[PT11] Organ Systems
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/163
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:04 AM on 11/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
1
New cards
skin
the first line of defense for the immune system. It waterproofs the body and is the major receptor for the sense of touch
2
New cards
cutane/o, dermat/o, derm/o
related combining forms of skin
3
New cards
sebaceous glands
secretes sebum (oil) to lubricate the skin and discourage the growth of bacteria on the skin
4
New cards
seb/o
related combining forms of SEBACEOUS GLANDS
5
New cards
sweat glands
secret sweat to regulate body temperature and water content, and these glands excrete some metabolic waste
6
New cards
hid/ro
related combining forms of SWEAT GLANDS
7
New cards
hair
aids in controlling the loss of body heat
8
New cards
pil/i. pil/o
related combining forms of hair
9
New cards
nails
protect the dorsal surface of the last bone of each finger and toe
10
New cards
onych/o, ungu/o
related combining forms of nails
11
New cards
skin
largest organ in the body in surface area and weight
12
New cards
2 square meters
coverage of the skin
13
New cards
4.5-5kg (16% of total body weight)
weight of the skin
14
New cards
0.5mm to 4mm
thickness of the skin
15
New cards
hirsut/o
word parts of hairy/rough
16
New cards
kerat/o
word parts of horny, hard
17
New cards
lip/o
word parts of fat, lipid
18
New cards
melan/o
word parts of black, dark
19
New cards
myc/o
word parts of fungus
20
New cards
onych/o
word parts of fingernail or toenail
21
New cards
py/o
pus
22
New cards
rhytid/o
wrinkle
23
New cards
seb/o
sebum
24
New cards
urtic/o
rash or hives
25
New cards
xer/o
dry
26
New cards
epidermis
the outermost layer of the skin made up of several specialized epithelial tissues
dependent on lower layers for nourishment
dependent on lower layers for nourishment
27
New cards
keratin
a fibrous, water-repellent protein
28
New cards
soft keratin
a primary component of the epidermis
29
New cards
hard keratin
found in the hair and nails
30
New cards
melanocytes
special cells that are also found in the basal cell layer, they produce and contain a dark brown pigment known as melanin
31
New cards
melanin
is the pigment that determines the color of the skin, which depends upon the type and amount of this pigment that is present
32
New cards
melanin
produces spots of color such as freckles and age spots; has the important function of protecting the skin from harmful ultraviolet rays
33
New cards
dermis
the thick layer of living tissue directly below the epidermis
34
New cards
corium
what is the dermis also known as?
35
New cards
connective tissue
blood
lymph vessels
nerve fibers
hair follicles
sebaceous glands
sweat glands
sensory nerve endings
blood
lymph vessels
nerve fibers
hair follicles
sebaceous glands
sweat glands
sensory nerve endings
what does the dermis contain?
36
New cards
decubitus ulcer (bedsore)
injuries to skin and underlying tissue resulting from prolonged pressure on the skin
areas with little fat and muscle over bony prominences are common sites
areas with little fat and muscle over bony prominences are common sites
37
New cards
subcutaneous layer
layer located below the dermis that contains loose connective tissues, adipose tissues, and major blood vessels that supply the skin
38
New cards
melanin
pigments responsible for pale yellow to tan and black colors
39
New cards
carotene
pigment with melanin that makes skin appear translucent
40
New cards
hemoglobin
pigment that's responsible for pink to red color
41
New cards
- due to the amount of melanin produced by melanocytes; number of melanocytes remains the same in all people
- distribution and size of pigment granules
- distribution and size of pigment granules
why are there differences in skin color?
42
New cards
freckles
accumulation of melanin in patches
43
New cards
liver (age) spots
flat skin patches from light brown to black
44
New cards
albinism
inherited inability of a person to produce melanin in hair, eyes, and skin
45
New cards
- environment (sunlight)
- amount of oxygen
-physiological factors
- biochemical factors (newborn-jaundice)
- amount of oxygen
-physiological factors
- biochemical factors (newborn-jaundice)
factors that influence skin color
46
New cards
- poor blood oxygenation
- oxygen-depleted hemoglobin (deep, purplish blue)
- oxygen-depleted hemoglobin (deep, purplish blue)
what can bluish cyanotic skin and/or nail beds indicate?
47
New cards
- build up of bilirubin in the blood
- liver disease
- liver disease
what can yellow to the skin and whites of the eyes indicate?
48
New cards
- capillary engorgement with blood in the dermis due to skin injury, heat exposure, infection, inflammation, or allergic reaction
what can skin redness indicate?
49
New cards
- hair
- nails
- sweat glands
- nails
- sweat glands
accessory structures of the skin
50
New cards
- palms
- palmar surfaces of the digits
- soles
- lips
- nipples
- parts of the external genitalia
- palmar surfaces of the digits
- soles
- lips
- nipples
- parts of the external genitalia
hair is not present in these surfaces
51
New cards
arrector pili muscle
smooth muscle that connects each hair follicle to the papillary layer of the dermis
52
New cards
arrector pili muscle
contracts pulling the slanted hair to upright and dimpling the skin surface with "goosebumps"
53
New cards
arrector pili muscle
exerts pressure to sebaceous glands resulting to release of sebum
54
New cards
- thermoregulation
- protection
- cutaneous sensation
- excretion and absorption
- vitamin D synthesis
- protection
- cutaneous sensation
- excretion and absorption
- vitamin D synthesis
functions of the skin
55
New cards
- liberating sweat at skin surface
- adjusting blood flow in the dermis
- adjusting blood flow in the dermis
two methods of thermoregulation in the skin
56
New cards
keratinocytes
resist invasion from microbes
57
New cards
oily sebum
protects skin and hairs from drying and kills surface bacteria
58
New cards
melanin
protects skin from UVR damaging effects
59
New cards
- touch
- pressure
- vibration
- tickling
- thermal
- pressure
- vibration
- tickling
- thermal
tactile sensations
60
New cards
400mL
how much water evaporates from humans daily?
61
New cards
calcitriol (most active form of vitamin D)
produced when UVR activates the vitamin D precursor molecule
62
New cards
calcitriol
helps absorption of calcium in foods from the GIT into the blood
63
New cards
bones
act as the framework for the body, protect the internal organs, and store the mineral calcium
64
New cards
oss/o, oss/i, oste/o, ost/o
related combining forms of bones
65
New cards
red bone marrow
located within the spongy bone, is a hemopoietic tissue that manufactures red blood cells, hemoglobin, white blood cells, and thrombocytes
66
New cards
yellow bone barrow
functions as a fat storage area composed chiefly of fat cells and is located in the medullary cavity of long bones
67
New cards
myel/o (also means spinal cord)
related combining forms of bone marrow
68
New cards
cartilage
creates a smooth surface for motion within the joints and protects the ends of the bones
69
New cards
chondr/o
related combining forms of cartilage
70
New cards
joints
work with muscles to make a variety of motions possible
71
New cards
arthr/o
related combining forms of joints
72
New cards
ligaments
connect one bone to another
73
New cards
ligament/o
related combining forms of ligament
74
New cards
synovial membrane
forms the lining of synovial joints and secretes synovial fluid
75
New cards
synovi/o, synov/o
related combining forms of synovial membrane/fluid
76
New cards
synovial fluid
lubricant that makes smooth joint movements possible
77
New cards
bursa
cushions areas subject to friction during movement
78
New cards
burs/o
related combining forms of bursa
79
New cards
bones
where is calcium stored?
80
New cards
spongy bone
where is red bone marrow located?
81
New cards
joints work in conjunction with muscles, ligaments, and tendons, making possible the wide variety of body movements
what do joints work in conjunction with?
82
New cards
ankyl/o
word part meaning crooked, bent, stiff
83
New cards
-desis
word part meaning bind, tie together
84
New cards
kyph/o
word part meaning bent, hump
85
New cards
spondyl/o
word part meaning vertebrae, vertebral column, backbone
86
New cards
-um
word part meaning singular noun ending
87
New cards
lord/o
word part meaning curve, swayback, bent
88
New cards
-lysis
word part meaning loosening or setting free
89
New cards
myel/o
word part meaning spinal cord or bone marrow
90
New cards
hemopoietic
pertaining to the formation of blood cells can also be spelled as hematopoietic
91
New cards
cartilage
smooth, rubbery, blue-white connective tissue that acts as a shock absorber between bones
92
New cards
cartilage
more elastic than bone which also makes up the flexible parts of the skeleton (e.g. outer ear, tip of nose)
93
New cards
articular cartilage
covers the surfaces of bones where they come together to form joints
94
New cards
meniscus
curved fibrous cartilage found in some joints such as the knee and temporomandibular joint of the jaw
95
New cards
axial skeleton
consists of the 80 bones of the head and body that are organized into the skull, middle ear, hyoid bone, thyroid, rib cage, and vertebral column
96
New cards
appendicular skeleton
consists of 126 bones that are organized into upper and lower extremities
97
New cards
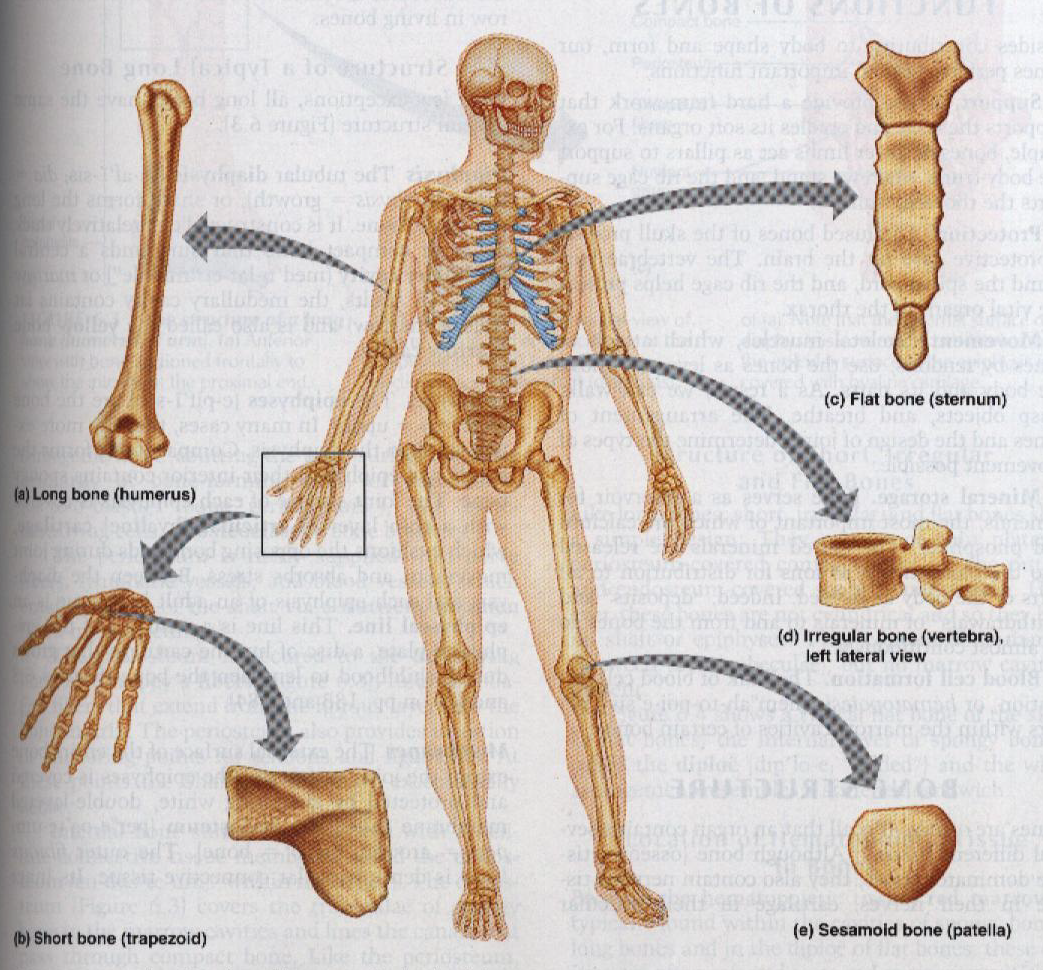
types of bones
98
New cards
epiphyses
located at each end of the bone and are covered with articular cartilage and articulate with other bones
99
New cards
diaphysis
known as the shaft of the bone
100
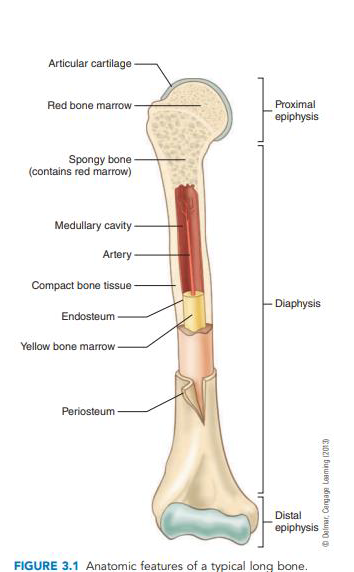
New cards
tissues of the bone