ecology and evolution exam 1
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
what is the scientific theory?
comprehensive explanation of a natural phenomenon supported by lots of evidence. used to interpret facts and make testable predictions
What are the two different species concepts discussed in class?
Morphological- defines a species by structural features (ex: grizzly x polar = grolar bear) ; can apply to asexual/sexual
biological- group of populations whose members have potential to interbreed in nature and produce viable, fertile offspring (ex: dog x dog) ; can’t apply to asexual
7 reproductive isolating mechanisms and which is pre zygotic or post zygotic?
Prezygotic
habitat isolation
temporal isolation
behavioral isolation
mechanical isolation
Postzygotic
reduced hybrid viability
reduced hybrid fertility
reduced hybrid fertility
offspring are viable, but sterile (ex:donkey x horse = mule)
reduced hybrid viability
offspring are produced but don’t survive (ex: gecko x gecko #2 = hybrid won’t survive)
gametic isolation
sperm of a species can’t fertilize egg of another species
mechanical isolation
morphological features prevent successful mating (ex: snails)
behavioral isolation
behaviors are different and don’t attract mates from other species (ex: blue footed boobies)
temporal isolation
species breed at different times (ex: spotted skunks)
habitat isolation
2 species don’t encounter each other, different habitats (ex: garter snakes)
crickets use species specific chirp patterns to identify a mate of their own species is…
behavioral isolation
Two species of butterfly mate where their ranges overlap and produce fertile offspring, but the hybrids are less viable than the parental forms is…
reduced hybrid viability
Two species of a plant cannot interbreed because their flowers differ in size and shape and require pollination by different species of bee is…
mechanical isolation
Two species of firefly occupy the same prairie and have similar flash patterns, but one is active for a half-hour around sunset while the other doesn’t become active until an hour after sunset is…
temporal isolation
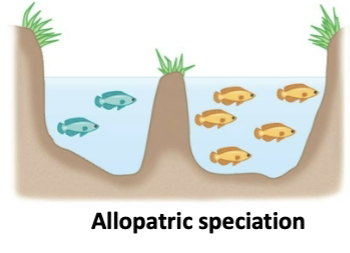
what is allopatric speciation?
formation of a new species due to geographic isolation of populations, no interbreeding
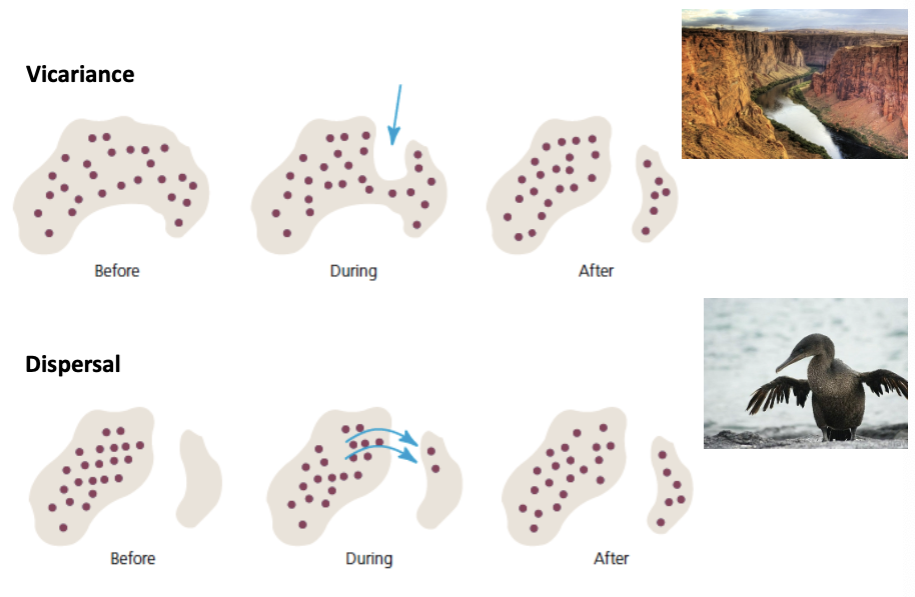
what two processes lead to allopatric speciation?
Vicariance- species on one island together and then island splits into 2, dividing population (canyon split by river)
Dispersal- separate and all species are on on island, then part of the species moves to other island and split in half
what is sympatric speciation?
no geographical barriers allowing ancestral and new species to exist in one space
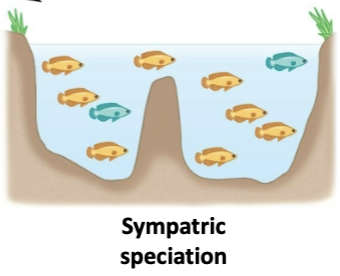
which type of speciation is more common, allopatric or sympatric?
allopatric because geographic barriers effect the gene flow
is allopatric speciation more likely to occur on an island close to a mainland or on a more isolated island of the same size?
more isolated island because it allows for the species to evolve independently away from mainland
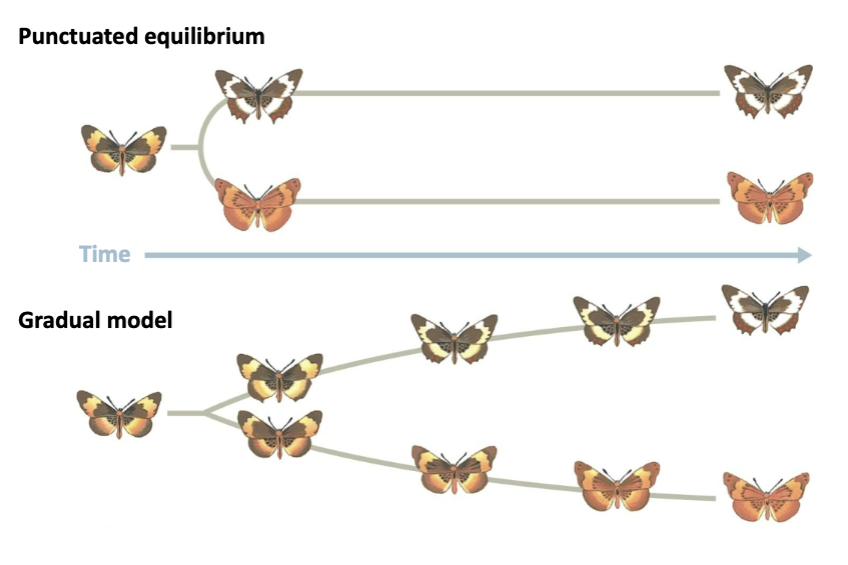
difference between punctuated equilibria and gradualism models of speciation?
punctuated- short periods of rapid evolution (stasis)
gradualism- small changes over long periods of time (gradual)
what is systematics? how is It used to develop phylogenetic trees?
specific characteristics of species and how they relate to other species throughout time. it creates the different branches of the tree
what are two components of every binomial name? how are they written?
genus (1st) and specific epithet (2nd)
what is the binomial name of human species?
homosapiens
correct order of taxonomic hierarchy? biggest to smallest
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
are organisms in the same phylum or in the same order more closely related?
order because it is more specific (Dear King Philip Came Over For Good Soup)
what is the difference between a shared derived character and an ancestral derived character? example?
Shared- characteristics from immediate ancestors
ancestral- characteristics shared from distant ancestors
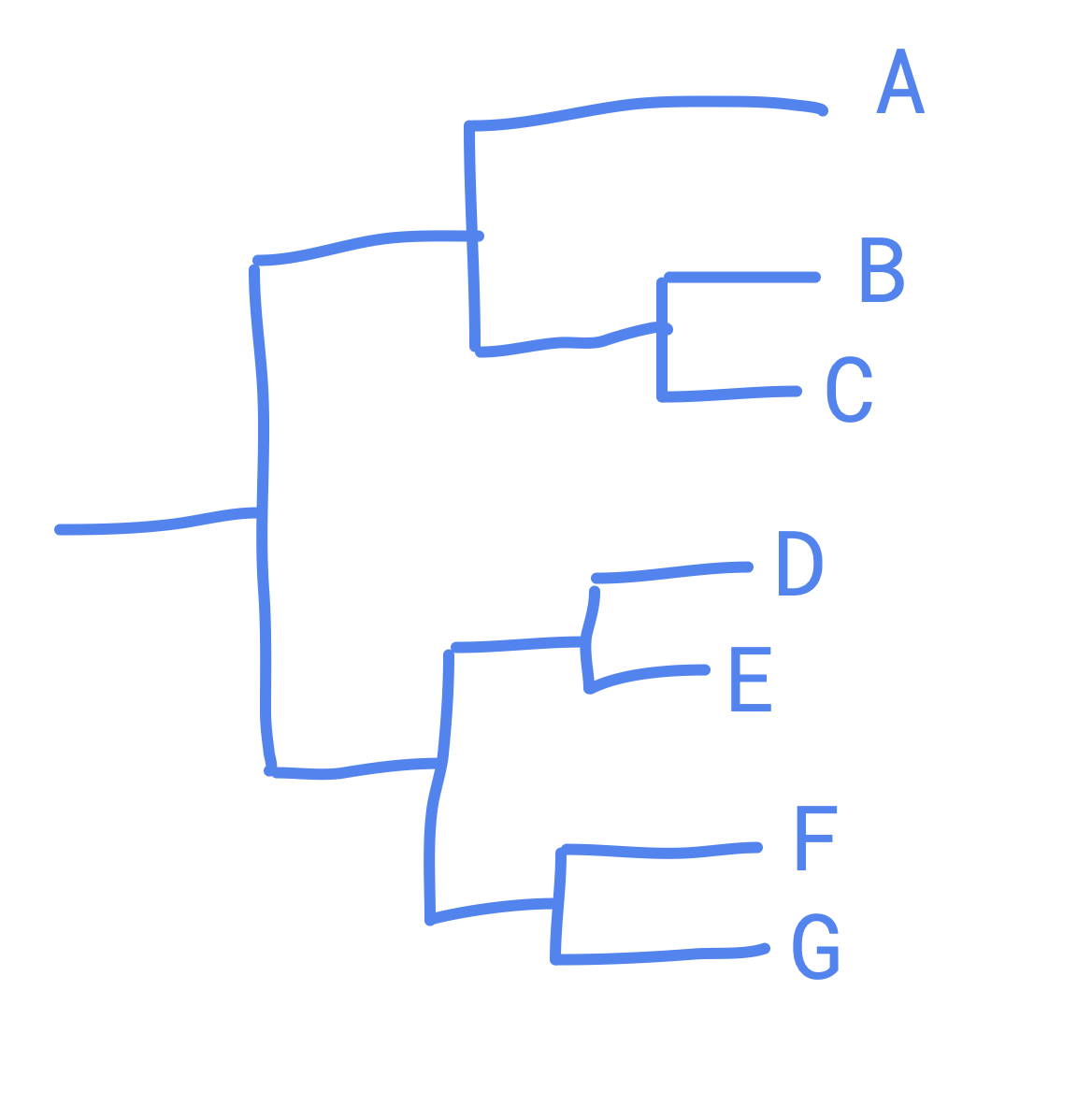
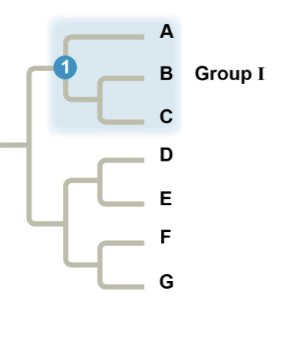
where is a true or monophyletic clade?
ABC
different steps in scientific method?
1) make an observation
2) ask a question
3) construct a hypothesis
4) test your hypothesis
5) analyze the data you collected
6) draw a conclusion
hypothesis
a specific, testable, and measurable explanation or “educated guess” ; also needs to be falsifiable
why is it important to have a large sample size in an experiment?
it helps detect real patterns, sample size allows for weather, time of season, and predators to be part of data, less incorrect information
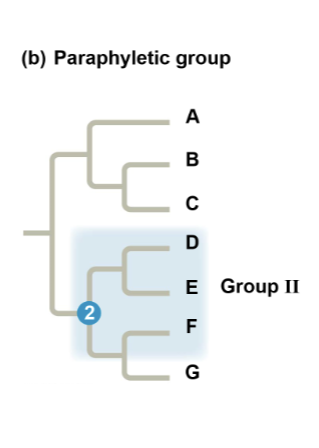
where is a paraphyletic group?
DEF
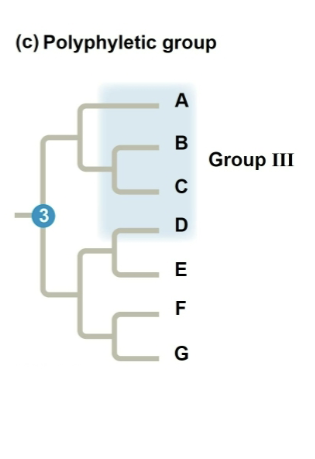
where is a polyphyletic group?
ABCD
what’s a homologous structure?
different species with the same bones but in different sizes and proportions
vestigal structures
remains of features that served an important function in a common ancestor (ex: tailbone in humans)
analogous characters
functionally similar features that evolved independently
what do analogous characters not provide us
ancestry details
convergent evolution
evolution of similar features in distantly related groups (ex: birds, bats, flies)
what is a clade also known as
monophyletic group
evolution
change in heritable traits over generations OR descent with modification
Aristotle
scala naturae
scala naturae
life is like a complex ladder with increasing complexity
Carlos linnaeus
founder of taxonomy, binomial nomenclature
binomial nomenclature
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
George cuvier
paleontology
James hutton and charles Lyell
uniformitarianism (earths features slowly eroded)
Lamaark
this person proposed the idea of use and disuse
inheritance of acquired characteristics
Darwin’s research: voyage of the beagle
living species resembled other species from nearby regions
artificial selection
selecting/breeding organisms for certain traits
Thomas malthus
this person said over reproduction and survival
humans limited food supplies/resources
natural selection
the process by which individuals with favorable inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce
adaptation
inherited traits of an organism that enhance their survival and reproduction in certain environments
wallace
similar idea to darwin
Darwins research paper name
the origin of species
microevolution
change in allele frequencies in a population overtime
macroevolution
broad patterns of evolution above the species level
speciation
process by which one species splits into two or more
gene flow
genetic information is being shared by populations (breeding) gooa
what makes a good hypothesis
specific
testable
measurable
falsifiable
vicariance
physical barrier forms, separating two populations
what does sister taxa look like
a “U”
what does a polytomy look like
a “W” or a “U” with a line down the middle
basal taxon
diverges early in group and originated near common ancestor
taxonomy
scientific discipline concerned with naming organisms
what is a phylogenetic tree used for
hypothesis about evolutionary relationships