Database systems
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
What two main problems does transactions solve?
Interruptions and Concurrency. They solve them by only allowing a group of actions to be completed together.
What are the advantages of using Transactions
Ensures data consistency
Preview data changes before making them permanent
Group logically related operations
When you execute a DDL or DCL command, it automatically executes an implicit commit before and after the command. True or false
True
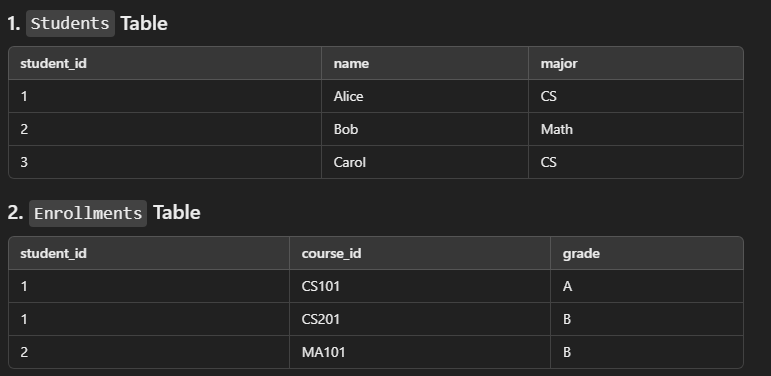
How many columns and rows would you have after a natural join?
SELECT *
FROM Students
NATURAL JOIN Enrollments;5 columns, 3 rows
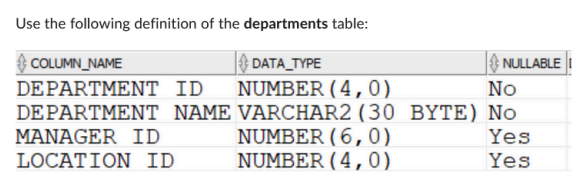
What is true about the following query:
select * from departments
minus
SELECT DEPARTMENT_ID,
DEPARTMENT_NAME,
MANAGER_ID,
LOCATION_ID,
FROM DEPARTMENTS;Which of the following:
Query returns all the departments without duplicates
Query executes successfully
Query returns an empty result set
The execution throws an error because there is a mismatch between the columns of the subqueries
Query executes successfully
Query returns an empty result set
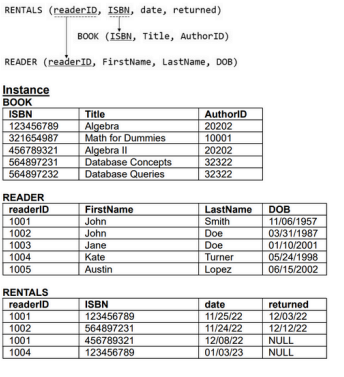
What is the output of the following query?
SELECT readerID FROM reader WHERE dob > '24-MAY-1998'
UNION
SELECT readerID FROM rentals WHERE returned IS NULL;1001, 1003, 1004, 1005
Within a query, where a subquery could appear?
In the FROM clause
In the HAVING clause
In the WHERE clause
IN the SELECT clause
All of the above
All of the above
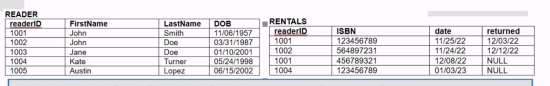
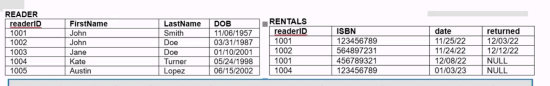
From the relational table and the following sql code find the MIN(dob).
SELECT MIN(dob), SUM(re.READERID), MAX(re.LASTNAME)
FROM RENTALS rt
RIGHT OUTER JOIN READER re
ON re.readerid = rt.readerid
WHERE rt.readerid IS NULL;MIN(dob)
A). 11/06/1957
B). 03/31/1987
C). 01/10/2001
D). 05/24/1998
E).06/15/2002
C). 01/10/2001
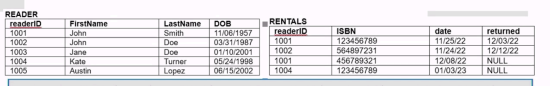
From the relational table and the following sql code find the SUM(re.READERID)
SELECT MIN(dob), SUM(re.READERID), MAX(re.LASTNAME)
FROM RENTALS rt
RIGHT OUTER JOIN READER re
ON re.readerid = rt.readerid
WHERE rt.readerid IS NULL;SUM(re.READERID)
A). 2003
B). 2008
C). 1001
D). 1004
E).2006
B). 2008
From the relational table and the following sql code find the MAX(re.LASTNAME)
SELECT MIN(dob), SUM(re.READERID), MAX(re.LASTNAME)
FROM RENTALS rt
RIGHT OUTER JOIN READER re
ON re.readerid = rt.readerid
WHERE rt.readerid IS NULL;MAX(re.LASTNAME)
A). Smith
B). Doe
C). John
D). Turner
E).Lopez
E). Lopez
Luca Modric’s row in the PAYROLL table has emp_id = 1001 and payroll_amount = 24000. A user issues the following statements:
Update payroll
SET payroll_amount = payroll_amount * 2
WHERE emp_id = 1001;
ALTER TABLE payroll ADD COLUMN email VARCHAR2(100);
UPDATE employees
SET payroll = 30000
WHERE emp_id = 1001;
After this, the user’s database session ends abnormally. What is Modric’s payroll_amount in the PAYROLL table now?
48000
Which of the following scenarios will NOT end an ORACLE transaction?
Alter statements are issued
User process terminates abnormally
ROLLBACK to SAVEPOINT is issued
GRANT statement is issued
INSERT statement is issued
ROLLBACK to SAVEPOINT is issued
INSERT statement is issued
The student table contains 73 rows. John insert three more students but does not COMMIT his changes.
User Mary now executes:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM students;
What result will Mary see?
73
Apps or programs should always _______ commit or roll back transactions before program close.
Explicitly
Pick the ones that do not belong together:
Durability
Atomicity
Concurrency
Insulation
Consistency
Concurrency
Insulation
Review the following transaction statements …
INSERT INTO emps SELECT * FROM employees;
SAVEPOINT Ins_Done;
DELETE FROM employees;
SAVEPOINT Del_Done;
CREATE TABLE A (a NUMBER);
UPDATE emps SET last_name = 'Smith';How to undo the last DML statements only?
ROLLBACK;
command used to mark the current point in the processing of a transaction
SAVEPOINT
After commit, the RDBMS makes the changes…
Permanent
Which of the following scenarios ends an Oracle transaction?
DML statements is issued
User disconnect from Oracle
ROLLBACK to SAVEPOINT is issued
COMMIT or ROLLBACK is issued
User Process terminates abnormally
User disconnect from Oracle
COMMIT or ROLLBACK is issued
User Process terminates abnormally
An entire transaction is rolled back without referencing any save points, what happens next?
The transaction finalizes
All of the others
All changes made by all of the SQL statements are undone
The transaction locks of data are released
all of the others
What is the command to name a transaction?
SET TRANSACTION NAME <transaction_name>
When logging out of the SQL Developer, your data changes are automatically rolled back.
False
When creating a SQL Trigger, which ones are not always required
Table
column name
Declaration of variables
Trigger timing
triggering event
column name
Declaration of variables
Triggers can be enabled or disabled with the ___ statement.
ALTER TABLE statement
To access the new value of the affected row after an INSERT or UPDATE command in the trigger body, you should use:
&new.column_name
:new.column_name
table.column_name
?new.colum_name
:new.column_name
Triggers can access both the OLD: and :NEW pseudo records. This statement is true for:
Row-level triggers fired because of an UPDATE
Some row-level triggers
All triggers with the FOR EACH ROW clause
Some statement level triggers fired because of an UPDATE
Row-level triggers fired because of an UPDATE
Some row-level triggers
For a row-level trigger body to be executed, the condition on the WHEN clause (if exists) must be true
True
The NEW and OLD have to be preceded with a colon '“:” everywhere they are used.
False
You can define a single DML trigger that fires for INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements on the same table
True
When referring to triggering events, which one does not belong?
Insert
Select
Update
Delete
Select
Which of the following are valid for AFTER UPDATE triggers.
Both, :new and :old
Neither :new nor :old
:new only
:old only
Both, :new and :old
Having a relation R(A, B, C, D, E, F) and a set of FDs F.
If AF is a super key. Calculate {AFE}+
Equal to {ADF}+
Same as {AF}+
All the other options are true
{A,B,C,D,E,F}
All the other options are true
Consider relation K = (X,Y,Z,W,V,U) with set F of FDs: F: {YZ → W, X → Y, Y → V, YZ → U, XZ → U, X → Z}
Which of the following are derived FDs of K via F?
YZ → WU
XZ → W
XZ → WU
none
X → V
YZ → WU
XZ → W
XZ → WU
X → V
Type of anomalies
Update
Insert
Redundancy
Delete
Update
Insert
Delete
What does normalization do?
eliminates redundancy
Candidate keys must be…
Minimal
What are some Armstrong axioms?
Transitivity
Reflexivity
Augmentation
Redundancy is the cause of …
Anomalies
How do we determine a closure?
by using FDs
X→ Y and WY → Z then WX → Z is an example of
Pseudo transitivity
X→ Y and Z → W then XZ → YW is an example of ….
Composition
X→ YZ and X → Y then X → Z is an example of ….
Decomposition
X → Y then XZ → YZ is an example of …
Augmentation
Let R(A, B, C, D, E) and F be a set of functional dependencies such that:
AD is a candidate key. C is a candidate key.
Then, CA is also a candidate key.
False
Data types in SQL are used to specify the domain of attributes. True or False
True
Domain
The set of values that an attribute can take
Candidate key
a minimal unique set of attributes that can be used to identify a tuple for the relation
Primary Key
A chosen candidate key, underlined in the schema whose values are unique and NOT NULL.
Foreign Key
A shared key that links two relations. Different rows can have the same foreign key.
What is the difference between a primary key and a foreign key?
Primary key is a chosen candidate key that’s unique and not null, and a foreign key is a shared key that links two relations.
What constraints are maintained by the Database Management system?
Domain constraints, key constraints, entity integrity, and referential integrity
What are domain constraints in a relational database?
In every tuple, the value of each attribute must come from its specified domain.
What are key constraints in a relational database?
Each tuple must have a unique set of values in each of its candidate keys
What is entity integrity in a relational database?
Each tuple must have a unique set of values in its primary key, and not NULL
Define referential integrity
Every foreign key value must appear as the value of the primary key in some of the relations it references.
Name the four sublanguages of SQL.
DDL (Data Definition Language)
DML (Data Manipulation Language)
DCL (Data Control Language)
TCL (Transaction Control Language)
What is DDL and what commands do you use in the DDL (Data Definition Language)?
Defines the structure of our database or schema.
CREATE,
DROP,
ALTER,
TRUNCATE,
RENAME
What is DML and what commands do you use in the DML (Data Manipulation Language)?
it’s used to Manipulate the data by using the commands: SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE.
What is DCL (Data Control Language) and what commands does it use?
Provides or removes access to the database and the structures within it by using the commands GRANT and REVOKE
What is TCL (Transaction Control Language) and what commands does it use?
Manages the changes made by the DML by using the commands COMMIT, ROLLBACK, SAVEPOINT
Whats the main purpose of the PRIMARY key constraint?
Uniqueness of values
What is the purpose of the UNIQUE key constraint in a database?
Ensures data integrity
what type of keys used in a relational database?
UNIQUE, PRIMARY, and FOREIGN
In SQL, data types specify the kind of data that can be stored in a column, effectively defining the domain of attributes. True or False?
True
What are the three older database models?
File systems, Hierarchical, Network
In the relational model, the data is represented using columns and attributes. True or False?
False, the data is represented using columns and rows
The ER Model gives a graphical view of the database design. True or False?
True
Define entity
Something that exists as itself
Navigation of relationships and impossibility to reorganize the data for queries are flaws of?
Hierarchical model and Network model
Relational models contain what?
Relations, tuples, and attributes
The ER Model contains what?
A graphical view of the database design. Along with Entities, relationships, and attributes.
In the relational model, the data is represented using columns and attributes. True or False?
True
How is a date defined in SQL, and what is the typical format used?
Using the DATE keyword, typically in the format 'yyyy-mm-dd'.
How do you update specific rows in a table based on a condition?
UPDATE TableName SET Column1 = Value1 WHERE Condition;
What is the difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE in SQL?
DELETE: Removes rows based on a condition.
TRUNCATE: Quickly removes all rows without logging individual row deletions.
How can you define a unique constraint on a single attribute in a SQL table?
Use the UNIQUE keyword
What is the purpose of the ALTER TABLE command?
Modifies a table’s structure by adding, modifying, or removing columns and constraints
What is the purpose of the WHERE clause in a SQL query?
It filters rows by specifying conditions that the rows must meet
List five comparison operators used in the WHERE clause.
=,≠ or <>,>,<,BETWEEN
What does the LIKE operator do in SQL?
It matches strings against patterns using wildcards % and _
What is the function of the AND operator in a WHERE clause?
It returns true only if both conditions are satisfied
How does the ORDER BY clause affect query results?
It sorts the output rows by specified columns in ascending or descending order
What is the default order for the ORDER BY clause?
Ascending order
How to search for a % or a _ character in the Oracle LIKE condition?
Use an Escape character
What function can replace NULL values in SQL output?
The NVL2 function
What are the steps for writing an SQL query?
Identify the table (
FROM).Define conditions (
WHERE).Specify sorting (
ORDER BY).Select columns (
SELECT).
How can you check if a value is NULL in SQL?
Use the IS NULL condition
How can you filter students who started more than six months ago?
Use a date comparison in the WHERE clause to filter rows
What is an aggregate function in SQL?
A function that computes a single result from a set of rows based on a column
List five common aggregate functions.
AVG, COUNT, MAX, MIN, SUM
How does COUNT(*) differ from COUNT(expression)?
One counts all rows meeting the condition, and the other counts non-null rows for the expression
What does the DISTINCT keyword do in aggregate functions?
It counts only unique, non-null values of an expression
How does the AVG function handle NULL values?
NULL values are ignored unless handled with COALESCE.
What does the GROUP BY clause do?
It groups rows by specified attributes, allowing aggregate functions to operate on each group
What restriction does the GROUP BY clause impose on the SELECT clause?
All non-aggregated columns in SELECT must appear in the GROUP BY clause
What is the purpose of the HAVING clause?
It filters groups based on aggregate conditions, similar to how WHERE filters rows
List three character manipulation functions in SQL.
SUBSTR, LENGTH, REPLACE
True or false.AVG and SUM can be used on any data type
False
True or false. MIN can be used on numbers and dates.
True
True or false. Using the WHERE clause makes possible to exclude rows before grouping them.
True