Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity Of Form & Function Chapter 3
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
cytology
scientific study of cells
cell theory
the theory that cells form the fundamental structural and functional units of all living organisms
cells
-functions: fight disease, store nutrients, connect things, line things, gather information and control body functions, involved in reproduction
-structure:
*nuclear envelope -> nucleus -> nucleolus
*plasma membrane
*cytoplasm -> cytoskeleton, organelles, inclusions, cytosol
intracellular fluid
fluid within cells; cytosol
extracellular fluid
fluid outside the cell; tissue fluid (ex. blood plasma, lymph, and cerebrospinal fluid
cytoplasm
fluid between the nucleus and surface membrane; contains the cytoskeleton, organelles, and inclusions
plasma (cell) membrane
-stick cells together to form tissues; regulates exchange of materials that go in and out of a cell; involved in intracellular communication; gives cell its shape
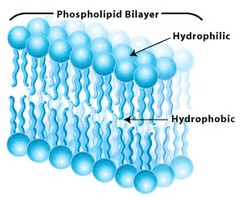
-made of proteins, lipids, & carbohydrates; phospholipids are major components; semi-permeable membrane
cytoskeleton
-supportive framework of protein filaments and tubules
-network of protein filaments and cylinders that structurally support a cell, determine its shape, organize its contents, direct the movement of materials within the cell, and contribute to movements of the cell as a whole
-composed of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules
organelles
diverse structures that perform various metabolic tasks for the cell
inclusions
-highly variable - fat droplets, glycogen granules, protein crystals, dust, bacteria, viruses; never enclosed in membranes
-foreign matter retained in cytoplasm
-(function) storage products or other products of cellular metabolism
phospholipids
75% of membrane molecules of the plasma membrane; drift laterally from place to place, spin on their axes, and flex their tails
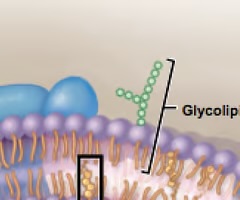
glycolipids
5% of membrane lipids molecules of the plasma membrane; phospholipids with short carbohydrate chains on the extracellular face of the membrane; help form the glycocalyx
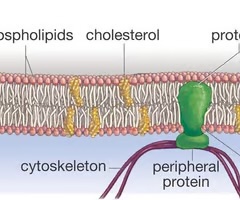
cholesterol
20% of membrane lipids molecules of the plasma membrane; molecules found near the membrane surfaces amid the phospholipids; interact with phospholipids and hold them still and stiffen the membrane; high concentrations can increase membrane fluidity by preventing phospholipids from becoming packed closely together
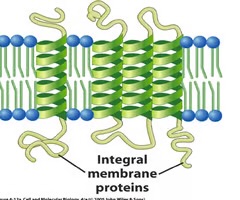
integral proteins
membrane protein; penetrate into the phospholipid bilayer or all the way through it
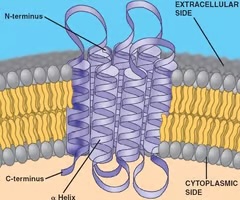
transmembrane proteins
membrane proteins that pass completely through
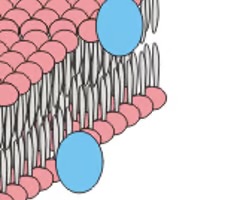
peripheral proteins
membrane proteins; do not protrude into the phospholipid layer but adhere to one face of the membrane
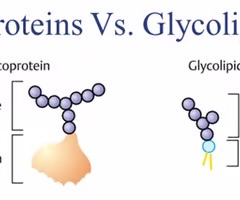
glycoproteins
most transmembrane proteins; bound to oligosaccharides on the extracellular side of the membrane
membrane proteins
receptors, second messenger systems, enzymes, channel proteins, carriers, cell identity markers, cell adhesion molecules
leak channels
always open and allow materials to pass through continually
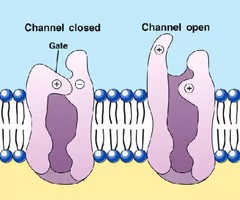
gated channels
open and close under different circumstances and allow solutes through at some times, but not others; respond to stimuli
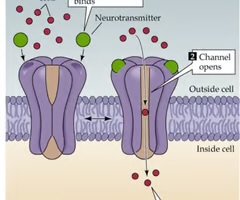
ligand-gated channels
respond to chemical messengers
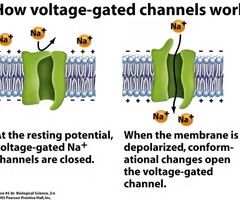
voltage gated channels
respond to electrical potential across the plasma membrane
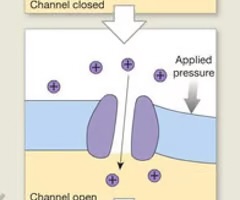
mechanically gated channels
respond to physical stress on a cell
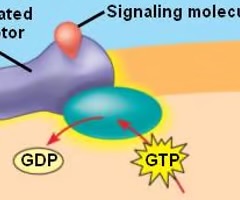
membrane receptors
binds to a transmembrane receptor on the outside of the plasma membrane because it cannot get across
G proteins
get their energy from GTP; relays the the signal to adenylate cyclase when activated by the receptor
adenylate cyclase
removes two phosphate groups from ATP and converts it to cAMP
cyclic adenosine mono phosphate
the second messenger; activates kinases
kinases
cytoplasmic enzymes that add phosphate groups to other cellular enzymes
glycocalyx
a bacterial capsule that is made of a fuzzy coat of sticky sugars
functions:
-protects the plasma membrane from physical/chemical injury
-enables the immune system to recognize and selectively attack foreign organisms
-defense against cancer
-forms the basis of compatibility of blood transfusions, tissue grafts, and organ transplants
-cell adhesion (binds cells together so tissues do not fall apart)
-enables fertilization
-guides embryonic development
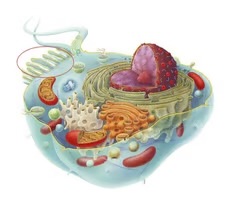
microvilli
-extensions of the plasma membrane that serve primarily to increase the cell's surface area, developed in cells specialized for absorption
-(function) increase absorptive surface area; widespread sensory roles
-some appear as a fringe called the brush border at the atypical cell surface
-show little internal structure, but some have a bundle of stiff filaments of a protein called actin, which attach to the inside of the plasma membrane at the tip of the microvillus, and at its base they extend a little way into the cell and anchor the microvillus to a protein mesh called the terminal web
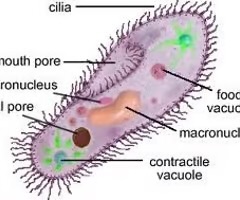
cilia
-long hairlike projections of apical cell surface; axoneme with a usually 9+2 array of microtubules
-(function) move substances along cell surface; widespread sensory roles; secrete mucus
-each bends stiffly and produces a power stroke that pushes along the mucus or other matter
-recovery stroke restores it to the upright position
-responsible for several hereditary diseases called ciliopathies
-beat within a saline layer at the cell surface
-chloride pumps in the apical plasma membrane produce the saline layer by pumping Cl- into the extracellular fluid; sodium ions follow by electrical attraction and water follows by osmosis
-structural basis for movement is a core called the axoneme, which consists of an array of thin projection cylinders called microtubles
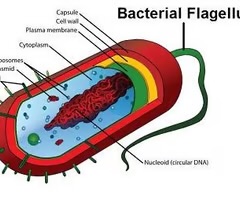
flagellum
whiplike tail of a sperm is the only function in humans; much longer than the cilium and has an identical axoneme, but between the axoneme and plasma membrane; long hair like extensions
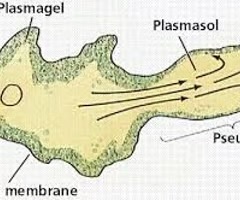
pseudopods
cytoplasm-filled extensions of the cell varying in shape from fine, filamentous processes to blunt fingerlike ones; change continually (ex. amoeba, neutrophils, macrophage)
selective permeability
allows some substances to cross it (like nutrients and wastes) more easily than others (like proteins and phosphates)
passive mechanisms
requires no ATP; filtration, diffusion (simple and facilitated), osmosis
active mechanisms
require ATP; active (primary and secondary) and vesicular transport
carrier-mediated transport
-movement of material through a cell membrane by carrier proteins
-carrier exhibits specificity for its ligand
-carrier exhibits saturation; as solute concentration rises, its rate of transport increases
-carriers don't chemically change their ligands, they simply pick them up on one side of the membrane and release them, unchanged, on the other
membrane transport
-transport without carriers (filtration, simple diffusion)
-carrier mediated transport (facilitated diffusion, primary active transport, secondary active transport, cotransport, countertransport)
-vesicular transport (endocytosis, exocytosis)
filtration
-movement of water and solutes through a selectively permeable membrane from higher pressure to lower pressure as a result of hydrostatic pressure
-transport without carriers
simple diffusion
diffusion of dissolved particles (nonpolar and lipid-soluble) from a higher concentration gradient (outside cell) to a lower concentration gradient (inside cell), without the aid of membrane carriers
factors that affect the rate:
-temperature (warmer substance = rapid diffusion)
-molecular weight (small molecules move quickly, large ones move slowly)
-steepness of the concentration gradient (greater difference = rapid diffusion)
-membrane surface area
-membrane permeability
osmosis
diffusion of water through semipermeable membrane from higher concentration to lower concentration; impermeable to solute molecules; large enough for water and sugar molecules (hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic solutions)
aquaporins
water channel proteins
nonpermeable solute
solute that cannot pass through the membrane pores because of its size or other properties (ex. proteins)
reverse osmosis
process of applying mechanical pressure to override osmotic pressure and drive water through a membrane against its concentration gradient; capillary filtration
hydrostatic pressure
force exerted by a fluid against the container wall
osmotic pressure
pressure that must be applied to prevent osmotic movement across a selectively permeable membrane
osmolarity
solute concentration expressed as molarity
tonicity
ability of a solution to affect fluid volume and pressure in a cell
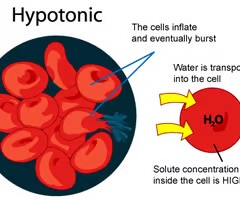
hypotonic solution
solution has a lower solute concentration than the intracellular fluid; cells absorb water, swell, and may burst
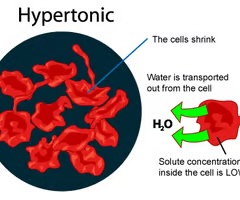
hypertonic solution
solution has higher solute concentration of non permeating solutes than the ICF; causes cell to lose water and shrivel; may die of torn membranes and cytoplasmic loss
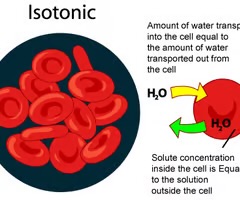
isotonic solution
total concentration of nonpermeating solutes is the same as the ICF; cause no change in cell volume or shape
uniport
carries only one type of solute
cotransport
simultaneous transport of two or more solutes in the same direction through a membrane by a carrier protein called symport, using either facilitated diffusion or active transport
countertransport
transport of two or more solutes in opposite directions through a membrane by a carrier protein called antiport, using either facilitated diffusion or active transport
facilitated diffusion
-transport of particles through a selectively permeable membrane, down their concentration gradient, by a carrier that does not directly consume ATP
-transports solutes that cannot pass through the membrane unaided
1. solute particle enters channel of a membrane protein
2. solute binds to a receptor site on carrier, which changes conformation
3. carrier releases the solute on the other side of the membrane
primary active transport
-transport of solute particles through a selectively permeable membrane, up their concentration gradient, by a carrier that consumes ATP, which transfers a phosphate group to the transport protein
-calcium pump uses this mechanism
secondary active transport
-transport of solute particles through a selectively permeable membrane, up their concentration gradient, by a carrier that does not itself use ATP but depends on concentration gradients produced by primary active transport elsewhere in the membrane
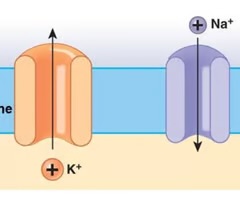
sodium potassium pump
good example of primary active transport; transmembrane protein; binds three NA+ simultaneously on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane, releases these to the ECF, binds two K+ simultaneously from the ECF, and releases these into the cell; each cycle consumes one ATP and exchanges three Na+ for two K+; keeps K+ concentration higher and Na+ concentration lower
functions:
-secondary active transport
-regulation of cell volume
-maintenance of membrane potential
-heat production
vesicular transport
movement of fluid and particles through a plasma membrane by way of membrane vesicles; consumes ATP
endocytosis
vesicular transport of particles into a cell (phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor-mediated)
exocytosis
process of eliminating material from a cell by means of a vesicle approaching the cell surface, fusing with the plasma membrane, and expelling its contents; used to release cell secretions, replace worn-out plasma membrane, and replace membrane that has been internalized by endocytosis
phagocytosis
process of engulfing large particles by means of pseudopods; "cell-eating"
pinocytosis
process of imbibing extracellular fluid in which the plasma membrane sinks in and pinches off small vesicles containing droplets of fluid; "cell-drinking"
receptor-mediated endocytosis
phagocytosis or pinocytosis in which specific solute particles bind to receptors on the plasma membrane, and are then taken into the cell in clathrin-coated vesicles with a minimal amount of extraneous matter
transcytosis
transport of material across a cell
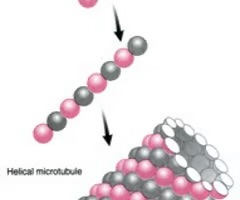
microtubles
-made up of tubulin
-(function) form axonomes of the cilia and flagella, basal bodies, centrioles, and mitotic spindles; enable motility of cell parts, form trackways that direct organelles and macromolecules to their destinations within a cell
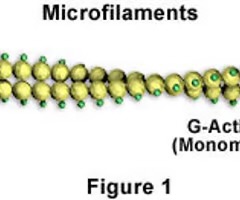
microfilaments
-thin protein filaments often in parallel bundles or dense networks in cytoplasm
-(function) support microvilli and plasma membrane; involved in muscle contraction and other cell motility, endocytosis, and cell division
-made of a protein called actin
-widespread throughout the cell but especially concentrated in a fibrous mat called the terminal web on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane
-web provides physical support, lipids provide a permeability barrier
intermediate filaments
-thicker protein filaments (8 to 10 nm thick) extending throughout the cytoplasm or concentrated at cell to cell junctions
-(function) give the cell its shape, resist stress, and participate in junctions that attach cells to their neighbors
-made of keratin in epidermal cells and fibrous things
nucleus
largest organelle in most cells, surrounded by a double membrane of nuclear pores
-(function) genetic control center of cell; directs protein synthesis; shelters the DNA
-enclosed in a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which is perforated with nuclear pores formed by a ring of proteins known as the nuclear pore complex
-inside the nuclear envelope is a narrow but fibrous zone called the nuclear lamina, composed of a web of intermediate filaments; it supports the nuclear envelope and pores, provides points of attachment and organization for the chromosomes inside the nucleus, and plays a role in regulating the cell life cycle
-material in the nucleus is called the nucleoplasm, which includes chromatin (fine, threadlike matter composed of DNA and protein) and one or more dark-staining masses called nucleoli, where ribosomes are produced
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
system of interconnected channels called cisterns enclosed by a unit membrane; cisterns are parallel, flattened sacks covered with ribosomes in rough ER; in smooth ER, cisterns are more tubular, branch more extensively, and lack ribosomes
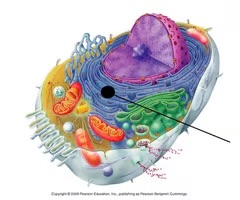
rough ER
-extensive sheets of parallel membranes with ribosomes on the outer surface
-(function) protein synthesis and manufacture of cellular membranes
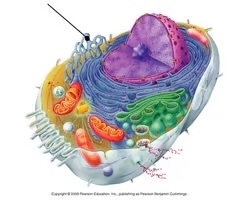
smooth ER
-branching network of tubules with smooth surface (no ribosomes); usually broken into numerous small segments in TEM photos
-(function) lipid synthesis, detoxification, calcium storage
ribosomes
-small dark granules free in cytosol or on surface of rough ER and nuclear envelope
-(function) interpret the genetic code and synthesize polypeptides
golgi complex
several closely spaced, parallel cisternae with thick edges, usually near nucleus, often with many golgi vesicles nearby
-(function) receives and modifies newly synthesized polypeptides, synthesizes carbohydrates, adds carbohydrates to glycoproteins; packages cell products into golgi vesicles
golgi vesicles
-round to irregular sacs near golgi complex, usually with light, featureless contents
-(function) become secretory vesicles and carry cell products to apical surface for exocytosis, or become lysosomes
lysosomes
round to oval sacs with single enclosing membrane, often a dark featureless interior but sometimes with protein layers or crystals
-formed by golgi
-(function) contain enzymes for intracellular digestion, autophagy, programmed cell death, and glucose mobilization
autophagy
lysosomal breakdown of a cell's own components
autolysis
destruction of cells by enzymes within the cells
peroxisomes
-similar to lysosomes; often lighter in color
-formed by rough ER
-(function) contain enzymes for detoxification of free radicals, alcohol, and other drugs; oxidize fatty acids
proteasomes
-small cytoplasmic granules composed of a cylindrical array of proteins
-(function) degrade proteins that are undesirable or no longer needed by a cell
mitochondria
-round, rod-shaped, bean-shaped, or threadlike structures with double-enclosing membrane and shelflike infoldings called cristae
-(function) ATP synthesis; powerhouse of the cell
centrioles
-short, cylindrical bodies, each composed of a circle of nine triplets of microtubules
-(function) form mitotic spindle during cell division; unpaired centrioles form basal bodies of cilia and flagella
centrosome
-clear area near nucleus containing a pair of centrioles
-(function) organizing center for formation of microtubules of cytoskeleton and mitotic spindle
basal bodies
-unpaired centriole at the base of a cilium or flagellum
-(function) point of origin, growth, and anchorage of a cilium or flagellum; produces axoneme
nuclear lamina
composed of proteins and maintains the shape of the nucleus
secretory vesicles
secrete substances outside the cell by exocytosis
unicellular
made of one cell
multicellular
made of many cells
cell junctions
connections between one cell and another
tight junctions
completely encircles each cell and provides seal that prevents passage of materials between cells
desmosomes
holds cells together
gap junctions
provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent animal cells; formed by a connexon
enzymes
carry out the final stages of starch and protein digestion in the small intestine, help produce second messengers, and break down hormones and other signaling molecules
receptors
binds to chemical messengers sent by other cells
channel proteins
passages that allow water and hydrophilic solutes to move through an individual membrane or protein tunnel
cell identity markers
bodies are enabled to tell which cells do and don't belong in our bodies
cell adhesion molecules
membrane proteins that cells adhere to one another and to extracellular material
second messengers system
when a messenger binds to a surface receptor, it may trigger changes within the cell that produce a second messenger in the cytoplasm
carrier proteins
transmembrane proteins that bind to glucose, electrolytes, and other solutes and transfer them to the other side of the membrane; come carriers, called pumps, consume ATP in the process
nucleolus
makes ribosomes and forms mRNA