All Terms AP World History
1/421
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
422 Terms
Devshirme
Annual practice by which the Ottoman Empire sent military to abduct boys, sons of their Christian subjects, who were then converted to Islam with the primary objective of joining Janissaries
World Trade Organization (WTO)
Created in 1993, it is an international organization that provides the institutional and legal framework for the trading system that exists between member nations worldwide, responsible for liberalizing trade, operating a system of trade rules and providing a forum for trade negotiations between governments, and for settling trade disputes.
North Atlantic Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
An agreement that created an essentially free trade zone among Mexico, Canada, and the United States, in hopes of encouraging economic growth in all three nations; after difficult negotiations, went into effect January 1, 1994.
Earth Day
A holiday conceived of by environmental activist and Senator Gaylord Nelson to encourage support for and increase awareness of environmental concerns; first celebrated on March 22, 1970.
Bollywood
One of the biggest film industries in the world in terms of the number of people employed and the number of films produced. It is an example of a global culture due to its popularity throughout Asia and Africa.
Mikhail Gorbachev
Head of the Soviet Union from 1985 to 1991. His liberalization effort improved relations with the West, but he lost power after his reforms led to the collapse of Communist governments in eastern Europe.
total war
A war that involves the complete mobilization of resources and people, affecting the lives of all citizens in the warring countries, even those remote from the battlefields.
Mao Zedong
He was the leader of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 1935 until his death in 1975, and he was chairman (chief of state) of the People's Republic of China from 1949 to 1959 and chairman of the party also until his death.
Firebombing
A bombing technique designed to damage a target, generally an urban area, through the use of fire, caused by incendiary devices, rather than from the blast effect of large bombs. It was used effectively in Dresden, Germany
Genocide
Systematic destruction of a political, religious, racial, or culture group. The main examples are the Armenian Genocide, the Holocaust and the Rwandan Genocide.
Tiananmen Square incident
Also called June Fourth incident or 6/4, series of protests and demonstrations in China in 1989 calling for political, social, and economic reforms to the communist system. It culminated on the night of June 3-4 with a government crackdown on the demonstrators in Tiananmen Square in Beijing.
Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes
This refers to those oppressed castes and tribes listed in "schedules" of the Indian Constitution of 1949. Scheduled castes and scheduled tribes are entitled to a certain number of government jobs and educational opportunities. Nonetheless the caste system still oppresses lower members of society.
United Nations Security Council
The Security Council is the United Nations' most powerful body. It has "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security." Five powerful countries sit as "permanent members" with veto power along with ten other member states, elected for two-year terms.
Cuban Revolution
An armed revolt in 1959 conducted by Fidel Castro's 26th of July Movement and its allies against the right-wing authoritarian government of Cuban President Fulgencio Batista. It started a close relationship between Cuba and the Soviet Union. In response the US placed a trade and travel embargo (ending trade and travel) which hurt many Cubans.
Apartheid
A system of legal racial segregation enforced by the National Party government in South Africa between 1948 and 1994, under which the rights of the majority black inhabitants of South Africa were curtailed and minority rule by whites was maintained.
Indian National Congress
A movement and political party founded in 1885 to demand greater Indian participation in government. Its membership was middle class, and its demands were modest until World War I. Led after 1920 by Mohandas K. Gandhi, appealing to the poor.
Boxer Rebellion
In 1900, in what became known as the Boxer Rebellion (or the Boxer Uprising), a Chinese secret organization called the Society of the Righteous and Harmonious Fists led an uprising in northern China against the spread of Western and Japanese influence there.
Tanzimat
This was a set of reforms to modernize and Westernize the declining Ottoman Empire. Government workers were encouraged to wear a more "western" style of dress. A European legal system based on the Napoleonic Codes were adopted. European style banks and post offices were created. The military abolished the devshirme system and adopted universal conscription (drafting).
Nineteenth Century Global Migrations
Between 1846 and 1940, some 55 million migrants moved from Europe to America. 65% went to the United States. Other major receiving countries were Argentina, Canada, Brazil and Uruguay. Also, 2.5 million Asians migrated to the Americas, most as indentured servant to the plantations of the Caribbean, but some also, notably Japanese, arrived in Brazil and the USA.
Mexican American War
an armed conflict between the United States of America and the United Mexican States from 1846 to 1848. It followed in the wake of the 1845 US annexation of Texas, which Mexico considered part of its territory, despite the 1836 Texas Revolution. It resulted in the the dramatic increase in US territory and decrease in Mexican territory.
bourgeoisie
A social class that derives social and economic power from employment, education, and wealth, as opposed to the inherited power of aristocratic family of titled land owners or feudal privileges. It's a term for the middle class common in the 19th century. It's characterized by their ownership of property and their related culture.
petit blancs
This group of poor whites (artisans or free holding farmers) during the Haitian Revolution wanted to preserve discrimination by having an advantage over free people of color.
Haitian Revolution
The only fully successful slave rebellion in world history; the uprising in the French Caribbean colony of Saint Domingue (later renamed Haiti) was sparked by the French Revolution and led to the establishment of an independent state after a long and bloody war (1791-1804).
American Revolution
The American Revolution was a political upheaval that took place between 1765 and 1783 during which rebel colonists in the Thirteen American Colonies rejected the British monarchy and aristocracy, overthrew the authority of Great Britain, and founded the United States of America.
mosque
A Muslim place of worship. They came to be used for many public functions—military, political, social, and educational. Schools and libraries were often attached to medieval ones. It also functioned as a court of justice until the introduction of secular (non-religious) law into many Islamic countries in modern times.
Umayyad Caliphate
First Islamic Empire, lasted 661-750 CE; conquered North India, North Africa, and Spain in 711, attempted to conquer Constantinople, but failed both attempts. The capital was Damascus, Syria. It was the largest Muslim empire in history.
jizya
Poll tax that non-Muslims had to pay when living within a Muslim governed territory.
Crusades
A series of holy wars from 1096-1270 AD undertaken by European Christians to free the Holy Land from Muslim rule.
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and their market towns that dominated trade along the coast of Northern Europe.
Sassanid Empire
The name of the last pre-Islamic Iranian(Persian) empire. It was one of the two main powers in Western Asia for a period of more than 400 years. The official religion was Zoroastrianism. Fought the Byzantines, which weakened both empires and allowed the Muslims to conquer the Middle East.
Equal-Field System
Official institution of land distribution and tax collection in traditional China and Japan. It provided for the assignment of agricultural lands to all adult peasants and thereby slowed the accumulation of lands by wealthy families. It worked on the basis that all land was owned by the government, which would then assign it to individual families. Every individual, including slaves, was entitled to a certain amount of land, the amount depending on their ability to supply labor.
Mali Empire
A Muslim trading empire that flourished on the Upper Niger River in West Africa from the 13th to the 16th century. Trading cities, such as Timbuktu and Gao flourished under the gold and salt trade.
Swahili
A Bantu language with Arabic words spoken along the East African coast.
Osman
Found the Ottoman Empire- He was a leader of a band of semi-nomadic Turks who migrated to northwestern Anatolia in the 13th century. The empire lasted until 1922.
Babur
A descendant of Timur and Ghengis Khan, who founded the Mughal Empire in 1526
Nanuk
(1469-1539) stressed meditation as a means of seeking enlightenment and drew upon both religions in his teachings.
Safavid Empire
One of the most significant ruling dynasties of Persia (modern Iran) after the fall of the Sasanian Empire - following the Muslim conquest of Persia in the seventh century A.D., and "is often considered the beginning of modern Persian history". 1502 - 1736
Sikhism
One of the youngest amongst the major world religions, is a monotheistic religion that originated in South Asia (sub-continental India) during the 15th century. Founded by by the first guru Nanuk
Mestizos
A person of mixed Native American and European ancestory. These two cultures mixted after the Spanish explorers came to the Americas.
Mughal Empire
An empire in India that ruled from 1526-1858 CE. It was the first to unite almost the entire subcontinent. The early empire established a policy of religious tolerance where Hindus and Muslims could openly practice. Ended by 1700 when Muslims began to persecute Hindus. Established trade relations with Europeans (namely British and Portuguese). It slowly lost power to the British.
Johann Gutenberg
German printer who invented movable type printing in 1439. It facilitated the Protestant Reformation by spreading ideas quickly such as Luther's 95 Theses (complaints again the Church), it increased literacy (book no longer had to be handwritten and because they were cheaper, more people could afford to purchase them and learn to read them).
Protestant Reformation
Religious reform movement within the Roman Christian Church beginning in 1519. It spit the Roman Catholic Church and resulted in the 'protesters' forming several new Christian denominations, including the Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican Churches, among many others.
Moksha
The Hindu concept of the spirit's 'liberation' from the endless cycle of rebirths.
Judaism
Religion with its roots in the teachings of Abraham (from Ur), who is credited with uniting his people to worship only one god. According to Jewish teaching, Abraham and God have a covenant in which the Jews agree to worship only one God, and God agrees to protect his chosen people, the Jews.
Cleopatra
Who/What: last queen of egypt and direct descendant of Alexander the Great's general Ptolemy; greek by descent, language, and culture; married Mark Anthony and had several children with him
When: 69-30 BCE
Where: egypt, rome
Why: important to Ancient Rome because she made attempts to form alliances with powerful Romans (bore Julius Caesar's child); sided with Mark Anthony after death of Julius; ended up on wrong side of deal and committed suicide
Cyrus the Great
Established massive Persian Empire by 550 B.C.E.; successor state to Mesopotamian empires., c. 530 B.C.E. A Persian ruler who captured Babylon. He was known for his mercy. He was tolerant of other religions and culture, and even incorporated different architectural styles into his buildings.
Satraps
Local governors set up in The Persian empire by Darius. They virtually had kingship powers in their provinces and they kept peace, collected taxes and provided troops when asked.
Epic of Gilgamesh
The world's oldest literary masterpiece, first composed in 2100 BCE. It centered about the King of Uruk. The book was made up of a series of adventures that focused around the themes of friendship, loyalty, ambition, and fear of death.
Ziggurats
A temple or tomb of the ancient Assyrians, Sumerians, or Babylonians, having the form of a terraced pyramid of successively receding stories
Periodization
The process or study of categorizing the past into separate, quantified named blocks of time in order to facilitate the study and analysis of history.
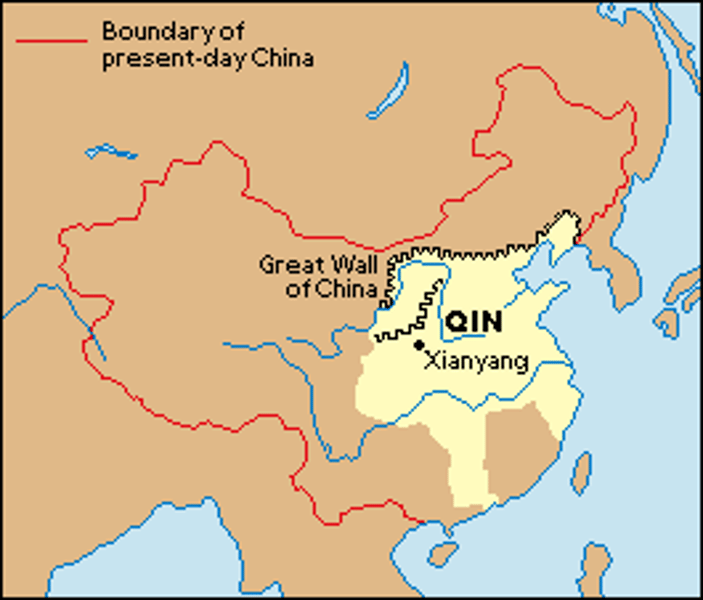
Qin Dynasty
A people and state in the Wei Valley of eastern China that conquered rival states and created the first Chinese empire (221-206 B.C.E.). The Qin sought to create an imperial state unified by highly structured political power and a stable economy able to support a large military. They standardized weights and measurements and began the building of the Great Wall.
Shi Huangdi
Founder of the short-lived Qin dynasty and creator of the Chinese Empire (r. 221-210 B.C.E.). He is remembered for his ruthless conquests of rival states, standardization of practices, and forcible organization of labor for military and engineering tasks. His tomb, with its army of life-size terracotta soldiers, has been partially excavated.
Lenin
Founder of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks), inspirer and leader of the Bolshevik Revolution (1917), and the architect, builder, and first head (1917-24) of the Soviet state. He built on the ideas of Karl Marx to form Marxism-Leninism, which became the Communist worldview in the twentieth century.
Green Revolution
The worldwide campaign to increase agricultural production from the 1940s to 60s, stimulated by new fertilizers and strains of wheat such as that by Norman Borlaug. The movement saved millions from starvation. Led to a radical population increase.
Polio vaccine
Developed in the early 1950s by American physician Jonas Salk. This vaccine contains killed virus and is given by injection. The large-scale use of IPV began in February 1954, when it was administered to American schoolchildren. It has saved millions of people worldwide.
Antibiotics
First produced in 1928, these drugs fight bacterial infections in the body. They were first used in World War II. They are the most important class of drugs in Western medicine.
HIV/AIDS
The virus spread from chimpanzees to humans sometime before 1931, most likely during "bush meat trading." By the 1980s, the disease hit epidemic proportions. Antiretroviral therapies made the drug treatable by the 1990. An estimated 78 million people have become infected with HIV and 35 million people have died of AIDS-related illnesses
Ebola
I first appeared in 1976 in 2 simultaneous outbreaks in Africa. It spreads by close bodily contact and spreads in countries with poor healthcare systems in Africa.
Rwandan Genocide
The killing of more than 500,000 ethnic Tutsis by rival Hutu militias in Rwanda in 1994. The conflict between the dominant Tutsis and the majority Hutus had gone on for centuries, but the suddenness and savagery of the massacres caught the United Nations off-guard. U.N. peacekeepers did not enter the country until after much of the damage had been done.
Al-Qaeda
A network of Islamic terrorist organizations, led by Osama bin Laden, that carried out the attacks on the US embassies in Tanzania and Kenya in 1998, the USS Cole in Yemen in 2000, and the World Trade Center and the Pentagon in 2001.
Margaret Thatcher
Britain's first woman prime minister, British Prime Minister from 1979 to 1990 who pledged to limit social welfare, restrict the power of labor unions, and to control inflation through a program which came to be known as "Thatcherism." She represents a leader in the movement towards more capitalist market-based reforms in the late twentieth century.
International Monetary Fund
An international financial institution founded in 1946 whose purpose is to make short-term loans to governments on commercial terms in order to stabilize exchange rate and help countries pay their foreign loans back. Some criticize it for the restrictions it places on governments who accept the loans.
Greenpeace
The most famous environmental group during that time. Created in 1970 by a small group of activists in Canada, concerned about the testing of a nuclear bomb off thEe coast of Alaska.
FIFA World Cup
Started just before World War II, this event became the most popular sporting event alongside the Olympics. It is an example of the rise of a global sports culture in the 20th and 21st centuries.
Special Economic Zones (SEZs)
In 1979, the Chinese government set up these places on the coast near Macao, Hong Kong and Taiwan. Improved transportation, lower taxes, and other incentives attracted investments from foreign businesses. They helped stimulate innovation and helped China grow economically.
Perestroika
A policy initiated by Mikhail Gorbachev that involved restructuring of the social and economic status quo in communist Russia towards a market based economy and society
Collapse of Soviet Union
By 1991, the Soviet Union dissolved replaced by 15 nation states which were no longer based on communism.
Iraq War
A protracted military conflict in Iraq that began in 2003 with an attack by a coalition of forces led by the United States and that resulted in the overthrow of Saddam Hussein's regime. The US falsely accused Iraq of developing Weapons of Mass Destruction. US combat troops were withdrawn in 2010, but a civil war against ISIS continues.
Glasnost
Policy of openness initiated by Gorbachev in the 1980s that provided increased opportunities for freedom of speech, association and the press in the Soviet Union.
1918 Influenza Pandemic
Often called the Spanish Flu, deadly influenza pandemic which infected 500 million people across the world, including remote Pacific islands and the Arctic, and killed 50 to 100 million of them—3 to 5 percent of the world's population at the time—making it one of the deadliest natural disasters in human history. Affected mostly people aged 20-40 and was spread by troop movements during WWI.
Tanks
They were designed as an armored fighting vehicle designed to overcome the deadlock of trench warfare in World War I. They led to high wartime casualties during WW II.
Trench Warfare
A type of land warfare using occupied fighting lines consisting largely of trenches. It occurred when advancements in firepower were not matched by similar advances in mobility, resulting in a grueling form of warfare in which the defender held the advantage. Poor hygiene also led to fungal conditions, such as trench mouth and trench foot.
Armenian Genocide
A campaign of deportation and mass killing conducted against the Armenian subjects of the Ottoman Empire by the Young Turk government during World War I (1914-18). Armenians charge that the campaign was a deliberate attempt to destroy the Armenian people and, thus, an act of genocide. The Turkish government has resisted calls to recognize it as such, contending that, although atrocities took place, there was no official policy of extermination implemented against the Armenian people as a group.
Five-Year Plans
Method of planning economic growth over limited periods, through the use of quotas, used first in the Soviet Union and later in other socialist states. In the Soviet Union, the first Five-Year Plan (1928-32), implemented by Joseph Stalin, concentrated on developing heavy industry and collectivizing agriculture, at the cost of a drastic fall in consumer goods. The second plan (1933-37) continued the objectives of the first.
League of Nations
A world organization established in 1920 to promote international cooperation and peace. It was first proposed in 1918 by President Woodrow Wilson, although the United States never joined the League. Essentially powerless, it was officially dissolved in 1946.
Women's Suffrage
The granting of voting rights to women in the early twentieth century (1900s). World War I and its aftermath speeded up the enfranchisement of women in the countries of Europe and elsewhere. In the period 1914-39, women in 28 additional countries acquired either equal voting rights with men or the right to vote in national elections.
Revival of the Olympics
The first celebration of the modern Olympic Games took place in its ancient birthplace of Athens in 1896. The revival reflected a growing interest in modern sports and sought to promote peace between competing nations prior to World War I.
M.A.N.I.A.
The causes of World War I: Militarism, Alliances, Nationalism, Imperialism, and Assassinations.
Balfour Declaration
Issued by the British government during WWI in an attempt to win Jewish support for the Allies. It expressed support for a Jewish national home in Palestine, but said that it shouldn't disturb those already living there. I encouraged even more Jews to migrate to Palestine, where violence flared between the Jewish and Muslim inhabitants.
Sykes-Picot Agreement
A secret agreement made during World War I between Great Britain and France for the dismemberment of the Ottoman Empire. The agreement led to the division of Turkish-held Syria, Iraq, Lebanon, and Palestine into various French- and British-administered areas. It resulted in many Middle East boundary lines which still exist as well as ethnic conflicts. It was similar to the Scramble for Africa in that territories divided up between European leaders drawing lines on maps.
War-Guilt Clause
Term of the Treaty of Versailles forcing Germany to admit sole responsibility for starting WWI. It was something that Adolf Hitler later used as a way to spread Nazi ideology in Germany and Austria.
Treaty of Versailles
An agreement made by the leaders victorious allies Nations (1918-19): France, Britain, US, and signed by Germany to help stop WWI. The treaty 1)stripped Germany of all Army, Navy, Airforce. 2) Germany had to rapay war damages($33 billion) 3) Germany had to acknowledge guilt for causing WWI 4) Germany could not manufacture any weapons.
Mandate System
Following the defeat of Germany and Ottoman Turkey in World War I, their Asian and African possessions, which were judged not yet ready to govern themselves, were distributed among the victorious Allied powers under the authority of the League of Nations. They violated agreements made to Palestinians and Jews over the future of Palestine.
Ataturk
A Turkish soldier, statesman, and reformer who was the founder and first president (1923-38) of the Republic of Turkey. He modernized the country's legal and educational systems and encouraged the adoption of a European way of life, with Turkish written in the Latin alphabet and with citizens adopting European-style names.
Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR)
Also known as the Soviet Union, it was a socialist state in Eurasia that existed from 1922 to 1991. A union of multiple subnational republics(Russia was just one), its government and economy were highly centralized. The Soviet Union was a one-party federation, governed by the Communist Party with Moscow as its capital.
Bolshevik Revolution
The overthrow of Russia's Provisional Government in the fall of 1917 by Lenin and his Bolshevik forces, made possible by the government's continuing defeat in the war, its failure to bring political reform, and a further decline in the conditions of everyday life.
Revolution of 1911
A nationalist democratic revolt that overthrew the Qing (or Manchu) dynasty in 1912 and created a republic. It ended more than 2000 years of Chinese imperial rule. The period of "The Republic" from 1912 to 1949, was weakened by a Communist revolt by Mao Zedong and the Japanese invasion.
Chiang Kai-shek
General and leader of Nationalist China after 1925. Although he succeeded Sun Yat-sen as head of the Guomindang, he became a military dictator whose major goal was to crush the communist movement led by Mao Zedong. He later created the Republic of China, the government that rules over Taiwan.
Long March
The 6,000-mile (9,600-kilometer) flight of Chinese Communists from southeastern to northwestern China. The Communists, led by Mao Zedong, were pursued by the Chinese army under orders from Chiang Kai-shek. It is part of the mythology of the Chinese Communist Party.
Guomindang
Nationalist political party founded on democratic principles by Sun Yat-sen in 1912. After 1925, the party was headed by Chiang Kai-shek, who turned it into an increasingly authoritarian movement.
The Great Depression
A worldwide economic downturn that began in 1929 and lasted until about 1939. It was the longest and most severe depression ever experienced by the industrialized Western world, sparking fundamental changes in economic institutions, financial policy, and economic theory. Although it originated in the United States, the Great Depression caused drastic declines in output, severe unemployment, and acute deflation in almost every country of the world.
The Manhattan Project
A secret project started in 1942 which resulted in production of the first atomic weapon, ushering in the age of atomic warfare when the US drops A-bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki leading to surrender of Japan on August 14, 1945 and the end of WWII.
Guernica
A Pablo Picasso painting of a Spanish town that was brutally bombed during the Spanish Civil War. It is a critical response to the militarism of the first half of the twentieth century.
The New Deal
A series of economic programs and reforms started by Franklin D. Roosevelt between 1933 and 1936. The goal was to give work to unemployed people and help business and the economy improve. It represents a greater role that Western democracies played in the economy as a result of the Great Depression.
Fascism
A form of authoritarian nationalism that came to prominence in early 20th-century Europe. The first fascist movements emerged in Italy during World War I, before it spread to other European countries. Nazis were the most extreme fascists. Their ideas include strong nationalism, one-party rule, and racism. They viewed the communists as the main enemy.
Benito Mussolini
An Italian leader. He founded the Italian Fascist Party, and sided with Hitler and Germany in World War II. In 1945 he was overthrown and assassinated by the Italian Resistance.
Joseph Stalin
Under his leadership, the Soviet Union defeated Hitler in Europe. He was Bolshevik revolutionary and head of the Soviet Communist Party after 1924, and dictator of the Soviet Union from 1928 to 1953. He led the Soviet Union with an iron fist, using Five-Year Plans to increase industrial production and terror to crush all opposition.
The Nanking Massacre
An episode of mass murder and mass rape committed by Japanese troops against the residents of Nanjing (then spelled Nanking), then the capital of the Republic of China during the Second Sino-Japanese War. The massacre occurred over a period of six weeks starting on December 13, 1937, the day that the Japanese captured Nanjing.
Holocaust
the systematic state-sponsored killing of six million Jewish men, women, and children and millions of others by Nazi Germany and its collaborators during World War II. This word was chosen because in the ultimate manifestation of the Nazi killing program—the extermination camps—the bodies of the victims were consumed whole in crematoria and open fires.
Blitzkrieg
A German term for "lightning war," blitzkrieg is a military tactic designed to create disorganization among enemy forces through the use of mobile forces(tanks and airpower) and locally concentrated firepower. Its successful execution results in short military campaigns, which preserves human lives and limits the expenditure of artillery.