6 Microscopy of urine (CASTS)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Where are casts made
in the nephron (loop of henle, distal tubule, collecting duct)
Cast composition
MAIN: tamm-horsfall protein (uromodulin)
Urinary stasis causes geling of uromodulin
Other contents of glomerular filterate that get trapped in gel matrix
Uromodulin
Tamm-horsfall protein
glycoprotein made by RTE at a constant rate
increased rate of production during stress or exercise → hyaline casts increase with stress/exercise
acts as a lubricant
mucus and cast component
Not detected by protein reagent strip test
Cast size and shape
Reflect where cast was formed
Broad casts may result from tubular distension or, in the case of extreme urine stasis, from formation in the collecting ducts.
Cylinduria
Casts in urine
Cast formation encouraging conditions
urinary stasis/ decreased flow
acidic pH
Increased electrolytes (Na, Ca)
Cast counting
10X (lpf)
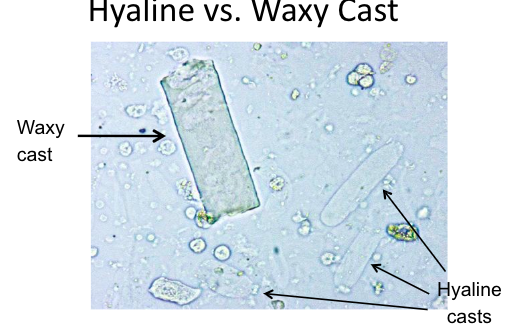
Hyaline Cast
most commonly seen
composed mostly of uromodulin
normal 0-2/lpf
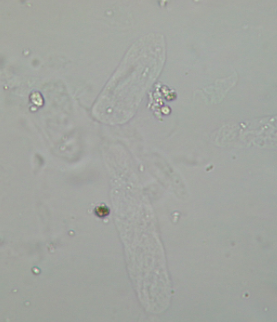
Hyaline cast: nonpathological cause
strenuous exercise (increased uromodulin production), dehydration (more stasis), heat exposure
Hyaline cast: pathological cause
acute glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, chronic renal disease, congestive heart failure
RBC cast
RBC inside cast
Accompanied by
free floating RBC
positive blood strip test
RBC cast: Pathological cause
Bleeding in nephron
RBC passing though glomerulus
glomerulonephtitsis
RBC cast: nonpathological cause
strenuous exercise (rare)
Orange, red, brown RBC cast
RBC cast with hemoglobinuria
Brown RBC cast
RBC cast with hemoglobinuria. Hemoglobin oxidized to methemoglobin
Hemoglobin RBC casts are associated with __________
Acute tubular necrosis (large amounts of hemoglobinuria toxic to kidneys)
WBC cast
mostly PMN inside cast
granular
easy to confuse with WBC clumps
accompanied by free floating WBC
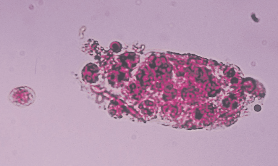
WBC cast cause
ALWAYS PATHOLOGICAL (inflammation or infection)
pyelonephritis - upper UTI
acute interstitial nephritis - kidney inflammation with not infection
glomerular nephritis
________ does not produce WBC casts
cystitis (lower UTI)
Bacterial casts
accompanied by WBCs and free floating bacteria
rare
looks like granular cast
confirm with gram stain
in pyelonephritis
Renal Tubule Epithelial casts
ALWAYS PATHOLOGICAL (BUT RARE)
tubular destruction, differentiate with WBC cast by looking at size of cell and nucleus (mononucleated)
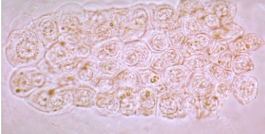
Fatty (oval fat body) cast
confirm with polarized light or fat stain
wont stain with sternheimer malbin
Cause:
nephrotic syndrome
tubular necrosis
crush injury
Mixed cellular cast
cast with multiple cell types
RBC and WBC mixed cellular cast
Common in glomerulonephtitis
WBC and RTE mixed cellular cast
Common in pyelonephritis
Granular cast
degradation of material in cast
Crystal, RBC, WBC, RTE
Begins as coarse and becomes fine during urinary stasis
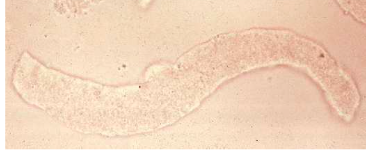
Waxy cast
further breakdown of granular cast with urinary stasis → chronic renal failure
usually seen with other casts
stains dark pink with usually squared ends
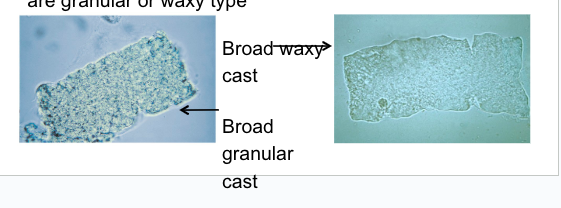
Broad casts
aka RENAL FAILURE CAST
2-6x wider than regular casts
can be any type but granular and waxy most common
Broad cast cause (2)
dilation or destruction of distal convoluted tubule
formation in collecting duct from SEVERE urinary stasis