PHYSIO BIO | Finals Coverage
1/86
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Epinephrine
“fight or flight”; when a person experiences stress or fear
Norepinephrine
strongly affects our nervous system; involved in sleep, alertness, arousal, and mood
Dopamine
“pleasure-reward”; involves voluntary movement, learning, memory, emotion, sleep, motivation, and reward
Serotonin
“happy pill”; involved in sleep, mood, appetite, and judgement
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
regulates anxiety, vision, and motor control
Endorphins
“pain reliever”; works in lowering the transmission of pain signals to the brain and promotes feelings of euphoria
Acetylcholine (ACT)
focused on muscle movements, memory, and learning, associated with motor neurons.
leads to depression
What happens when you have low levels of norepinephrine?
leads to mania, anxiety, and schizophrenia
What happens when you have high levels of epinephrine?
leads to depression and Parkinson’s disease
What happens when you have low levels of dopamine?
leads to mania, anxiety, bipolar, addiction and schizophrenia
What happens when you have high levels of dopamine?
leads to depression and Parkinson’s disease
What happens when you have low levels of serotonin?
leads to mania, anxiety, and schizophrenia
What happens when you have high levels of serotonin?
leads to bipolar, anxiety, schizophrenia, mania and ADHD
What happens when you have low levels of GABA?
leads to hypersomnia, depression, or lack of energy
What happens when you have high levels of GABA?
leads to depression, anxiety, mood swings, and chronic physical pains
What happens when you have low levels of endorphins?
leads to addiction to exercise or physical activity
What happens when you have high levels of endorphins?
leads to motor disabilities, dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, paralysis, stroke, muscle weakening, and learning and memory impairments
What happens when you have low levels of ACTs?
leads to increased salvation, muscle weakening, blurry vision, and paralysis
When happens when you have high levels of ACTs?
Ablation
removal of the brain area
Lesion
damage to the brain area, often done for research
Stereotaxic Instrument
this is used to damage structures in the interior of the brain
Injecting chemicals
kills neurons or inactivates them temporarily
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
intense magnetic field application that temporarily inactivates a brain area; active, inactive, then active again
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
records electrical activity from scalp; distinguishes wakefulness from stages of sleep

Magnetoencephalograph (MEG)
measures faint magnetic fields generated by brain activity
Positron-emission Topography (PET)
records emission of radioactivity; produces high resolution images
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
uses oxygen consumption in the brain to provide a moving and detailed picture; safer and less expensive than PET
Computerized axial tomography Scan (CAT Scan)
injects dye into the blood; maps brain areas and requires exposure to x-ray
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
applies powerful magnetic field to image the brain
Spinal Cord
passage for motor activities; communicates with all the sense organs and muscles except those of the head
Hindbrain
consists of the medulla, pons, and cerebellum
Medulla (Medulla Oblongata)
controls vital reflexes; enlarged extension of the spinal cord
Pons
Latin word for bridge; hindbrain structure that lies anterior and ventral to the medulla; allows hemispheres to control the left and right sides of the body
Cerebellum
contributes to movement control; for balance and coordination
Midbrain
a relay system, transmitting information necessary for vision and hearing
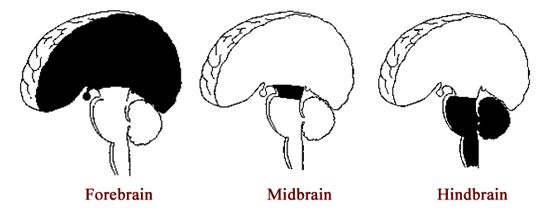
Forebrain
most prominent part of the brain and has two cerebral hemispheres; responsible for voluntary actions, thinking, and processing
Amygdala
most central for evaluating emotional information especially with regard to fear
Hypothalamus
controls our appetite for eating, drinking, temperature control, and reproductive behaviors; the master control of the autonomic system
Thalamus
where most sensory information go first; receives input from a sensory system and transmits information to a single area of the cerebral cortex
Pituitary Gland
synthesizes hormones that the blood carries to organs throughout the body
Hippocampus
essential for certain types of memories and monitors where you are and where you’re going
Cerebral Cortex
outer layer of the cerebrum; responsible for motor areas, sensory areas, and association areas
Cerebrum
largest part of the brain; initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature
Occipital Lobe
targets visual information
Parietal Lobe
essential for spatial and numerical information; monitors all information about the eye, head, and body positions and passes it on to brain areas that control movement
Temporal Lobe
primary cortical target for auditory information
Frontal Lobe
involves voluntary movement, expressive language and for managing higher level executive functions
damage in the Cerebellum (Cerebellar Damage)
damage in this area may cause clumsiness or make them lose their balance; they may also have difficulty in shifting their attention back and forth between auditory and visual stimuli
damage in the Broca’s Area (Broca’s aphasia)
is located in the frontal lobe; damage in this area causes difficulty in articulation
damage in the Wernicke’s Area (Wernicke’s aphasia)
is located in the temporal lobe; damage in this area makes the person formulate sentences that makes no sense or meaning
damage in the Hypothalamus
damage in this area causes abnormalities in motivated behaviors such as feeding, drinking, temperature regulation, sexual behavior, fighting or activity level
damage in the Hippocampus
damage in this area may cause memory impairments
damage in the Primary Visual Cortex (Occipital Lobe)
damage in this area may cause cortical blindness; may have no conscious visual perception and no visual imagery
tumor in the Temporal Lobe
damage in this area may cause visual or auditory hallucinations
tumor in the Occipital Lobe
damage in this area may evoke simple sensations like flashes of light
Kluver-Bucy Syndrome
a syndrome where the temporal lobe is damaged and that a rare behavioral impairment that causes people to put objects in their mouths and engage in inappropriate sexual behavior
Visual Agnosia
damage in the occipital lobe that leads to the inability to visually recognize objects
Prefrontal Lobotomy
among its common consequences were apathy, a loss of ability to plan and take initiative, memory disorders, distractibility, and loss of emotional expressions
Delayed-Response Task
leads to an abnormality of delay in response after hearing or seeing something
Prefrontal Cortical Damage
damage in this area would cause people to act impulsively because of their failure to weigh the pros and cons
Mouth
where digestion begins
Mother’s milk
What do newborn mammals consume in order to survive?
Lactase
enzyme necessary for metabolizing lactose
Lactose
the sugar in milk
Sham feeding
any procedure that mimics normal food consumption but where food and drink are not actually digested or absorbed.
Cranial Nerve X or Vagus Nerve
the cranial nerve that conveys information to the brain about the stretching of the stomach walls
Duodenum
part of the small intestine adjoining the stomach; major site for absorbing nutrients; it is the first digestive site that absorbs a significant amount of nutrients.
Cholecystokinin (CKK)
acts to limit meal size
Pancreas
increases the release of insulin and glucagon
Insulin
enables glucose to enter the cell; is produced to keep blood glucose from rising too high.
Glucagon
stimulates the liver to convert some of its stored glycogen back to glucose; keeps blood glucose from dropping too low
Leptin
limited to vertebrates; signals your brain about your fat reserves
Arcuate Nucleus
has one set of neurons sensitive to hunger signals and a second set sensitive to satiety signals
Ghrelin
acts to increase appetite; triggers stomach contractions.
insulin, CKK, and leptin increase satiety
Name three hormones that increase satiety
Syndromal Obesity
when a gene causes a medical problem that includes obesity
Monogenic Obesity
occurs when a single gene leads to obesity without other physical or mental abnormalities
Polygenic or Common Obesity
relates to many genes, each of which slightly increases the probability of obesity
Bulimia Nervosa
condition which people alternate between binges of overeating and periods of strict dieting; many induce themselves to vomit
Anorexia Nervosa
characterized by refusal to eat enough to maintain a healthy body weight; it can become life-threatening
Carnivores
are also called meat eaters
Herbivores
are also called plant eaters
Omnivores
those who eat both plants and meat
Conditioned Taste Aversion
a robust phenomenon that occurs reliably after just a single pairing of food with illness.
Splanchnic Nerves
convey information about the nutrient contents of the stomach
Glucose
an important source of energy throughout the body and nearly the only fuel used by the brain.