Ch 4 Part 5: modifications of mendelian ratios (SEPT 24th)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Endosymbiotic, origins of eukaryotes
Eukaryotic cells evolved from a symbiotic relationship where a larger host cell engulfed smaller prokaryotic cells,
which then developed into mitochondria and chloroplast
(Extranuclear) Endosymbiotic inheritance…
-what type of fission & chromosomes
-what is relocated to the nucleus
-what sort of parental inheritance
-what is it inherited as
-prokaryotic fission & circular, compact chromosomes
-regulatory genes relocated to nucleus
-uniparental inheritance
-inherited as haplotype
what does carl corrnes discover
define veriagation
-he discovers that patterns of chloroplast inheritance are not explainable by mendelian genetics
-variegation: explained by inheritance of two different kinds of chloroplasts
Define heteroplasmy
the phenomenon in which plastids or mitochondria with different genes are inherited
Mitochondrial mutations context of DNA
what was discovered in
1952,1953, 1963
1952: DNA is identified as hereditary material
1953: structure of DNA is explained
1963: DNA is discovered in mitochondria
Mitochondrial Mutation, reciprocal crosses in Neurospora crassa (1952)
what was observed and what was the hypothesis
-poky phenotype is transmitted by one parent to all offspring; never appears to be heterozyous
-hypothesis: something in the cytoplasm of the recipient
Mitochondrial Mutation, reciprocal crosses in Saccharomyces cervesiae (1956)
what was observed
-petite mutation in yeast shows similar pattern as poky
-slow growth of petite associated with known mitochondrial function
Mitochondrial mutations in humans…
what about the human mitogenome
how many protein, tRNA and rRNA
how do mutations affect humans and how many mt disease are known
The human mitogenome is highly reduced
-13 proteins, 22 tRNA, 2 rRNA
-because every gene is essential, mutations tend to be harmful. there are 150 known mitochondrial diseases
why are mtDNA mutations rarely passed in generations
-because egg-cell has many mitochondria at time of fertilization.
-Mitochondrial DNA encodes mostly proteins essential for cellular respiration, so most mutations would be selected against the cell.
-Only mother can pass on mitochondrial mutations, so only half of mitochondrial mutations that take place are heritable.
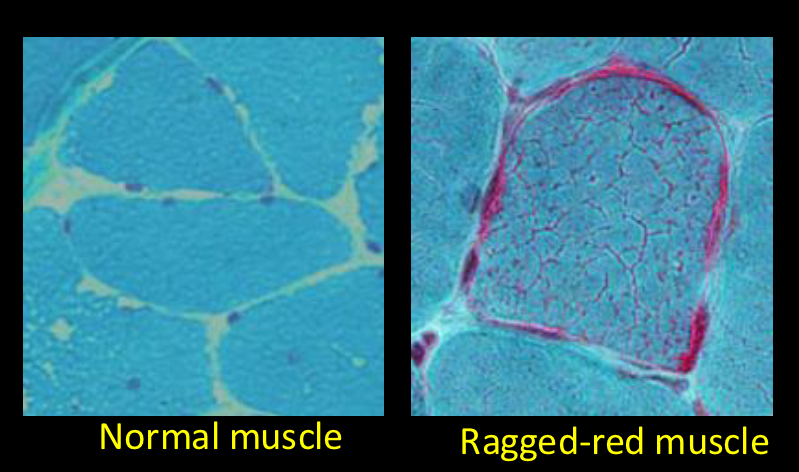
Describe Myoclinin Epilepsy and Ragged-red Fiber disease MERRF (mt mutation in humans):
what does tRNA mutation casue
what could it be lethal without
what is most strongly impacted
how is the ragged red appearance caused
-tRNA mutation results in inefficient protein assembly and ultimately inefficient respiration
-would be lethal without heteroplasmy
-because brain uses so much energy, it is most strongly impacted
-ragged red appearance caused by aggregatoin of mutant mitochondria at the plasma membrane
MERRF symptoms
ataxia
deafness/blindness
epilepsy
dementia
muscle weakness
How do maternal effects alter phenotypic expectations?
what is already present at fertilization
-phenotype of the offspring depends on genotype of the mother
-on fertilization regulatory proteins already present in egg cell guide development
Describe the maternal effects in bicoid gene, what happens?
bicoid: accumulation in Drosophila egg cell determines embryonic anterior-posterior axis
bc-: recessive allele that prevents embryogenesis (formation and development of embryo)
bicoid gene, bc-/bc- in mother results in what?
failure of embryogenesis (formation and development of embryo)
How is the inheritance of mitochondrial and chloroplast encoded traits different from nuclear inheritance?
Mitochondrial and chloroplast inheritance: It is extranuclear (patterns of chloroplast inheritance does not follow mendelian genetics), uniparental (from the mother), undergoes prokaryotic fission, and inherited as haplotype, circular chromosomes
Nuclear inheritance: Inherited biparental (from both parents), and follows mendelian patterns (linear chromosomes undergo meiosis and separate into haploid gametes, offspring inherit one chromosome from each parent).