maths formulas or theory memorise
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Vector cross product
a2b3-a3b2
A3b1-a1b3
A1b2-a2b1
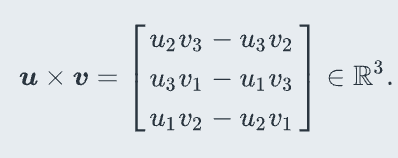
Projection of U onto V
Proj v (U) = [(U•V)/|V²|] V
Taylor series
T_n(x) =f(a)+f’(a)(x-a)+f’’(a)(x-a)²/2…..+f^(n)(a)(x-a)²/n!
Maximums minimums and concavity
f’’(x)>0
f’’(x)>0 concave up minimum
f’’(x)<0 concave down maximum
f’’(x)=0 inflection
criteria for invertibility of a matrix
Determinant does not equal 0
Criteria if a matrix is diagnosable
Can be written in the form A=PDP^-1
N x N matrix has
N number of unique eigenvalues
What does P and D equal in A=PDP^-1
P = columns are the eigenvectors stacked on each other
D = eigen values as the diagonal of the matrix
How to calculate eigenvector/eigenspace
Lagranges formula
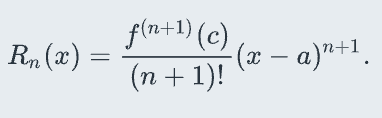
injective / Surjective
Injective - one to one (horizontal line test) distinctive outputs.
Surjective - range is equal to Codomain.
elementary limit
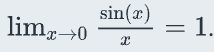
First principle differentiation
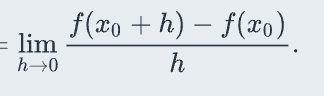
sum of infinite geometric series
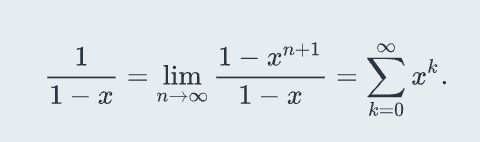
Riemann sum
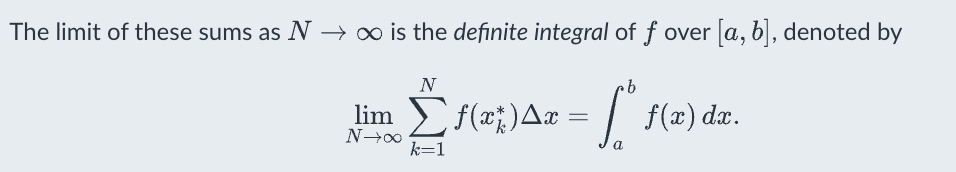
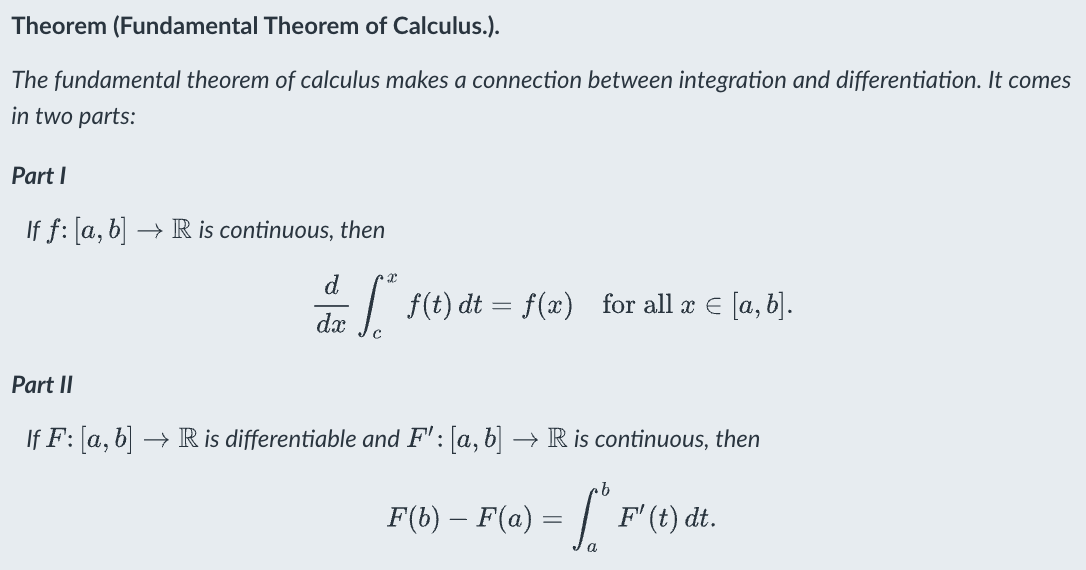
fundamental theorems of calculus
Fundamental theorem of calculus for a differentiable limit
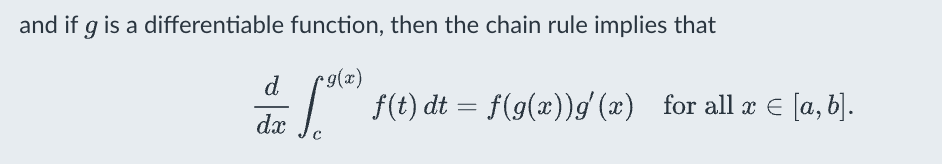
Length of a graph formula
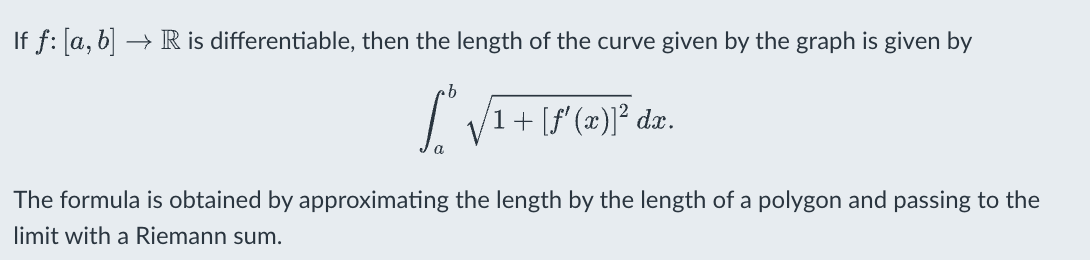
Disc Method
x axis ,
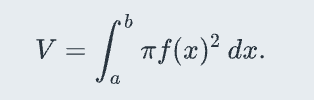
Shell method
y axis
Four forms of vector
Matrix invertible theorem

Eigenvalue/Eigenspace
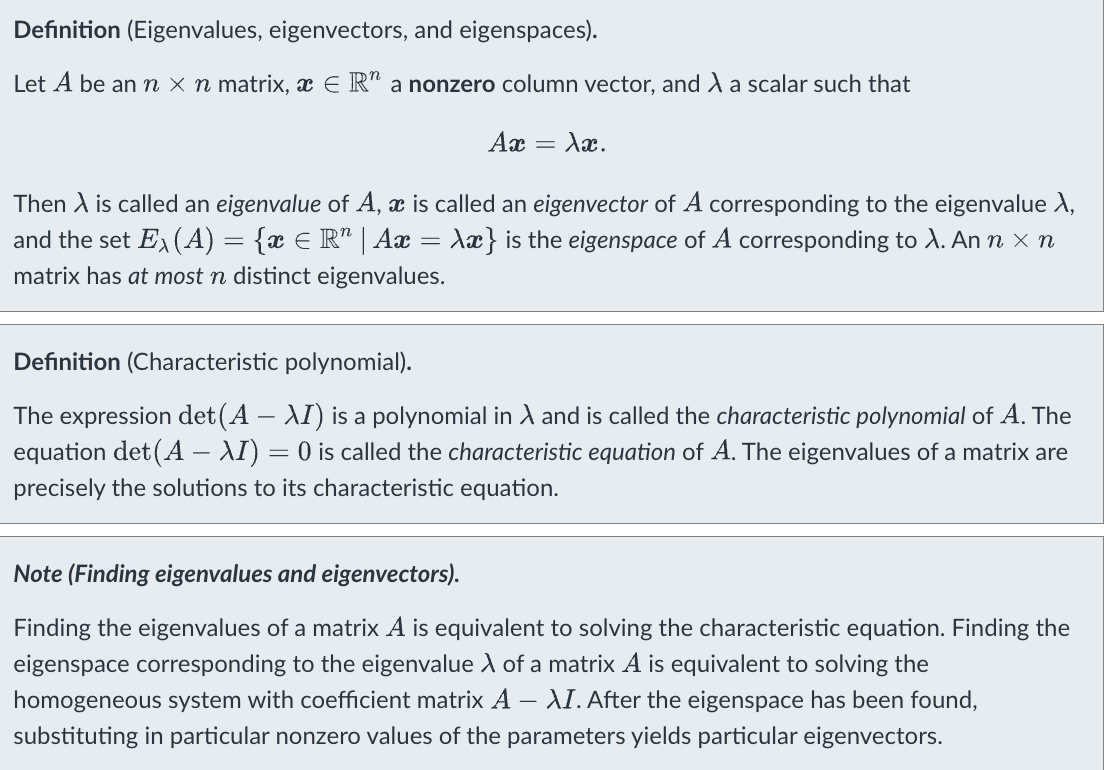
Algebraic/geometric multiplicity

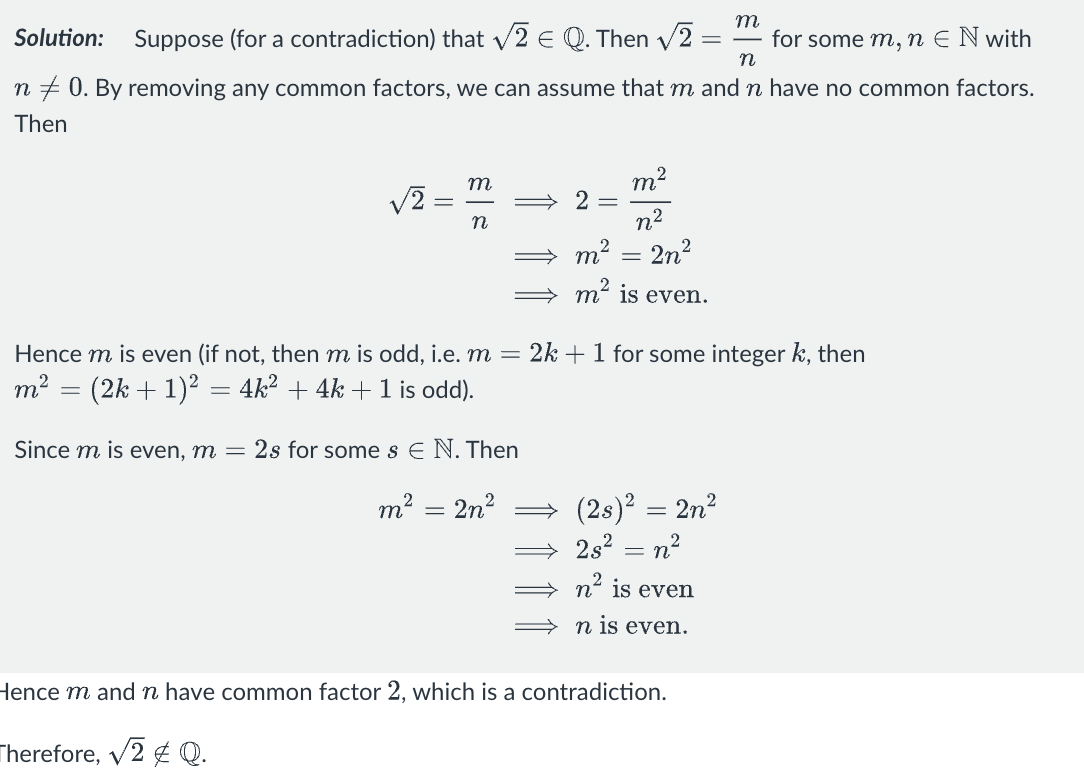
prove sqrt of 2 is irrational

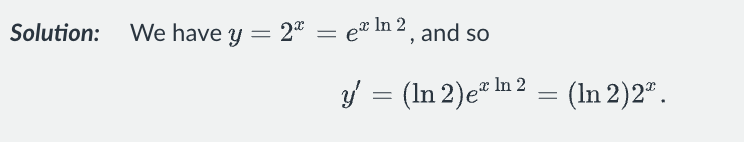
Taylor series for e^x, cosx, sinx, coshx, sinhx, ln(1+x)
