Physical Science Terms
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Density
the compactness of matter described by a ratio of mass (or weight) per unit volume
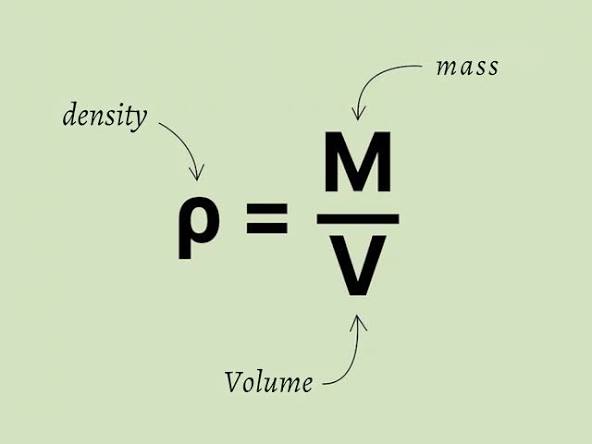
Direct Proportion
when two variables increase or decrease together in the same ratio (at the same rate)
English system
a system of measurement that originally used sizes of parts of the human body as referents
Fundamental properties
a property that cannot be defined in simpler terms other than to describe how it is measured; length, mass, time, and charge
Inverse proportion
the relationship in which the value of one variable increases while the value of the second variable decreases at the same rate (in the same ratio)
Metric system
a system of referent units based on invariable referents of nature that have been defined as standards (entire world uses, expect U.S.)
Proportionality constant
a constant applied to a proportionality statement that transforms the statement into an equation
Scientific law
A relationship between quantities described by an equation in physical sciences
Scientific principle
a relationship between quantities concerned with a specific or narrow range of observations and behavior
Variable
a changing quantity usually represented by a letter or symbol
3 properties of motion
speed, velocity, acceleration
Net Force
sum of ALL forces acting on an object
distance
1/2(acceleration)(time)²
d=1/2(a)(t)²
average velocity
final velocity+initial velocity/2
v-bar=vf+vi/2
Compound motion
when an object is projected into the air. split into vertical & horizontal parts. acceleration due to gravity = g (9.8 m/s²)
Newton’s first law of motion
law of inertia.
object will remain in state-of-rest unless a net force acts on it
Newton’s second law of motion
describes relation between net force, mass, and acceleration. F=ma, more force=more acceleration
Newton’s third law of motion
force is produced by the interaction of two different objects.
Equal in size, opposite in direction.
Newton
Force needed to give a 1.0kg mass an acceleration of 1.0m/s²
momentum
momentum=mass x velocity
p=mv
Centripetal force
force that pulls an object out of its straight-line path
force needed to keep depends on the mass, velocity, and radius of the circle
Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
relationship between masses of two objects, distance, and proportionality constant
provides the centripetal force that keeps the Moon in orbit.
acceleration
a=vf-vi/t
Centrifugal force
an apparent outward force on an object following a circular path that is a consequence of the third law of motion
Force
a push or pull capable of changing the state of motion of an object; has magnitude (strength) as well as direction
Free Fall
when objects fall toward Earth with no forces acting upward; air resistance is neglected when considering an object to be in free fall
Impulse
a change of motion is brought about by the product of the size of an applied force and the time the force is applied
Mass
a measure of inertia, which means a resistance in the change of motion
Weight
weight=(mass)(gravity)
w=mg
g=9.8m/s²
How is Force, F (newton) calculated
F=ma (general)
or
F=mv²/r (when talking of centripetal forces)
Chemical energy
a form of energy involved in chemical reactions associated with changes in internal potential energy; a kind of potential energy that is stored and later released during a chemical reaction
Electrical energy
a form of energy from electromagnetic interactions;
one of five forms of energy—mechanical, chemical, radiant, electrical, and nuclear
energy
the ability to do work
Geothermal energy
heat from beneath Earth’s surface, usually reaching the surface in the form of geysers, steam, or hot water
Horsepower
a measurement of power defined as a power rating of 550 ft•lb/s
joule
the metric unit used to measure work and energy; can also be used to measure heat; equivalent to newton-meter
joule
the metric unit for measuring work and energy, equivalent to newton-meter.
mechanical energy
the form of energy associated with machines, objects in motion, and objects having potential energy that results from gravity
nuclear energy
the form of energy from reactions involving the nucleus, the innermost part of an atom
potential energy
energy due to position; energy associated with changes in position (e.g., gravitational potential energy) or changes in shape (e.g., compressed or stretched spring)
power
the rate at which energy is transferred; defined as work per unit of time
radiant energy
Energy from electromagnetic radiation (ex: visible light)
watt
the metric unit for power; equivalent to J/s
work
when this is done on an object, it gains energy
Calculate Potential Energy
PE = mgh
(mass)(gravity)(height)
Calculate Kinetic Energy
KE=1/2mv²
Calculate Power
P=work/time
P=w/t
Calculate velocity final (vf)
𝑣𝑓 = √2𝑔ℎ (whole problem is square-rooted)
g=gravity
h=height
Scientific Method
collect observations, develop explanations, and test explanations