Geography 5 UCLA Gillespie Midterm
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Did the Greeks know the earth was round? How? (3 ways)
1. Clouds and boats- clouds touch horizon and boats are in front
2. The lunar eclipse of the moon (the earth's shadow on the moon)
3. North star rises as you go more north
Tundra or Alpine/ Artic:
1. Where is it
2. Why is it there
3. Plant Adaptations
4. CA?
5. Conservation status
6. Adapated to fire?
1. N America and N Europe, Russia, Siberia, high elevations
2. 7 months of freezing temperature and little rainfall (less than 25cm)
3. Herbs- short plants that are perennial (over 1 year age); berries and edible plants
4. Yes, S. Sierra Nevada and Yosemite
5. Good, hard to get up there to destroy it.
6. Not adapted to fire, takes long to recover
Boreal Forest
1. Where is it
2. Why is it there
3. Plant Adaptations
4. CA?
5. Conservation status
6. Fire
1. In bands across N America, Europe (Scandinavia and N Germany), Russia, S. America-- only N. hemisphere
2. Warmer temperatures for over 7 months, over 50 cm of rain
3. Conifers (no leaves, but needles and cones); soft wood
4. Yes, redwood and sequoias, mountains
5. Pretty good, able to regenerate and be sustainable. What's awful is the Old grove forests that cant grow back. Only 4% left.
6. Yes. Needs fire to reproduce.
Temperate Deciduous Forest
1. Where is it
2. Why is it there
3. Plant Adaptations
4. CA?
5. Conservation status
6. Adapted to fire?
1. E America, W Europe (France), Asia, China, Japan, S. Chile, New Zealand, Tasmania
2. Occurs near warm water. Cold winters (like Artic), hot and wet summers (like Tropics)
3. Old/primitive flowering plants/trees (no cones- flowers and fruits YES): oaks, magnolias, Laurel
4. NOPE
5. Good, grows back quickly. Bad that air pollution and acid rain kills trees
6. No no
Temperate Grasslands
1. Where is it
2. Why is it there
3. Plant Adaptations
4. CA?
5. Conservation status
6. Adapted to fire?
1. US prairies, Pampas of Argentina, S Africa, Steppes of Europe
2. Between deserts and mountains; summer is hot and winter is cold; less rainfall so trees aren't prominent; drier than TD Forest
3. Perennials; short or tall grasses
4. Yes, central valley and pre-UCLA
5. Ugly, used for farm and BEEF
6. Fire maintains the land, 80% biomass underground so it's all good in the grass-hood)
Mediterranean Scrub
1. Where is it (5 places important to know)
2. Why is it there
3. Plant Adaptations
4. CA?
5. Conservation status
6. Adapted to fire?
1. Mediterranean
2. CA West Coast
3. Central Chile
4. S Africa
5. SW Australia
2. Summers are hot, winters are wet because ocean currents
3. Shrubs (multi-stemmed, single trunk, about 2 m tall);
-All med. plants have tiny leaves because heat
-Evergreen plants- green all year round
-Light color because it reflects light
-Plants point up to avoid direct sun
-Smell acts as defense; rosemary
4. Yes
5. Bad, more population puts pressure on ecosystems, expanding agriculture
6. Yes very well
Tropical Rain Forest
1. Where is it
2. Why is it there
3. Plant Adaptations
4. CA?
5. Conservation status
6. Adapted to fire?
1. Amazon, Congo Basin, SE Asia, N Australia, Madagascar
2. ITCZ- InterTropical Convergence Zone)- rain making machine as warm hits cold air
-Not stable: T of Cancer (summer) to Equator (fall) to T of Capicorn (winter)
-Ogrographic precipitation on the mountains: warm air rises and squeezes water out of clouds/ wet side
3. Tall, closed canopy (no sun on ground)
-Shallow roots, soil poor(Biomass is 95% in plants itself)
-Most diverse (In area 100x100m, over 300 tree types)
-Epiphytes: plants on plants on plants man
-Lianas: woody vines that crawl to canopy
-Agriculture
4. No
5. Bad, one of most endangered. Hard to colonize and many diseases.
6. Nope
Tropical Dry Forest
1. Where is it
2. Why is it there
3. Plant Adaptations
4. CA?
5. Conservation status
6. Adapted to fire?
1. Mexico, Central America, India, Caribbean, Brazil, Australia
2. ITCZ, seasonal nature of it makes it have wet and dry seasons
3. Short canopy
-Deciduous
-Few epiphytes
4. No
5. Ugly as ya momma
Tropical Savannas
1. Where is it
2. Why is it there
3. Plant Adaptations
4. CA?
5. Conservation status
6. Adapted to fire?
1. Brazil, Venezuela, Africa, India, Australia
2. Low precipitation (50-100 cm)
3. Annual grasses (grow, die, fire, repeat!)
-Scattered trees, animals
-In wet season: tall grass; As ITCZ moves, grasses brown and catch on fire, their thick bark burns your loins but roots are thin
4. Nah
5. Ugly, we suppress the fire in its loins and it cant flourish!
-wheat agriculture takes over
-grasses become shrubs
6. Yes it needs the fire in the loins.
Desert (Cold and Hot)
1. Where is it
2. Why is it there
3. Plant Adaptations
4. CA?
5. Conservation status
6. Adapted to fire?
1. Hot: Mexico, Sahara, Saudi Arabia, Australia
Cold: Iran, Gobi Desert, Temperate Beaches
2. Low rainfall (less than 50 cm)
3. Hot: succulents, store water (cacti), shrink in drytime, Annual plants
Cold: Not succulents (Joshua tree, adapt to hot weather), live a long time (creosote- shrub that can live thousands of years)
4. Yes, both
Hot: Sonora, Colorado desert
Cold: Mojave (joshua tree), Great Basin, Vegas
5. noo
6. Nope
Orographic Precipitation and Rain Shadow
Warm air rises, then cools/condenses to form precipitation. This squeezes air out of the mountains in a way that makes the other side dry.
Rain occurs upwind a mountain range as orographic clouds form.
Orographic: relating to mountains, resulting from effects of mountains in forcing moist air to rise
ITCZ (Inter Tropical Convergence Zone)
-Located near the equator// More so near Tropic of Cancer in summer, equator in fall, and Tropic of Capricorn in winter
-Region it's in is Tropical Dry Forest
-low pressure belt that circles around designated area
-This is because winds converge from the North and South Hemisphere
-It is a rain-making machine that causes the wet and dry seasons Tropical Dry Forests
Epiphytes
Plants on plants on plants, man.
-Plants that grow on other plants
-Found in tropics but not the topical rain forest
Lianas
Woody vines
-Vines wind up the tree to carry water to the top
How are plants adapted to Mediterranean climate?
-Small leaves point up to sunlight to prevent direct sunlight
-light pigment to reflect heat
-distinct smell as a defense mechanism
How are Mediterranean plants adapted to fire?
-Fire must cause the seeds of the plant to open in order to germinate
-re-sprouting occurs underground (Mediterranean is similar to grasslands with lots of biomass underground)
-ribbon like bark that wants to be burnt
-turpentine allows plants to combust on their own
500 MYA
1. Before Present/Animal
2. Common Ancestor
3. Predators
1. Sea squirt
2. Invertebrate with invert backbone
3. None
400 MYA
1. Before Present/Animal
2. Common Ancestor
3. Predators
1. Fish
2. Backbone and Eyes
3. Big fish predators
300 MYA
1. Before Present/Animal
2. Common Ancestor
3. Predators
1. Reptiles
2. Nails and Brain
3. Bigger Reptiles
225 MYA
1. Before Present/Animal
2. Common Ancestor
3. Predators
1. Early mammals, shrew
2. Hair and Glands for sweat
3. Big reptiles
36 MYA
1. Before Present/Animal
2. Common Ancestor
3. Predators
1. Primates
2. Thumbs and Tails
3. Big carnivore predators
2 MYA
1. Before Present/Animal
2. Common Ancestor
3. Predators
1. Homo genus (chimps)
2. Tailbone and Appendix
200,000 years ago
1. Before Present/Animal
2. Common Ancestor
3. Predators
1. Homo-sapiens "smart and same"
DNA
1. Name
2. Discovered by?
3. Similarities between species
4. True Religion
1. deoxyribonucleic acid
2. double helix by watson and clark--- jk, Rosaland Franklin
3. Humans share 99.5% DNA
Humans share 50% DNA with worms
Humans share 99% DNA with apes
4. Ancestor worship
Eve Age
1. When is our common mother from?
2. Where is this evidence extracted from?
1. 150k years ago
2. Mitochondrial DNA
Adam Age
1. When is our common mother from?
2. Where is this evidence extracted from?
1. 120-150k
2. Y chromosome
Megafauna
-large mammals (mammoth, grizzly)
-competition is good or else they will be vulnerable or lose fear of predators
Paul Martin's Overkill (Or Munch) Hypothesis
60 year old hypothesis that humans MUNCHed their way from N to S America and killed off all the megafauna.
-Used clovis: weak knifes similar to spears that killed megafauna
5 Megafauna in LA
1. sloth
2. CA rhino
3. mammoths
4. camels
5. saber tooth tigers
New Zealand 1,000 years ago
1. Moa
2. Mauri
1. Moa was a bird that got to New Zealand to find that there were no mammal predators, so it went to the top of the food chain.
-was gigantic
2. Mauri were elephant birds
Island Gigantism
Excessive largeness and growth
-Moa birds
Island Dwarfism
When species get smaller physically in a specific area; reduction of size when their gene pool is limited to small environments
-Pygmy mammoth was big but got small on Catalina island
Amount of People on Eath
1650: 1/2 billion
1820: 1 billion
1930: 2 billion (grandparents)
1975: 4 billion
2000: 6 billion
2011: 7 billion
Thomas Malthus Theory
Population= exponential
Resources= linear
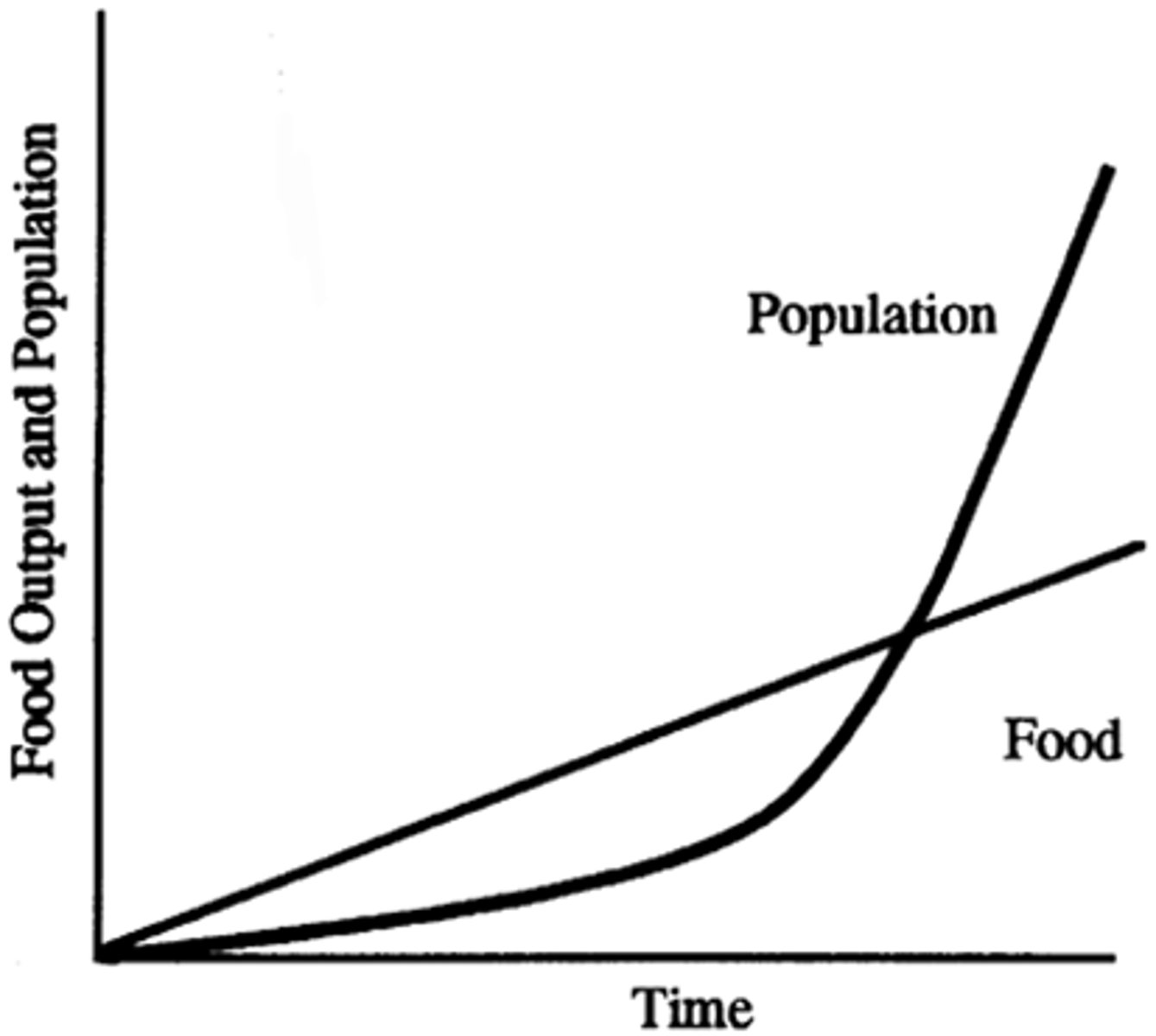
Thomas Malthus's Prediction and Outcome
1798: Predicted that England would suffer a catastrophe as people were growing faster than rate of agriculture.
Wrong because:
1. People left the UK
2. Technology produced higher yields.
How do family planning programs work?
1. Local
2. Women
3. Access based
1. UN supplied local control
2. Targeted women to take care of themselves/educated vaginas
3. Access based, not incentive based. Gave out freebies.
What happened to Cuban agriculture after the fall of the Soviet Union?
Used to be sustained by USSR, but then became sustainable on its own
1. Went backward- back to bikes then back to oxen
2. Used natural pesticides and intercropping
3. Used natural fertilizers and night soils
Current status of Population by Region
Current Status of Population by Region:
Central and S. America - 50% population was under 16, now 30%
E. Europe- people leave
W. Europe-Negative birth rates, yet increasing due to immigration
Africa:-Growing rapidly yet controlled by disease (AIDS)
India
-Bad
-1.2 billion people with 1.5 million each month
3% growth yearly
Pakistan
-Bad
-176 million that will double every 40 years
Nigeria
-Bad
-162 million that will double every 30 years!
Mexico
-114 million
-Improved
Growth rate 2% now because education
Iran
-Awesome sauce
-Medical schools targeted to women
Less than 2% fertility (used to be 5 kids a family)
South East Asia
-Awesome sauce
Less than 2% fertility rate
China
-Awesome sauce
-1979 One Child Policy
Where did measles and TB come from? (and small pox)
Cattle
Where did flu come from?
Pigs and ducks
Where did HIV/AIDS come from?
monkey
HPV/ Venereal Warts
How many people have it in US?
30 to 50% in US, but 80% in urban areas
Herpes
How many people have it in US?
20% in US
Syphilis
How many people have it in US?
Less than 1% in US
-We gave it all to Native Americans
HIV/AIDS
How many people have it in US?
1 in 300 infected in US
Potato (Solanum tuberosum)
1. Where is it from?
2. How is it grown?
3. Ecological Impact
1. Andes
2. Planted underground
3. Good because sustainable and small impact
Sugar (Saccharum officinarum)
1. Where is it from?
2. How is it grown?
3. Ecological Impact
1. New Guinea, but US subsidizes Florida
2. Before becoming sucrose, fields are burnt down to extract it
3. Bad- Single greatest threat to Florida Everglades
Chocolate (Theobroma cacao); Aztec "Food of the Gods"
1. Where is it from?
2. How is it grown?
3. Ecological Impact
1. Andes
2. Fermented beans from small tree turn from white to brown
3. Good
Tea (Camellia sinensis)
1. Where is it from?
2. How is it grown?
3. Ecological Impact
1. China
2. Leaves picked off shrubs
3. Bad because monoculture
Coffee (Coffea arabica)
Organic/Shade coffee/Sun coffee
1. Where is it from?
2. How is it grown?
3. Ecological Impact
1. Ethiopia
2. Shade coffee: Organic, native tree canopy remains, so pesticides (insects)
Sun coffee: Monoculture, grows in full sun, cut down all other trees
3. Shade/shaken- Good; Sun- Bad
Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis)
1. Where is it from?
2. How is it grown?
3. Ecological Impact
1. Brazil
2. Rubber sap collected in buckets at the bottom of the tree
3. Good when organic (Brazil way)
Bad when monoculture
Maize (Zea mays)
1. Origin
2. Significance
1. Mexico, 5000 BC
2. Bad in monoculture, good in intercropping because it reduces pesticides. biofuel
-50% from US
Wheat (Triticum)
1. Origin
2. Significance
1. Iran, 7500 BC
2. First cereal in production. used for livestock
Rice (Oryza sativa)
1. Origin
2. Significance
1. S. Himalayas
2. 2/3 of harvesting
Coco (Erthroxylum coca)
1. Origin
2. Significance
1. Andes
2. Coca is first in calories, protein, carbohydrates, fiber
-Rich in calcium, phosphorous, iron, vitamin A and E
Number 1 Cash Crop in CA
-Hemp (2012 top seller)
Exports from CA: Top 5 Crops
1. Grapes
2. Almonds
3. Hay
4. Cotton
5.oranges
cali supplies
1/3 of all vegetables and 2/3 of all fruits to U.S.
GMOS & Frankenfood: The Positives
1. Larger yields
2. Nutrition like vitamins
3. Disease and pest resistant
4. Increase environmental tolerance (gives trees ability to live on less water)
5. Vaccines to livestock
6. not sure about bad effects
Hello in tongva
miyiiha me-hee-haw
Ethnobotany
Ethno "human"; Botany "plants"
-The study of peoples use and knowledge of plants and their medical, religious, and other uses.
Oaks
Quercus sp.
Acorns were the primary food source for a number of California Indians. Acorns were collected, leached with water in stream and basket to remove tannins (Wine) then heated with rocks for mush.
-Native to CA, pointy leaves
Elderberry
Sambucus sp.
One of the richest sources of vitamin C! Stems used for arrow shaft and flutes. Raw berry can cause nausea, but dried or cooked are OK.
Laurel Sumac
Rhus sp.
Indians would use the leaf as mosquito repellent. Lemonade Berry (Rhus intergrifolia) has berries that are soaked and hairs removed to make pink lemonade.
Yucca
Yucca sp.
Our Lord's Candle
The leaves are very strong and used for water proof baskets. The leaves were used as a needle and thread to make clothes and homes. The root is used for soap.
Cactus
Opuntia sp.
The red fruits are edible but watch for very small spines. The green leaf can be cooked and eaten and is still commonly done in LA.
California Coastal Sage
Artemesia californica
Burned for ceremonial reasons.
1891 Forest Reserve Act
1. Created national forests service and watershed agency
2. Took land and made it into federal land
3. Beginning of large patches of gov land and national forests
1960 Multiple Use and Sustained Use Act: 5 Things
National forests needed to be maintained so this allowed for:
1. Outdoor recreation
2. Rangeland- cows
3. Timber- forests can be used for the economic benefit of trees
4. Watershed protection
5. Protect wildlife and fish habitat
1964 Wilderness Act
Created the National Wilderness Preservation System to protect national parks and wildlife
What is clear cutting?
1. ID section of forest (sell it and it becomes privatized)
2. Build a road into the area
3. Cut down every tree
4. Cable logging- drag logs which gets rid of life and soil
Problems with Clearcutting
1. Soil erosion
2. Herbicides to kill weeds so only trees grow
3. Monoculture
4. loss of wildlife
United States Department of Agriculture
-where National Forest Service resides
Department of Interior
-US Fish and Wildlife Services
-National Park Service
-Bureau of Land Management (not forest but needs to be maintained for resources)
Why did we lose 1.3 billion dollars a year in the 80's?
Reagans policies allowed for timber to be sold to private companies; build roads; 60% forests gone
Land Ownership Percents
Private, Non-profit- 55%
Native America- 3%
State and Local- 7%
Federal- 35%
Nature Conservancy
Gets rich republicans to buy a=land and turn it into a non-profit area
Sierra Club
Lobbies for sustainable forests
activist like Greenpeace
campaigns; prevents adverse events from happening
Where are the redwoods today?
-Redwoods are the tallest trees
-96% of redwoods have been cut
-Out of 4% left:
--2% are private
--2% are federal or state owned
Sequoia
Largest tree
Ancient Bristle Cone Pine
Oldest Tree (4800+ years)
How have forests in the west changed in the last 100 years?
-Used to be numerous with small fires
-After colonization, there is more brush with larger and worse fires
# of highways in US
# of logging roads in US
-44,000 miles of highways
-380,000 miles of logging roads
1. Fire Policy
2. Problems
3. Choices
1. Smokey the Bear didnt want you to start forest fires because the government wanted to log the wood
2. -Litter build up makes fires worse
-Bug outbreaks
-Crown/canopy fires will burn down the whole forest
3. -Thinning biomass so fires arent as bad- burn it for energy or xmas trees
-Reintroduce fire but hard because air regulations
-nothing
3 things that define old growth forests
1. Trees of different sizes
2. dead trees- snass, insects live on them
3. over 200-500 years old
highly developed, moderately developed and less developed countries
1.U.S., Japan, Australia
2.India, Mexico, China
3.Somalia, Afghanistan, Tanzania
How many additional earth's would we need if everyone consumed the same level as the United States?
4
The current restoration project in the Florida Everglades is using all but which one of the following strategies?
degradation
What is interesting about the city Curitiba, Brazil?
compact development in a moderately developed country
What are minerals and economic geology?
Minerals - elements or compounds that occur naturally in earth's crust, deposits enable industrialization
The 18th century British economist Thomas Malthus said that population grows exponentially, while food supply grows in a linear fashion. He predicted this would cause famine, disease, and war.
An age structure diagram that represents rapid growth for a population looks like a
pyramid
What is a Wildlife corridor
a protected zone that connects isolated unlogged or undeveloped areas