A Level CIE Geography: Coastal Environments
1/301
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
302 Terms
coast
narrow zone where land and sea meet and directly interact [varied and rapidly changing of al landscapes]
coasts are the most…
rapidly changing of all landscapes
four factors affecting the coastline
marine, human, atmospheric, terrestrial
two atmospheric factors affecting the coastline
climate - wind, temperature, rainfall etc.
climate change e.g. global warming, ice ages
three terrestrial factors affecting the coastline
tectonic movements
geology - rock type and rock structure
ecosystems - sand dunes, salt marshes, mangroves
five marine factors affecting the coastline
wave action
longshore drift
currents
tides
salinity
nine human factors affecting the coastline
coastal settlements
recreation and tourism
port construction
farming
land reclamation
sand and gravel extraction
pollution - land-based and marine
conservation
coastal management
what are the main agents of change in coastal environments
waves
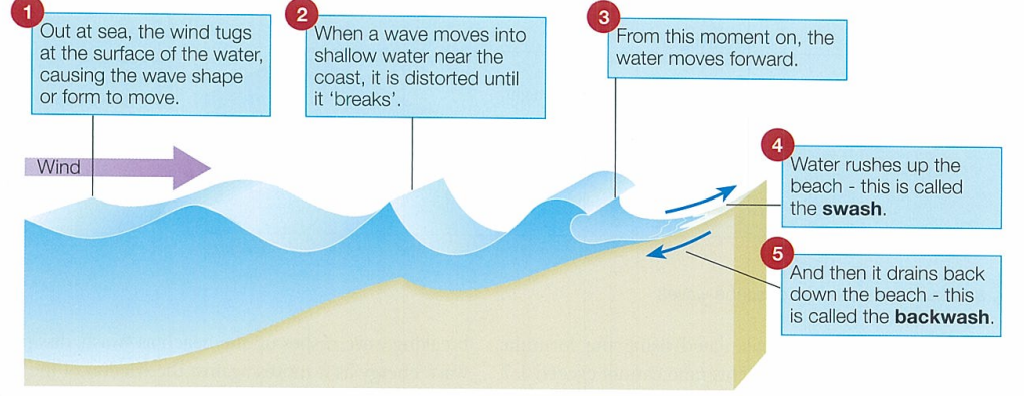
what are waves caused by
frictional drag of the wind as it blows across open water
wave direction is a reflection of
wind direction
what three factors do the size of wave and wave energy depend on
wind speed
length of time that wind blows in constant direction
length of the fetch
fetch:
distance of sea over which wind can blow
which coastlines have larger fetches and which have smaller
coastlines that face large ocean e.g. west ireland = larger. coastlines around enclosed sea e.g. south france = smaller
the greater each of the three wave size factors is…
the bigger the waves
where are the biggest waves and why
southern ocean at forty and sixty s where westerly winds blow continuously, avg five m in height w/ some twice the height
where are the smallest waves and why
around equator where wind speeds are low particularly where winds fetch is limited by islands e.g. indonesia and enclosed seas e.g. mediterranean and caribbean bc reduced fetch available for wave gen.
once created, waves move in what direction
same of the wind that created them
why is it only the wave form that moves
water particles simply rotate in circular/elliptical movement as the wave passes through, it is the energy of the wave that moves towards the shore, not the water.
when does wave energy translate into the movement of water towards the shore
when a wave breaks
wave crest:
as the water in a wave rises, it forms the wave crest. top of the wave
wave trough:
as the water in a wave falls, it forms wave trough - low point between two wave crests
wave height:
difference in height between wave crest and wave trough
wave length:
distance between two wave crests. not usually evenly spaced
wave period:
time taken for a wave to travel through one wave length
wave velocity:
speed of movement of the wave crest calculated by avg wl/avg wave period
wave frequency:
no. waves that break on beach in given period of time
wave steepness:
calculated by wave height/wl. ratio cant exceed [1:7/0.14] bc at that point wave breaks
wave energy:
in deep water energy of wave is proportional to the wave length multiplied by the wave height squared meaning a small increase in wave height = large increase in wave energy. wave energy directly related to wave height and energy released when breaks.
plunge line:
point which wave breaks
swash:
body of foaming water that rushes up beach when a wave breaks. obtains energy from energy released by breaking wave.
backwash:
water which returns down beach after wave has broken
how are waves classified
often depending on how they break when they approach the shore and move into shallow water
nature of breaking wave is related to…
its energy
as waves moves into shallow water what happens to the movement of the water and why [depth of water less than half the wavelength]…
the movement of the water within the wave is slowed because of friction with the sea bed which reduces wave velocity reducing wavelength and increasing wave height.
as waves move into shallow water what happens to the movement of water particles and base of wave
the movement of water particles becomes elliptical rather than circular and the base of the wave slows down compared to crest.
what happens as wave steepens when moving into shallow water
breaks and rushes up the beach as swash dissipating wave energy as it moves against the friction of the beach.
what happens when waves break directly against cliff or sea
wave energy is directed against the vertical surface and erosion can be extremely effective
what kind of beach protects the coastline behind the beach against erosion and why
wide, gently sloping bc it can absorb most of the energy
high energy wave example
storm wave [type of destructive wave]
how are storm waves formed
strong winds blowing from the ocean directly onto the coastline
how are plunging breakers formed
when storm waves break on a steeply sloping beach
what happens when storm waves break
become vertical and plunge down onto beach
destructive wave features seven
remove sediment from beach
steep
high
short wl
high wave frequency [over ten per min]
often storm waves
driven onto beach by strong onshore wind
what happens when destructive waves break
they crash down onto beach and much of water in breaking wave returns to sea rather than rushing up the beach so as a result they have weak swash and strog backwash
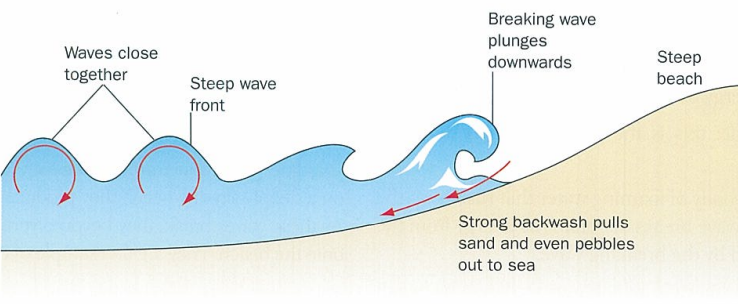
what happens to sediment in destructive waves
removed from beach by strong backwash and often builds up as longshore bars near low tide mark1
low energy waves example
swell waves
how are swell waves formed
when wind that made waves dies down over ocean, wave1s will continue to move in same direction until coastline reached without stimulus of wind so wave height decreases and wave length increases.
what is the effect of swell waves on a beach
they arent very steep so as they approach the beach, the crest of the wave stays smooth and the wave slides or surges up beach even if beach is steep resulting in surging breakers
constructive waves example
surging breakers
constructive wave features five
low
gentle
add sediment to beach
long wave length
low wave frequency [less than eight per min]
what happens when constructive waves break
spill up on the beach producing a strong swash but the backwash is weak especially on gently sloping beaches.
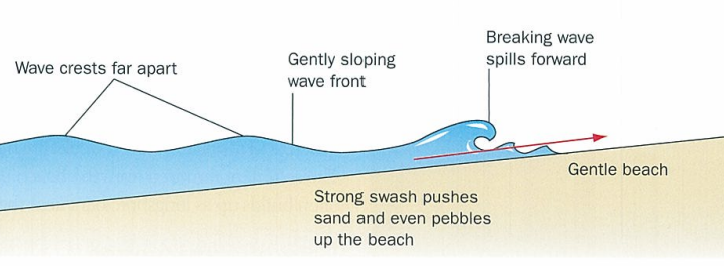
breaking waves diagram
breaking waves
what do constructive waves do to sediment and how are berns formed
push sand and sediment up the beach and the backwash is not strong enough to pull it back down so they tend to form berns at the top of the beach.
in winter and summer which waves frequent
winter - destructive, summer - constructive
what happens when waves approach an irregular coastline
they are refracted and increasingly take on the shape of the coastline
waves slow down in shallow water infront of a ______ because… so…
headland, friction with sea bed, so the waves in deeper water move ahead
orthogonals:
lines drawn at right angles to wave crests showing how energy is concentrated upon a headland enhancing its erosion
how are bay beaches formed
refraction sets up longshore currents that move sediment from the headlands into bays
what provides bays with sediment
longshore currents help maintain bay beaches
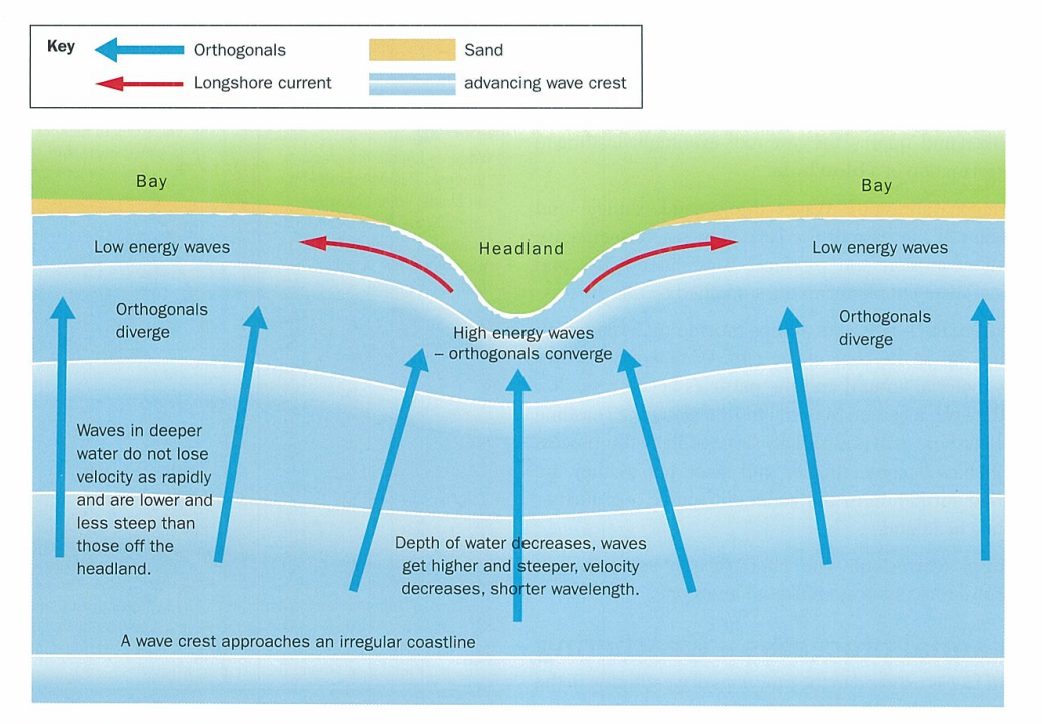
wave refraction at a headland diagram
what seven processes affect the coastline
weathering
mass movement
erosion
transportation
deposition
sedimentation
earth movements
weathering as a coastal process
weathering on a coastline is sub-aerial and mostly operates on cliff face leading to disintegration and crumbling
mass movement as coastal process
sub aerial
e.g. rock falls and rotational slumping
loosens material on cliff face as water in rocks makes them heavy and lubricates them and erosion at cliff foot undermines cliff so when conditions are right, gravity causes cliff face to collapse adding material onto beach
erosion as a coastal process
mostly by action of waves
marine process
hydraulic action, cavitation, abrasion/corrasion, attrition are the main processes + solution in areas of chalk and limestone
transportation as a coastal process
material moves up and down beach and along by longshore drift
wave action provides energy for these movements
tidal currents and longshore currents important
wind moves sand up beach = sand dunes
deposition as a coastal process
beach made by deposited material
dynamic system as material constantly moving
spits and tombolos produced by beach movement
dunes made by depos. of blown sand and mudflats
salt marshes prod. by depos. of alluvium [river silt] in river estuaries
sedimentation as a coastal process
usually only on sea bed
well away from coast
large deltas can eventually produce beds of sediment
earth movements as a coastal process
delta depos. can weigh down crust
leads to subsidence and relative rise in sea level
tectonic movements = uplift in land [raisd beaches]
both = isostatic of local sea level change e.g. venice.
four ways in which waves can erode coastline
hydraulic action
cavitation
corrasion
attrition
+solution/corrosion
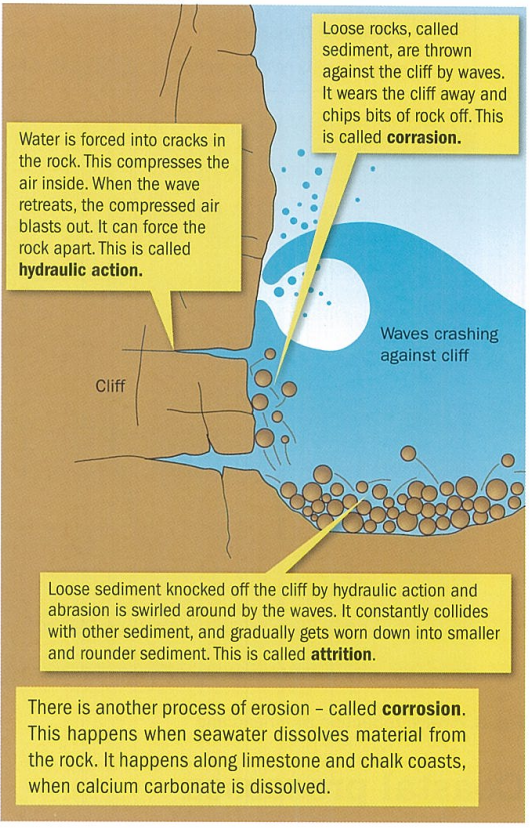
hydraulic action as marine erosion
big waves have lots of energy
water is a dense material [one cubic metre of water weighs one ton]
storm waves hitting sea wall or cliff foot can generate shocks of thirty+ tons per square metre
pressure can = erosion
cavitation [form of wave quarrying] as marine erosion
water trapped in cracks in rock is compressed by pounding of waves
when pressure released, bubbles form in water which escape from crack w/ explosive force widening crack quickly
air pockets compressed inside cave at high tide can weaken and quarry cave roof leading to blowhole formation
corrasion/abrasion as marine erosion
waves throw sand, shingle and cobbles at cliff base
effective erosion bc produces wave-cuts and notches and caves
wave-cut platforms smoothed by this process
attrition as marine erosion
rock falls and slumps provide material which builds up at cliff base
wave energy moves material around and particles become smaller as they rub together
material moved along coastline by longshore drift is susceptible to this
pebbles become smaller and smoother as they are moved further from sediment source e.g. further from headland
solution/corrosion as marine erosion
chemicals in seawater can dissolve rocks such as chalk and limestone
marine and sub-aerial processes example
read

what weathering occurs on cool temperature coastlines
frost shattering can be very effective as water seeps into cracks in cliff face and freezes overnight
when liquid water turns into ice it expands by 9% which widens and weakens the crack
repeated freezing and thawing can make the rock crumble and split.
what weathering occurs on desert coastlines
extremes of temperature between day and night can cause expansion and contraction of the surface layers of rock on the cliff face
the stresses caused by these changes weaken the rock and surface layers peel off
increased availability of water at coastlines can speed up exfoliation
why does staining and crumbling happen at coastlines
many rocks contain iron compounds
iron oxide = rust which weakens
decomposes rocks on cliff face
how does biological weathering happen on coastline cliffs
cliffs often contain cracks
halophytic/salt-loving plants can grow in these cracks widening them
how does chemical weathering occur on cliffs
seabirds nest on ledges on cliffs away from predators
their guano/poo is extremely corrosive
can lead to the chemical weathering of some types of rock
how do crystals form on cliffs
in the spray zone towards cliff bases, salt water can soak into rock pores
when water evaporates, salt crystals form inside the rock.
salt crystals are perfect cubes but pores are irregular
stresses are formed as square pegs in round holes
rock easily decomposes and crumbles
how do mass movement such as rock falls and rotational slumps occur on cliff faces
weathering weakens rocks on cliff face by expanding cracks and disrupting rock from within
rainwater seeping from land as through/baseflow lubricate cracks which weakens internal cohesion of rocks of cliff face
water adds weight to rocks
marine processes working at cliff base undermine it and remove support
what is the main mass movement in cliffs made of hard rock
rock falls, often after heavy rain
what is the main mass movement in cliffs made of unconsolidated material such as clay/glacial deposits
rotational slumping
what is cliff retreat a result of
all these processes
sources of coastal sediment diagram
read
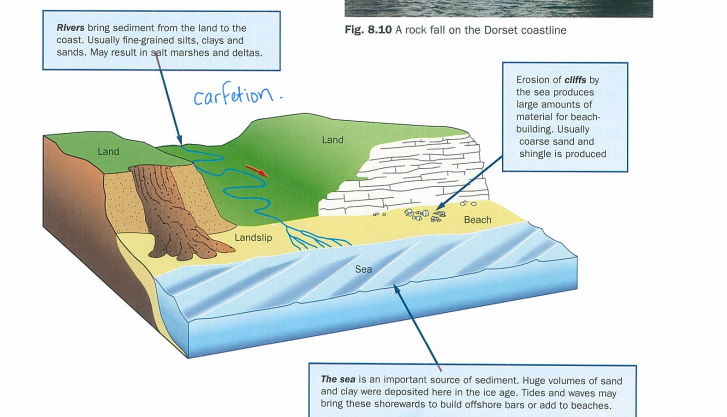
what three sources do coastlines receive sediment from
rivers flowing from land to sea - alluvium, most of the sediment that reaches the coastline comes from rivers
erosion of the coast - rockfalls and slumps
material moved on to the coastline from the sea bed - mostly by constructive waves
how does sediment move up and down the beach, how are berns, longshore bars and sand dunes formed
swash carries material up the beach and backwash carries it back down
waves can sort the beach material
constructive waves move material up the beach forming berns
destructive waves comb it downwards forming longshore bars
wind can blow sand up beach and deposit it at top of beach forming sand dunes
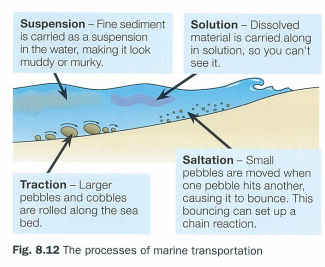
suspension
fine sediment is carried as a suspension in water making it look muddy/murky
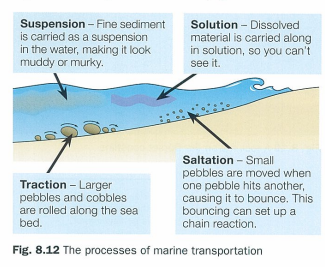
traction
larger pebbles and cobbles are rolled along the sea bed
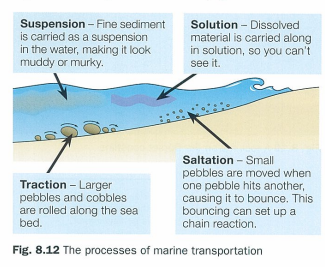
solution
dissolved material is carried along in solution so you can’t see it
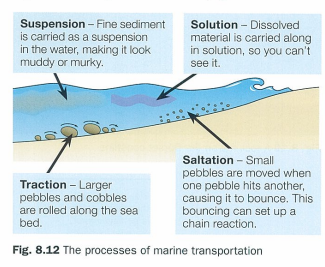
saltation
small pebbles are moved when one pebble hits another causing it to bounce which sets up a chain reaction
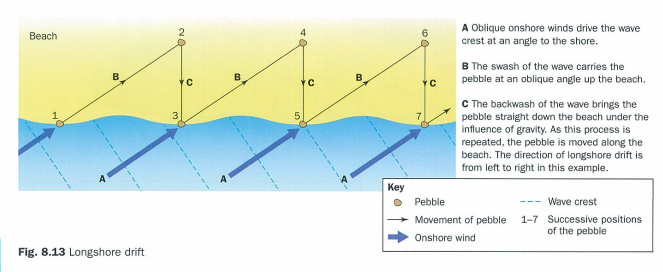
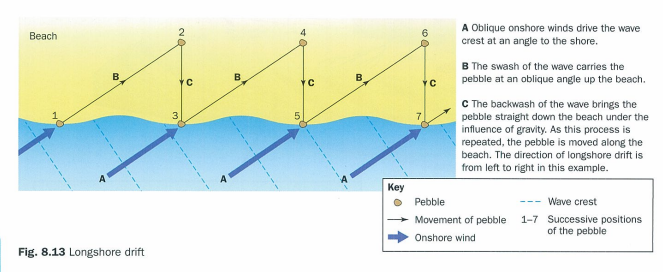
how does sediment move along the coastline, groynes + longshore drift
waves arrive at an angle to the beach
wave angle and swash direction is determined by wind direction and wave refraction
backwash runs straight back down beach under influence of gravity
swash and backwash operate to cause zigzag movement of material which moves it along the beach like a conveyor belt
groynes interfere with movement of beach material by longshore drift
deposition takes place on updrift side of obstacle making beach wider encouraging tourists and protecting coast from erosion but further along beach is starved of material and becomes thinner = increased erosion rates in downdrift areas
types of sediment, sizes & types
cobbles
pebbles
shingle
sand
mud
where are larger sediment particles from and formed
storm beaches at the top of the beach
where are smaller sediments formed
wider, more gently-sloping loewr beach
what is sediment moved along beach by
longshore drift
when does deposition take place and where
whenever the movement of coastal sediment slows down/stops. this happens updrift of a groyne or in sheltered locations e.g. estuary or bay.
also where the coastline changes abruptly. spits can develop as the beach is built out across the inlet, estuary or bay
wave refraction around an island close to coast can also lead to deposition between island and coast = cuspate tombolo
coastlines can be divided into…
sediment cells with smaller sub-cells within them
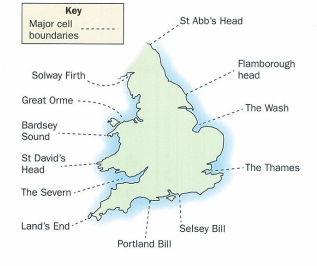
sediment movement is ______ within each sediment cell
self-contained