CMPP: Acute Kidney Injury
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
an abrupt decline in GFR
an increase in serum creatinine
* initially may have normal lab values and only a decreased urine output
in acute kidney injury, labs reveal...
decreased urine output
earliest finding in an acute kidney injury
hypovolemia
a normally functioning kidney interprets decreased GFR as...
GFR
the best overall laboratory indicator of kidney function is the...
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
estimates how much blood is filtered through the glomeruli each minute
creatinine clearance (inversely proportional to GFR)
what lab value is used to estimate the GFR?
completely filtered and neither reabsorbed or secreted
--> since it is testing filtration rate
the ideal substance to measure the GFR should be...
age, gender, and muscle mass
the "normal" serum creatinine level is affected by...
elderly, female, and/or have low muscle mass
what are some factors that can DECREASE GFR
50% decrease in renal function
a doubling of creatinine from baseline results in...
identifies acute kidney injury
stages of CKD
Contraindicates certain meds/IV contrast administration
requires adjustment of med doses/frequency
sensitivity/specificity issues based on age, gender, and muscle mass
significance of low GFR
inversely
BUN is typically _____ related to the GFR
increased; increases (>20:1)
in dehydration, there is significant _________ reabsorption, which does what to the BUN:creatinine ratio?
GI bleeding and high protein diets
BUN may be elevated due to...
liver disease and low protein diets
BUN may be decreased due to...
Azotemia
accumulation of nitrogenous waste products in the blood
Uremia
symptoms of multi-organ damage due to renal disease
drop in renal blood flow
pre-renal AKI is caused by...
direct kidney injury
renal AKI is caused by...
obstruction of the urine flow
post-renal AKI is caused by...
pre-renal
what is the most common form of kidney injury?
volume depletion (dehydration, hemorrhage)
decreased CO (CHF, MI, valvular heart disease)
systemic vasodilation (sepsis, anaphylaxis)
Afferent arteriolar vasoconstriction (NSAIDs, IV contrast)
Renal artery stenosis
reasons for decreased renal blood flow
ACEi/ARBs
--> preferentially vasodilate efferent arterioles
Aminoglycosides
Amphotericin B
IV radiocontrast agents
Prerenal AKI may be precipitated borderline volume-depleted states in what kind of situations?
volume depletion
a normal kidney interprets decreased GFR as...
Reabsorbing H2O by ADH
Reabsorbing Na/H2O via RAAS
how does the kidney compensate for decreased GFR?
high urine specific gravity
low urinary Na concentration
low fractional excretion of NA
Serum BUN:creatrinine ratio >20:1
decreased GFR results in what manifestations?
Fractional excretion of sodium
measures the fraction of the total amount of filtered Na (total Na entering Bowman's space) that is ultimately excreted in the urine
Excreted Na = filtered Na+secreted Na-reabsorbed Na
formula for FeNa
low % of urinary Na excretion (secondary to increased Na absorption)
low FeNa indicates...
volume depletion -- since kidney is reabsorbing Na (anything it can) to try and replete volume
--> kidneys are doing what they are supposed to be doing
what condition is associated with low FeNa if renal function is intact and why?
low urine specific gravity (urine is not appropriately concentrated to try and conserve fluid)
urine Na high (kidney is not appropriately reabsorbing Na+ to try and gain fluid)
FeNa high (see above)
*kidney is detecting low GFR but the kidneys are funky
what are some manifestations of renal AKI?
Obstructive (thrombotic, embolic, secondary to dissection
Microangiopathy (TTP, HUS, DIC, preeclampsia)
Malignant HTN
Transplant rejection
vascular causes of renal AKI
Acute immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis
--> post-strep infxns (pharyngitis/impetigo)
--> SLE
Antibody mediated (Goodpasture's syndrome, Wegener's granulomatosis)
glomerular causes of renal AKI
Drug induced: Abx (beta-lactams, sulfa drugs, fluoroquinolones), NSAIDs, diuretics, PPIs
Pyelonephritis
SLE, leukemia, lymphoma
interstitial causes of renal AKI
acute tubular necrosis
what is the #1 cause of renal AKI?
drugs, abnormal pigments, or crystal formation
Nephrotoxin-induced ATN involves direct damage to the renal tubules secondary to...
secondary to ischemia or exposure to a nephrotoxin
-->pre-renal that goes unrecognized can turn into this
what causes acute tubular necrosis?
Drug induced (aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, chemotherapy, IB contrast, lithium)
Heme pigment -- rhabdo/intravascular hemoylsis
Crystals --
Ethylene glycol toxicity
what are some causes of ATN?
aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, chemotherapy, IB contrast, lithium
what drugs are indicated in causing ATN?
"muddy brown casts" visual on microscopic exam of the urine
what is commonly seen on UA for one with ATM?
Isothenuria
injured tubules are unable to maximally concentrate or dilute the urine; hallmark of ATN
respond to stressful situations
Isothenuria results in an inability of the kidneys to...
Urinary casts
cluster of urinary particles that forma mold in various areas of the renal tubular lumens; dehydration, stasis, and acidic urine favor the formation of these.
glomerulonephritis
red cell casts are classically seen in...
acute pelonephritis
white cell casts are classically seen in...
tubular image secondary to epithelial sloughing
epithelial cell casts indicate...
renal disease (nonspecific)
coarse/fine granular or waxy casts indicate...
healthy individuals -- acute dehydration
hyaline casts can be seen in...
Hepatorenal syndrome
occurs when AKI develops in patients with advanced liver disease
oliguria, increased creatinine & AKI
proteinuria
features of hepatorenal syndrome
the glomeruli
what needs to be damaged to cause proteinuria?
urethral caliculi
tumors
inadvertent legation during pelvic surgery
post-renal AKI can be caused by ureteral obstruction secondary to...
BPH #1 cause
Intraluminal blood clots
Prostate or bladder cancer
Drugs (antihistamines/decongestants, tricyclic antidepressants)
Neurogenic bladder
Cauda equina syndrome
Urethral structure, tumor
post-renal AKI can be caused by bladder obstruction secondary to...
increased, increased, decreased
conditions that lead to post-renal AKI can lead to ______ resistance, _______ intratubular pressure, and ultimately __________ GFR.
antihistamines/decongestants, tricyclic antidepressants
what medications are indicated in causing post-renal AKI?
foley catheter
-->suprapubic catheter if unable to insert a foley
what is the therapy of choice for post-renal AKI
ureteral stent -- hollow coiled tube inserted cystoscopically
what is the therapy of choice for a ureteral obstruction?
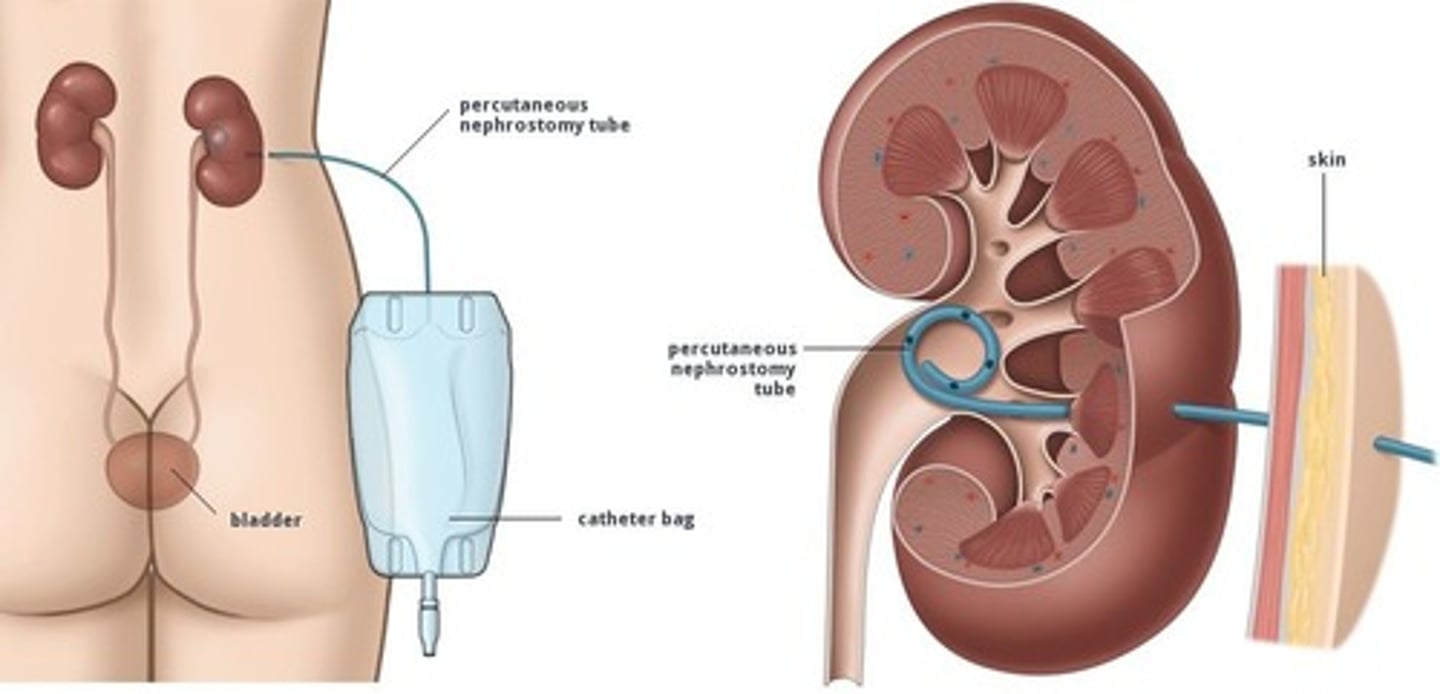
nephrostomy tube -- inserted directly in the kidney
how would you treat a pt with a ureteral obstruction that cannot get a ureteral stent placed?
reduced urine output
what finding is present in all cases of AKI?
low oral intake, vomiting, diarrhea, hemorrhage
what are some important historical factors for prerenal AKI?
only with generalized weakness, confusion, or anorexia
how may elderly people present with pre-renal AKI?
recent pharyngitis/skin infection (impetigo) -- glomerular
Nephrotoxic drug ingestion, recent exposure to IV contrast, recent trauma or unaccustomed exertion (rhabdo) -- ATN
what are some important historical factors for renal AKI?
lower abdominal pain/distension
inability to urinate
severe low back pain
associated neurologic symptoms
hx of BPH
antihistamines/decongestants, TCA use
what are some important historical factors for post-renal AKI?
CMP, CBC, UA with microscopy, bladder scan
how to begin the workup for AKI
WBC to evaluate for pyelonephritis
Blood smear to evaluate for hemolysis/schistocytes (TTP, HUS, vascular causes)
why do you get a CBC for AKI?
urine electrolytes (FeNa)
why do you get a UA with microscopy for AKI?
if suspected bladder neck/urethral obstruction
when would you get a bladder scan for AKI?
increased BUN/creatinine (creatinine more specific)
what lab findings are characteristic of AKI?
urea reabsorption increases (since kidneys are doing their job correctly) and BUN:creatinine > 20:1
what lab findings are characteristic of pre-renal AKI?
BUN:creatinine <20:1 (diseased kidneys cannot reabsorb urea)
what lab findings are characteristic of renal AKI?
glomerulonephritis, rhabdomyolysis
reddish-brown urine can indicate...
ethylene glycol poisoning (tubular cause)
Calcium oxalate crystals in the urine are characteristic of...
pros:
--> assesses size and quality of renal tissue
--> evaluates for dilatation of calyces and renal pelvis (hydronephrosis)
--> may detect mass/kidney stone
--> doppler evaluates renal blood flow
--> no ionizing radiation or contrast risks
--> can be done at bedside
what are some pros/cons of using U/S as a radiologic study for AKI?
pros:
--> provides more anatomic details
--> better at identifying post-renal causes
cons
--> cannot be done at bedside
--> significant IV contrast/radiation risks
what are some pros/cons of using CT as a radiologic study for AKI?
identify and treat underlying cause
always check patient's baseline creatinine
how to treat AKI (gen)
restore adequate perfusion
therapeutic options for pre-renal AKI
identify site od damage and treat the underlying disease
manage resultant fluid and electrolyte abnormalities
therapeutic options for renal AKI
relieve or bypass the urinary tract obstruction
therapeutic options for post-renal AKI
volume overload -- CHF/HTN
AKI can lead to retention of Na+/H2O, this can lead to...
serum Na+ (water follows the salt)
what lab value is usually normal in AKI?
hyperkalemia
AKI can lead to retention of K+, this can lead to...
metabolic acidosis (U in MUDPILES)
AKI can lead to retention of acids, this can lead to...
Azotemia/Uremia
AKI can lead to retention of nitrogenous wastes, this can lead to...
N/V, anorexia, altered mental status, seizures
Azotemia/Uremia can present as...
hyperphosphatemia and subsequent hypocalcemia
AKI can lead to retention of phosphate, this can lead to...
immunosuppression/infections
what is the leading cause of death in AKI?
anemia (low EPO)
platelet dysfunction (absolute number is normal)
what are some hematologic complications of AKI?
early restoration of renal blood flow
what is the most important prognostic indicator for AKI?