Cast Gold Restorations (Guest Lecture)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
every dental material is the best material for certain indications, but?
no dental material is best for all indications
what are the advantages of gold restorations over amalgam?
1) no discoloration of tooth - as amalgam ages, it releases Ag ions into tooth, darkening it
2) longevity
3) no cracking of tooth - divergent prep, amalgam is convergent
4) support of marginal edges
why do you remove all of the old restorations, even if it looks okay?
there may be hidden decay, cracks (oblique cracks need to be chased and removed); you need to evaluate remaining tooth strength
when an instrument is dull, why do we see light reflecting off of it
it is no longer a thin sharp line, but a dull flat surface that is able to reflect light
what is the basic assumption in making a gold restoration by the indirect method
the die is the same size as the tooth! —> it is usually not as all gypsum materials tend to expand
what kind of stone should we use for casting if we are concerned w expansion
a low expansion stone wow
why do we not wash or soak the dies in water?
die stone is soluble in water!
what is the relationship between the units of measurements of mL, cc, and grams
1 mL = 1 g = 1 cc
primarock tends to have more expansion so we do not want to use it for inlays, but it is suitable for?
making cast posts
why else is primarock (Type IV die stone) suitable?
its yellow color allows it to photograph nicely
what are the advantages of direct gold restorations
1) no lab work
2) perfect fit (nothing between gold and tooth)
what is gold's wear compared to natural teeth
highly durable, long-lasting, and have a wear rate similar to natural enamel, meaning they won't excessively wear down opposing teeth
what are disadvantages of direct gold restorations
gold is softer; so you may get more pitting and anatomical occlusal changes, but the seal to the tooth is still preserved
what is the first step of cavity preparation
establishing outline form: depth, taper, and extension
what is the purpose of pins in restorations
to increase retention
what do we use for isolation (what is best)
rubber dam! has better vision and control; protects pt tissues
gold has cohesion, meaning?
it binds to itself!
when trying to visualize or get rid of cracks in a tooth, which burs are more suitable to do so
a straight bur will disguise the crack but a round bur will allow you to see the crack in the tooth
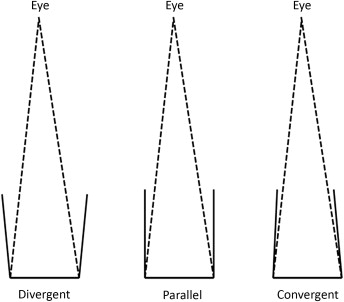
what kind of preparation do we want for a direct gold restorations
a divergent preparation! gold relies more on condensation and marginal adaptation, so it is okay to not have heavy undercuts in order to retain the restoration