Topic 2 - States of Matter and Mixtures
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What are the three States of Matter?
Solid
Liquid
Gas
What is the particle model?
A model which shows the arrangement of particles as represented by solid spheres
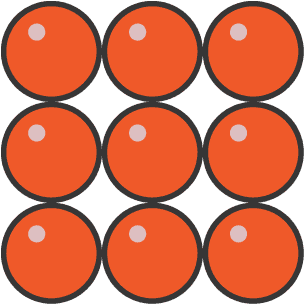
What is this state?
Solid as the particles are closely packed and in a regular lattice pattern
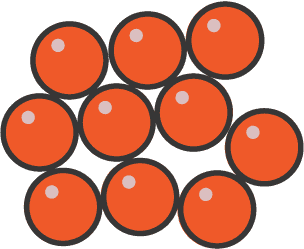
What is this state?
Liquid as the particles are free to move past each other but they tend to stick together
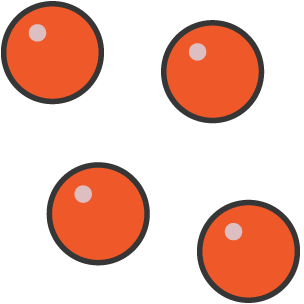
What state is this?
Gas as the particles are free to move randomly
What are the properties of a solid?
Strong forces of attraction between particles
Fixed positions in a regular lattice arrangement
Definite shape and volume
Not much energy
Vibrate around a fixed point
Expand slightly when heated
What are the properties of a liquid?
Some forces of attraction between particles
Free to move past one another
Tend to stick together
Don’t keep definite shape
Flow to fill container
Definite volume
More energy than solid state
Expands slightly when heated
What are the properties of a gas?
Almost no forces of attraction between particles
Free to move
Travel in straight lines and only interact when they collide
Don’t keep definite shape or volume
Fill any container
Exert pressure on walls when bouncing off
More energy than liquid and solid states
Constantly moving randomly
Speed increases with temperature
Pressure increases with heat
Gas expands with heat
What is the name for the changing of state from Solid to Liquid?
Melting
What is the name for the changing of state from Liquid to Gas?
Evaporation
What is the name for the changing of state from Gas to Liquid?
Condensation
What is the name for the changing of state from Liquid to Solid
Freezing
What is the name for the changing of state from Solid to Gas?
Sublimation
What causes the change of state?
An increase in temperature provides energy to particles which causes them to vibrate more and weaken the forces of attraction until at their Boiling or Melting Point, these forces are completely overcome and the changing of state occurs
Are physical changes easy or hard to reverse?
Easy to reverse
Are chemical changes easy or hard to reverse?
Hard to reverse
Why is it difficult to reverse chemical reactions?
The atoms are rearranged to form different substances
What is a pure substance?
A substance containing only one element or compound
What is a mixture?
A substance containing more than one element or compound
What is an example of a mixture?
Air as it is made up of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour and other gases
How can melting point be used to test for purity?
Pure substances have a specific, sharp melting and boiling point whereas impure substances melt gradually over a range of temperatures
What is simple distillation?
A process used to separate liquid from a solution
Describe the distillation of pure water from saltwater
Pour the sample of saltwater into a distillation flask
Connect the bottom end of the condenser to a cold tap using rubber tubing, run cold water through the condenser to keep it cool
Gradually heat the distillation flask, the part of the solution with the lowest boiling point will evaporate first (water in this experiment)
The water vapour passes through the condenser where it is called and condenses into a liquid, it flows into a beaker and is collected
Salt will remain in the flask
What is an issue with simple distillation?
It can only be used to separate substances with very different boiling points
What is fractional distillation?
A process used to separate a mixture of liquids with a range of boiling points that are relatively similar
Give an example of industrial level fractional distillation
Fractional distillation of crude oil in a refinery
Describe the a method for fractional distillation
Pour the mixture into a flask, attach a fractionating column and condenser
Gradually heat up the flask, the different liquids will all have different boiling points so will evaporate at different temperatures
The liquid with the lowest boiling point will evaporate first, when the temperature on the thermometer matches the boiling point of this liquid, it will reach the top of the column
Liquids with higher boiling points might start to evaporate but the column is cooler towards the top (CREATING A TEMPERATURE GRADIENT) so they will only get part of the way up before condensing and running back down towards the flask
When the first liquid has been collected, raise the temperature until the next one reaches the top
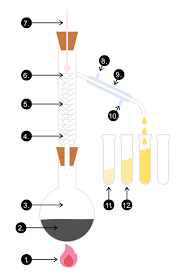
What separation technique is this diagram depicting?
Fractional distillation
What is filtration?
A process that removes an insoluble solid from liquid
What equipment is needed for filtration?
Filter paper,a funnel and a beaker
What is the name of the solid left in the filter paper after filtration?
Solid residue
What is the name of the liquid produced by filtration?
Filtrate
What is crystallisation?
A process which separates a soluble solid from a solution by evaporation
Describe a simple method of crystallisation
Pour a solution into an evaporating dish and gently heat the solution, some water will evaporate and the solution will become more concentrated
Once some of the water has evaporated when crystals begin to form (point of crystallisation), remove the dish from the heat and leave the solution to cool
The salt should start to form crystals as it becomes insoluble in the cold, highly concentrated solution
Filter the crystals out of the solution then rinse them with distilled water
Leave them in a warm place to dry. You can use a dying oven or a desiccator or pat them dry
What separation method would you use to separate Sodium Chloride from a Saltwater solution?
Crystalisation
What is chromatography?
A process used to separate a mixture of soluble substances and identify them
What is the mobile phase?
Where the molecules can move as a liquid or gas
What is the stationary phase?
Where the molecules cannot move as a solid or viscous liquid
What is the stationary phase in paper chromatography?
Filter paper
What is the mobile phase in paper chromatography?
The solvent
e.g. water or ethanol
Describe the setup of paper chromatography
Draw a line near the bottom of the paper in pencil, this is the baseline
Put a spot of the mixture to be separated on the line
Put some of the solvent in a beaker, dip the bottom of the paper (NOT THE SPOT) into the solvent
Put a watch glass on the top of the beaker to prevent evaporation of the solvent
The solvent will start to move up the paper, when the chemicals in the mixture dissolve in the solvent, they will move up the paper too
You will see the different chemicals in the sample separate out, forming spots at different places on the paper
Remove the paper from the beaker before the solvent reaches the top, mark the distance the solvent has moved (the solvent front) in pencil
Why is pencil used to draw the base line?
Pencil is insoluble so it won’t move with the solvent
What does it mean if a component does not move in the mobile phase?
It is insoluble
How does solubility in the solvent affect the time spent in each phase?
Molecules with a higher solubility in the solvent will spend more time in the mobile phase than the stationary phase and will be carried further up the paper
How does attraction the the stationary phase affect time spent in each phase?
Molecules that are less attracted to the stationary phase (paper) will spend more time in the mobile phase than the stationary phase so will be carried further up the paper
What is the name of the piece of paper left at the end of paper chromatography?
A chromatogram
What is a locating agent used for?
To show the locations of colourless chemicals in a chromatogram
What is an Rf value?
The ratio between the distance travelled by the dissolved substance (solute and the distance travelled by the solvent
What is the equation for Rf?
Distance travelled by solute ÷ Distance travelled by solvent
How do you find the distance travelled by the solute?
Distance between the centre of the spot and the baseline
What does it mean if a pure sample of a chemical has the same Rf value as a spot on the chromatogram?
They are likely the same chemical
What is an SRM?
A standard reference material which is a sample of a pure substance that chemists use to compare to a mixture to check identities of its components
They have a controlled concentration and purity
Why can chromatography be used as a purity test?
A pure substance won’t be separated by chromatography and will move as one spot
What is potable water?
Water that is fit to drink
What is surface water?
Water from lakes, rivers and reservoirs, commonly used in much of England and Wales
Run dry during summer months
What is ground water?
Water trapped underground by aquifers
As much as 70% of south-east England’s water comes from ground water
What is waste water?
Water that has been contaminated by a human process
e.g. by-product of industrial processes
Treating waste water can make it potable
What is filtration?
When a wire mesh screens out large twigs and then gravel and sand beds filter out smaller solids
What is sedimentation
Iron sulfate or aluminium sulfate is added to water which makes fine particles clump together and settle to the bottom
What is chlorination?
Chlorine gas is bubbled through to kill harmful bacteria and other microbes
How do very dry countries obtain potable water?
Through distillation of sea water
Why doesn’t the UK use distillation to produce potable water?
It requires huge amounts of energy and is very expensive when trying to produce large quantities of fresh water
What is deonised water?
Water that does not contain any ions such as calcium or iron that are present in normal tap water
Why is deionised water used in chemical reactions?
Ions can interfere with reactions leading to false results