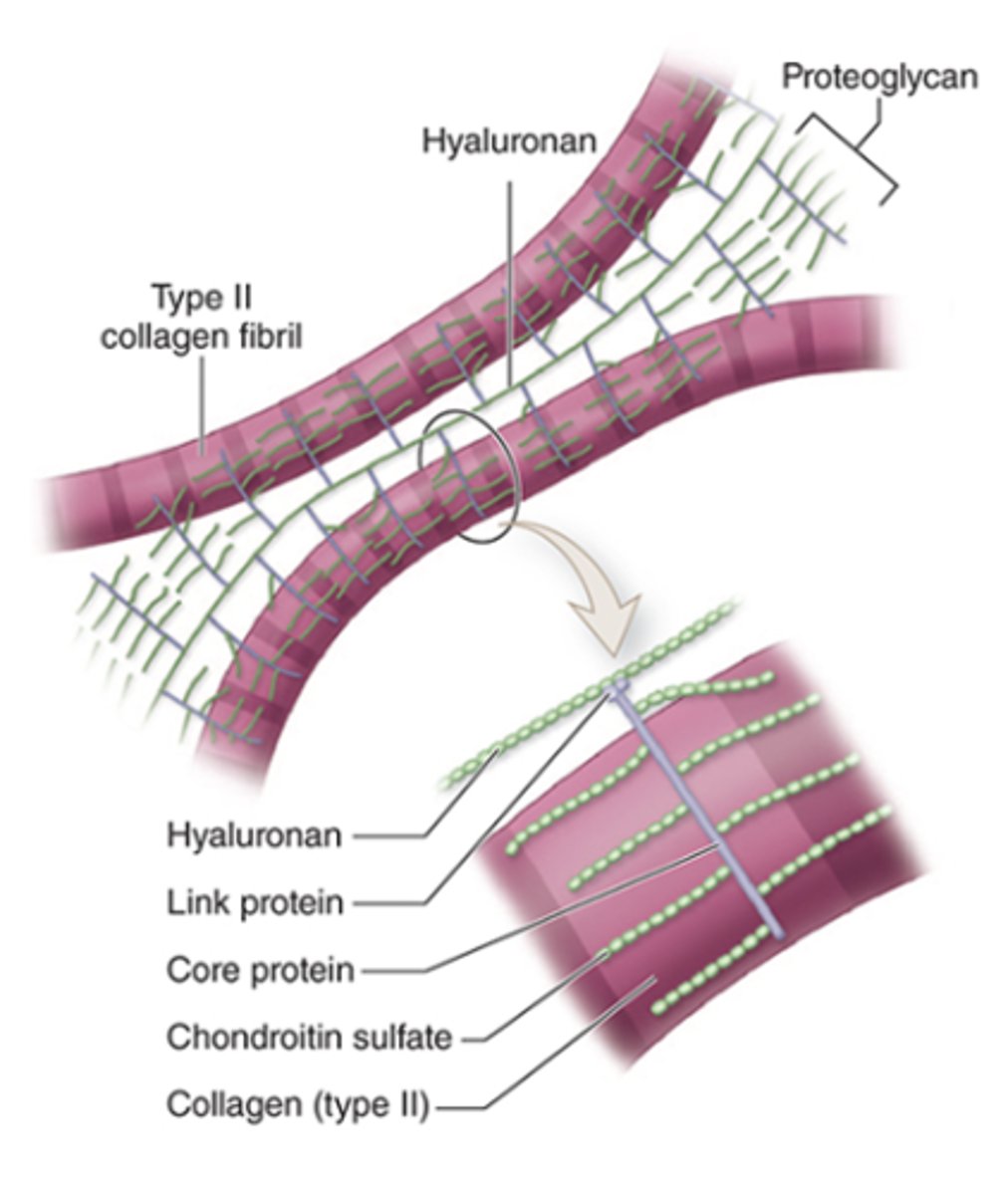
How are proteoglycan complexes organized in the ECM?
They are bound to type II collagen.
What proportion of ECM in fresh hyaline cartilage is water?
60%–80%, bound to proteoglycans.
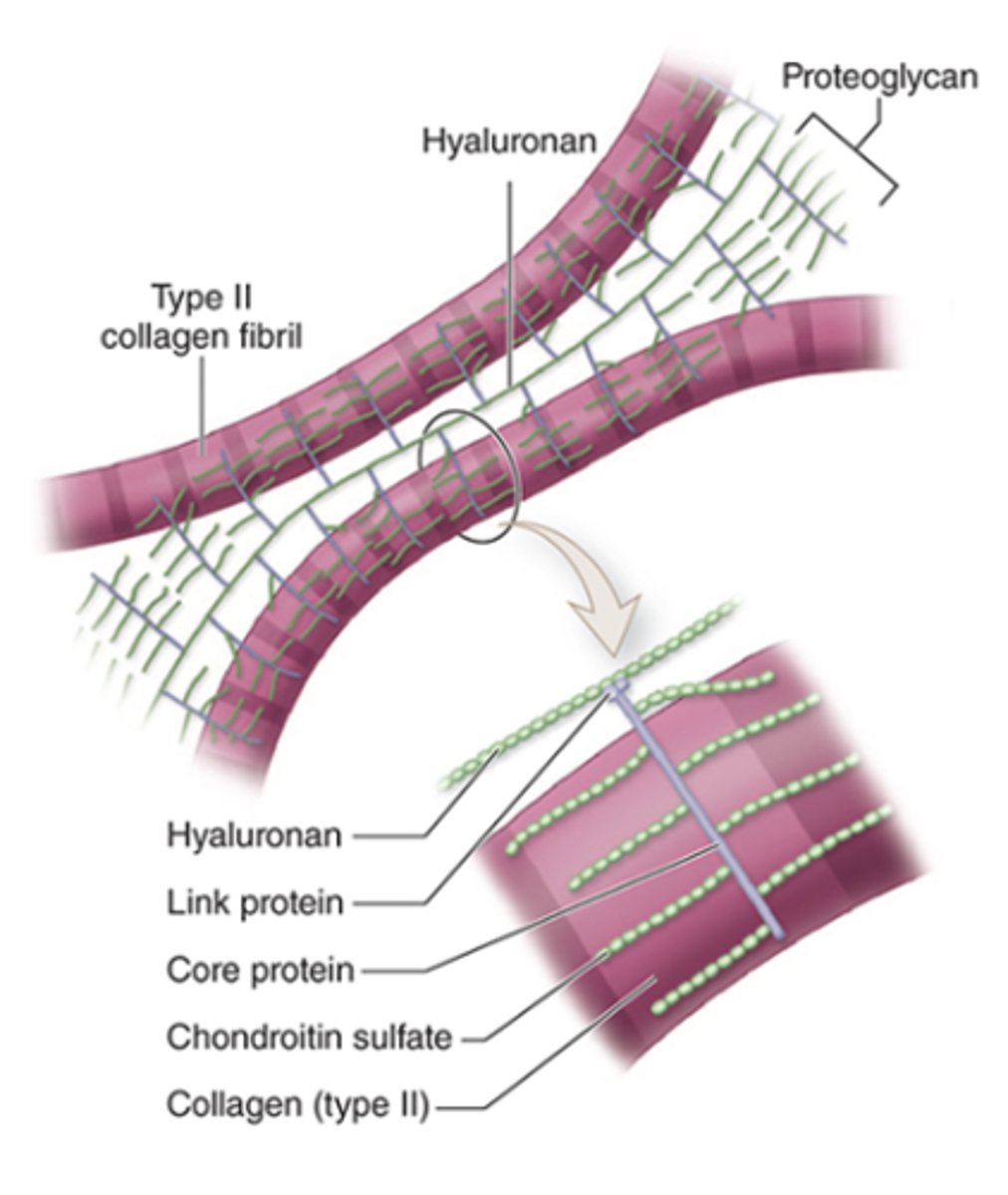
What protein mediates the adherence of chondrocytes to ECM components?
Chondronectin (a multiadhesive protein).
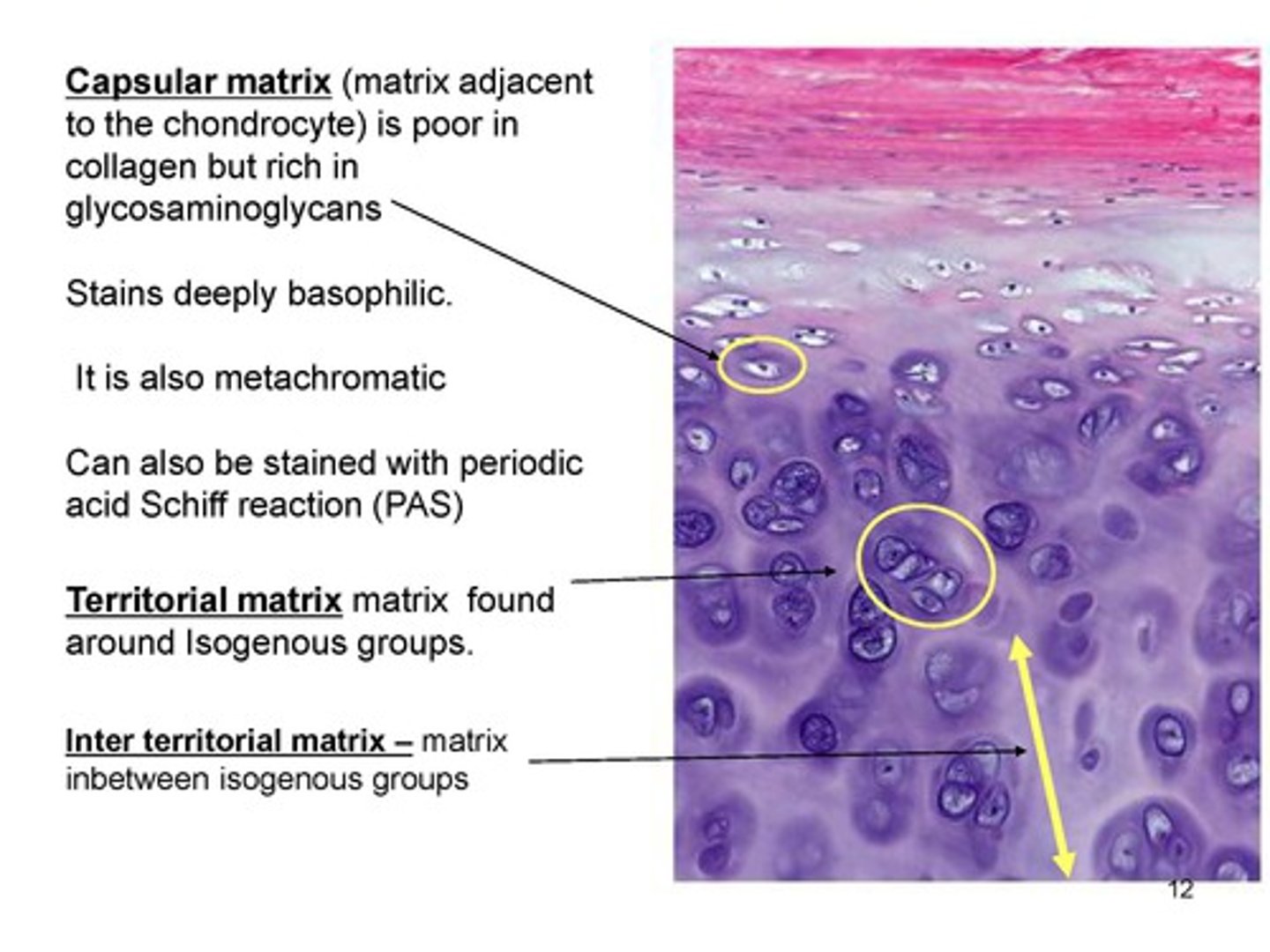
What is the capsular matrix in cartilage ECM?
- Densely staining matrix surrounding the cell
- Highest concentration of proteoglycans
- Contains type VI collagen
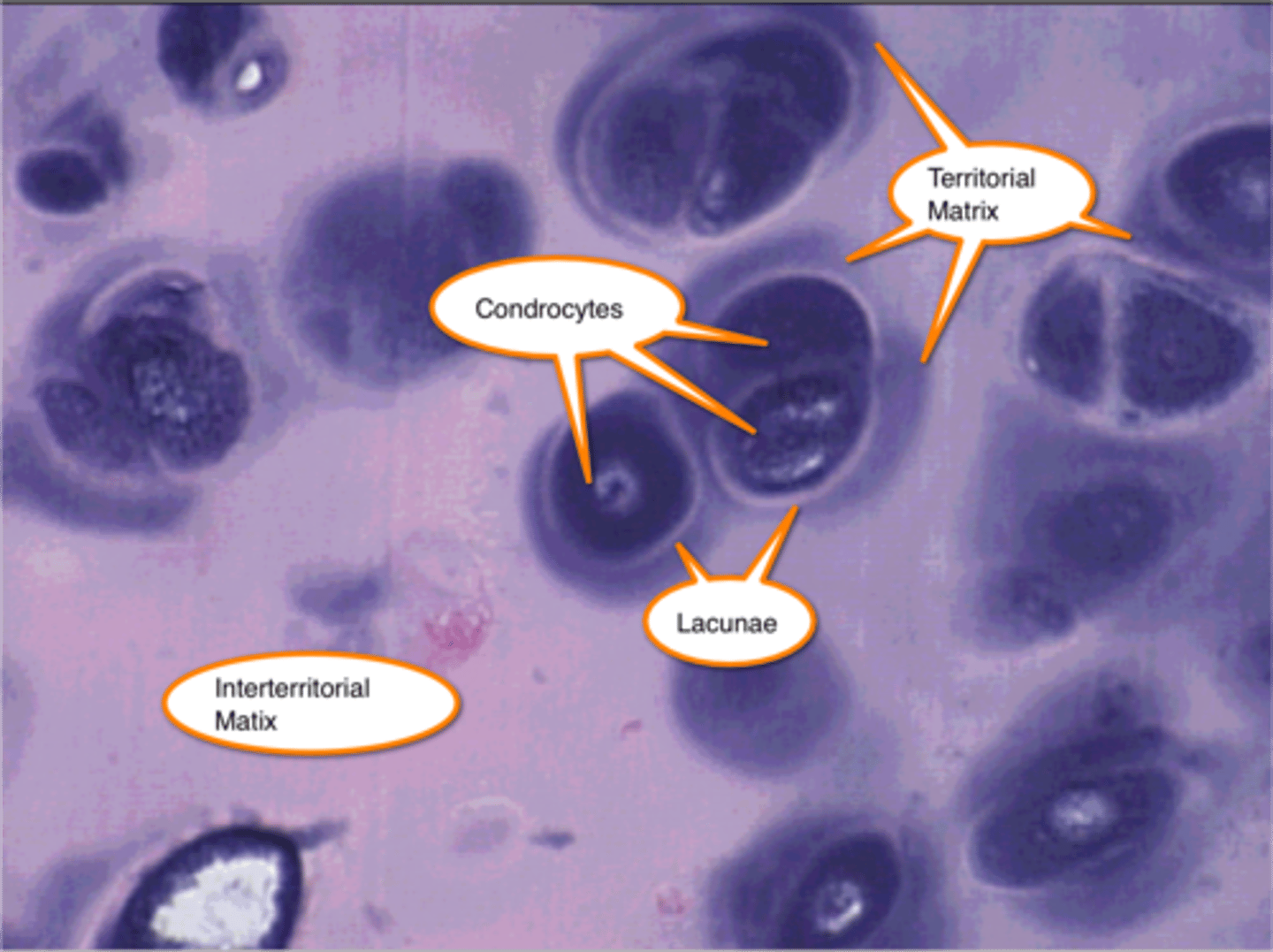
What is the territorial matrix in cartilage ECM?
- intensely basophilic
- More GAGs than collagen (mainly type II)
- Surrounds isogenous groups of chondrocytes
What is the interterritorial matrix in cartilage ECM?
- Weaker basophilia
- Less GAG content
- Found between groups of chondrocytes
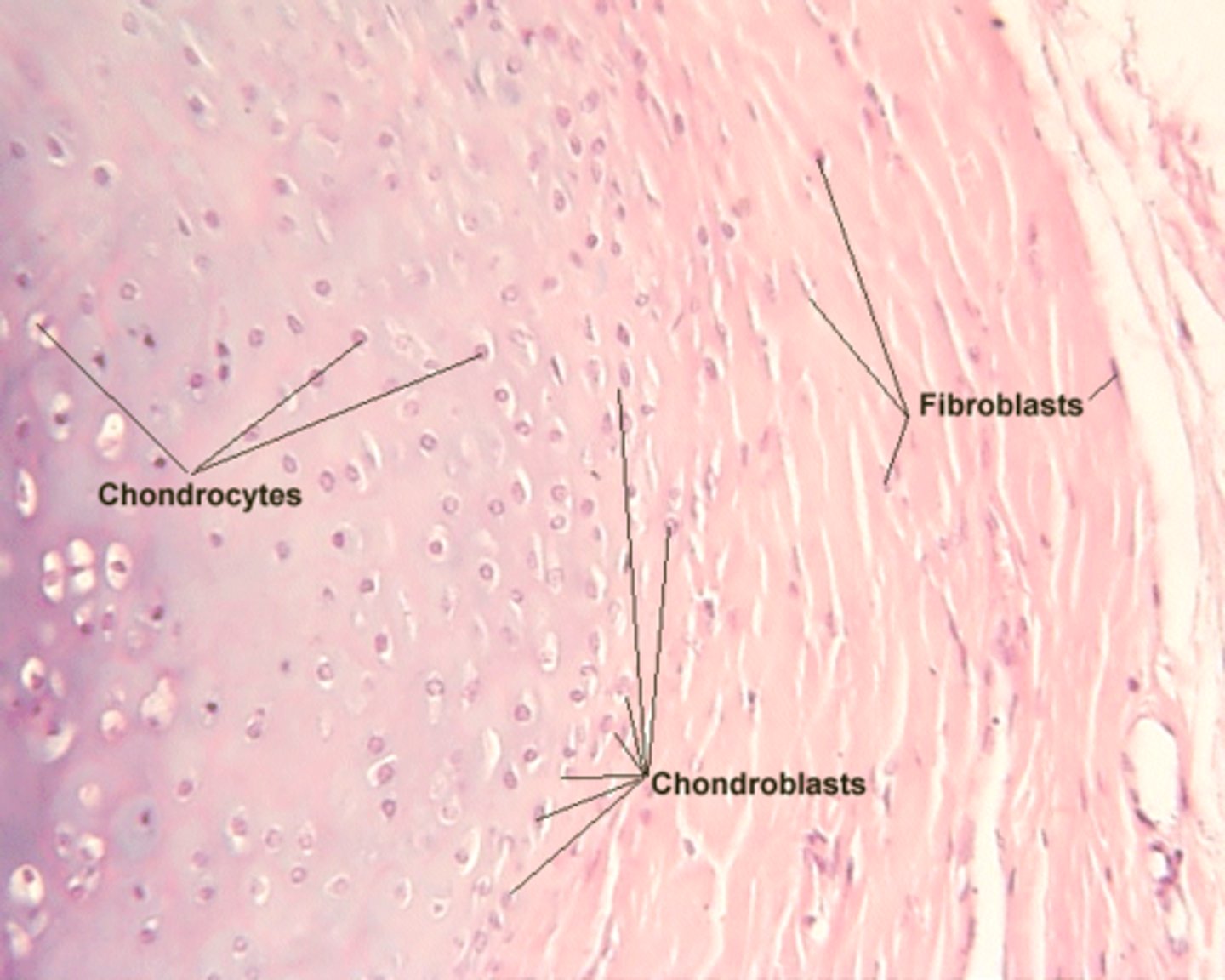
What are chondroblasts and where are they located?
Young chondrocytes located peripherally
Elliptic in shape with long axes parallel to the surface
What are chondrocytes and where are they found?
Mature cartilage cells located deeper in cartilage
Reside within lacunae
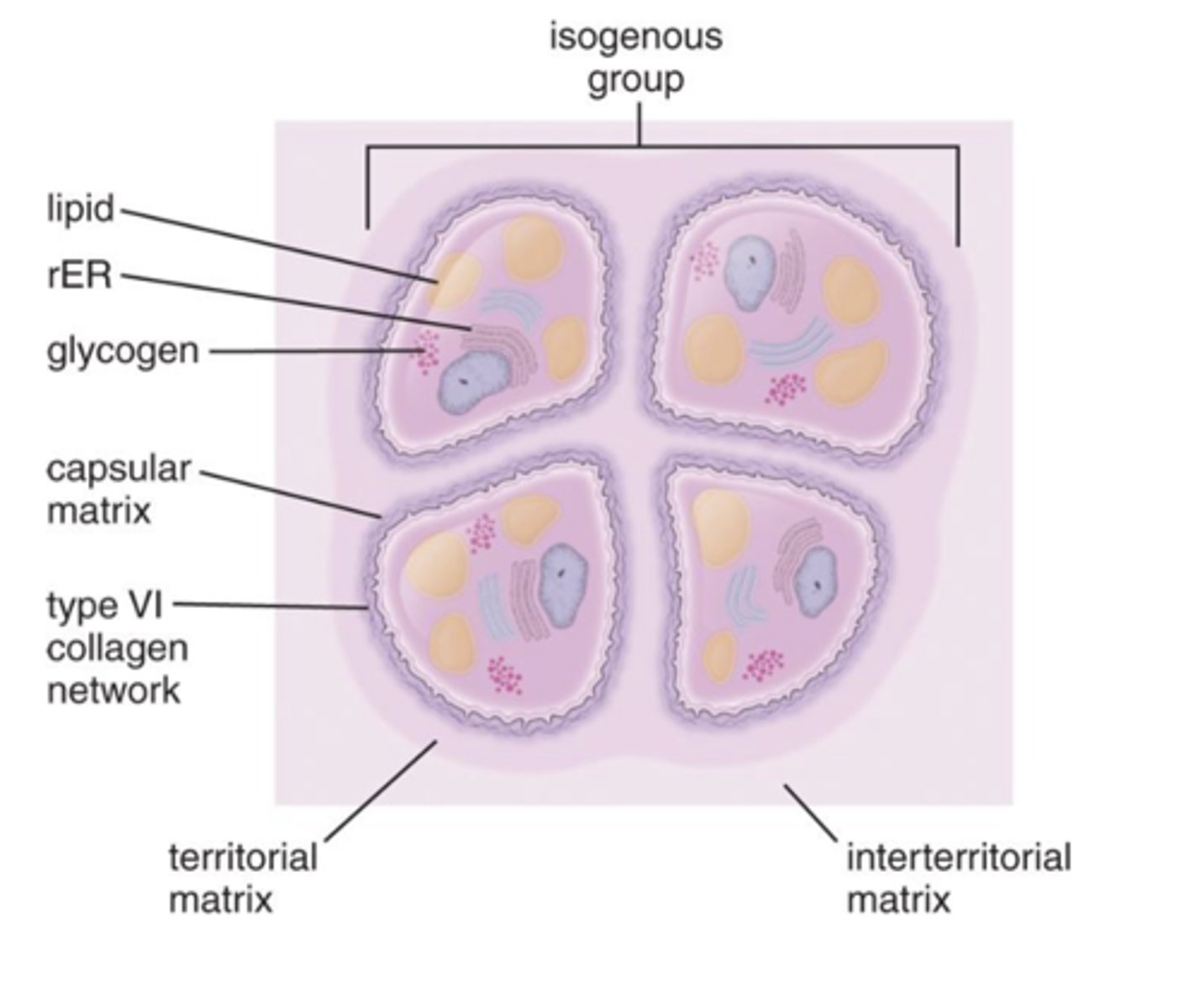
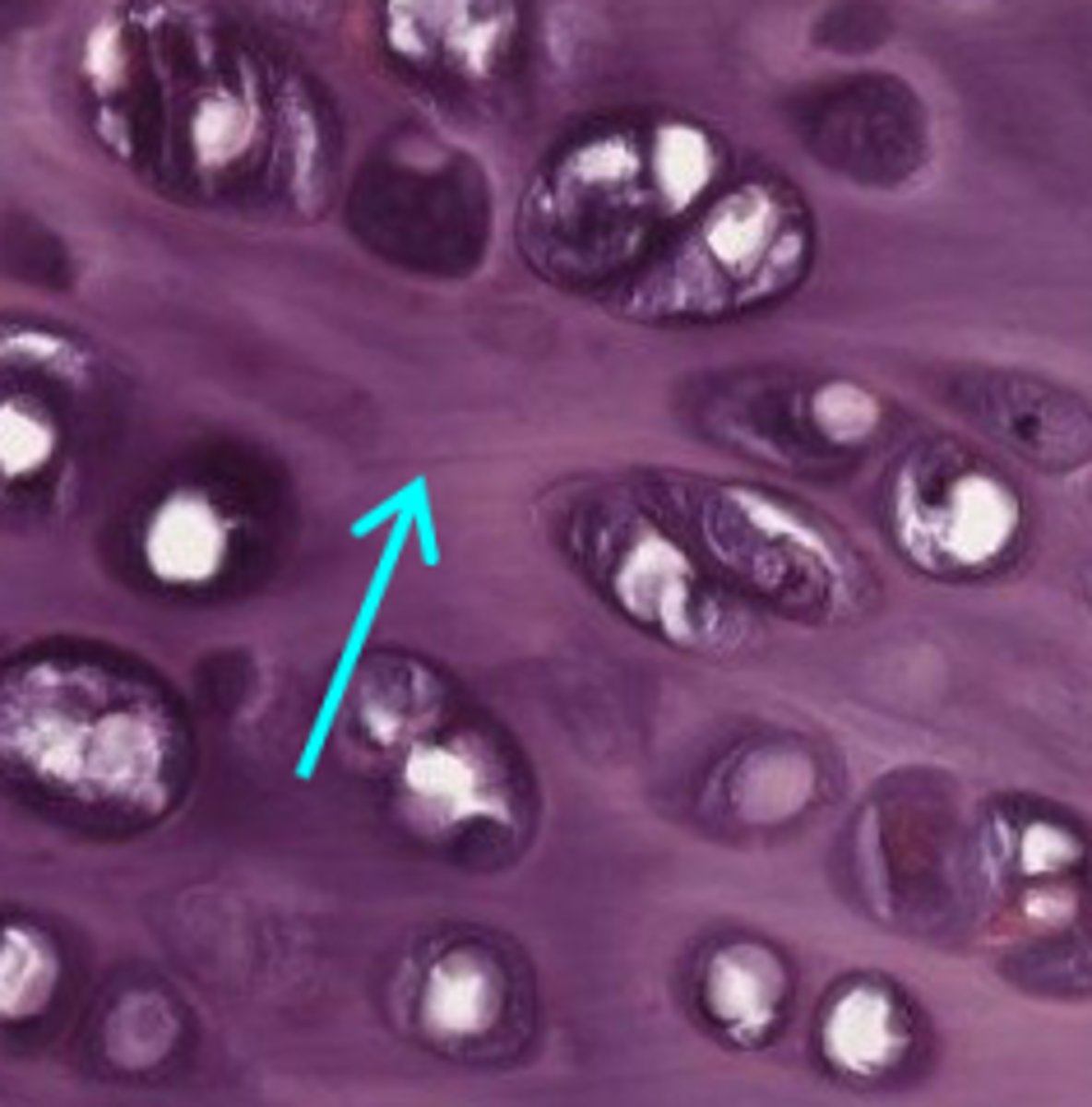
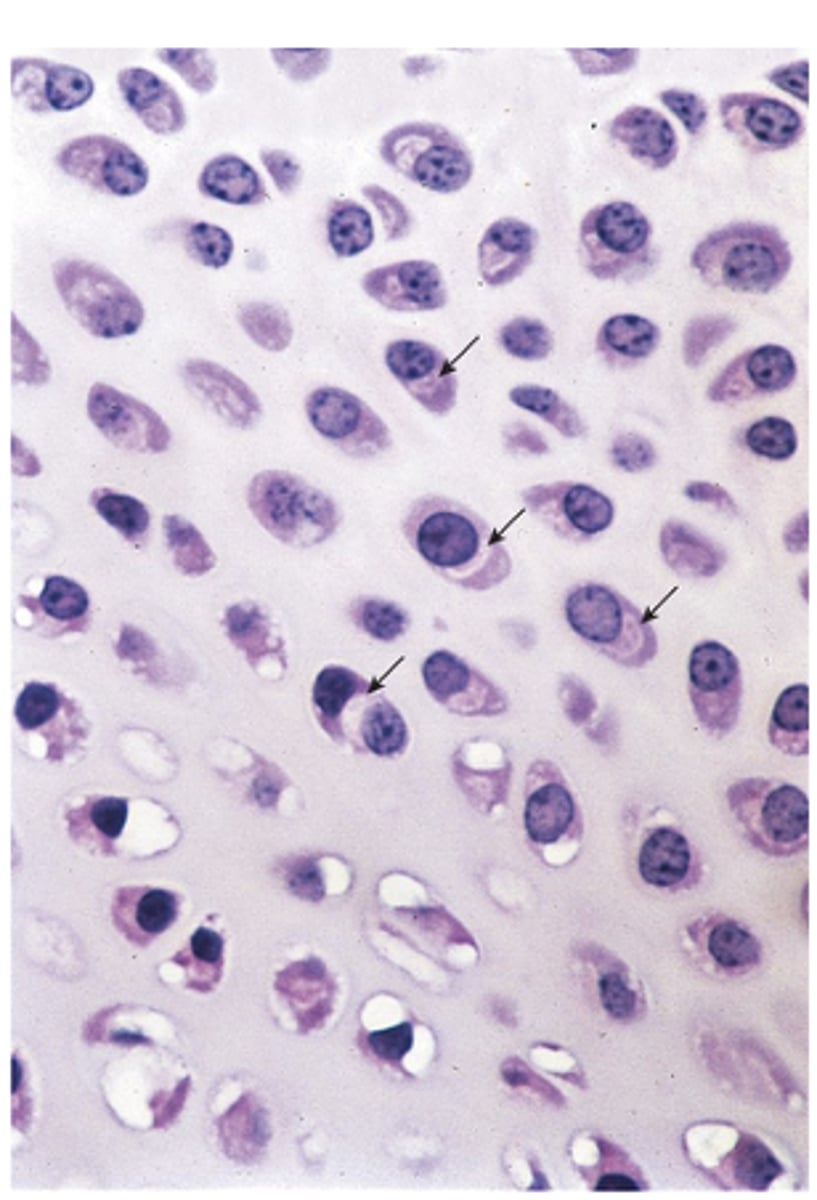
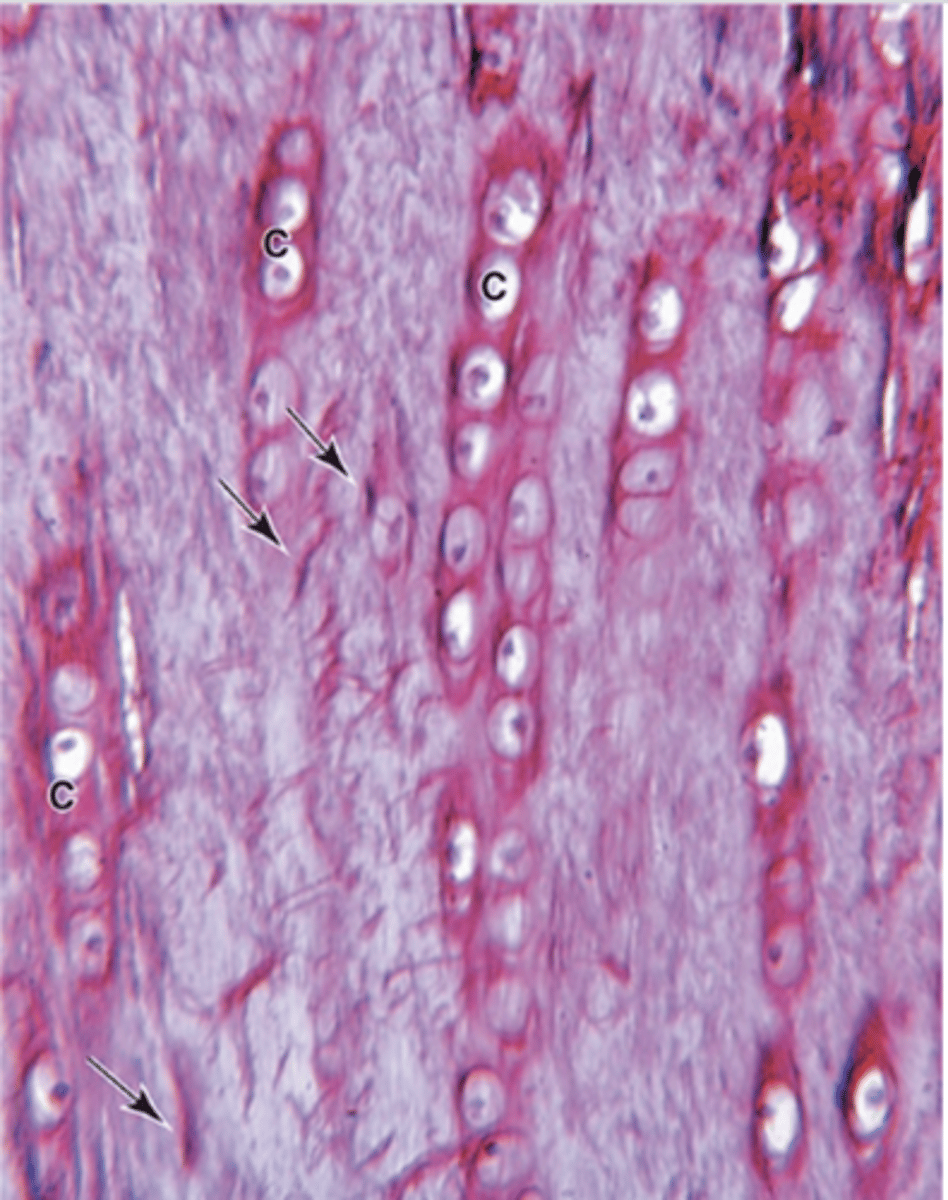
What is an isogenous group?
- A cluster of up to eight chondrocytes formed by mitosis of a single chondroblast
- ECM synthesis separates them into individual lacunae
What is the main type of metabolism in chondrocytes***?
Anaerobic glycolysis.
What stimulates chondrocytes to synthesize ECM?
Somatomedins (insulin-like growth factors) from the liver.
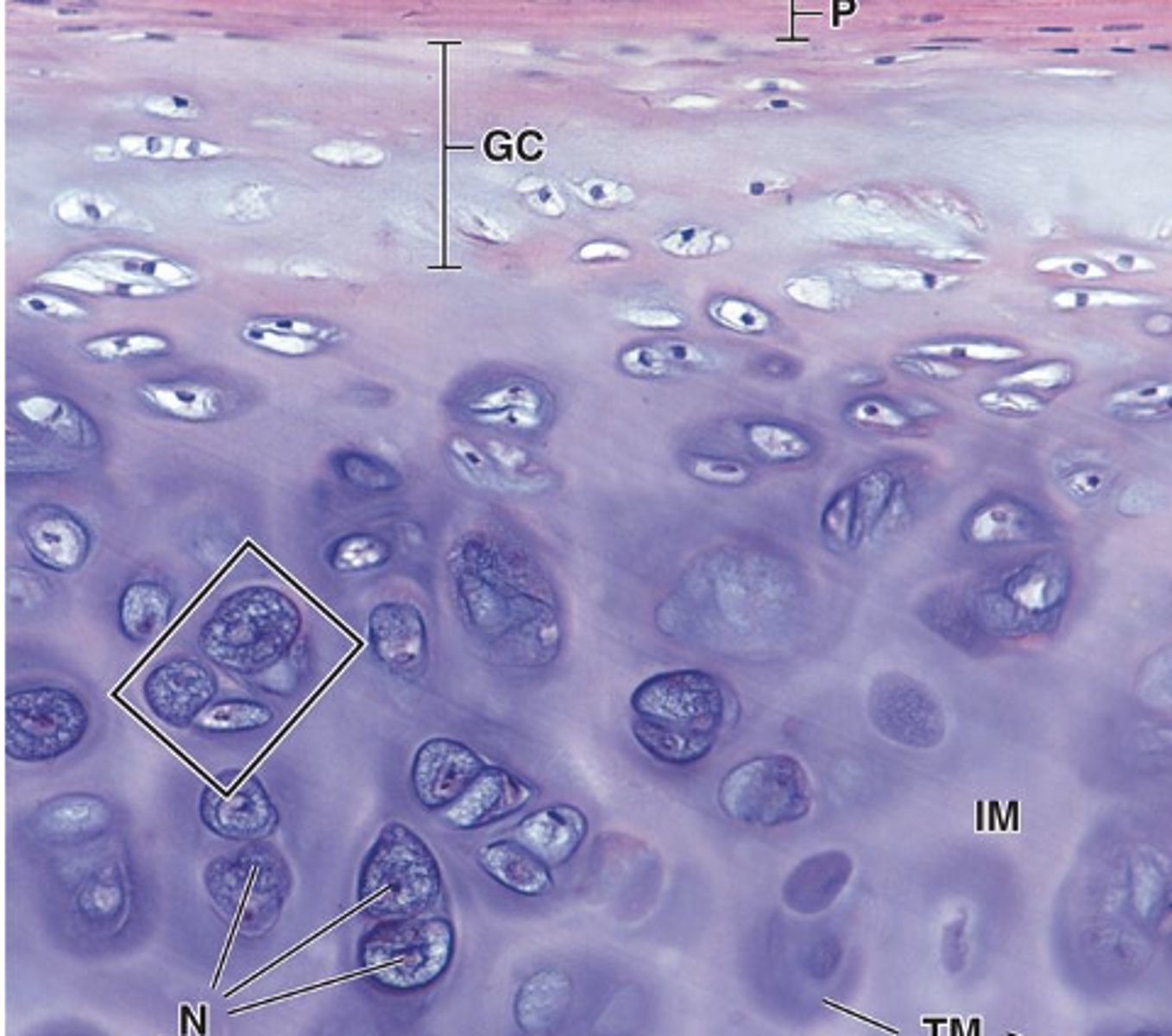
How does an active chondrocyte appear under light microscopy? (3)
- Cytoplasmic basophilia (active protein synthesis, RER)
- Clear areas representing large Golgi apparatus
- Euchromatic nucleus (active)
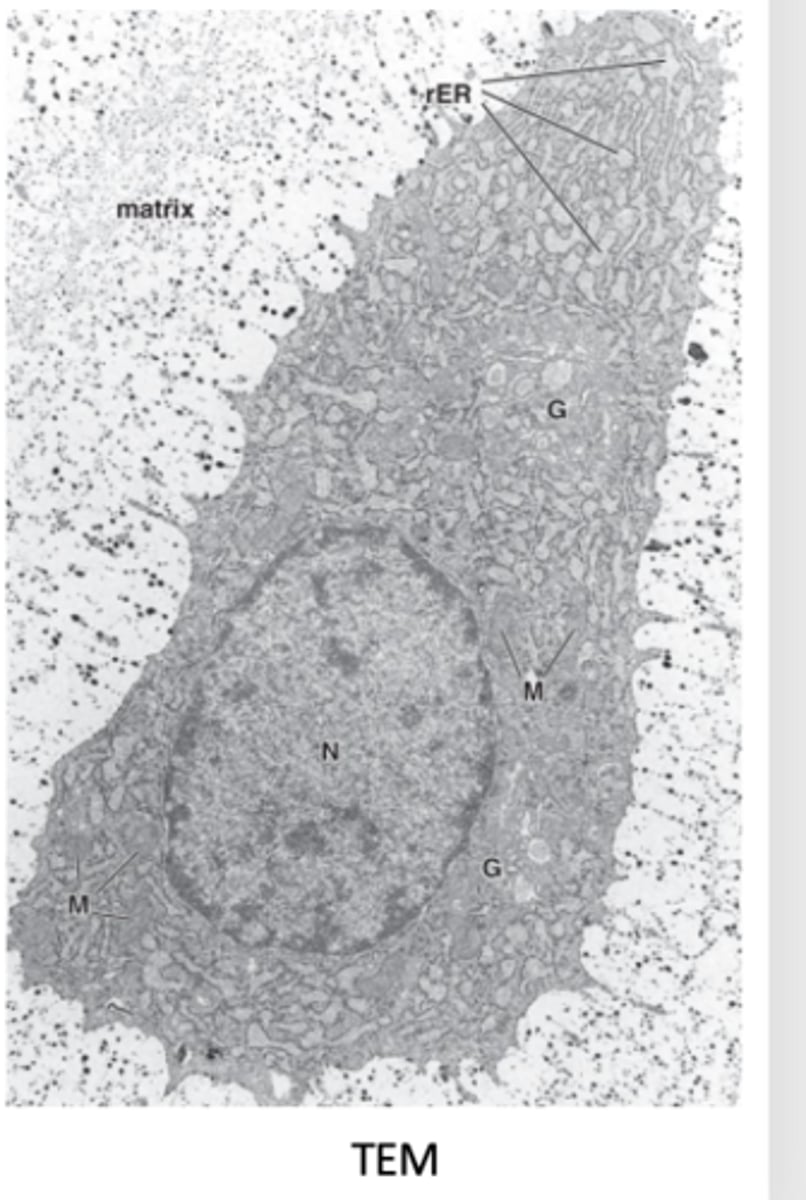
What organelles and structures are visible in chondrocytes under TEM? (5)
1. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
2. Large Golgi apparatus
3. Secretory granules and vesicles
4. Cytoskeleton: intermediate filaments, microtubules, and actin filaments
5. Eccentric euchromatic nucleus
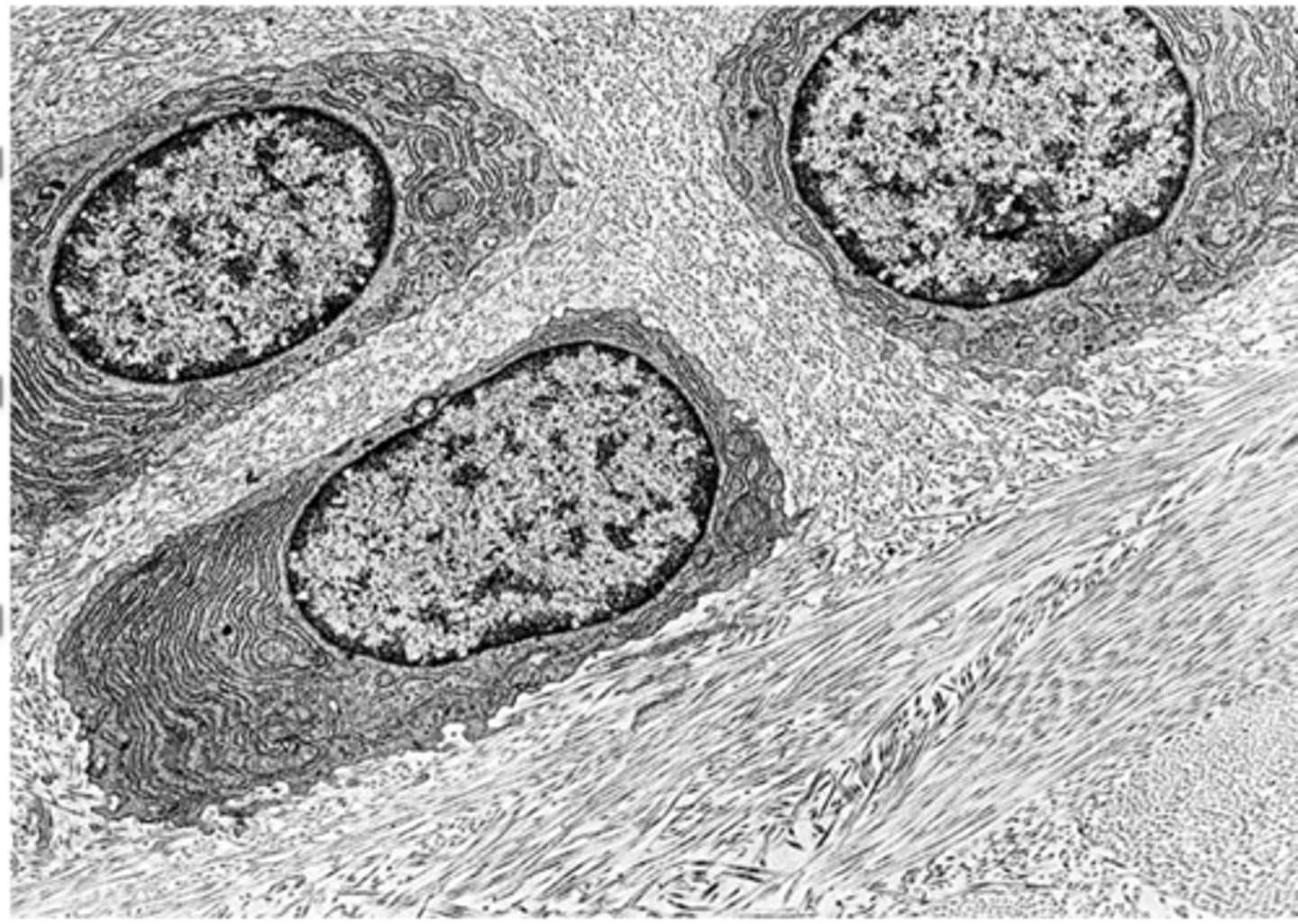
How do active chondrocytes in growing cartilage appear under TEM?
•Chondrocytes of fibrocartilage
•Abundant RER
•Euchromatic, eccentric nucleus
•Prominent Golgi apparatus
•Collagen fibers around the cells
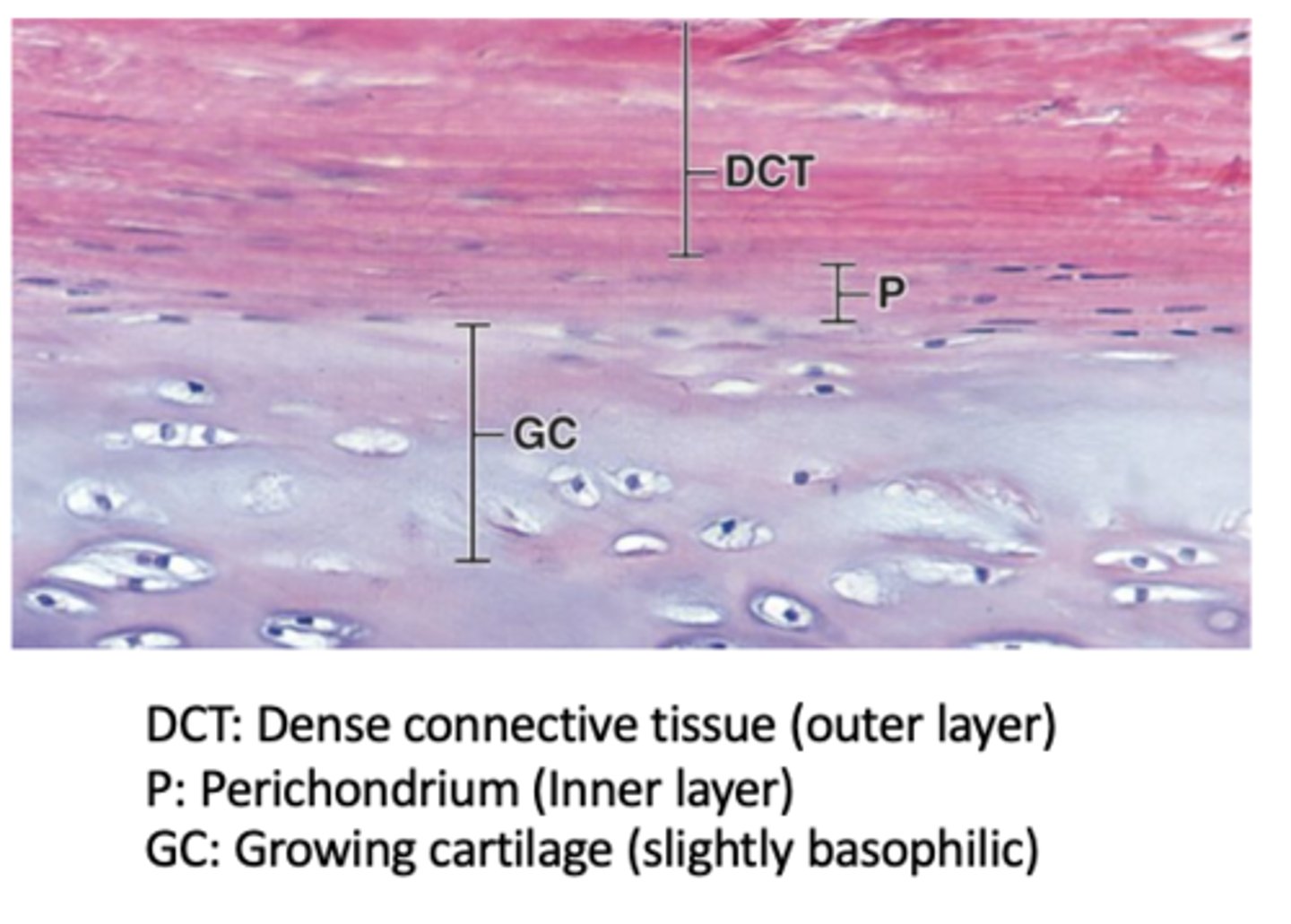
Which hyaline cartilage surfaces are covered by perichondrium?
All hyaline cartilage surfaces except articular cartilage and epiphyseal cartilage.
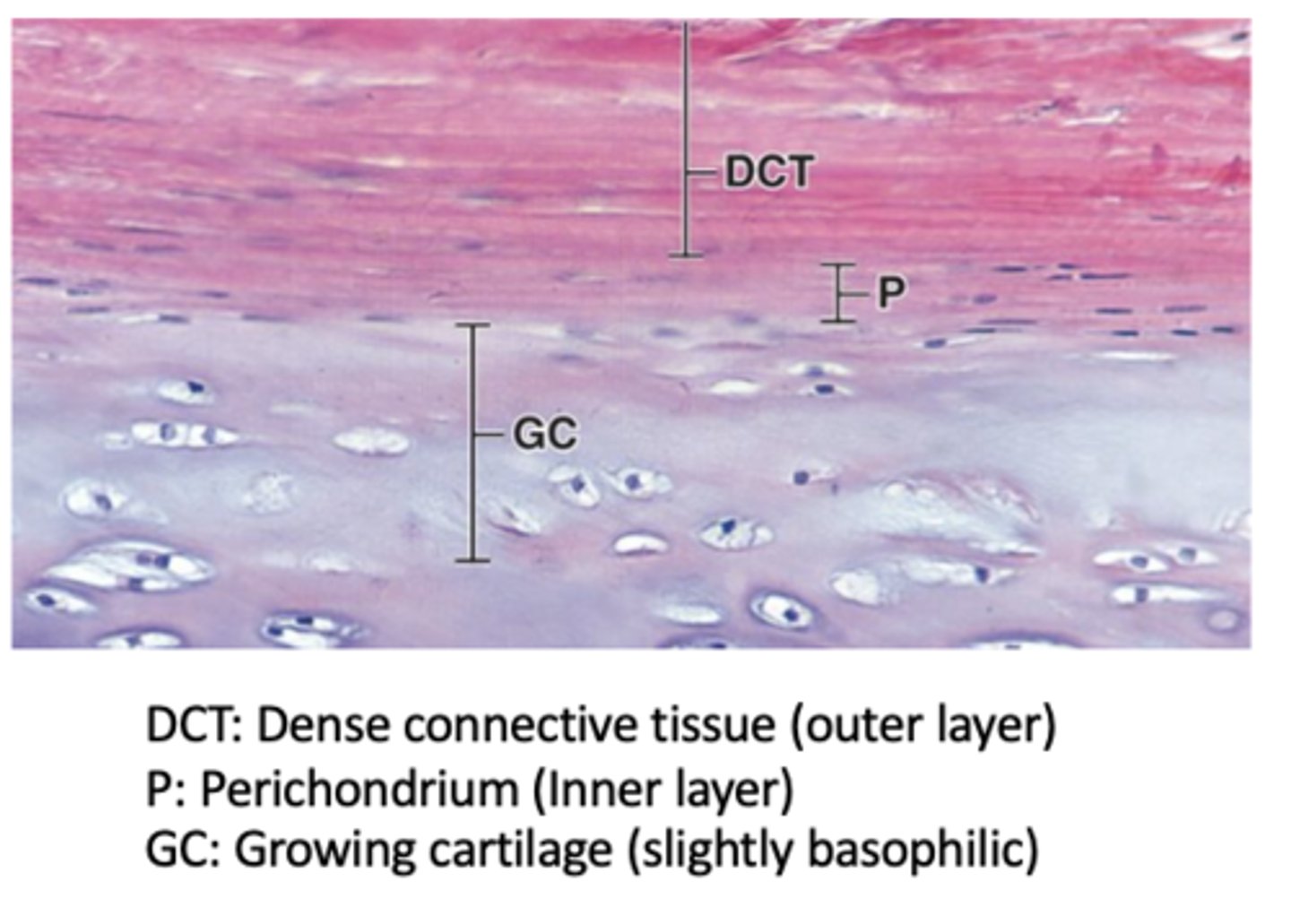
How many layers does the perichondrium have in actively growing cartilage?
Two layers: an outer fibrous layer and an inner cellular layer.
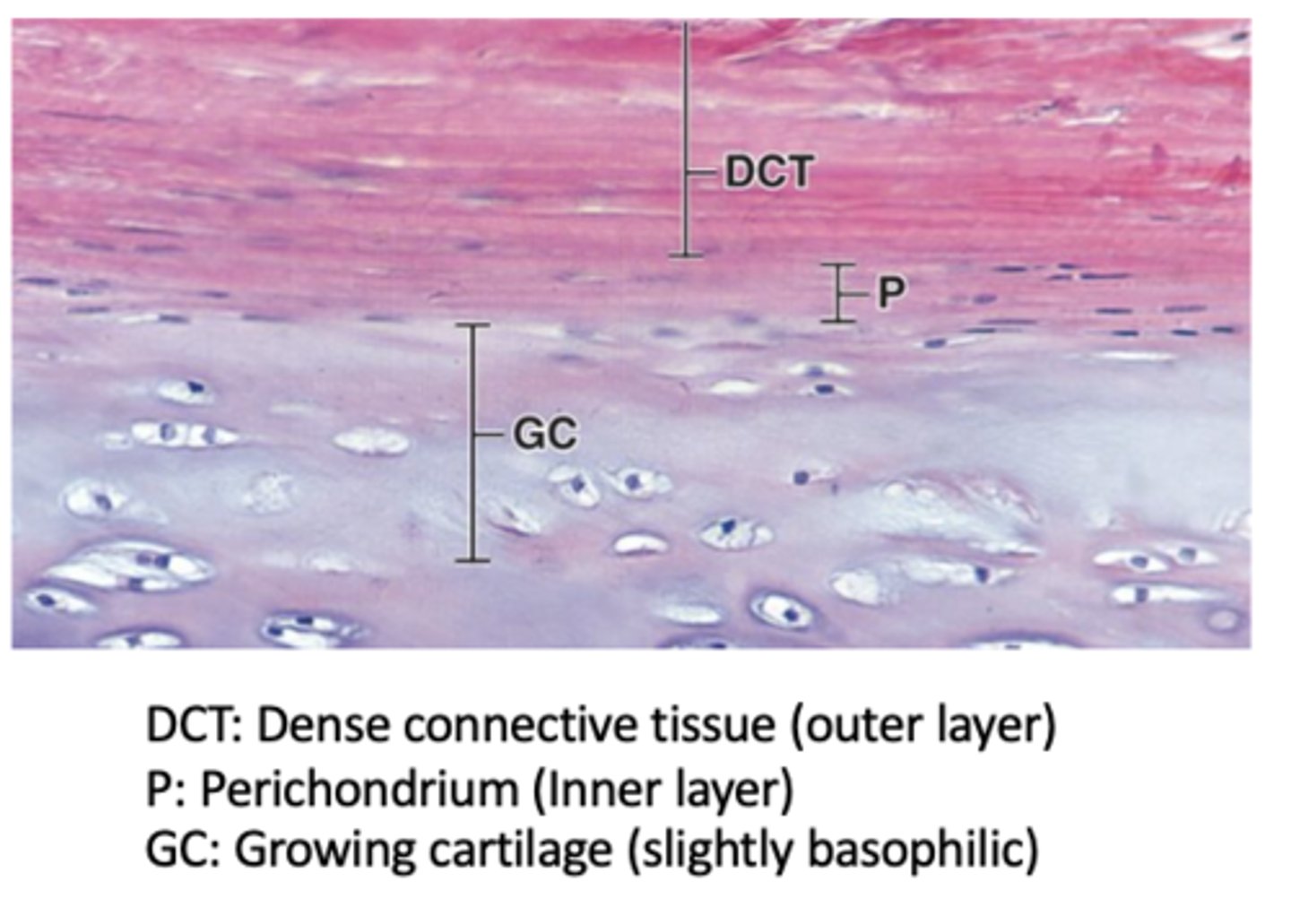
What is the composition of the outer fibrous layer of the perichondrium? (2)
Type I collagen and fibroblasts.
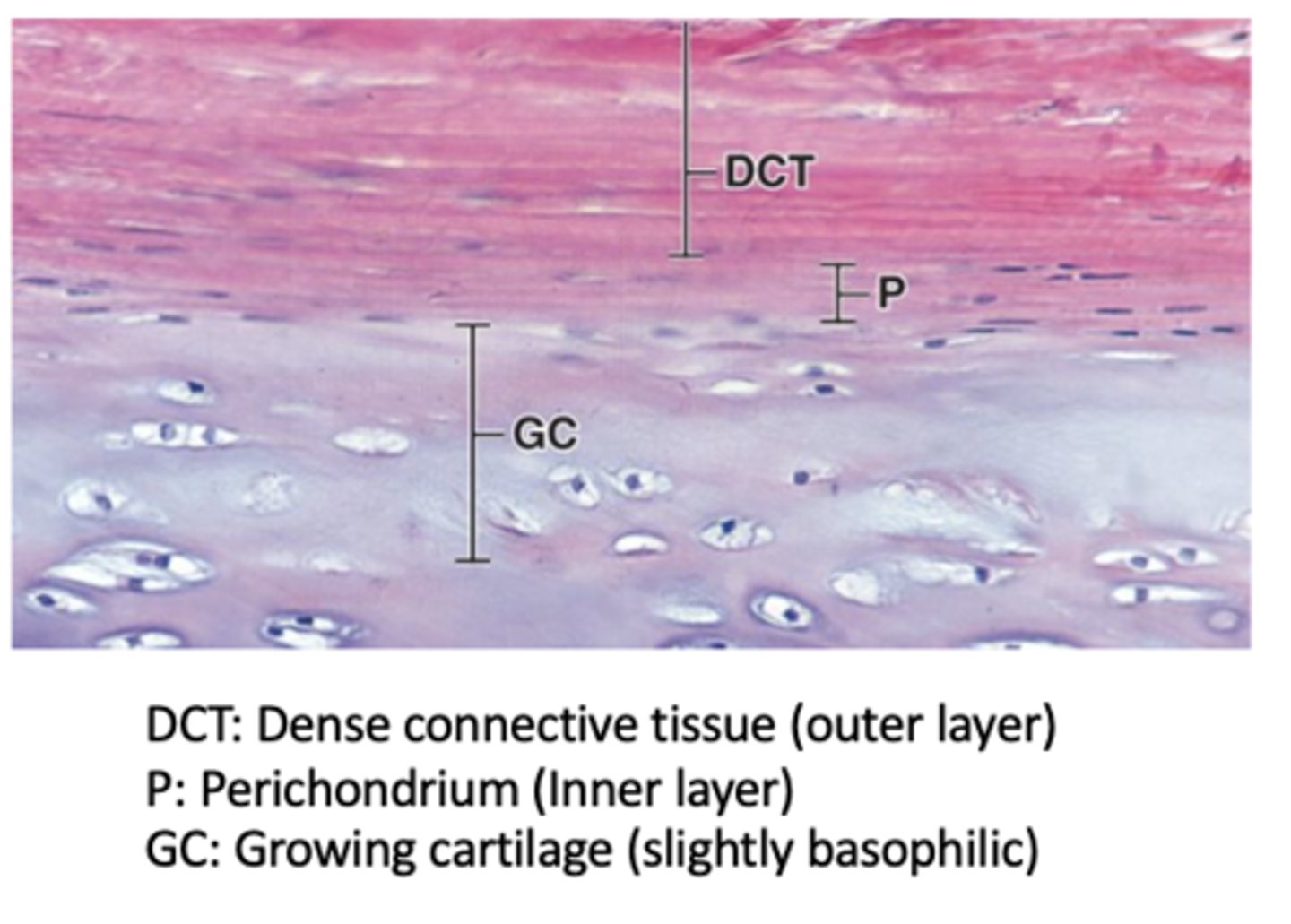
What is the composition and function of the inner cellular layer of the perichondrium?
next to cartilage matrix with mesenchymal stem cells
- Contains mesenchymal stem cells that can divide and differentiate into chondroblasts → chondrocytes
What is the sequence of differentiation from stem cells in the perichondrium?
Mesenchymal stem cells → chondroblasts → chondrocytes.
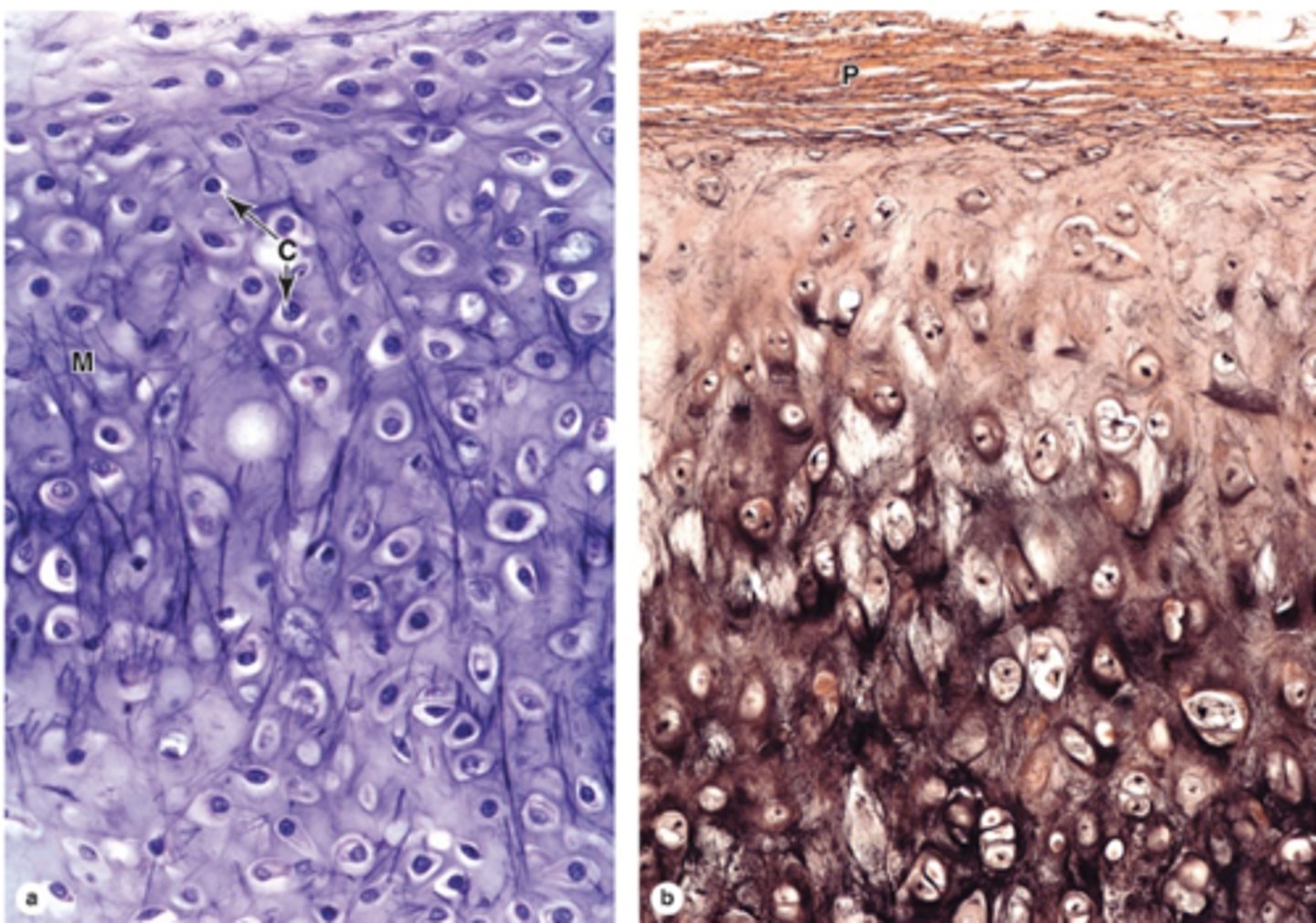
How does elastic cartilage compare to hyaline cartilage?
Similar structure but with an abundant, unevenly distributed network of elastic fibers.
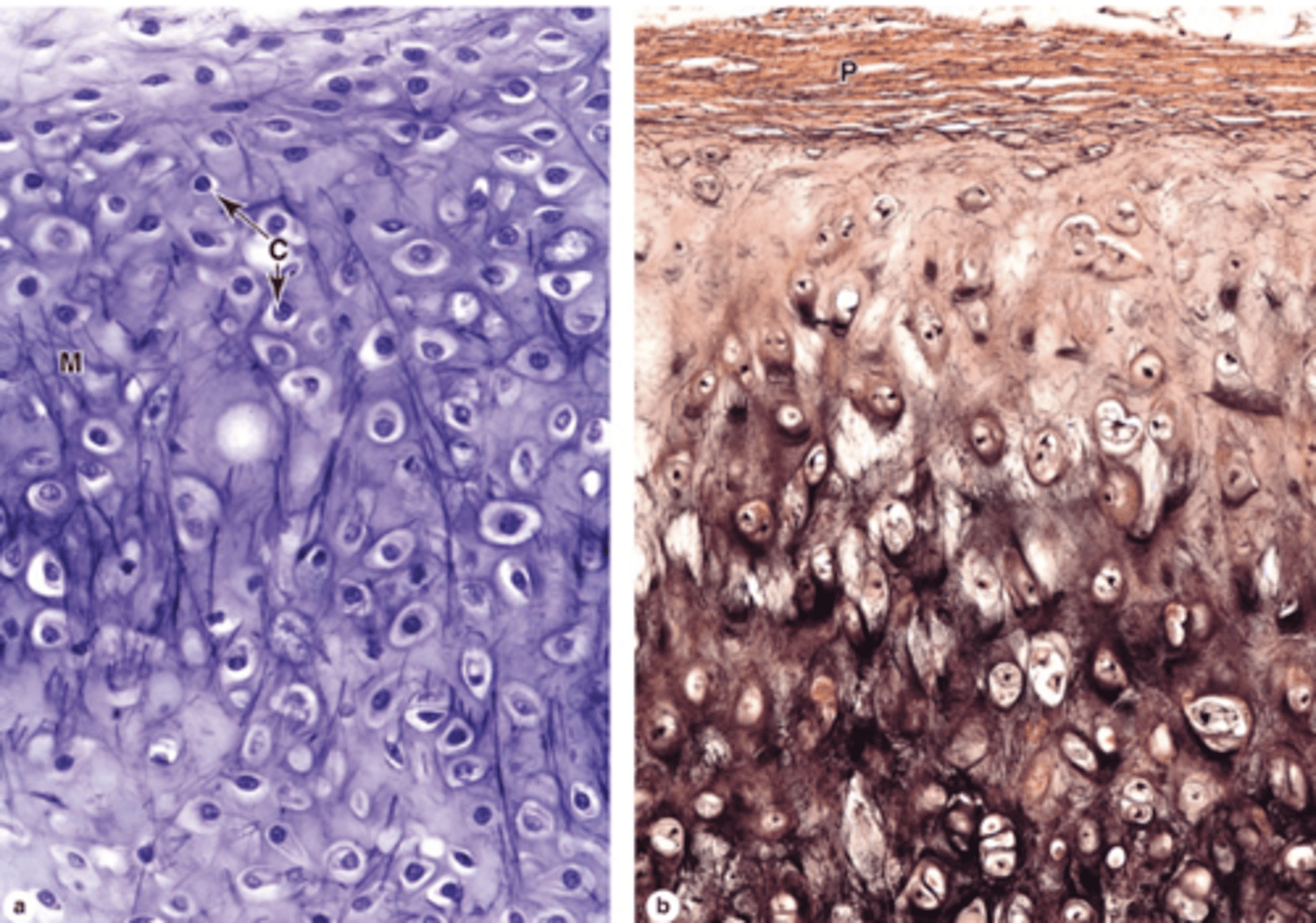
What fibers form the meshwork in elastic cartilage ECM?
Type II collagen fibers.
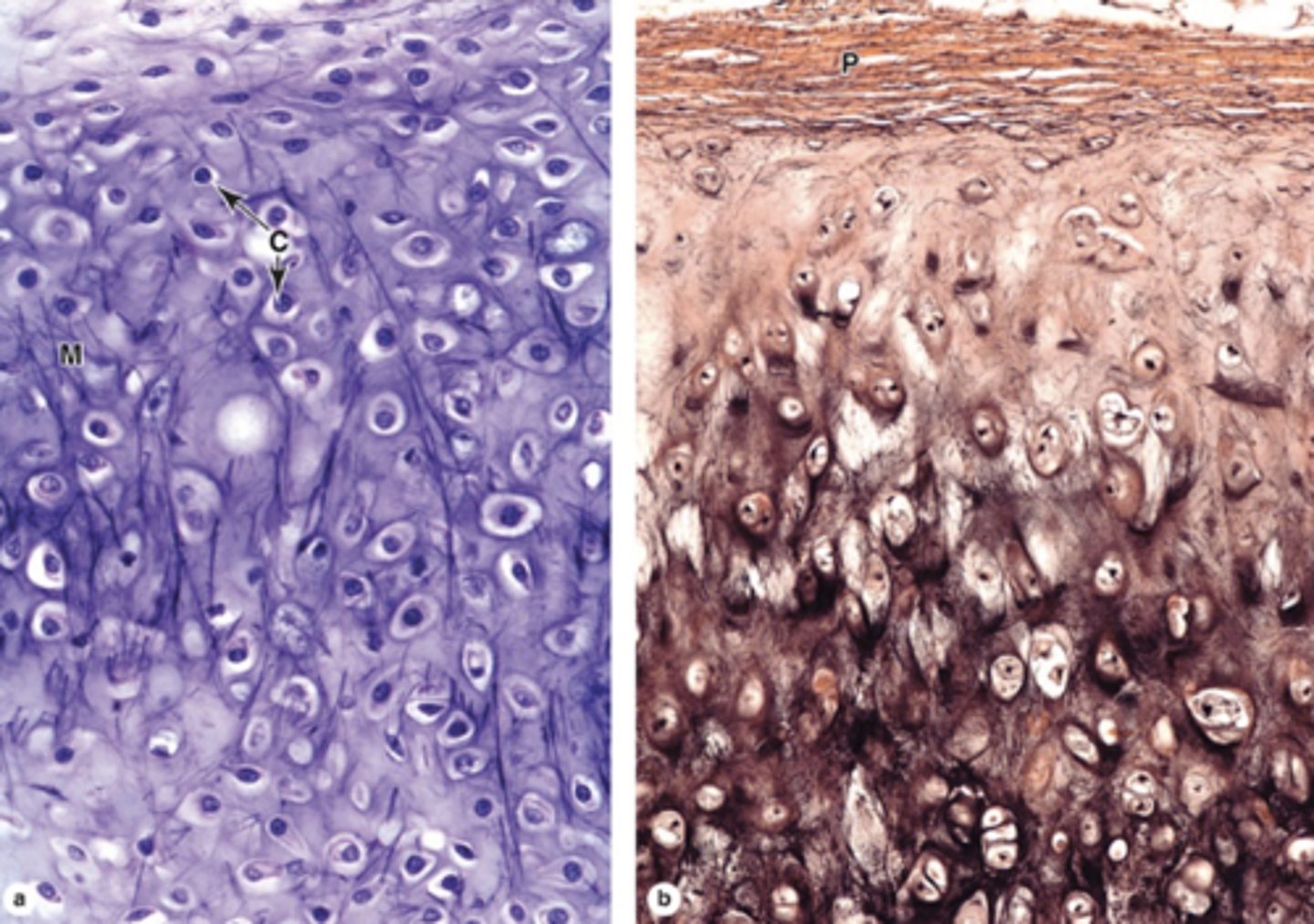
What is a key functional property of elastic cartilage?
Highly flexible
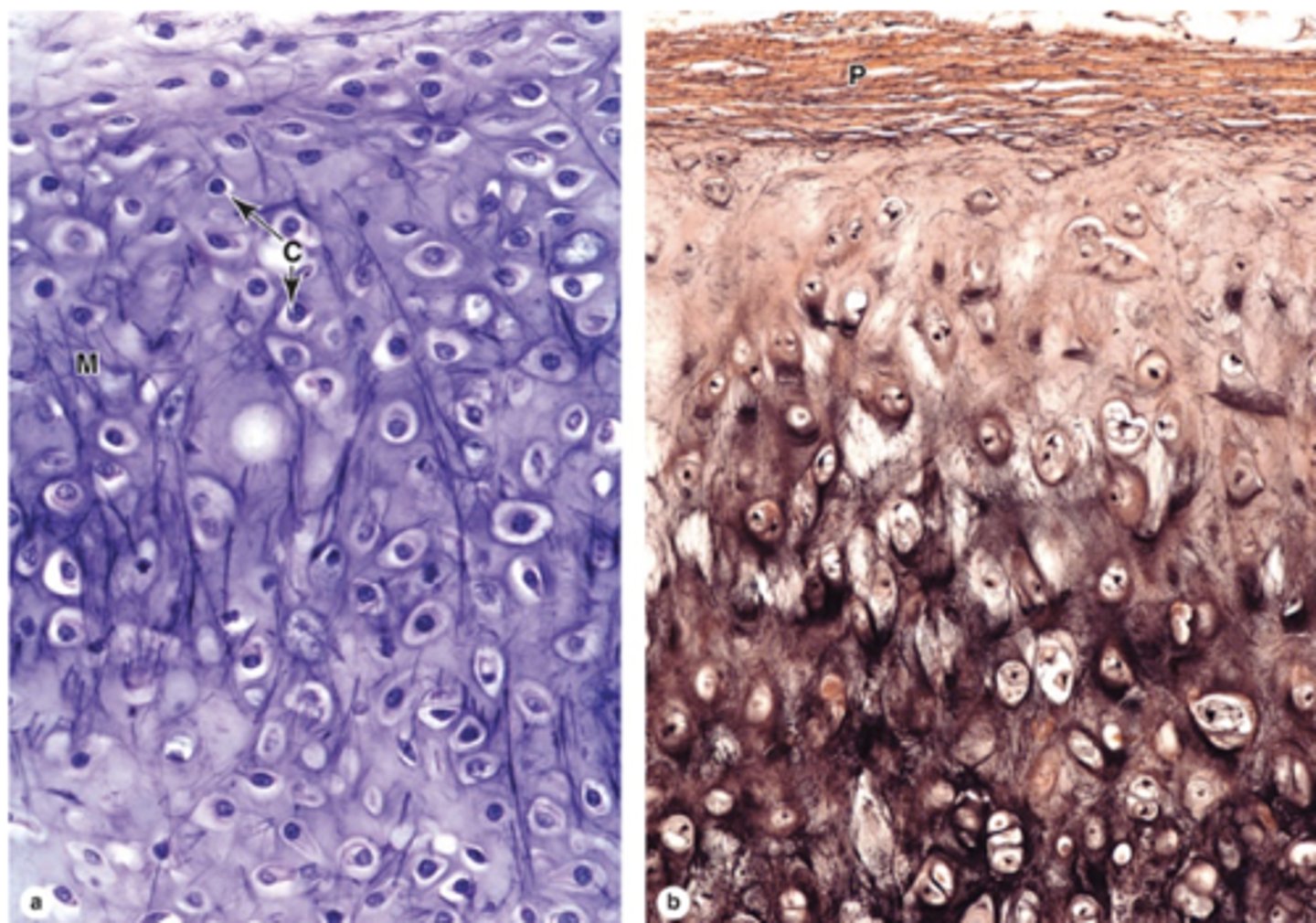
Where is elastic cartilage found? (5)
1. Auricle of ear
2. Walls of external auditory canal
3. Auditory tubes
4. Epiglottis
5. Upper respiratory tract
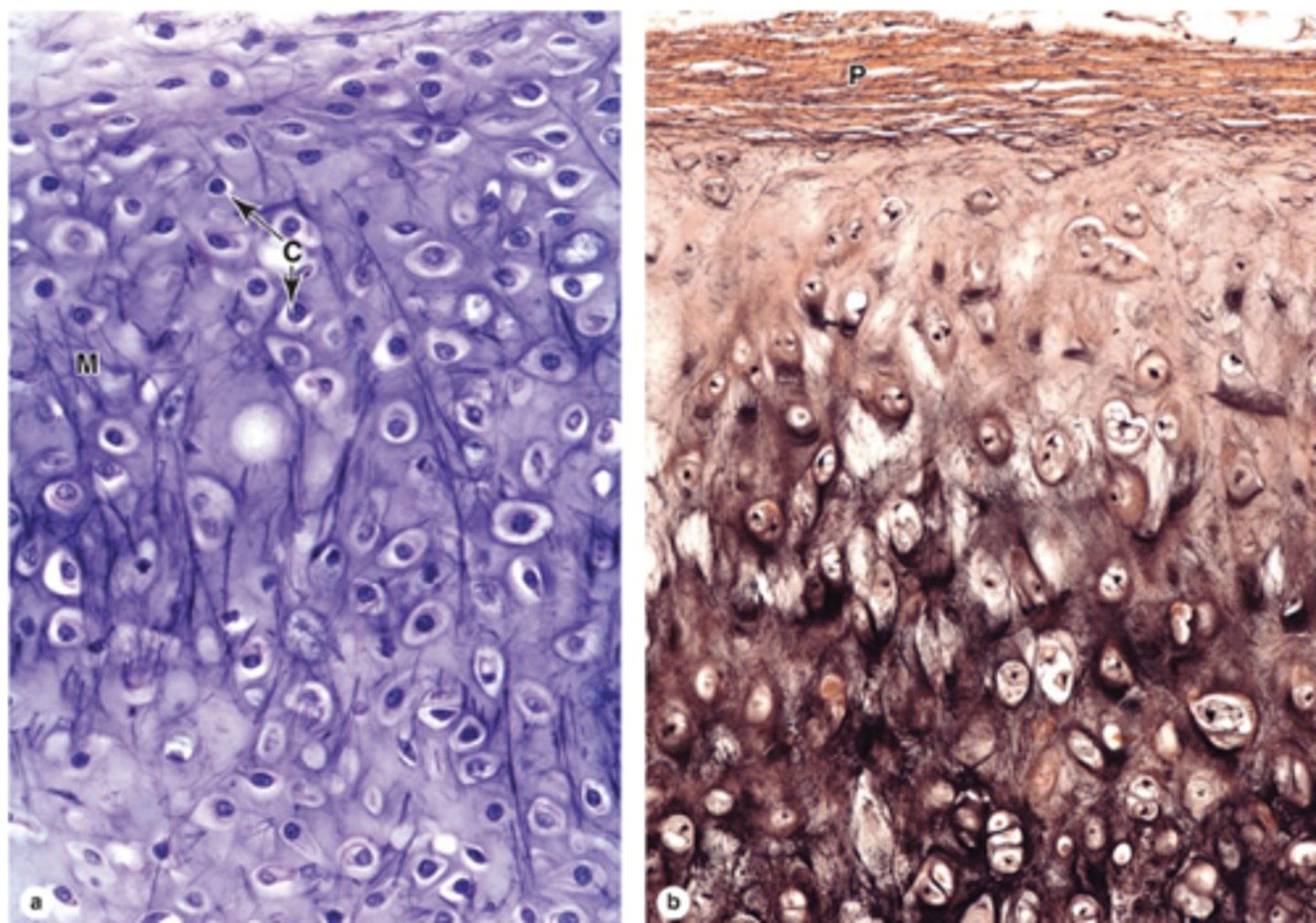
Does elastic cartilage have a perichondrium?
Yes, perichondrium is always present
What tissues is fibrocartilage a combination of? (2)
Hyaline cartilage and dense regular connective tissue.
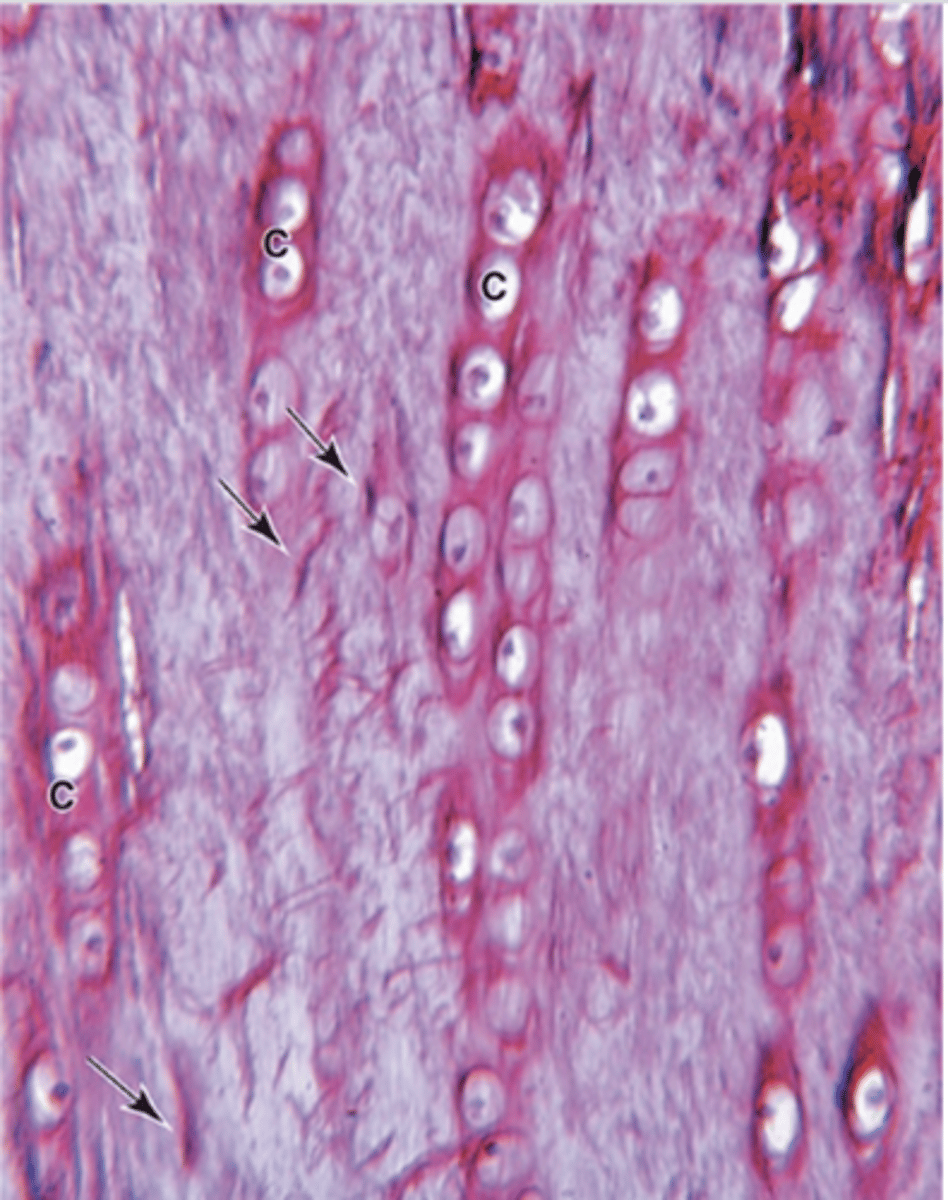
What is the main function of fibrocartilage?
Provides cushioning and support for bones.
Where is fibrocartilage commonly found? (3)
1. Intervertebral discs
2. Attachment of some ligaments
3. Pubic symphysis
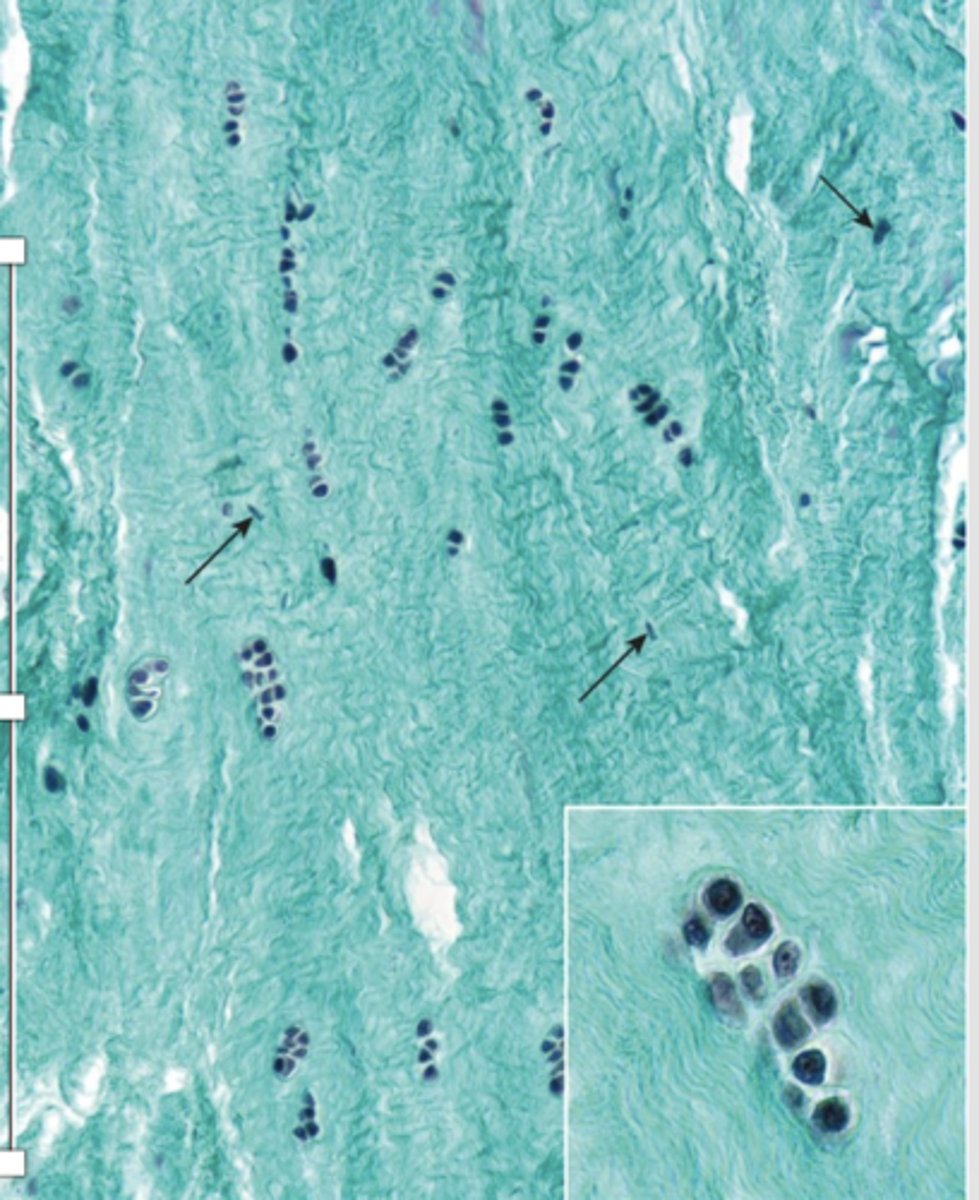
How are chondrocytes arranged in fibrocartilage?
Single or aligned in isogenous aggregates.
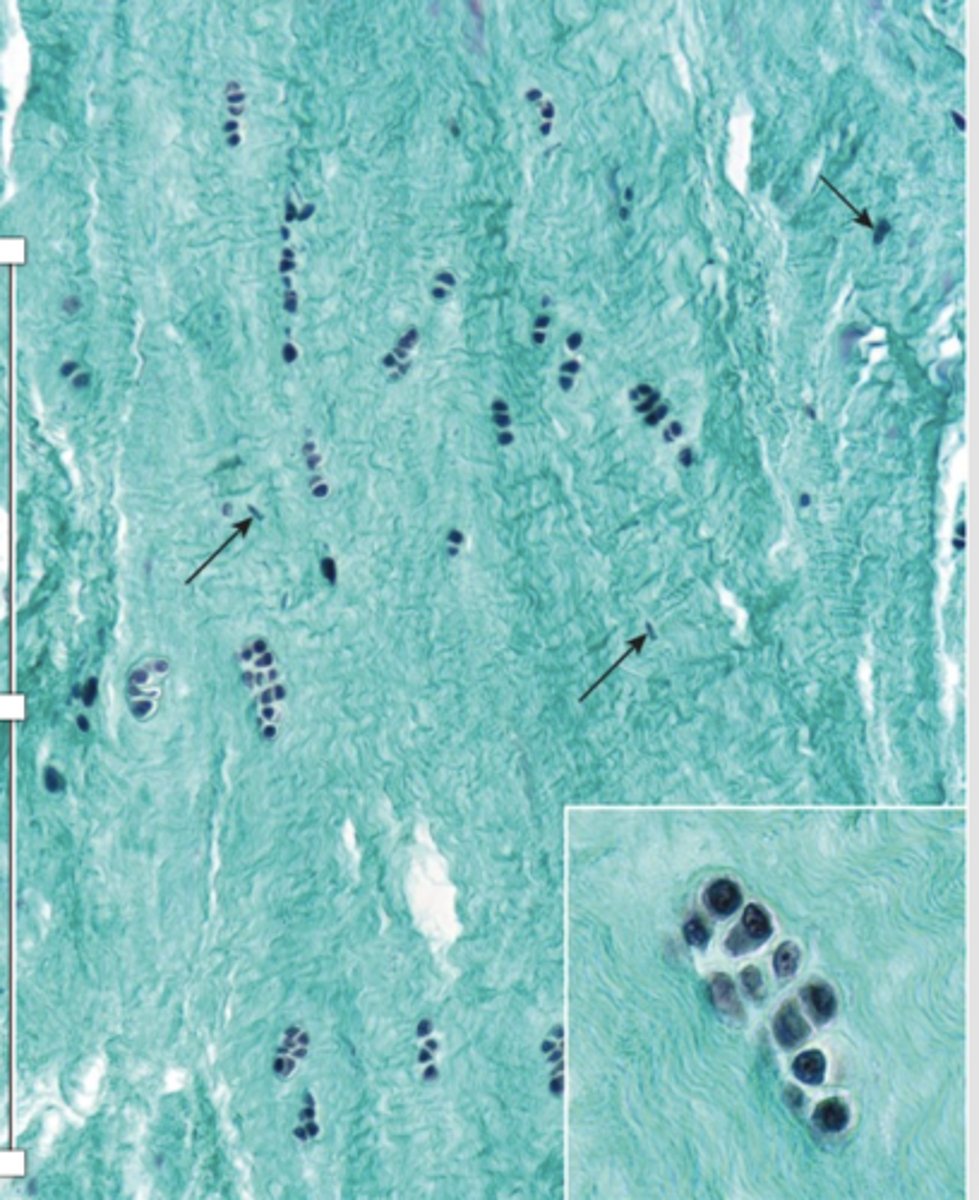
What do fibrocartilage chondrocytes synthesize?
Type I collagen and the usual components of ECM.
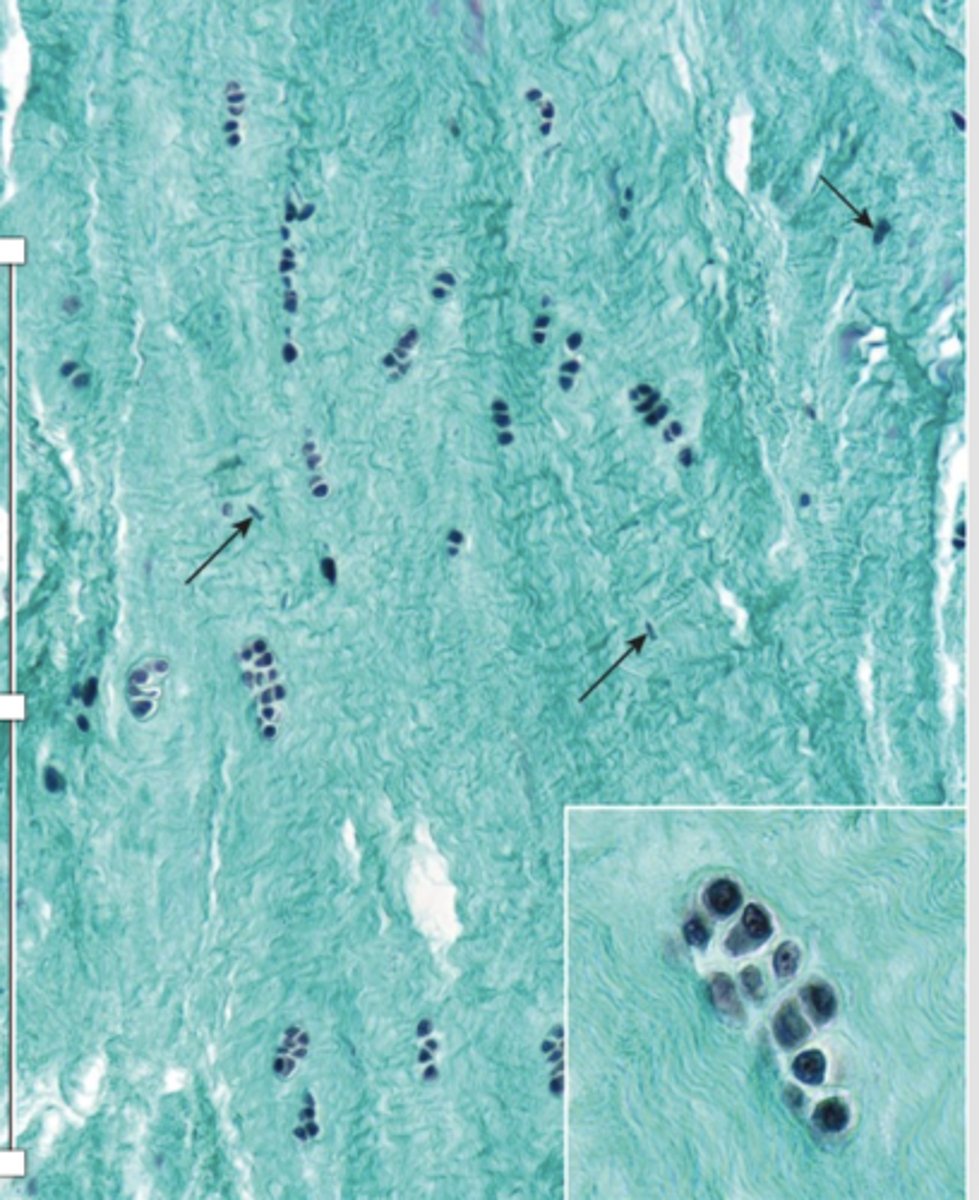
What do regions with fibrocartilage that contain fibroblasts and type I collagen do? (2)
- Separate areas with chondrocytes and hyaline matrix
- Provide extra tensile strength
How does the fibrocartilage matrix stain and why?
Acidophilic due to high type I collagen content.
- less proteoglycans
Does fibrocartilage have a perichondrium?***
NO PERICHONDRIUM
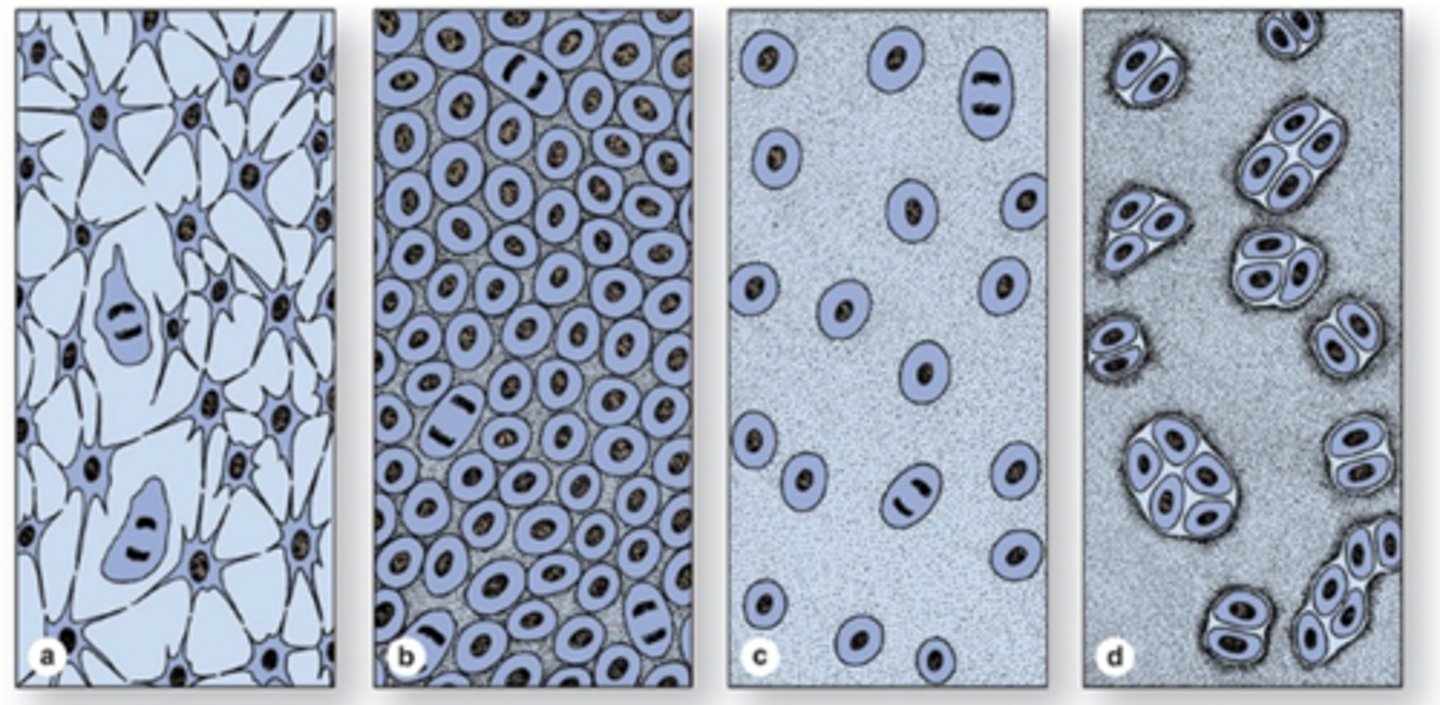
What are the steps of cartilage formation (condrogenesis)? (4)
a) Embryonic mesenchymal cells retract their processes, round up, and rapidly multiply
b) New chondroblasts become densely packed
c) Synthesis and swelling of ECM separates the cells (now chondrocytes)
d) Mitosis of single chondrocytes leads to formation of isogenic groups
What is appositional growth in cartilage?
- Chondroblasts differentiate from progenitor perichondrial cells
- Synthesis of matrix contributes to cartilage growth
- More important during postnatal development
- Never occurs in articular cartilage
What is interstitial growth in cartilage?
- Mitosis of pre-existing chondrocytes
- Synthesis of matrix contributes to cartilage growth
- Important for increasing the length of long bones
- Seen in articular cartilage
What type of cartilage growth is seen in articular cartilage?
Interstitial growth
How effective is cartilage repair in general?
Slow and incomplete, except in young children
Where does new cartilage come from during repair?
From perichondrial cells invading the injured tissue, but this is very limited.
What often forms in damaged cartilage areas instead of new cartilage?
A scar of dense connective tissue.
Why is cartilage repair difficult and incomplete?
Due to avascularity and slow metabolism.
Which type of cartilage is most prone to calcification?
Hyaline cartilage
What determines the sites of cartilage calcification? (3)
1. Portion of articular cartilage in contact with bone tissue (growing and adult bones)
2. During endochondral ossification in growth
3. As part of the aging process in adult hyaline cartilage
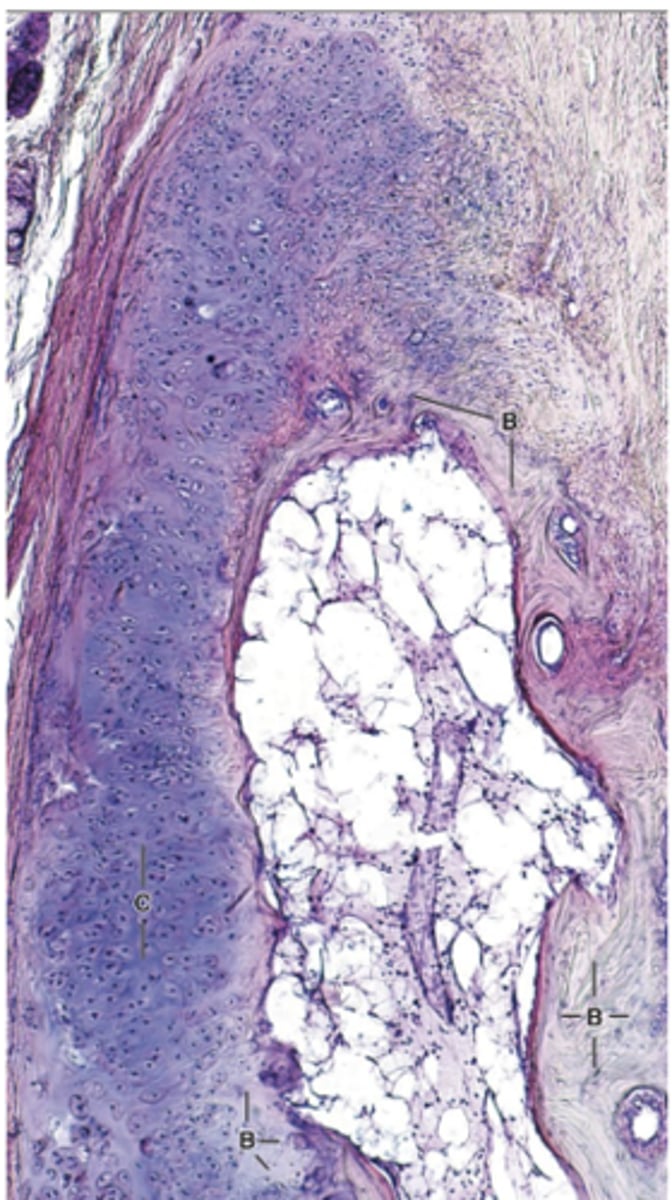
How long does cartilage calcification take?
a lengthy process
What always happens to calcified cartilage?
It is eventually replaced by bone.
How does calcification affect nutrient diffusion in cartilage?
The calcified matrix impedes diffusion of nutrients.
What happens to chondrocytes during calcification?
Chondrocytes swell and die.
What happens to the calcified matrix after chondrocytes die?
It is removed and replaced by bone.
What type of tissue is cartilage?
Special connective
What type of cartilage has abundant type I collagen fibers?
Fibrocartilage
How do Chondrocytes receive their nutrients
by diffusion
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease that limits the movement of synovial joints by affecting the articular cartilage, which is made up of ________
Hyaline cartilage