COMMERCE 10 EXAM
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/194
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
195 Terms
1
New cards
buyer (vocab)
consumers that require the goods and services, they make the demand for the services
2
New cards
contraction (vocab)
(phase of the business cycle)
a period of economic decline marked by falling real GDP
a period of economic decline marked by falling real GDP
3
New cards
deflation (vocab)
the general decline of the price level of goods and services
4
New cards
depression (vocab)
a major downturn in the business cycle characterised by sharp and sustained declines in economic activity
5
New cards
demand (vocab)
the amounts of goods and services that buyers will purchase at a given price
6
New cards
law of demand
PRICE = INCREASE → quantity demanded falls less people want to buy at a high price
PRICE = DECREASE → quantity demanded rises - more people want to buy at the reasonable price
-- don't want to spend their money when expensive so they buy cheap
PRICE = DECREASE → quantity demanded rises - more people want to buy at the reasonable price
-- don't want to spend their money when expensive so they buy cheap
7
New cards
exports (vocab)
an injection into the circular flow of income
8
New cards
expansion (vocab)
real gross domestic product (GDP) grows for two or more consecutive quarters, moving from a trough to a peak
9
New cards
Economic downturn/downfall (vocab)
a significant decline in economic activity spread across the market, lasting more than a few months
10
New cards
how to track economic downturn/downfall?
- real GDP
- real income
- employment
- industrial production
- wholesale-retail sales
- real income
- employment
- industrial production
- wholesale-retail sales
11
New cards
GDP/gross domestic product (vocab)
standard measure of the value added created through the production of goods and services in a country during a certain period
12
New cards
investment (flow of income) (vocab)
an injection into the circular flow of income
13
New cards
imports (flow of income) (vocab)
a leakage from the circular flow of income
14
New cards
inflation (vocab)
an increase in the level of prices of the goods and services that households buy
15
New cards
market (vocab)
exchange process between sellers and buyers
16
New cards
Market Equilibrium
point when the demand and supply curves meet
17
New cards
Price mechanism
refers to the forces of supply and demand in determining price and quantity of goods sold
EXAMPLE:
if demand increases, prices will rise, causing a movement along the supply curve
EXAMPLE:
if demand increases, prices will rise, causing a movement along the supply curve
18
New cards
Ressesion
two consecutive quarters, 6 months of negative GDP growth
19
New cards
one quarter =
3 months
20
New cards
saving (flow of income)
a leakage from the circular flow of income
21
New cards
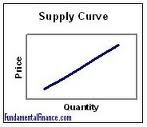
supply
The amount of goods and services that producers make available for sale at a given price
22
New cards
law of supply
price = ⬆️ = quantity supplied rises
price = ⬇️ = quantity supplied falls
demand = equal to supply = MARKET EQUILIBRIUM
price = ⬇️ = quantity supplied falls
demand = equal to supply = MARKET EQUILIBRIUM
23
New cards
why is the law of supply like that?
- higher price = induces producers to supply a higher quantity to the market.
- businesses seek to increase revenue, when they expect to receive a higher price for something, they will produce more of it.
- if prices fall, suppliers are disincentivized from producing as much.
- businesses seek to increase revenue, when they expect to receive a higher price for something, they will produce more of it.
- if prices fall, suppliers are disincentivized from producing as much.
24
New cards
seller
Producers of goods and services which make supply available
25
New cards
trough
stage of the economy's business cycle
= marks the end of a period of declining business activity and the transition to expansion
= marks the end of a period of declining business activity and the transition to expansion
26
New cards
leakages
withdrawals from an economy's circular flow
DECREASE:
- level of income
- GDP
DECREASE:
- level of income
- GDP
27
New cards
leakages examples
- savings
- taxes
- imports
- taxes
- imports
28
New cards
leakages and injections
exceptions in the circular flow of income
29
New cards
injections
spending which is not generated by households
INCREASE:
- level of income
- GDP
INCREASE:
- level of income
- GDP
30
New cards
injections examples
- investment
- government spending
- exports
- government spending
- exports
31
New cards
are exports an injection or leakage
INJECTION
32
New cards
are imports an injection or leakage
LEAKAGE
33
New cards
what does the household sector do?
- holds economic resources such as land, labour, capital and enterprise
- sells their resources to firms in exchange for an income
- sells their resources to firms in exchange for an income
34
New cards
who makes up the household sector?
individuals or groups of individuals as consumers
&
entrepreneurs producing market goods and non-financial and financial services
&
entrepreneurs producing market goods and non-financial and financial services
35
New cards
production firms sector
use resources of households to produce goods and services
36
New cards
consumption firms (and household) sector
households will then use their income to buy various goods and services (known as consumption)
37
New cards
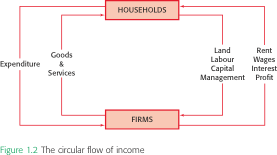
(two-factor) circular flow model
money flows
households → businesses
= consumer expenditures in exchange for goods and services produced by the businesses
flows back
businesses → households
= for labor that individuals provide
households → businesses
= consumer expenditures in exchange for goods and services produced by the businesses
flows back
businesses → households
= for labor that individuals provide
38
New cards
household and firms sector on circular flow
household → firms
- economic resources
- consumption (C)
firms → households
- goods and services
- income (Y) = wages, rent, interest, profit
- economic resources
- consumption (C)
firms → households
- goods and services
- income (Y) = wages, rent, interest, profit
39
New cards
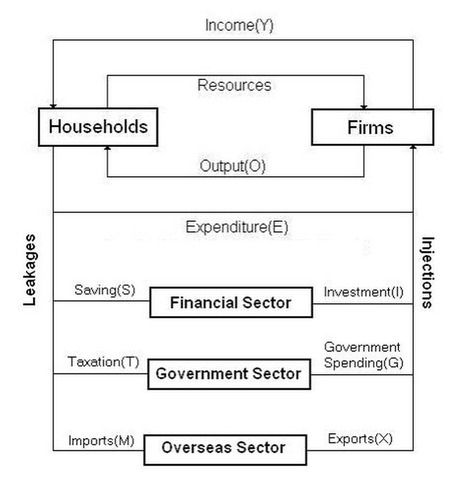
financial and gov sector's role on 3 sector economic model
FINANCIAL
- gets savings (S) from households
- invests (I) in firms
GOV
- gets tax (T) from households
- gov expenditure (G) to firms
- gets savings (S) from households
- invests (I) in firms
GOV
- gets tax (T) from households
- gov expenditure (G) to firms
40
New cards
financial sector
financial institutions (e.g banks) that act as intermediaries between the savers and borrowers in an economy

41
New cards
what does the financial sector do in the economy?
they receive the savings of individuals and businesses and then lend this money to others who need to borrow money
42
New cards
gov sector
refers to the local, state, and federal governments
43
New cards
gov's role in circular flow of income
Taxation (leakage) = the government collects taxes from individuals and businesses when they earn an income or profit
Government expenditure (injection) = when governments spend money raised through taxation on things such as infrastructure, welfare payments, education, and healthcare
Government expenditure (injection) = when governments spend money raised through taxation on things such as infrastructure, welfare payments, education, and healthcare
44
New cards
income symbol
Y
45
New cards
consumption symbol
C
46
New cards
savings symbol
S
47
New cards
taxation symbol
T
48
New cards
investment symbol
I
49
New cards
Gov expenditure symbol
G
50
New cards
imports symbol
M
51
New cards
exports symbol
X
52
New cards
S + T + M = I + G + X
equilibrium
GDP remains the same, stable, unchanged
GDP remains the same, stable, unchanged
53
New cards
S + T + M > I + G + X
Disequilibrium
54
New cards
Disequilibrium
when quantity supplied is not equal to the quantity demanded
either be a surplus or shortage
either be a surplus or shortage
55
New cards
business cycle
fluctuations in the level of economic activity in the economy
56
New cards
what happens during contractions? (examples with goods purchased)
less goods are purchased = business produces less goods = business needs less labour = increased unemployment.
57
New cards
production during expansion
- production increases
- producing more services
- producing more services
58
New cards
unemployment during expansion
- decreases
- fewer people are out of work as businesses need more workers
- fewer people are out of work as businesses need more workers
59
New cards
wages during expansion
- wages increase
- business is doing well
- they attract works by offering higher wages
- business is doing well
- they attract works by offering higher wages
60
New cards
consumer prices during expansion
households spend more as their wages are higher
61
New cards
prices during expansion
prices decrease as households spend more
62
New cards
production during contraction
production decreases = businesses produce less goods and services
63
New cards
unemployment during contraction
more people are out of work = businesses need less workers
64
New cards
wages during contraction
business are not doing as well = employ less staff = lower wages
65
New cards
consumer prices during contraction
households spend less = wages are lower & have less disposable income to spend
66
New cards
prices during contraction
prices increase as households spend less
67
New cards
What happens to price if demand is greater than supply?
causes a shortage and prices often get increased by the businesses
68
New cards
what happens on a graph if there is an increase in demand shifts?
the demand curve to the right
69
New cards
what does it mean if there is an increase in demand shifts?
results in an increase in price and quantity
70
New cards
what happens on a graph if there is an decrease in demand shifts?
shifts the demand curve to the left
71
New cards
what does it mean if there is an decrease in demand shifts?
results in a decrease in price and quantity
72
New cards
demand curve to the right
increasing demand
73
New cards
demand curve to the left
decreasing demand
74
New cards
why is there increase/decrease in demand?
- rise in customer income
- changes in consumer tastes and preferences
- increase in the size of the population
- substitute becomes more expensive
- complementary good becomes cheaper
- prices are expected to rise in the future
- changes in consumer tastes and preferences
- increase in the size of the population
- substitute becomes more expensive
- complementary good becomes cheaper
- prices are expected to rise in the future
75
New cards
five-sector circular flow of income
Circular flow model of income is a simple five sector model of income in the economy, where the main flow is between households and business, with a series of leakages from the circular flow (savings, taxes and imports) and a series of injections into the circular flow (investment, government spending and exports). GDP in an economy, referred to as national income, is equal to C + I + G + (X-M)
76
New cards
what will happen if injections are greater than leakages in an economy
disequilibrium
- GDP will increase
- period of expansion due to less money leaving the circular flow via leakages
means that:
- production
- employment
- wages will increase
+ add to more consumption
- may cause increase interest rates and initiate inflation
- GDP will increase
- period of expansion due to less money leaving the circular flow via leakages
means that:
- production
- employment
- wages will increase
+ add to more consumption
- may cause increase interest rates and initiate inflation
77
New cards
Define Equilibrium in the context of the circular flow model of income
Equilibrium, in the context of the circular flow model of income refers to the state where leakages (savings, taxes and imports) equal injections (investment, government spending and exports) and the level of output in the economy (GDP) is stable and will not change.
78
New cards
common phases of the business cycle
TROUGH - lowest point of contraction
PEAK - highest point of expansion
CONTRACTION - reduction in GDP
EXPANSION - growth of GDP
RECESSION - two quarters of contraction
PEAK - highest point of expansion
CONTRACTION - reduction in GDP
EXPANSION - growth of GDP
RECESSION - two quarters of contraction
79
New cards
impact on price when supply is greater than demand
In this case, there is excess supply. Producers supply more of the good than the consumers demand, leading to excess supply at that price. Seeing this, producers drop their prices and supply less of the good (contract supply).
80
New cards
Outline the impact on price when demand is greater than supply
When demand is greater than supply prices increase as sellers know they can charge more as the product is sought after.
81
New cards
positives of moving out
- learn how to be independent
- manage finances
- privacy
- meeting new people
- no rules
- manage finances
- privacy
- meeting new people
- no rules
82
New cards
negatives of moving out
- possible financial difficulties
- chores/responsibilities
- dealing with roommates
- maintenance
- chores/responsibilities
- dealing with roommates
- maintenance
83
New cards
reasons for moving out
- family disputes
- employment
- choosing to live with partner
- employment
- choosing to live with partner
84
New cards
questions with living independently
- can you afford to leave home?
- How much will it cost and where will the money come from?
- can i cope on my own and not rely on anyone else?
- lonely?
- Have the skills to be able to move out of home? E.g. cooking, cleaning and managing a household budget
- How much will it cost and where will the money come from?
- can i cope on my own and not rely on anyone else?
- lonely?
- Have the skills to be able to move out of home? E.g. cooking, cleaning and managing a household budget
85
New cards
what age can I leave home?
- under guardianship until 18
- although don't have to live at home until that age
can leave home at 16 years of age
- if safe supportive place is avaliable
- although don't have to live at home until that age
can leave home at 16 years of age
- if safe supportive place is avaliable
86
New cards
reasons young people are choosing to live at home for longer?
1. expenses - house prices and finances
2. people staying in education longer = don't have full time job = not financially stable = dependent on others
3. cultural backgrounds
2. people staying in education longer = don't have full time job = not financially stable = dependent on others
3. cultural backgrounds
87
New cards
key documentation
1. medicare card
2. birth certificate
3. photo ID
2. birth certificate
3. photo ID
88
New cards
medicare card
- access to free medical treatment
- claim a rebate on private treatment
- apply for own at 15 years (Department of Human services)
- claim a rebate on private treatment
- apply for own at 15 years (Department of Human services)
89
New cards
birth certificate
- official registration of your birth by the NSW registry.
- key form of identity when applying for other documentation eg passport
- key form of identity when applying for other documentation eg passport
90
New cards
photo ID
- people over 16 can apply from Service NSW
- alternative to a driver's licence.
- alternative to a driver's licence.
91
New cards
gov organisations that support
- Department of Social Services
- Department of Communities and Justice
- Centrelink
- Department of Communities and Justice
- Centrelink
92
New cards
religious organisations that support
- Salvation Army
- Anglicare
- St Vincent De Paul
- JewishCare NSW
- Muslim Care NSW
- Anglicare
- St Vincent De Paul
- JewishCare NSW
- Muslim Care NSW
93
New cards
community organisations that support
- Youth refuge
- Community centre
- Lifeline
- Community housing
- Drop-in centres
- Kids Helpline
- Community centre
- Lifeline
- Community housing
- Drop-in centres
- Kids Helpline
94
New cards
condition report
details the exact condition of the property when you move in
95
New cards
landlord
person who owns the premises being rented
96
New cards
tenant
person or persons who rent the property
97
New cards
residential tenancy agreement
an agreement between the landlord and the tenant that outlines all the terms that both parties must follow
98
New cards
reservation fee
usually one week's rent that will reserve the premises for you while your application for tenancy is being considered
99
New cards
lease
contract between two parties, usually regarding the renting of an asset such as a house, flat or motor vehicle.
100
New cards
renting a property process
1. find property
2. obtain Residential Tenancy Agreement
3. Complete condition report
4. pay a reservation fee
5. sign lease
6. pay rental bond
7. pay rent in advance
8. take possession and move in
2. obtain Residential Tenancy Agreement
3. Complete condition report
4. pay a reservation fee
5. sign lease
6. pay rental bond
7. pay rent in advance
8. take possession and move in