AP Human Geography Unit 1
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Human Geography Unit 1 - The Cultural Landscape
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
abiotic
composed of nonliving or inorganic matter
acculturation
the process of changes in culture that result from the meeting of two groups, each of which retains distinct cultural features
assimilation
the process by which a group's cultural features are altered to resemble those of another more dominant group
atmosphere
the thin layer of gases surrounding Earth
behavioral geography
the study of the psychological basis for individual human actions in space
biosphere
all living organisms on Earth, including plants and animals, as well as microorganisms
biotic
composed of living organisms
citizen science
scientific research by amateur scientists
climate
the long-term average weather at a particular location
concentration
the spread of something over a given area
conservation
the sustainable management of a natural resource
contagious diffusion
the rapid, widespread diffusion of a feature or trend throughout a population
cultural ecology
a geographic approach that emphasizes human-environment relationships
cultural landscape
an approach to geography that emphasizes the relationships among social and physical phenomena in a particular study area
culture
the body of customary beliefs, social forms, and material traits that together constitute a group's distinct tradition
density
the frequency with which something exists within a given unit of area
diffusion
the process of spread of a feature or trend from one place to another over time
distance decay
the diminished importance and eventual disappearance of a phenomenon with increasing distance from its origin
distribution
the arrangement of something across Earth's surface
ecology
the scientific study of ecosystems
ecosystem
a group of living organisms and the abiotic spheres with which they interact
environmental determinism
a nineteenth- and early twentieth-century approach to the study of geography that argued that the general laws sought by human geographers could be found in the physical sciences. Geography was therefore the study of how the physical environment caused human activities
expansion diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend among people from one area to another in an additive process
formal region
an area in which everyone shares in common one or more distinctive characteristics; also known as a uniform region.
nodal region
an area organized around a node or focal point
geographic information science
the development and analysis of data about Earth acquired through satellite and other electronic information technologies
geographic information system (GIS)
a computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data
geography
the study of where things are found on Earth's surface and the reasons for the locations
geotagging
identification and storage of a piece of information by its precise latitude and longitude coordinates
Global Positioning System (GPS)
a system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers
Greenwich Mean Time
the time in the zone encompassing the prime meridian, or 0° longitude
hearth
the region from which innovative ideas originate
hierarchical diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places
humanistic geography
the study of the different ways that individuals form ideas about place and give those places symbolic meanings
hydrosphere
all the water on and near Earth's surface
international date line
an arbitrary line approximately along the 180th meridian designated as the place where each calendar day begins
latitude
the numbering system used to indicate the location of parallels drawn on a globe and measuring distance north and south of the equator (0°)
lithosphere
Earth's crust and a portion of upper mantle directly beneath the crust
location
the position of anything on Earth's surface
longitude
the numbering system used to indicate the location of meridians drawn on a globe and measuring distance east and west of the prime meridian (0°)
map
a two-dimensional, or flat, representation of Earth's surface or a portion of it
mashup
a map that overlays data from one source on top of a map provided by a mapping service
mental map
a representation of a portion of Earth's surface based on what an individual knows about a place that contains personal impressions of what is in the place and where the place is located
meridian
an arc drawn on a map between the North and South Poles
network
a chain of communication that connects places
nonrenewable resource
something produced in nature more slowly than it is consumed by humans
parallel
a circle drawn around the globe parallel to the equator and at right angles to the meridians
participatory GIS
community-based mapping, representing local knowledge and information
pattern
the geometric or regular arrangement of something in a particular area
place
a specific point on Earth, distinguished by a particular characteristic
polder
land that the Dutch have created by draining water from an area
possibilism
the theory that the physical environment may set limits on some human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action from many alternatives
poststructuralist geography
the study of space as the product of ideologies or value systems of ruling elites
preservation
the maintenance of resources in their present condition, with as little human impact as possible
prime meridian
the meridian, designated as 0° longitude, that passes through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England
projection
a system used to transfer locations from Earth's surface to a flat map
region
an area of Earth distinguished by a unique combination of trends or features
relocation diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend through bodily movement of people from one place to another
remote sensing
the acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or from other long-distance methods
renewable resource
something produced in nature more rapidly than it is consumed by humans
resource
a substance in the environment that is useful to people, is economically and technologically feasible to access, and is socially acceptable to use
scale
generally, the relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole
site
the physical character of a place
situation
the location of a place relative to another place
space
the physical gap or interval between two objects
space-time compression
the reduction in time it takes to diffuse something to a distant place as a result of improved communication and transportation systems
spatial association
the relationship between the distribution of one feature and the distribution of another feature
stimulus diffusion
the spread of an underlying principle even though a specific characteristic is rejected
sustainability
the use of Earth's renewable and nonrenewable natural resources in ways that do not constrain resource use in the future
syncretism
the combining of elements of two groups into a new cultural feature
toponym
the name given to a portion of Earth's surface
transnational corporation
a company that conducts research, operates facilities, and sells products in many countries, not just where its headquarters or shareholders are located
uneven development
the increasing gap in economic conditions between the core and peripheral regions as a result of the globalization of the economy
vernacular region
an area that people believe exists as part of their cultural identity; also known as a perceptual region
volunteered geographic information
creation and dissemination of geographic data contributed voluntarily and for free by individuals
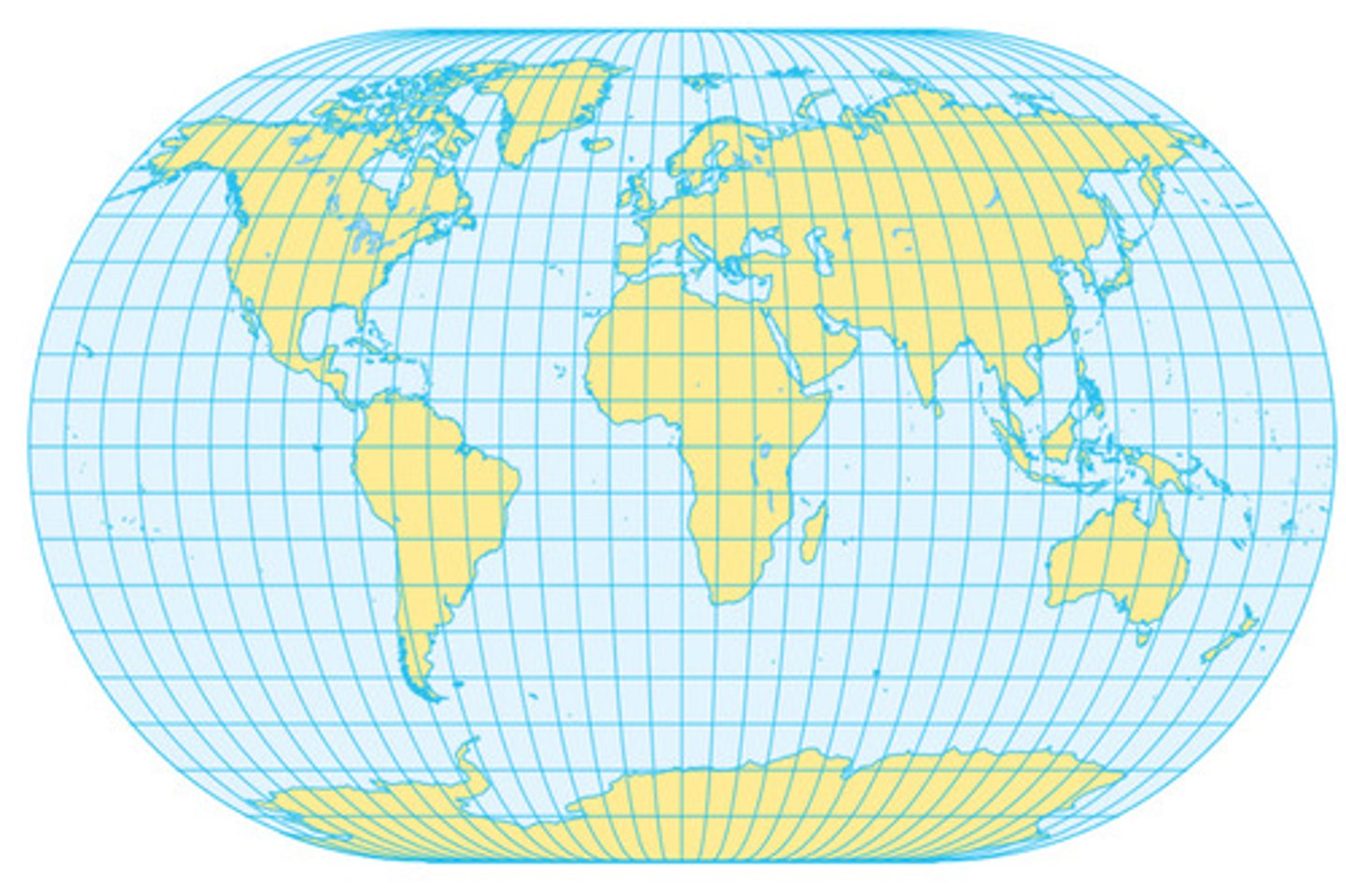
Winkel Projection
The relative sizes of the landmasses on the map are the same as in reality. The projection minimizes distortion in the shapes of most landmasses
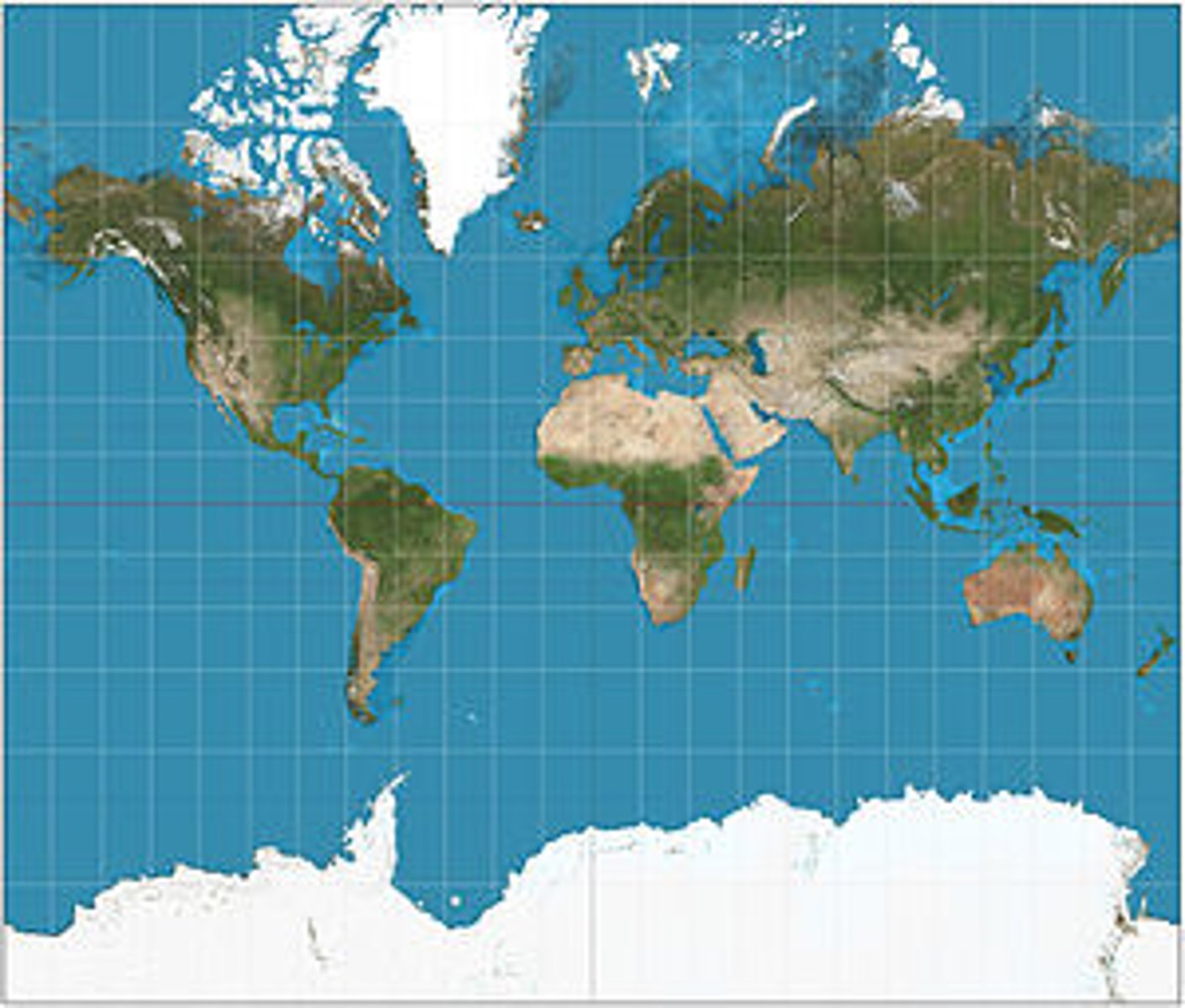
Mercator Projection
Shape is distorted very little, direction is consistent, and the map is rectangular. However, relative size is grossly distorted toward the poles, making high-latitude places such as Antarctica look much larger than they actually are.
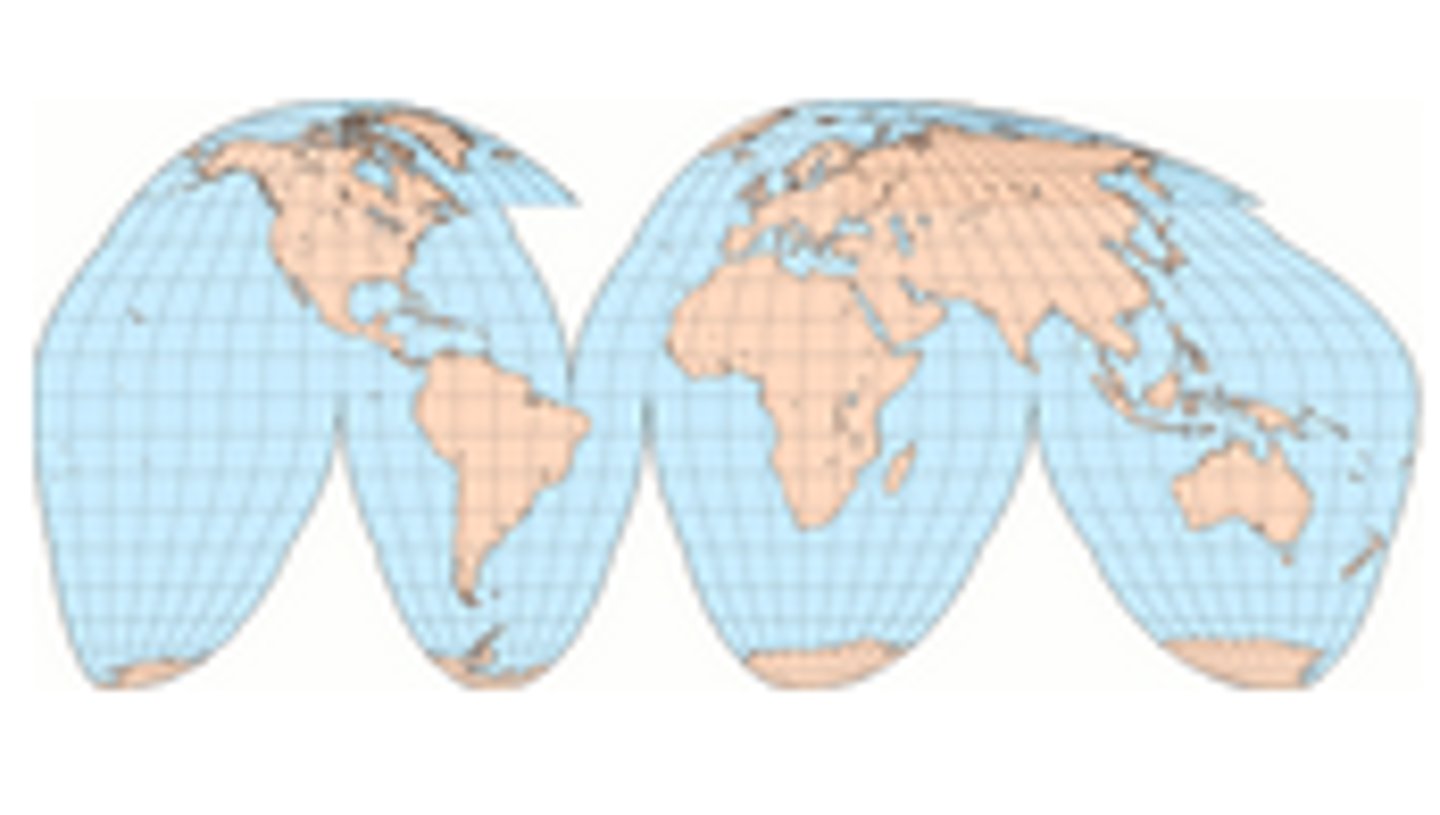
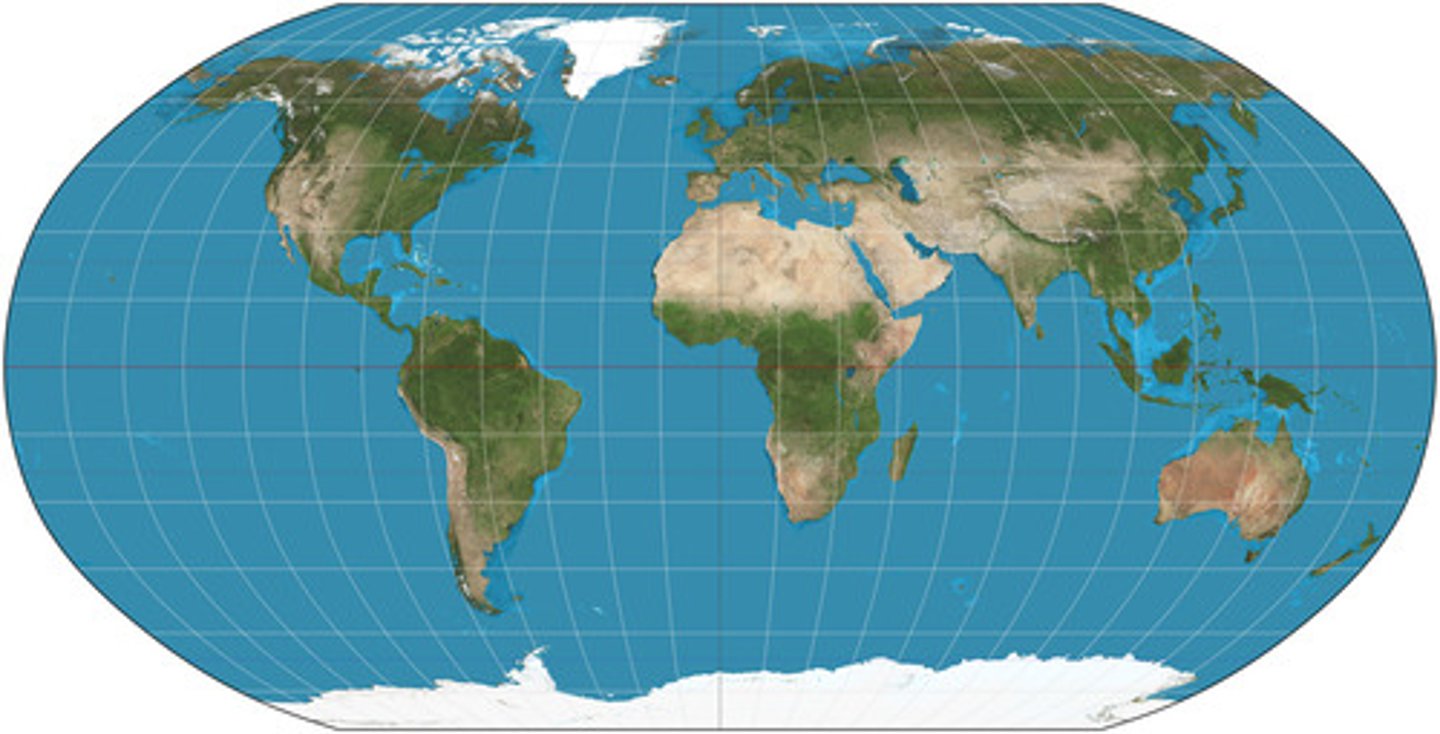
Goode Homolosine Projection
This projection separates the Eastern and Western hemispheres into two pieces, a feature known as interruption. It gives more prominence to the landmasses
Gall-Peters Projection
This projection does not distort relative size but does distort shape.
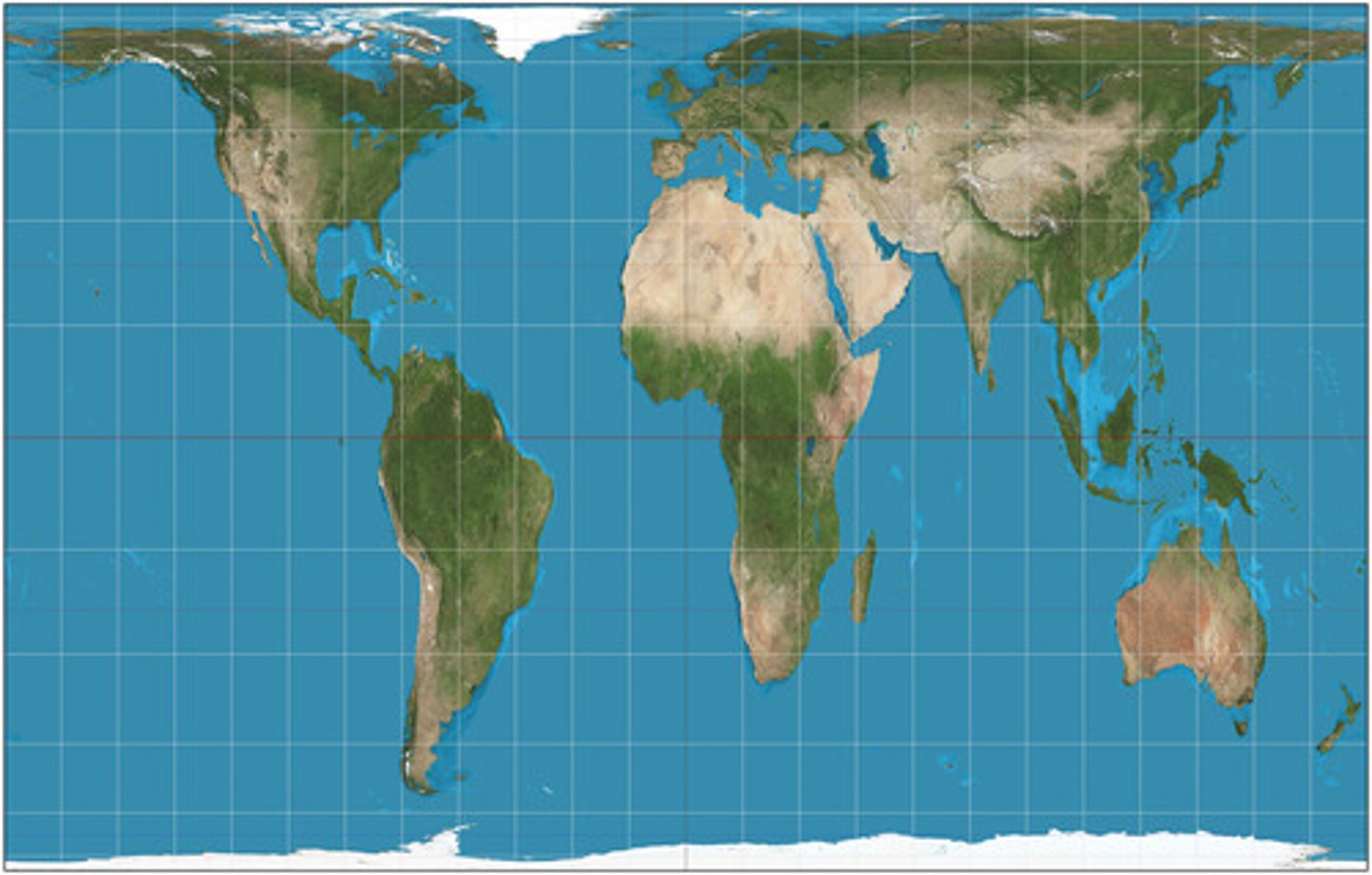
Robinson projection
Shape is distorted very little, direction is consistent, and the map is rectangular, relative size better in Mercator, results in some distortion in all areas throughout the map
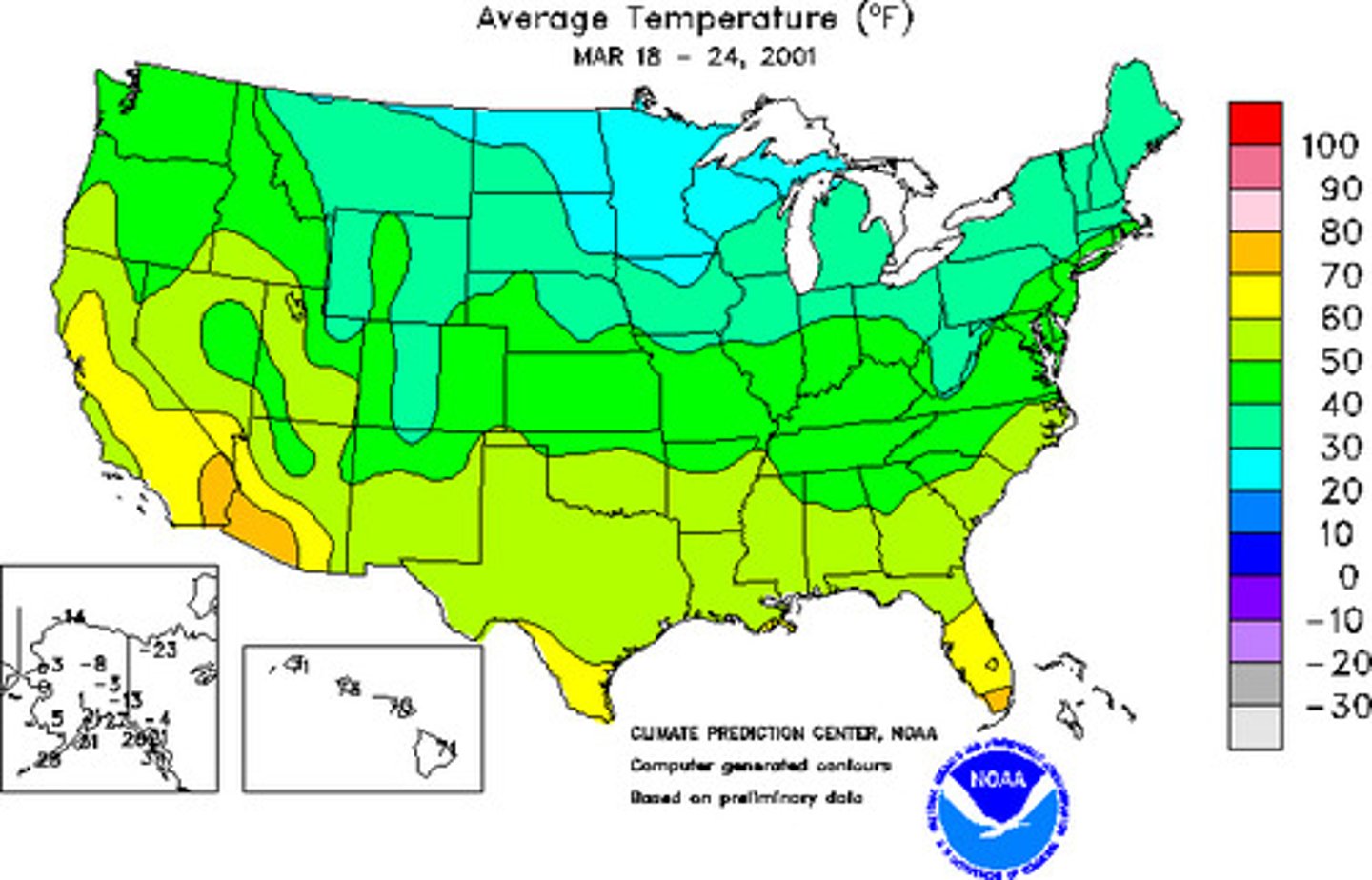
Isoline Map
A map that connects places of a particular value by lines.
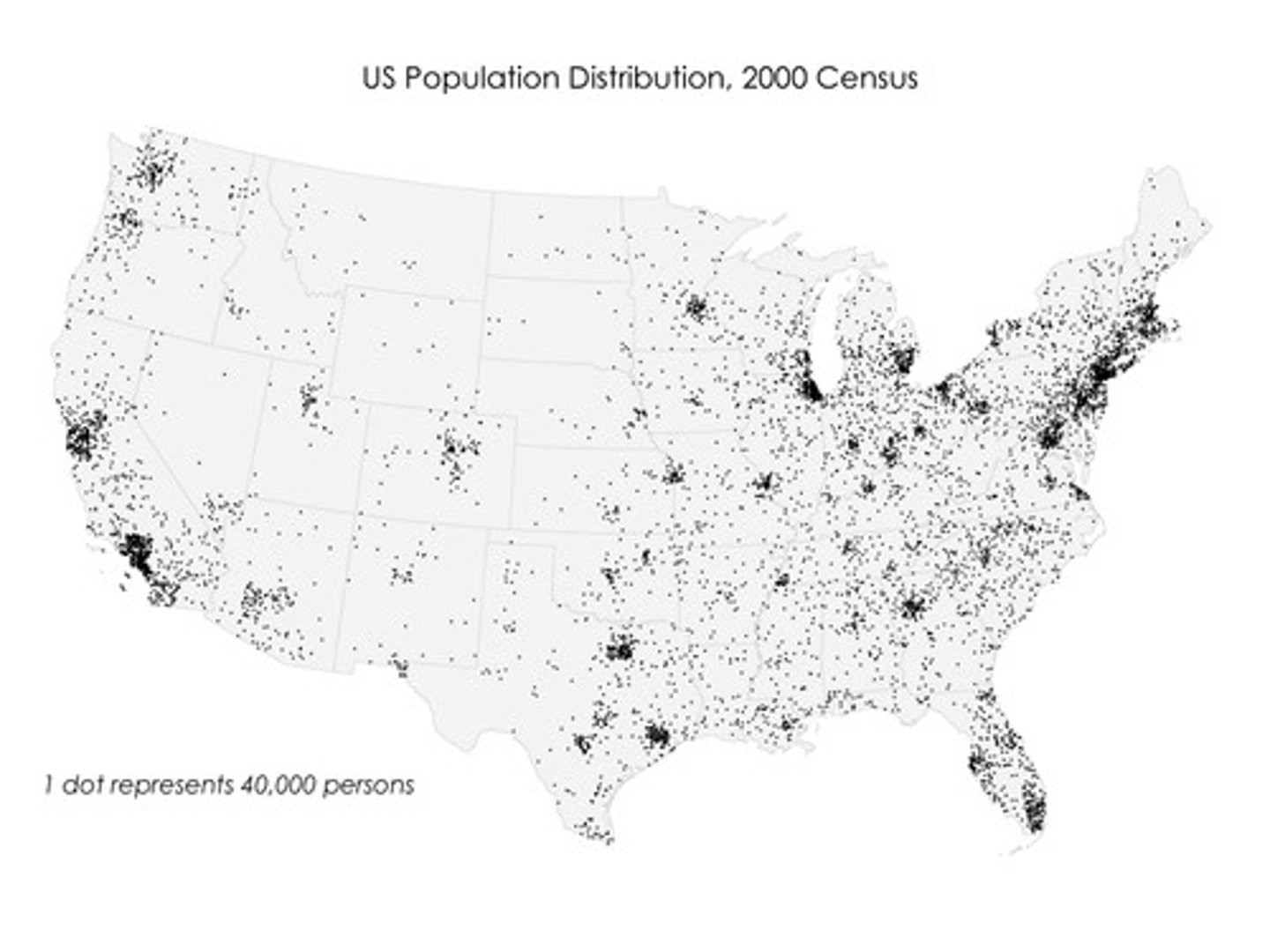
Dot Distribution Map
This map depicts data as points and shows how those points are clustered together or spread out over an area. Each dot represents a predetermined number of observations, which could be one or many (Figure 1-24).
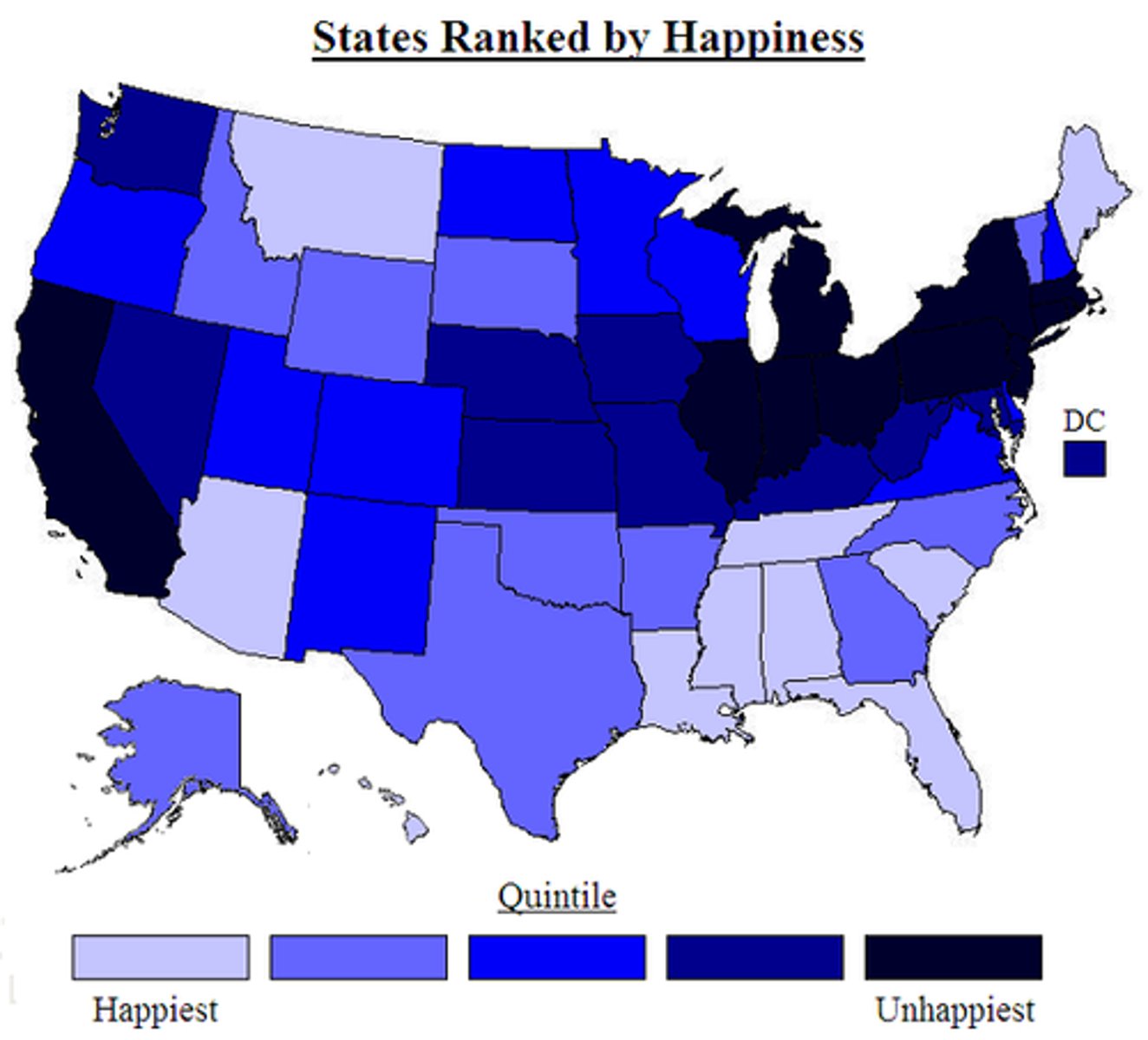
Chloropleth Map
This map is a map where recognizable areas are shaded or patterned in proportion to the measurement of the variable. For example, areas with darker colors may represent the highest range of the data
graduated symbol map
This map displays symbols that change in size according to the value of the variable. A higher value is typically represented by a larger symbol