DH 103 Concorde
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Radiology
The science or study of radiation as used in medicine.
Radiography
The art and science of making radiographs by the exposure of film to x-rays.
Radiograph
an image or picture produced on a receptor (radiation-sensitive film, phosphor plate, or digital sensor) by exposure to ionizing radiation; a two-dimensional representation of a three-dimensional object.
Atom
A tiny, invisible particle that is the fundamental unit of matter; the smallest part of an element that has the properties of that element.
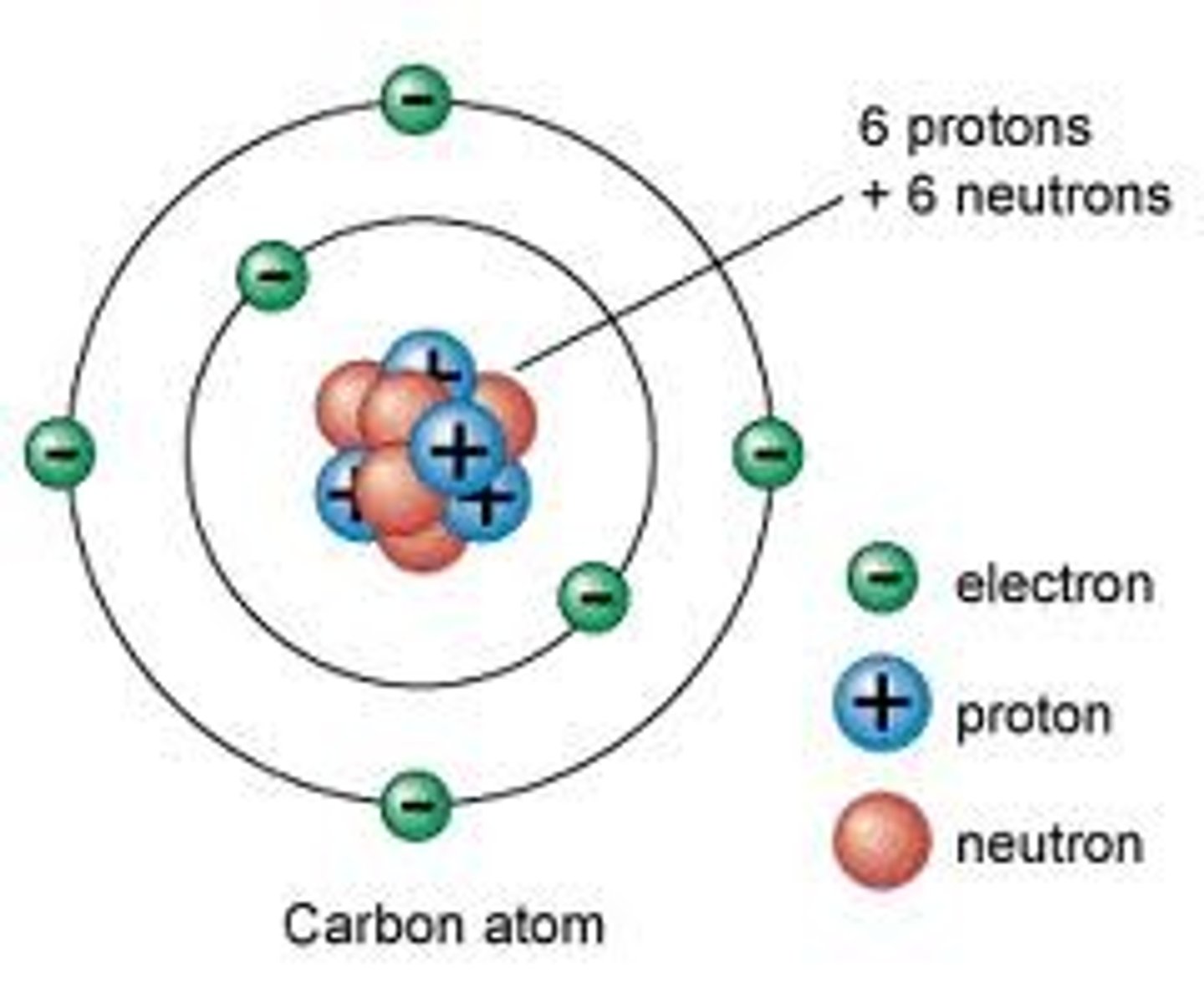
Electron shell
An energy level representing the distance of an electron from the nucleus of an atom. Like a miniature solar system.

Binding energy
The attraction between the positive nucleus and the negative electrons that maintains electrons in thier orbits; determined by the distance between the nucleus and the electrons. K is the strongest O is the weakest.
Radiation
A form of energy carried by waves or a stream of particles.
Radioactivity
a process in which certain unstable atoms or elements undergo spontaneous disintegration, or decay, in an effort to attain a more balance nuclear state.
Cathode
The purpose of the cathode is to supply the electrons necessary to generate x-rays.
Anode
The purpose of the anode is to convert electrons into x-rays photons.

Thermionic emission
The release of electrons from the tungsten filament when the electrical current passes through it and heats the filament.
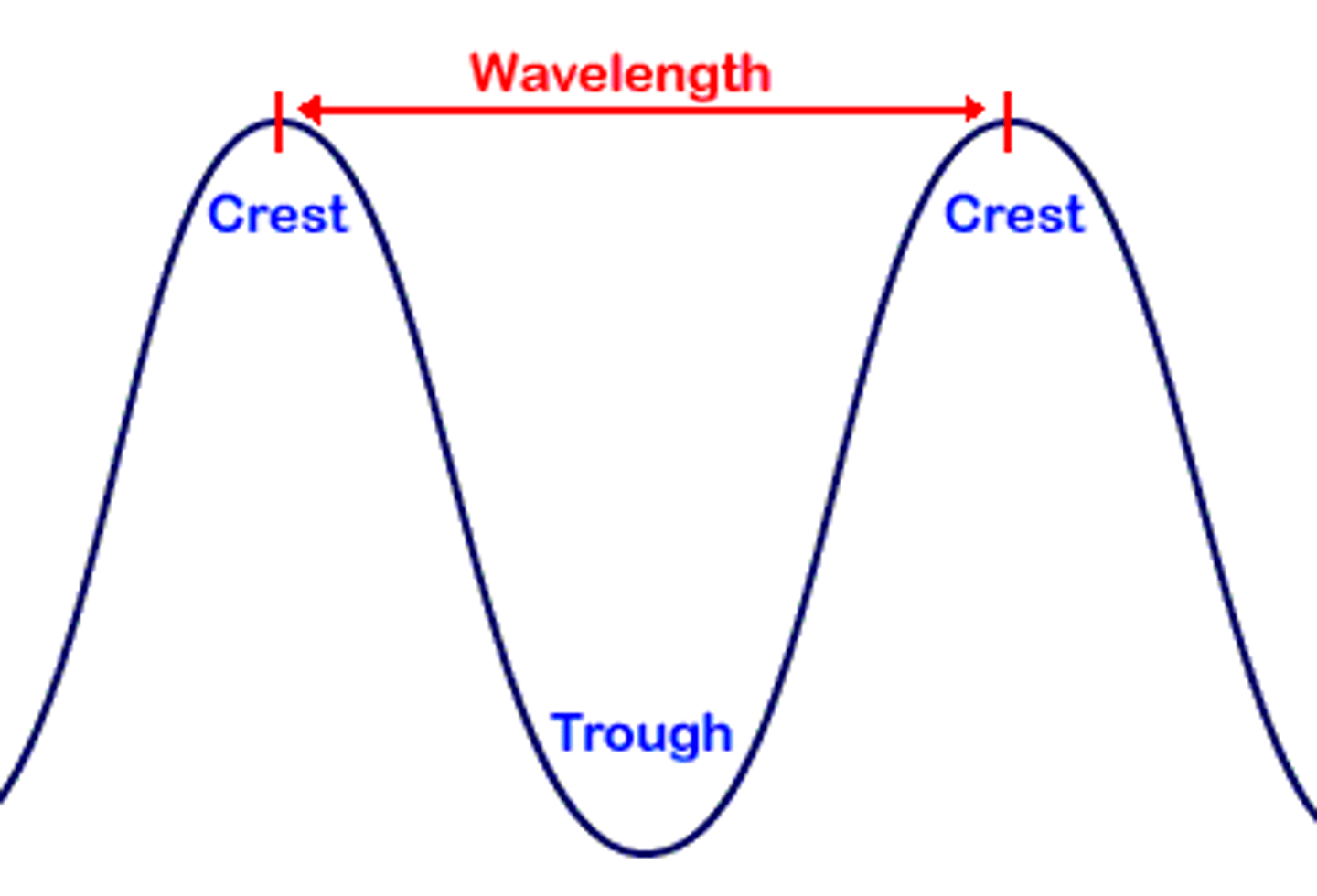
Wavelength
The distance between the crest of one wave and the crest of the next.
Frequency
The number of wavelengths that pass a given point in a certain amount of time.

Velocity
The speed of the wave. Speed of light.
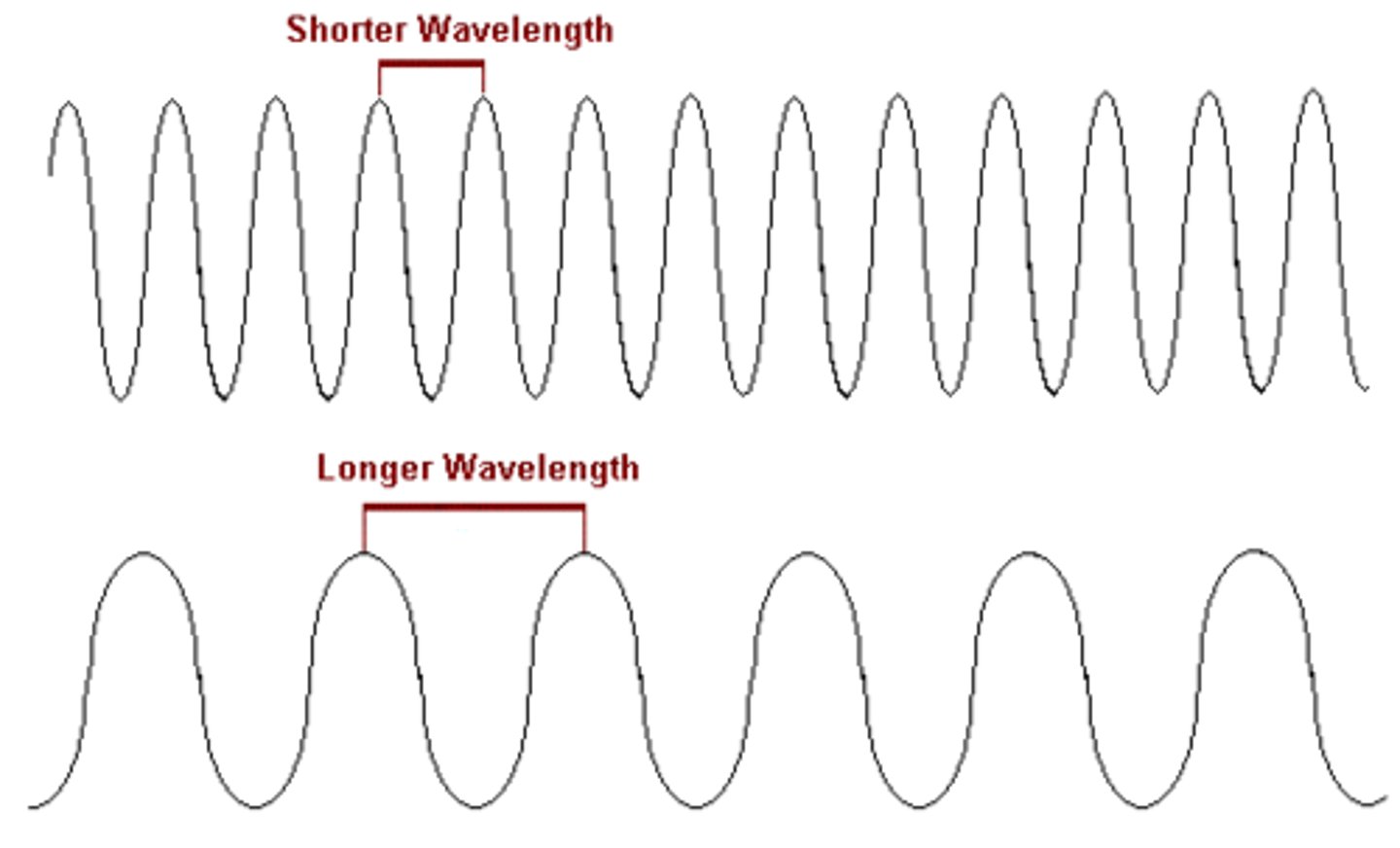
Long wavelength
Lazy
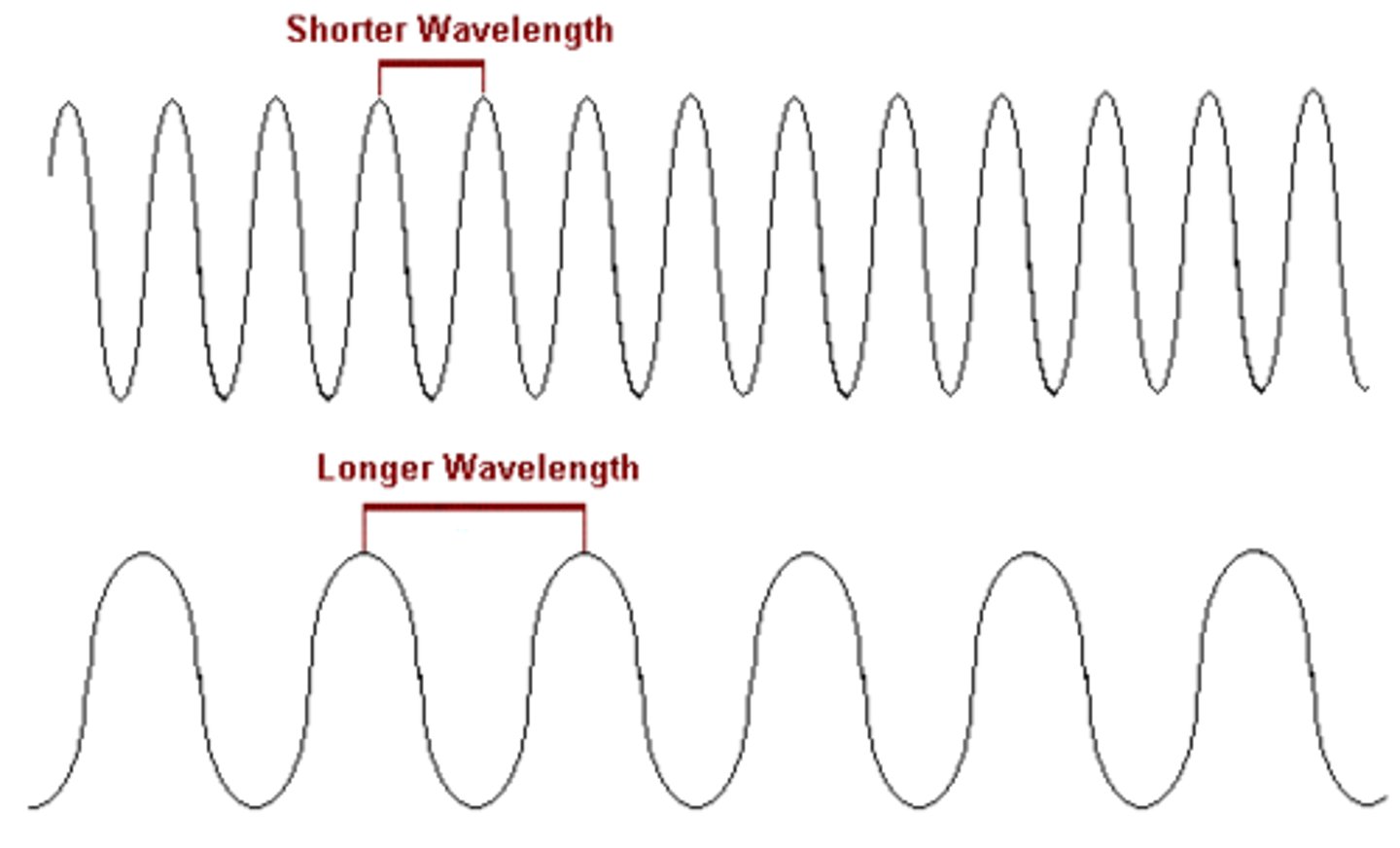
Short wavelength
Strong
Inherent filtration
Takes place when the primary beam passes through the glass window of the x-ray tube, the insulating oil, and the tubehead seal.
Added filtration
Refers to the placement of aluminum disks in the path of the x-ray beam between the collimator and the tubehead seal in the dental x-ray machine.
Collimator
Is used to restrict the size and shape of the x-ray beam and to reduce patient exposure.
Lead apron
Flexible shield placed over the patient's chest and lap to protect the reproductive and blood forming tissues from scatter radiation.
Thyroid collar
A flexible lead shield that is placed securely around the neck to protect the thyroid gland from scatter radiation.
Contro Panel
A part of the x-ray machine that contains an on-off switch and an indicator light, an exposure button and indicator light, and control devices to regulate the x-ray beam.
Receptor holder
Device used to hold an intraoral receptor in the mouth; used to stabilize the receptor's position during exposure.
Beam alignment device
A device used to align the position-indicating device (PID) in relation to tooth and receptor; positions the intraoral receptor in the mouth and retains the receptor in position during exposure; helps stabilize the receptor in the mouth and reduces the chances of movement, thus reducing the patient's exposure to x-radiation.
Radipaque
The portion of an image that is light or white; a radiopaque structure resists the passage of the x-rays that reach the receptor.
Radiolucent
The portion of an image that is dark or black; a radiolucent structure readily permits the passage of the x-ray beam and allows more x-rays to reach the receptor.
Purpose of radiographs
• To detect lesions, diseases, and conditions of the teeth and surrounding structures that cannot be identified clinically
• To confirm or classify suspected disease
• To localize lesions or foreign objects
• To provide information during dental procedures (e.g., root canal therapy, placement of dental implants)
• To evaluate growth and development
• To illustrate changes secondary to caries, periodontal disease, and trauma
• To document the condition of a patient at a specific point in time
• To aid in development of a clinical treatment plan
Critical instruments
Item used to penetrate soft tissue or bone
Semicritical instruments
Items that come in contact with intact skin only. Mirrors, Receptor holder and beam alignment device.
Periapical X-ray
The radiograph that shows images of the entire length of the tooth including the apex.
Bitewing x-ray
Used to examine the inter-proximal surfaces of teeth. includes the crowns of MX and MN teeth, inter-proximal areas and areas of crestal bone on the same image.
How to take a bitewing x-ray
Use Rinn XCP beam alignment device. Placed parallel to teeth. +10 angulation.
Vertical bitewing
Used to examine the level of alveolar bone in addition to caries detection. To check bone loss.
What do you need for digital imaging
X-ray unit, sensor, computer, charge-couple device (CCD), complementary metal oxide semiconductor/active pixel sensor & charge injection device.
Reduced radiation on digital imaging
50% to 90% less than conventional radiography.
Digital imaging and shades of gray
Uses up to 256 shades of gray compared to 16 to 25 shades of gray on conventional film.
How to care for sensors
The sensor must be covered with a disposable barrier because it cannot be sterilized.
Direct Imaging
When digital image is transferred directly to a computer with imaging software.
Indirect Imaging
Image is converted by suing a scanner so it can be seen on a computer monitor.
Charge-coupled device (CCD)
Solid-state silicon chip detector that converts light or x-ray photons into an electrical charge or signal.
Unexposed receptor
Image appears clear, no image.

Underexposed receptor
Image appears light.
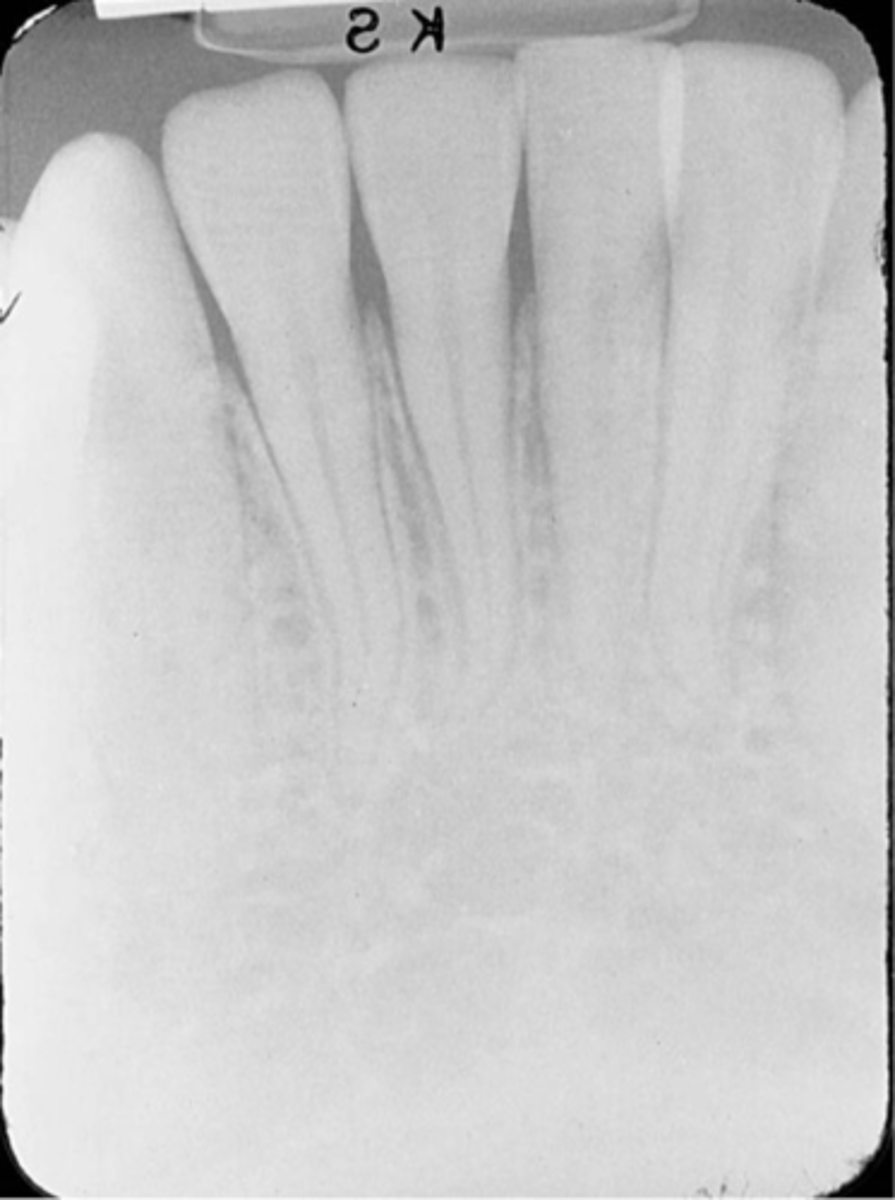
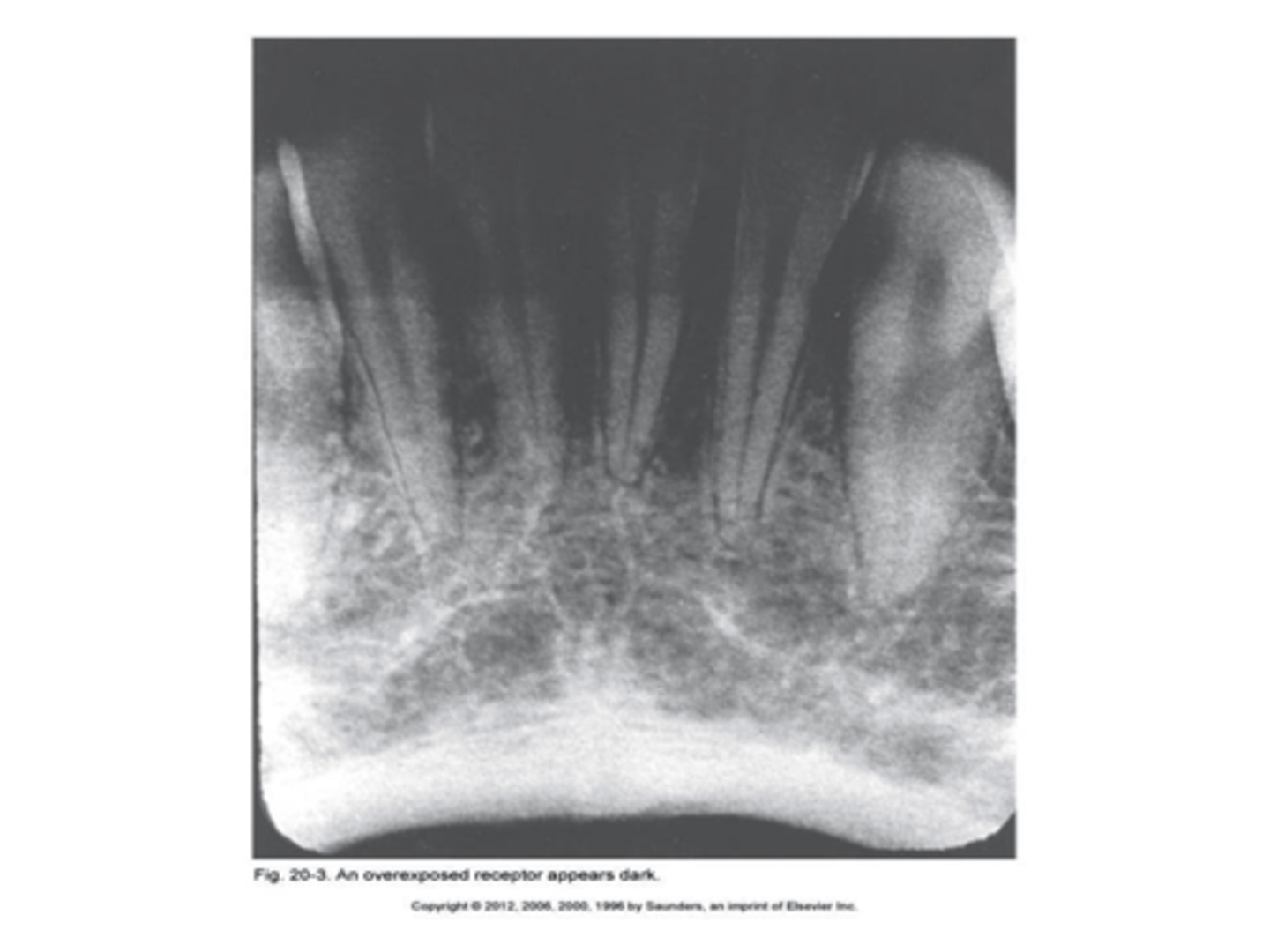
Overexposed receptor
Image appears dark.
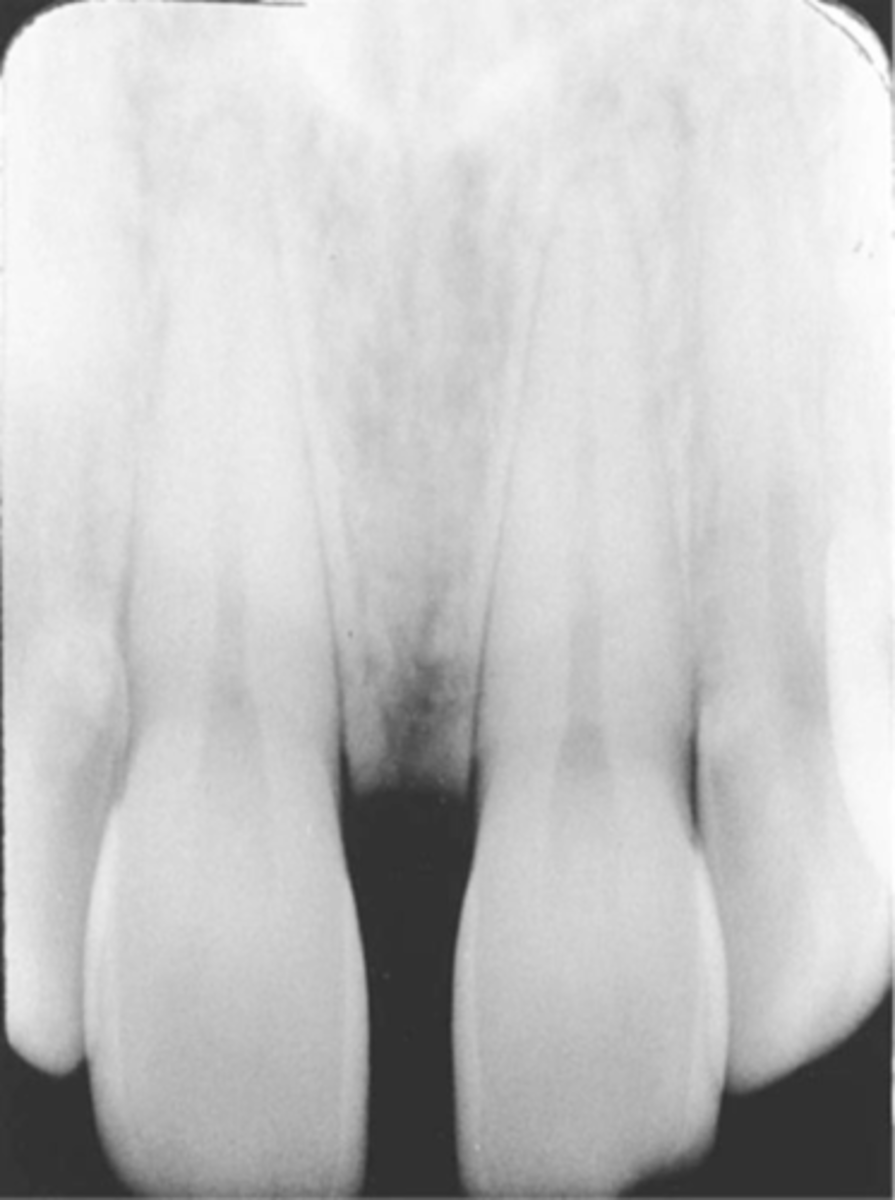
Absence of apical structures
No apices are seen on image - receptor not positioned to cover apical regions of teeth.
Dropped receptor corner
The occlusal plane appears tipped or tilted.
Overlapped contacts
The area where the contact area of one tooth is superimposed over the contact area of an adjacent tooth.
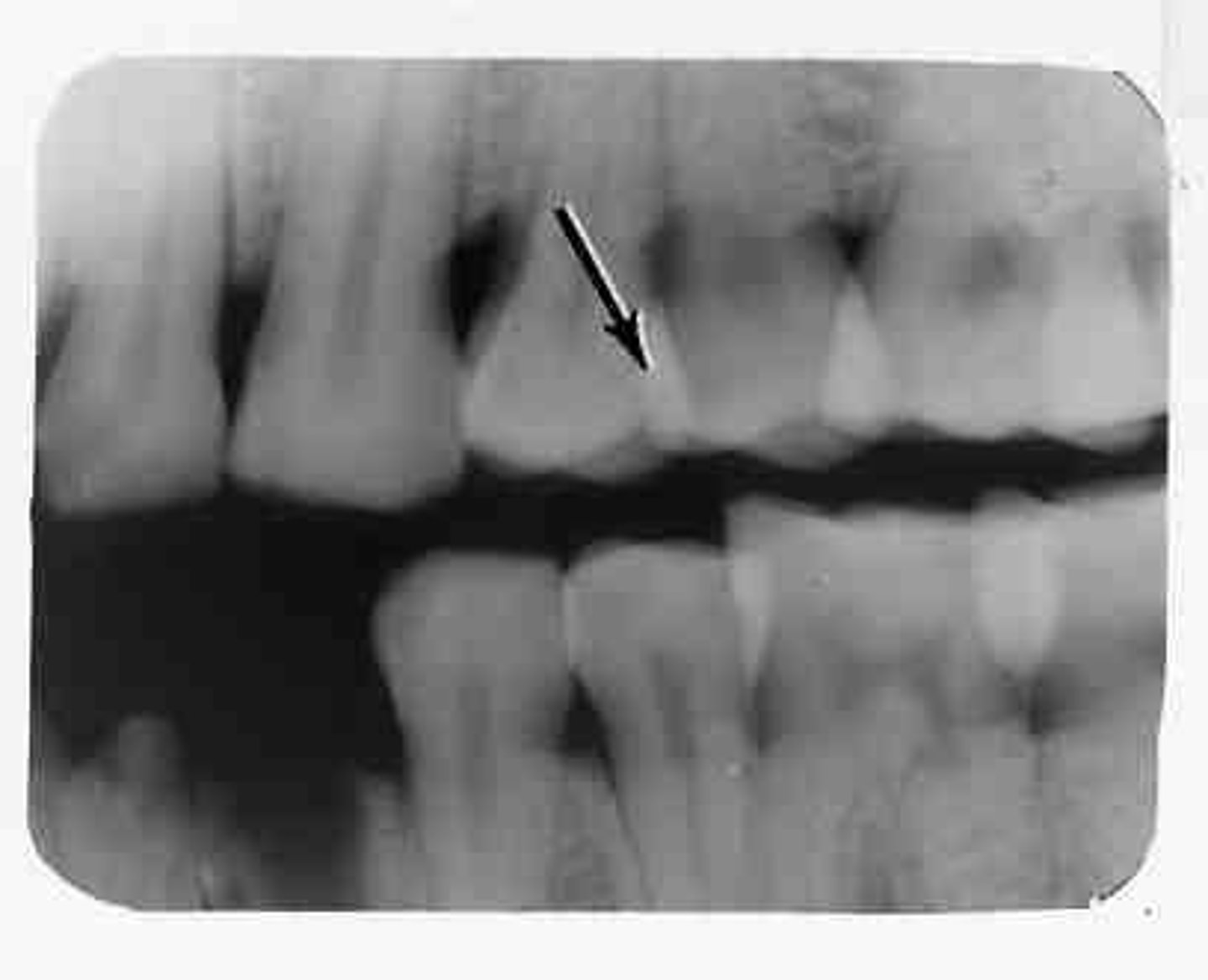
Elongated images
Long distorted teeth. Too little vertical angulation.
Cone-Cut with Beam Alignment Device
-A clear unexposed area is seen.
-PID was not properly aligned with the PA beam alignment device and the beam did not expose the entire receptor, resulting in a clear unexposed area resembling the outline of the PID is seen.
-To avoid make certain that the PID and the aiming ring are aligned.
Cone-Cut without Beam Alignment Device correction
Make certain that the x-ray beam is centered over the receptor and that the entire receptor is covered by the diameter of PID.
Bending
The image appears stretched and distorted.
Creasing
When using a film, a thin radiolucent line is seen on the image. When using a PSP receptor, it appears as a white line. Sensor is damaged.

Debris Acumulation
Debris on the surface of the sensor may cause permanent radiopaque artifacts or radiolucent scratch marks on the sensor.
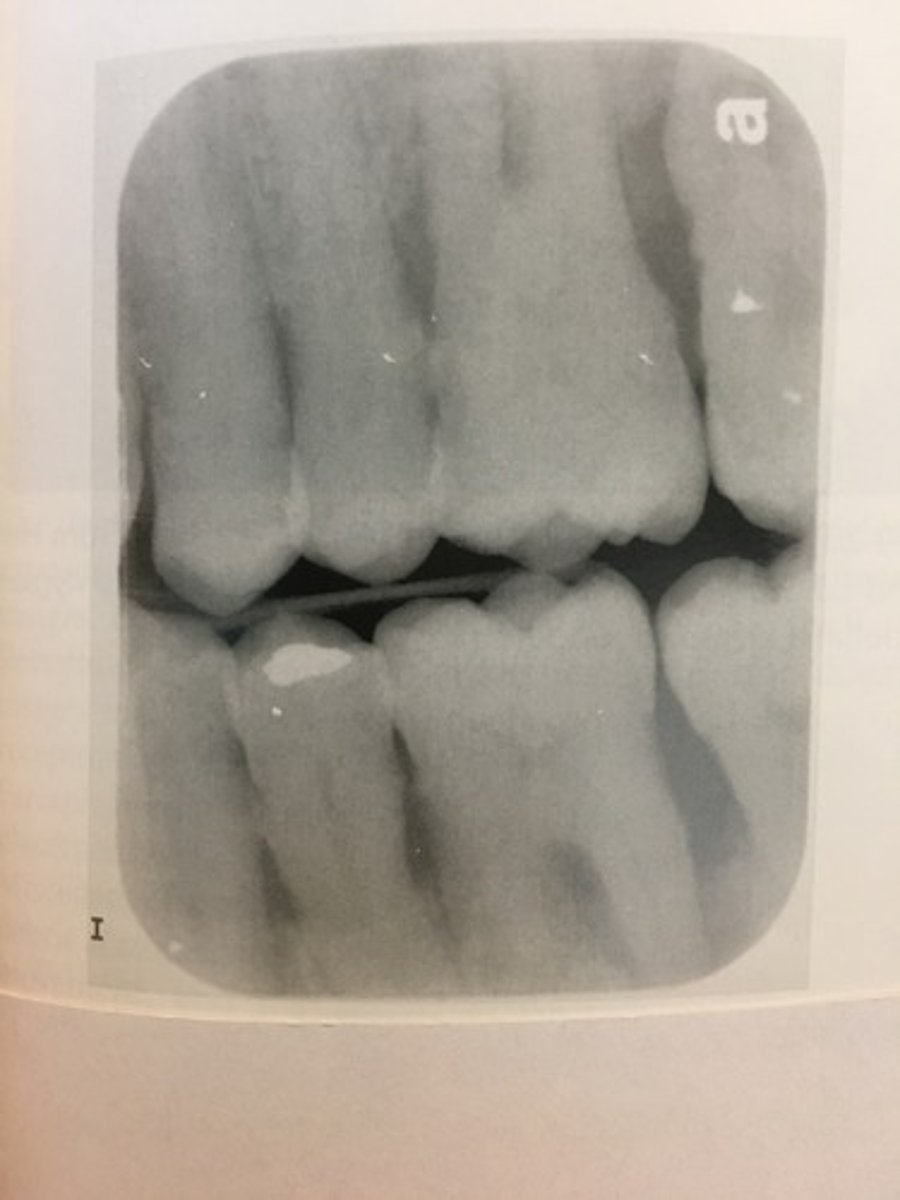
Phalangioma
Patient's finger appears on the film.
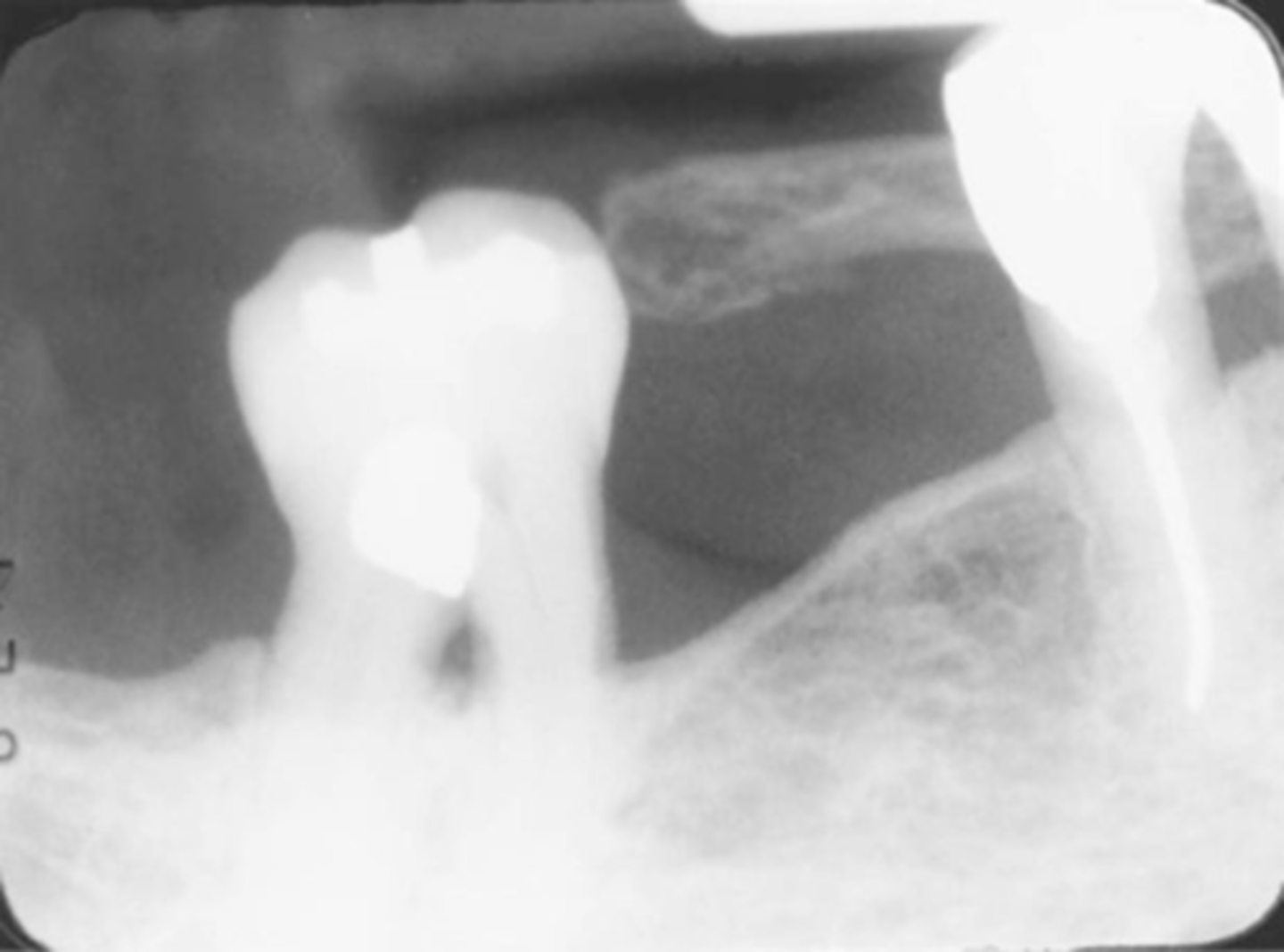
Double image
Double image appears dark with super impose structures.
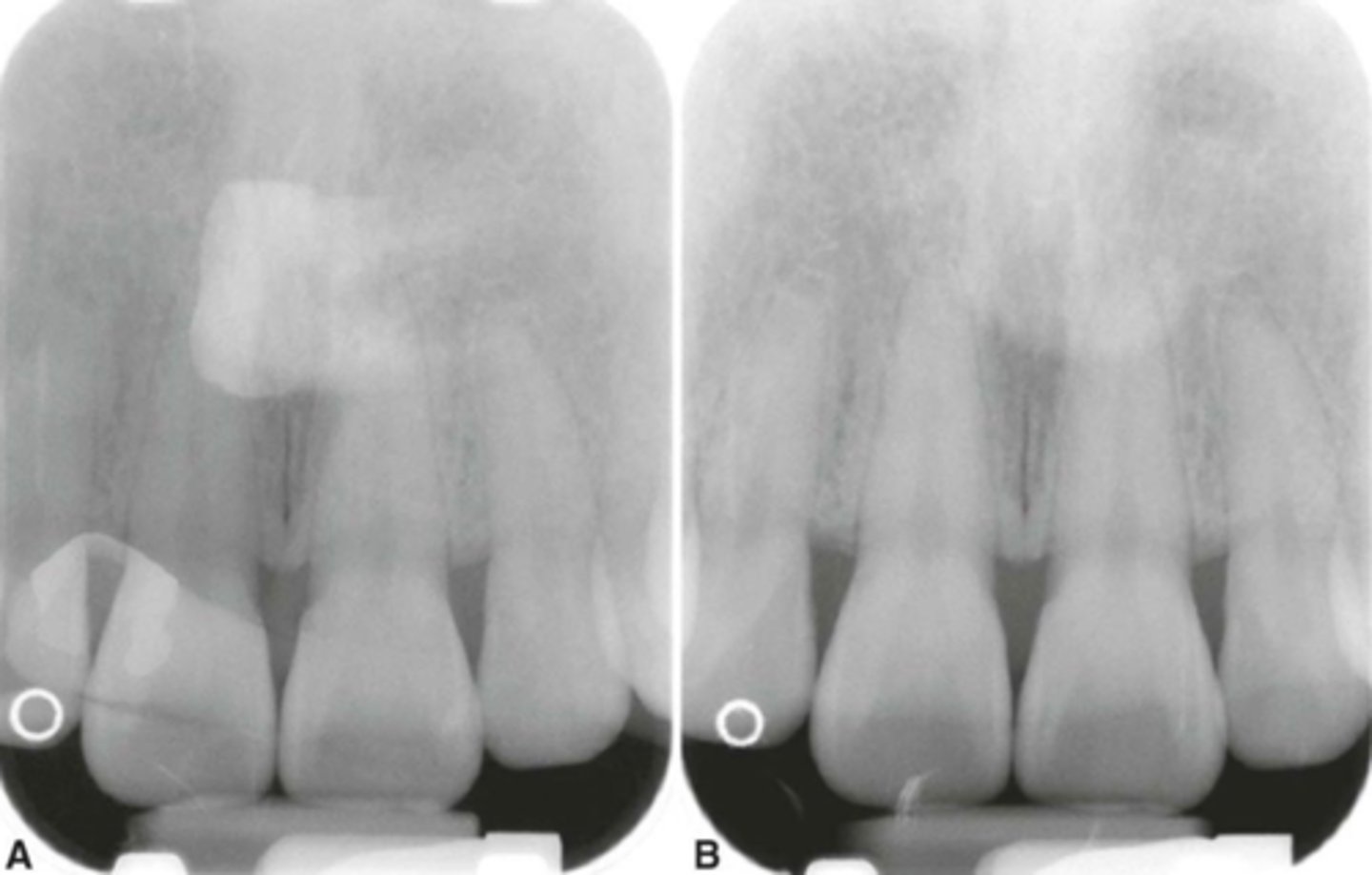
Movements/motion unsharpness
A blurred image results.
Reverse/Backward Placement
Blank or white image is seen with no anatomic structures recorded.
White cable issues
The wired cable appears as a radiopaque outline.
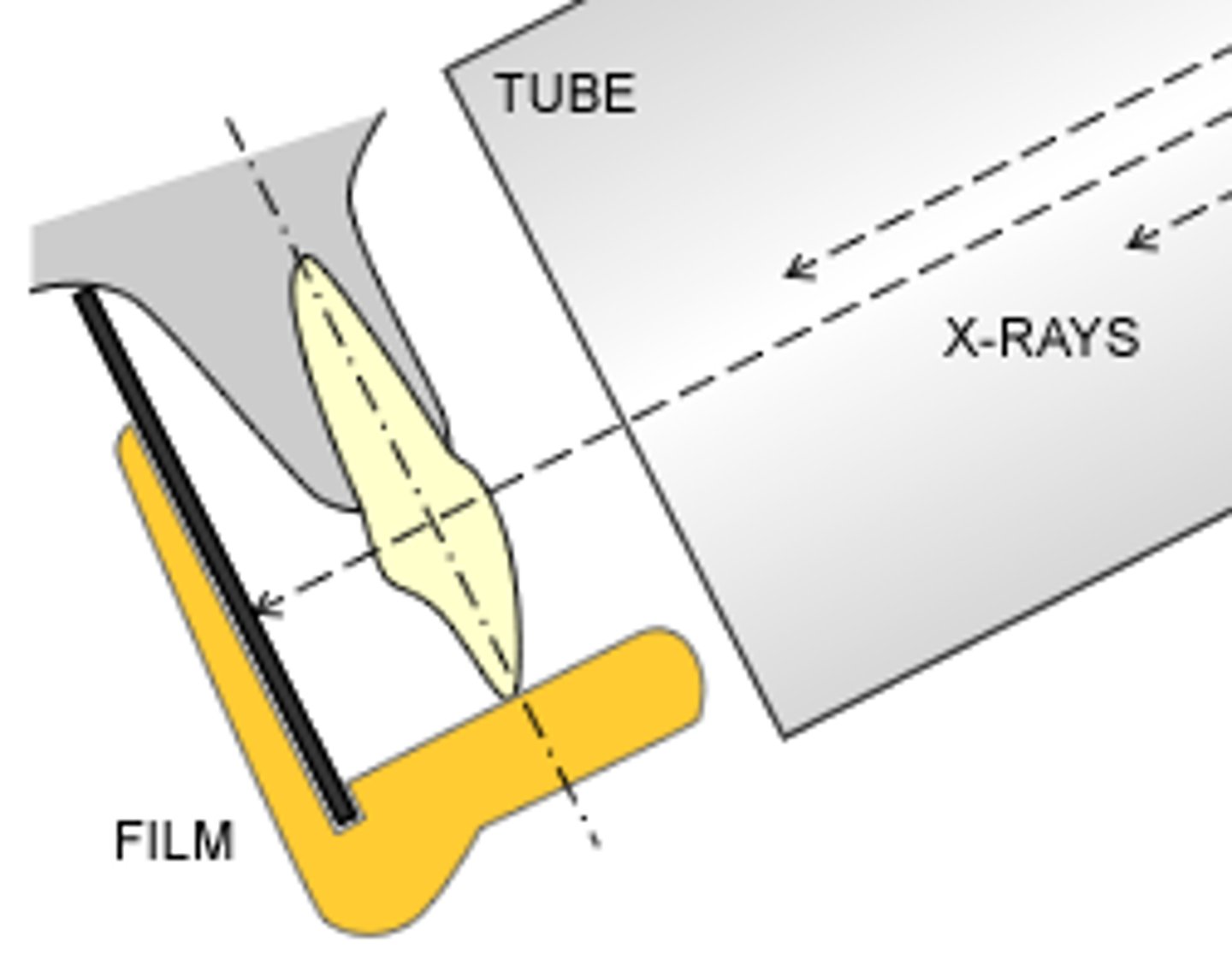
Paralleling technique
An intraoral imaging technique used to expose periapical receptors; the receptor is placed parallel to the long axis of the tooth; the central ray is directed perpendicular to the receptor and the long axis of tooth; a beam alignment device must be used to keep the receptor parallel to the long axis of the tooth.
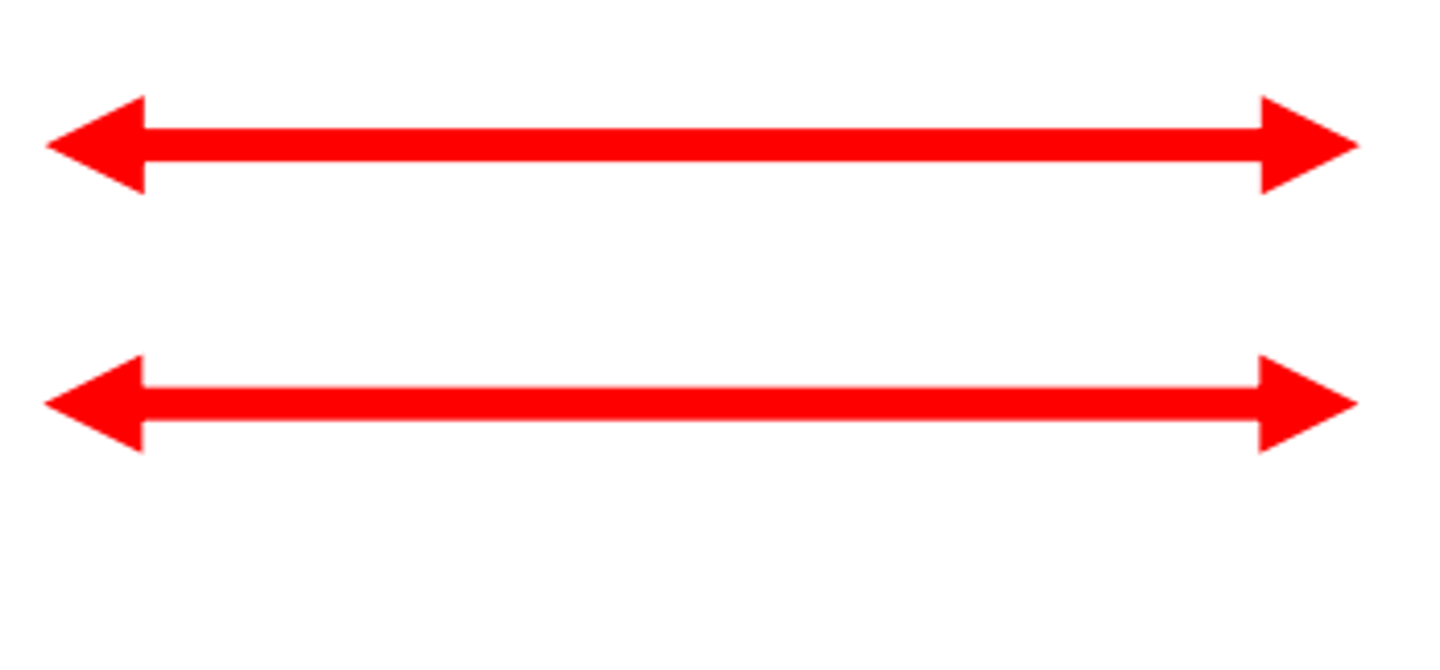
Parallel lines
Moving or lying in the same plane, always separated by the same distance.

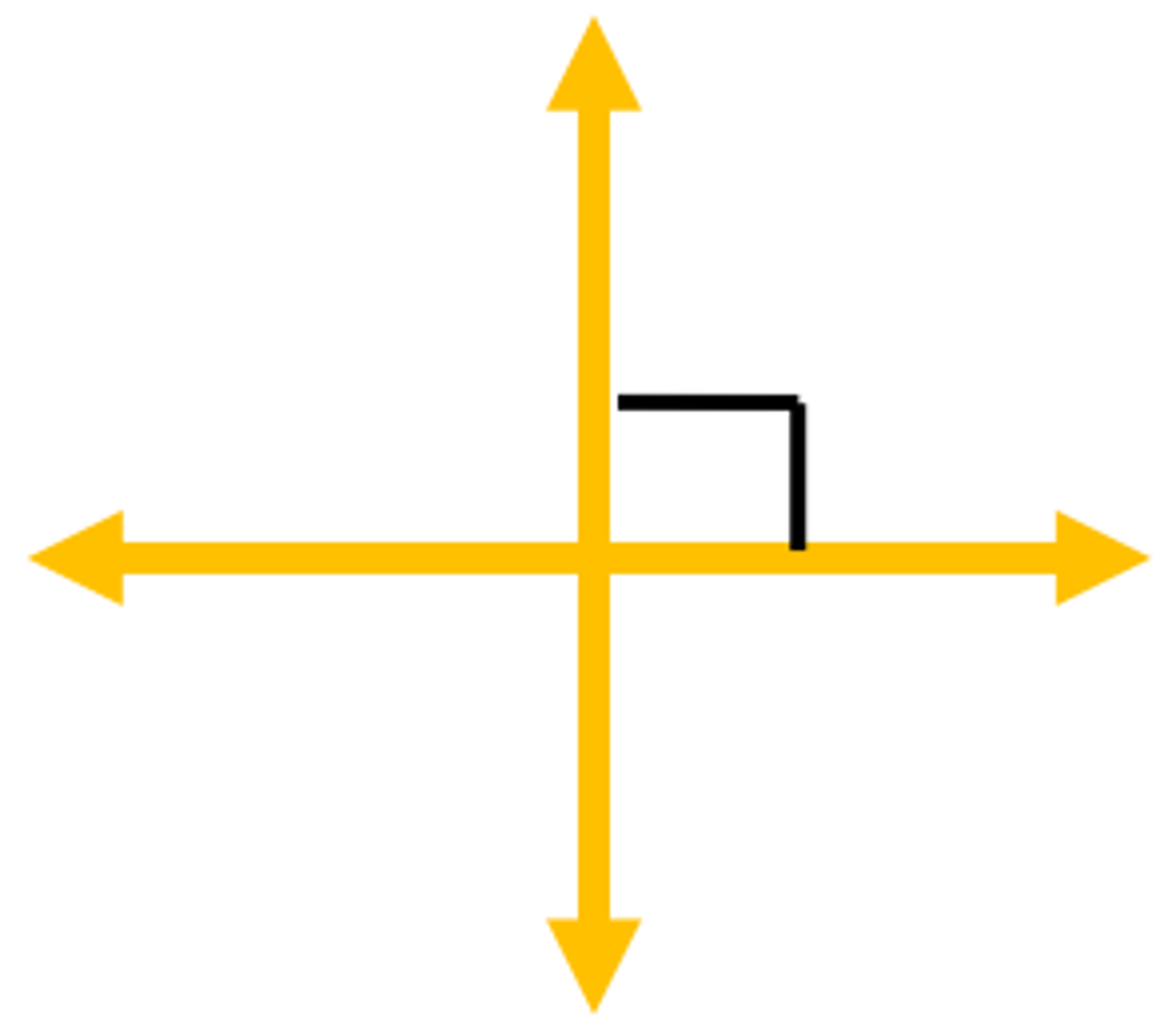
Perpendicular lines
Intersecting at or forming a right angle
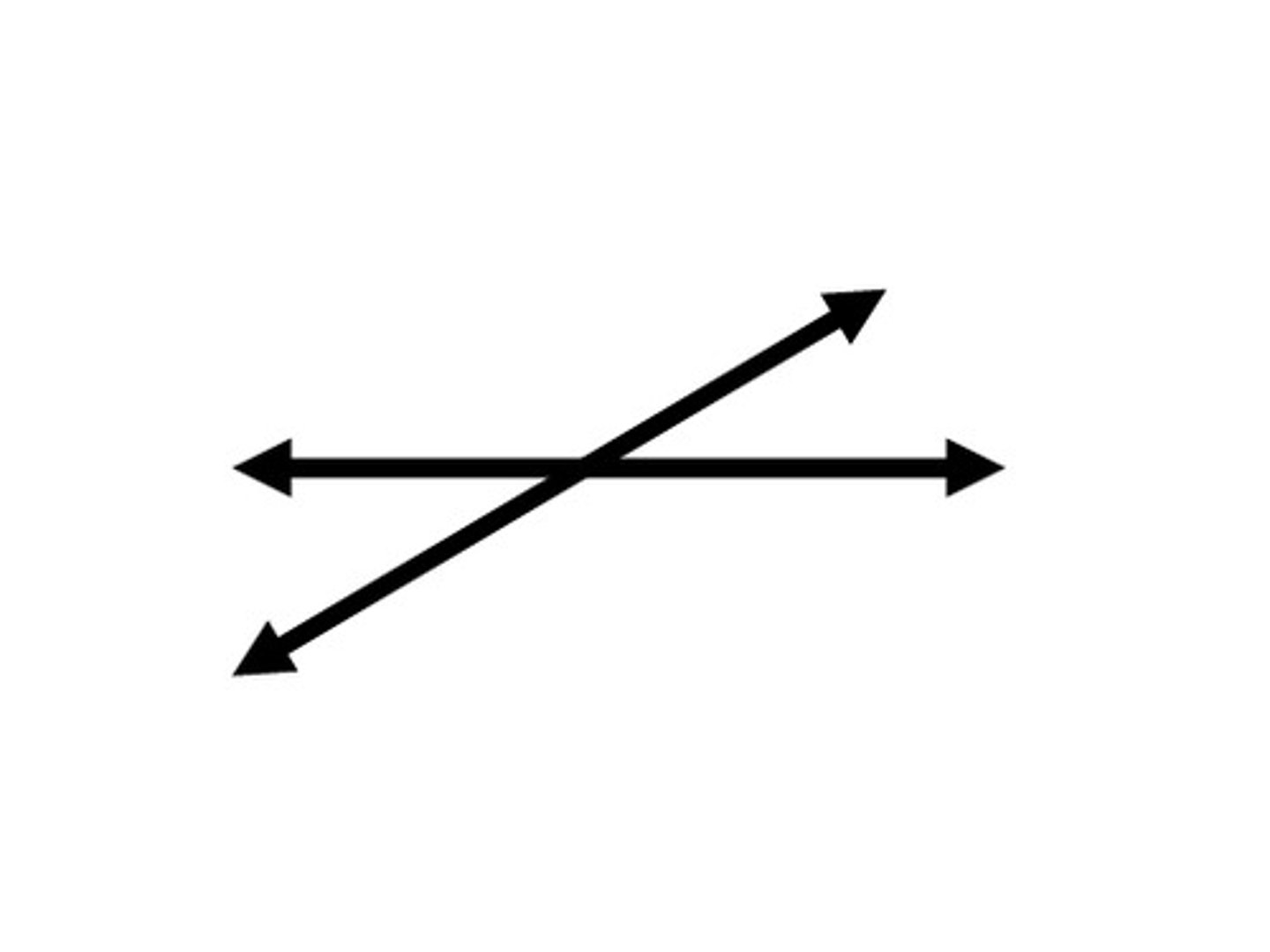
Intersecting lines
To cut across of through
Basic principle of paralleling technique
The receptor is placed in the mouth parallel to the long axis of the tooth.
Rinn XCP
Includes three plastic bite-blocks, three plastics aiming rings, and three metal indicator arms.