Biology Unit 1 Grade 12 Test
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Macromolecules
large chain molecules
carbs, proteins, lipids & nucleic acids
referred to as —> polymers
connected with covalent bonds
polymers
large molecules made by repeating subunits (monomers)
carbohydrates
short term energy, large term energy, structure molecules
made of CHO (1:2:1)
lots of hydroxyl endings (-OH)
makes molecules polar —> water soluble
monosaccharides
1 sugar
Glucose, fructose, galactose
Disaccharides
2 sugars
surcrose
Polysaccharides
72 sugars combined
starch, glycogen, cellulose
Lipids
made of CHO
non polar
few hydroxyl endings
smaller complex molecules
Function
long term energy storage
protects organs
insulation
hormones (communication molecules)
dissolving fat-soluble vitamins
Phospholipids —> cell membrane
nervous system —> myelination of nerves (protect from signal loss)
ear wax (prevents fungi/bacteria in ears)
Fatty Acids
Hydrocarbon chains with carboxyl ending
Saturated fat
single bond between carbons
max num of H
straight linear molecule
stackable + will do LDF
solid at room temperature
animal fats —> butter +lard
Unsaturated fats
carbon atoms have double bonds between
less hydrogen per molecule
no stacking
liquid at room temperature (oil)
plant fats
Steroids
molecules with 4 carbon rings attached to a functional group
(testosterone, estrogen, cholesterol, communication, growth)
*note: cholesterol: maintains cell fluidity*
waxes
large hydrophobic molecules
non polar
water proving
ex:
ear wax
Proteins
most diverse of macromolecules
25,000 in human body
Polymer made out of amino acid monomers
Amino acids —> CHONS
Make up enzymes (biological catalysts)
20 amino acid monomers —> sequence is determined by DNA (codon)
Structure, Movement (of substances), Hormones, Immune System (SHIMoS)
Sequence of Protein
1) (image)
2) (image)
3) sheet + helix structure (tertiary)
4) Polypeptide chain
*3 and 4 are functional groups*
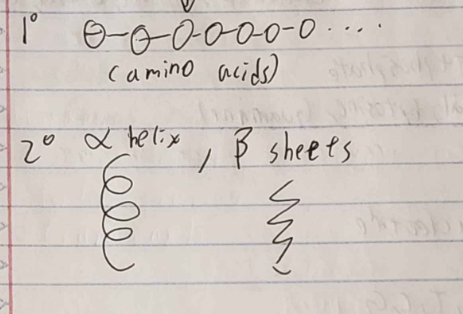
Denature
2°, 3°, 4° don’t work anymore
pH and temp sensitive
Digest
breaking into 1°st structure
Nucleic Acids
DNA —> deoxyribonucleic acid —> deoxy ribose phosphate base (A T G C)
RNA —> ribonucleic acid (ribose sugar + phosphate) (A U G C)
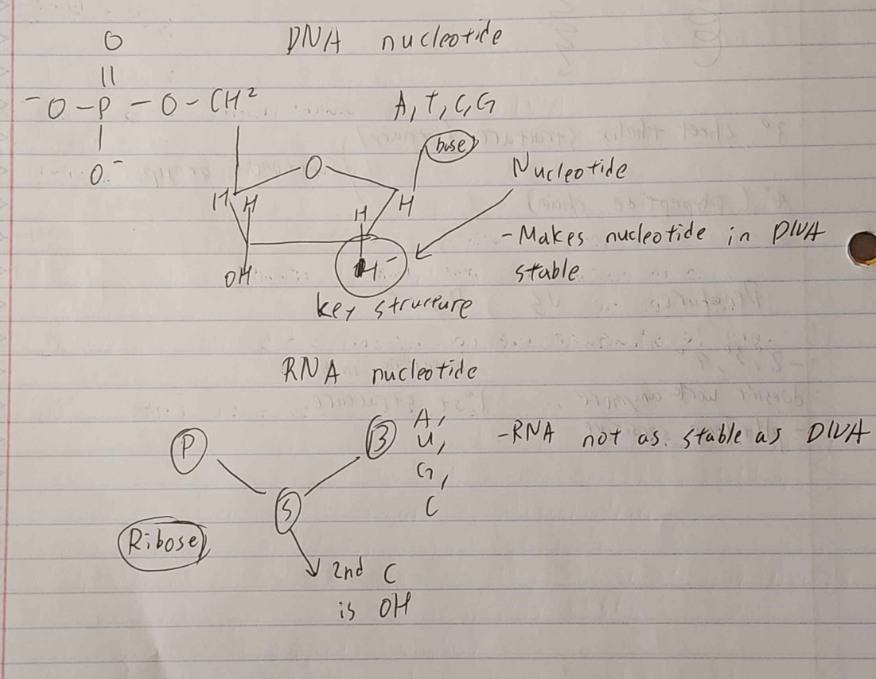
DNA
provides code for amino acid sequence
information molecule
stable molecule
double stranded
forms helix with H bonds in middle
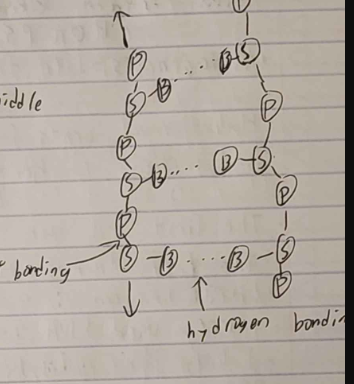
RNA
does a lot in cells
single stranded (can form small double)
small(er) molecule
variable structure bc OH and 2nd C
examples:
mRNA
rRNA
siRNA
TRNA
snRNA
Intramolecular forces
found within molecule: ionic/covalent bonds
Intramolecular forces can affect intermolecular forces
electronegativity of atoms
results in polar molecules(dipole)
polar molecules - molecule w unbalanced electric charges
Polarity of biological molecules greatly affect behavior and function in cell
Origin of Life
need certain elements and molecules (CHONPS) + universal solvent (water)
abiogenesis = life from not life
hydrothermal cells were prokaryotic (3.5-3.8 bya) (lived in hydrothermal)
last universal common ancestor —> single celled organism
lived between 3-4 bya
likely used RNA to store info + had phospholipids in membrane
rRNA and ribosomes present
Two prokaryotic domains
Eubacteria
Archaea
Endosymbiosis
Two prokaryotic cells bond together to make a eukaryotic cell
archaea engulfed an ancestor of purple bacteria
purple bacteria —> good at generating ATP (origin of mitochondria)
Binary fission reproduction
Mitochondrial ribosomes are essentially bacterial ribosomes
Happened again —> origin of chloroplasts 1.5bya
some evidence to support chloroplast
other organelles —> membrane based formed by in-folding of phospholipid membranes
origin of nuclear membrane and endoplasmic reticulum and golgi body
other vesicles are part of this continued process
cell membrane
regulates what enters and exits body
only selective materials enter
control movement of substances near, or inside the cell
cytoplasm
holds molecules for cellular process
protects it from any damage
nucleus
contains genetic information
responsible for cell division
responsible for ribosomes
nucleolus
denser than nucleus
stores RNA
protein chromatin
responsible for ribosomes
nuclear envelope
double membrane consisting of double phospholipid bilayer
separating nucleus from rest of the cell
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum
synthesizes lipids and lipid-containing molecules (ie: Phospholipids)
performs other functions depending on location
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum
located w ribosomes
synthesizes protein
transports protein
folds proteins
vesicles
transport materials within cell
such as
water
hormones
communication
Golgi Apparatus
processes and sends proteins/lipids within cell
sorts them based on location
packages into vesicles for transport
Lysosomes
breaking down and recycling cellular waste or foreign invaders
maintains cellular health
Chloroplasts
organelle in plant cells
captures light energy from sun
stored as high - energy molecules (ie: glucose)
Mitochondria
eukaryotic cells
break down stored energy
converts into visible energy
Cell Wall
composed of proteins or carbohydrates
gives cell its shape
structural support and protection
Cytoskeleton
extends through cytoplasm
provides structure
anchors cell membrane/organelles in place
Cillia
move fluids, mucus, small particles across surface of cell
moves the whole cell in unicellular organisms
Flagella
propels cell through liquids
Peroxisomes
contains enzymes that transfer hydrogen from substances to oxygen —> H2O as byproduct
formed in Endoplasmic reticulum
various functions:
break fatty acids down into smaller molecules for cellular respiration
detoxify alcohol in liver
Lysosomes
used by cell to digest macromolecules
sac of hydrolytic enzymes
apoptosis
(usually) found only in animal cells
formed in golgi body
what are phospholipids composed of?
two fatty acids
glycerol unit
phosphate group
Phosphate heads are attracted to (1)_______ and hydrocarbon tails are attracted to (2)_______ but not ______(same as (1))
(1) water
(2) each other
Due to this, the phospholipids are arranged in (1)_______ with the hydrophilic heads pointing out on either side and the hydrophobic tails facing (2)_______
(1) bilayer
(2) inward
Describe fluid mosaic model
Visualizes the cell membrane as a mosaic of proteins and other molecules in a fluid phospholipid bilayer.
consists of: phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, carbohydrates
these components give membrane fluid character
Hydroxyl (include properties, structural formula, an example, and what it’s found in)
Polar
Ex: Ethanol
Found in
carbohydrates
proteins
nucleic acids
lipids
Carbonyl
Polar
Ex: acetaldehyde
Found in:
carbohydrates
nucleic acids
Carboxyl
Polar (acidic )
Ex: Acetic Acid
Found in:
Proteins
Lipids
Amino
Polar (basic )
Ex: Alanine
Found in:
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Sulfhydryl
Slightly Polar
Ex: cysteine
Found in:
Proteins
Phosphate
Polar (negatively charged )
Ex: glycerol phosphate
Found in:
Nucleic Acids
Endomembrane system
internal membranes formed by in-folding of phospholipid membrane
origin of nuclear membrane and later ER and golgi body
series of membrane based organelles that create, modify, process and deliver cell products within/outside cell
RER and SER, goldgi and transport vesicles (peroxisomes, lysosomes, secretory vesicles)
continuous process-membranes bud and merge; dynamic/fluid system
Endoplasmic Reticulum
made uup of membranous tubules and cisternae (sacs)
smooth ER; no ribosomes
synthesis and transport of lipids
controls glucose ←→ glycogen conversion in liver muscles
detoxification of drugs/poisons
rough ER: ribosomes attached
synthesis and transport of proteins
Golgi apparatus
products of ER are modified and storied here
modifies and packages proteins
Endocytosis
cell membrane engulfs material by folding inward which pinches off to create vesicle within the cell
Phagocytosis
cell engulfs solid particles
Pinocytosis
cell engulfs liquid particles
Receptor Mediated Endocytosis
receptor proteins on the cell membrane bind to specific molecules
Exocytosis
Secretory vesicle fuses with the cell membrane and releases contents to exterior of cell
Osmosis and solute
solutes in solution determine osmotic concentration
if two solutions have unequal osmotic concentrations —> solution w higher concentration is hypertonic and solution with lower is hypotonic
if they have osmotic concentration —> isotonic
water flows from hyper to hypo
*cells in solution: hypotonic*
Hemolysis and what is the process in plant cells?
when too much water is in the cell (animal cells)
in plant cells they prevent lysis and becomes turgid
cells in solution: hypertonic
crenation
crinkling/shriking of cell
(in plants: plasmolysis wilting)
Factors Affecting Rate of Movement
concentration : steepness of gradient
polarity of molecule
shape/size of particle
temperature
pressure
presence/absence of facilitated particles
Active Transport across cell membrane
against concentration gradient
requires energy in the form of ATP
adenosine + triphosphate(ATP_ →(H2O) = Adenosine + diphosphate+phosphate + energy (ADP)
Primary Active Transport
Move molecules or ions across membranes against a concentration gradient
ex: sodium-potassium pump
Secondary Active Transport
uses concentration gradient of an ion established by primary pump as energy source
creates an electrochemical gradient which creates electrical potential energy
Membrane Assisted Transport
larger molecules must move into or out of the cell through membrane assisted transport
requires endo and exocytosis
Fluid Mosaic Model of Phospholipid Bilayer
semi fluid phospholipid bilayer w variety of proteins and carbohydrates attached to lipids or proteins
fluid nature —> heads out, tails in (viscosity like vegetable oil)
factors affecting fluidity: temp, how bendy, fatty acid length)
longer length=less fluid
Presence of cholesterol
high temps: decreases fluidity
low temps: breaking up and increases fluidity
Bilayers are made up of phospholipids; act as scaffolding (where proteins/macromolecules embedded)
glycoproteins and glycolipids —> proteins and lipids covalently bonded to carbohydrates
proteins in layers —> integral and peripheral
Integral proteins
embedded
Peripheral
Attached to one side
Passive transportation
movement of materials across cell membrane w/o expenditure of energy
simple diffusion
osmosis
facilitated diffusion
facilitator protein required 1) channel proteins 2)currier proteins
Diffusion
movement of molecules from area of high to low concentration
Osmosis
diffusion of water across semi-permeable membrane
Facilitated Diffusion
movement of molecules from high to lower w/ assistance of membrane protein
membrane protein have hydrophilic interiors that allow passage of polar/charged molecules