Cosmology
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
What is the Big Bang theory?
The Big Bang theory
Around 14 billion years ago, the Universe began from a very small region that was extremely hot and dense
Then there was a giant explosion, which is known as the Big Bang
This caused the universe to expand from a single point, cooling as it does so, to form the universe today
Each point expands away from the others
This is seen from galaxies moving away from each other, and the further away they are the faster they move
As a result of the initial explosion, the Universe continues to expand

All galaxies are moving away from each other, indicating that the universe is expanding
An analogy of this is points drawn on a balloon where the balloon represents space and the points as galaxies
When the balloon is deflated, all the points are close together and an equal distance apart
As the balloon expands, all the points become further apart by the same amount
This is because the space itself has expanded between the galaxies
Therefore, the density of galaxies falls as the Universe expands

A balloon inflating is similar to the stretching of the space between galaxies
What is the evidence that supports the Big Bang theory?
Evidence for the Big Bang
Since there is more evidence supporting the Big Bang theory than the Steady State theory, it is the currently accepted model for the origin of the Universe
The two main pieces of evidence supporting the Big Bang are
Galactic red-shift
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation
Evidence from galactic red-shift
By observing the light spectrums from supernovae in other galaxies there is evidence to suggest that distant galaxies are receding (moving further apart) even faster than nearby galaxies
These observations were first made in 1998
The light spectrums show that light from distant galaxies is redshifted, which is evidence that the universe is expanding
As a result, astronomers have concluded that:
All galaxies are moving away from the Earth
Galaxies are moving away from each other
This is what is expected after an explosion
Matter is first densely packed and as it explodes it, it moves out in all directions getting further and further from the source of the explosion
Some matter will be lighter and travel at a greater speed, further from the source of the explosion
Some matter will be heavier and travel at a slower speed, closer to the source of the explosion
If someone were to travel back in time and compare the separation distance of the galaxies:
It would be seen that galaxies would become closer and closer together until the entire universe was a single point
If the galaxies were originally all grouped together at a single point and were then exploded a similar effect would be observed
The galaxies that are the furthest are moving the fastest - their distance is proportional to their speed
The galaxies that are closer are moving slower

Tracing the expansion of the universe back to the beginning of time leads to the idea the universe began with a “big bang”
Evidence from CMB radiation
The discovery of the CMB (Cosmic Microwave Background) led to the Big Bang theory becoming the currently accepted model
The CMB is a type of electromagnetic radiation which is a remnant from the early stages of the Universe
It has a wavelength of around 1 mm making it a microwave, hence the name Cosmic Microwave Background
In 1964, Astronomers discovered radiation in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum coming from all directions and at a generally uniform temperature of 2.73 K
They were unable to do this any earlier since microwaves are absorbed by the atmosphere
Around this time, space flight was developed which enabled astronomers to send telescopes into orbit above the atmosphere
According to the Big Bang theory, the early Universe was an extremely hot and dense environment
As a result of this, it must have emitted thermal radiation
The radiation is in the microwave region
This is because over the past 14 billion years or so, the radiation initially from the Big Bang has become redshifted as the Universe has expanded
Initially, this would have been high energy radiation, towards the gamma end of the spectrum
As the Universe expanded, the wavelength of the radiation increased
Over time, it has increased so much that it is now in the microwave region of the spectrum

The CMB is a result of high energy radiation being redshifted over billions of years
The CMB radiation is very uniform and has the exact profile expected to be emitted from a hot body that has cooled down over a very long time
This phenomenon is something that other theories (such as the Steady State Theory) cannot explain
The CMB is represented by the following map:

The CMB map with areas of higher and lower temperature. Places with higher temperature have a higher concentration of galaxies, Suns and planets
This is the closest image to a map of the Universe
The different colours represent different temperatures
The red / orange / brown regions represent warmer temperature indicating a higher density of galaxies
The blue regions represents cooler temperature indicating a lower density of galaxies
The temperature of the CMB is mostly uniform, however, there are minuscule temperature fluctuations (on the order of 0.00001 K)
This implies that all objects in the Universe are more or less uniformly spread out
What happens when a wave source is moving relative to an observer?
This is called the Doppler Effect. If something that emits a wave moves whilst it is doing so (imagine a noisy motorbike coming towards you then going further away, emitting sound waves the whole time) then the wavelength of the sound will become shorter as it is moving towards you, increasing the frequency, and stretched as it is moving away, decreasing the frequency.
You will hear this as a change in pitch, getting higher as it approaches and lower as it moves away. The same thing happens for a moving object that is emitting light waves –e.g. a galaxy. |
How is red-shift in light received from galaxies at different distances away from the Earth?
Galactic redshift
The Doppler effect affects all types of waves, including light
Light emitted from stars and galaxies will be at a certain wavelength in the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum
If an object moves away from an observer the wavelength of light increases
This is known as redshift as the light moves towards the red end of the spectrum
The redshift definition is therefore:
The phenomenon of the wavelength of light appearing to increase when the source moves away from an observer
If an object moves towards an observer the wavelength of light decreases
This is known as blueshift as the light moves towards the blue end of the spectrum

Light from a star that is moving towards an observer will show blueshift and light from a star moving away from an observer will show redshift
An increase in wavelength (redshift) is a decrease in frequency and vice versa
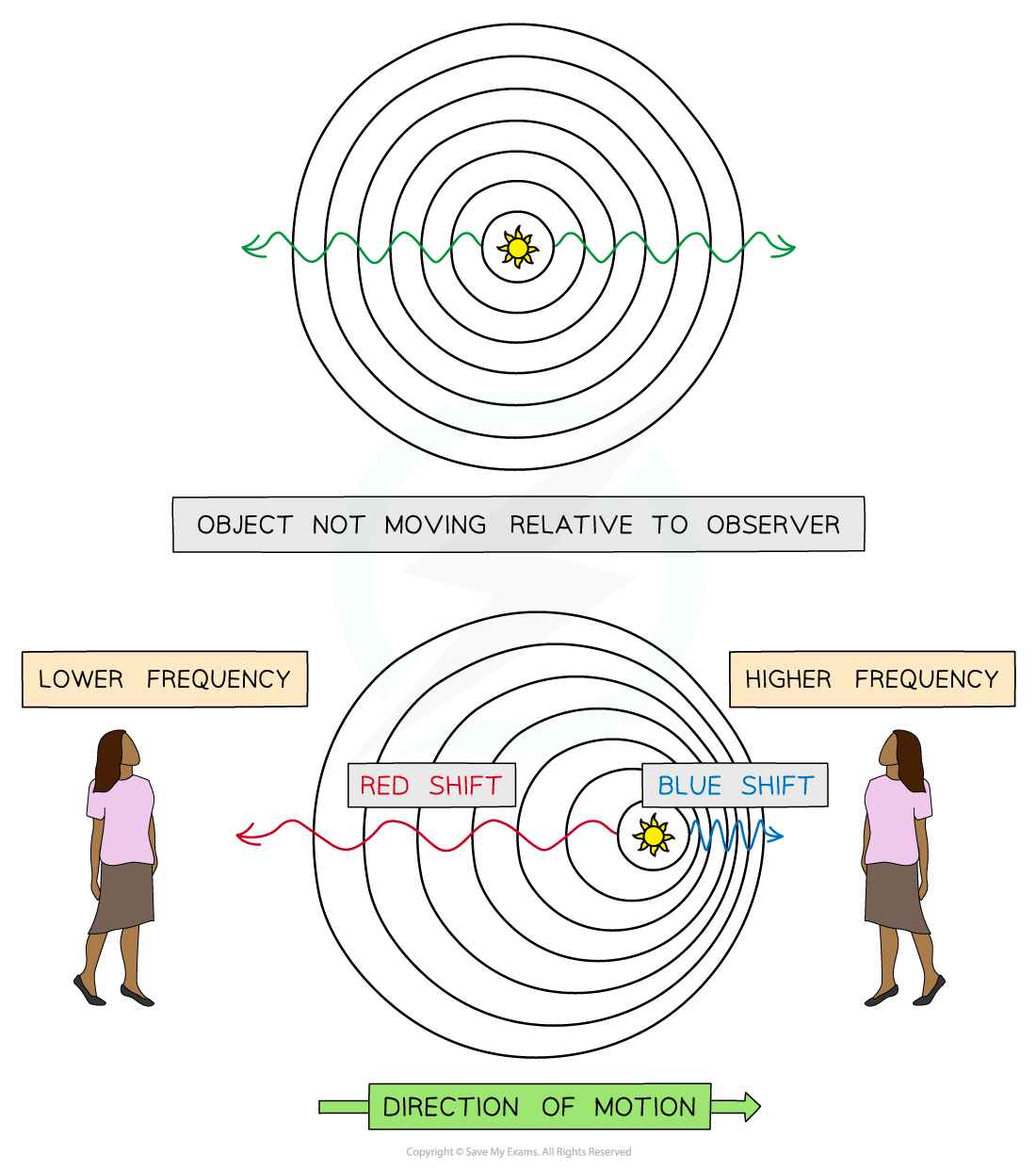
The observer in front observes a blue shift, the observer behind observes a redshift
The expanding Universe
Galactic redshift provides evidence for the Big Bang Theory and the expansion of the universe
The diagram below shows the light coming to us from a close object, such as the Sun, and the light coming to the Earth from a distant galaxy
Redshift diagram for a light spectrum
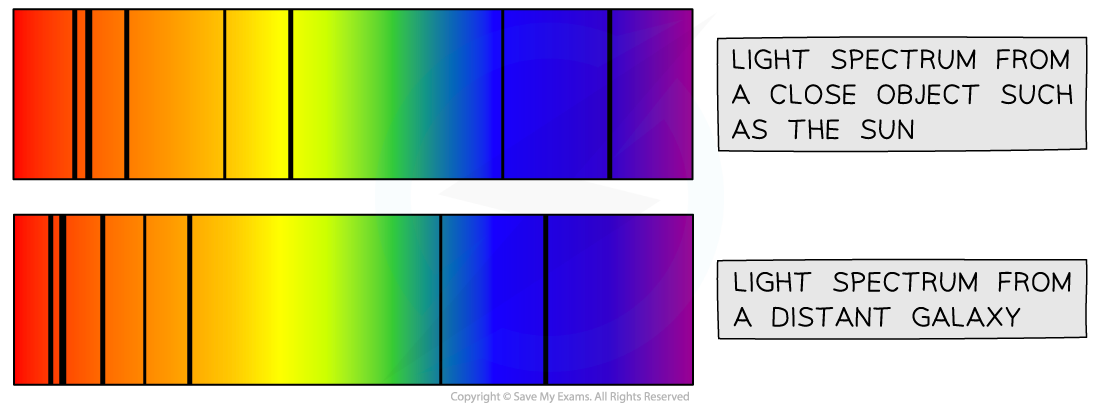
Comparing the light spectrum produced from the Sun and a distant galaxy. The spectral lines from the distant galaxy are redshifted.
Red shift provides evidence that the Universe is expanding because:
Red shift is observed when the spectral lines from the distant galaxy move closer to the red end of the spectrum
This is because light waves are stretched by the expansion of the universe so the wavelength increases (or frequency decreases)
This indicates that the galaxies are moving away from us
Light spectrums produced from distant galaxies are red shifted more than nearby galaxies
This shows that the greater the distance to the galaxy, the greater the redshift
This means that the further away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from the Earth
These observations imply that the universe is expanding and therefore support the Big Bang Theory

Graph showing the greater the distance to a galaxy, the greater the redshift