maternal and fetal factors
1/253
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
254 Terms
A high-risk OB patient is one who is at an increased risk for an ________ pregnancy outcome.
Adverse
To identify the high-risk pregnancy, which two factors should be considered?
Mother
Fetus
Risks for a high-risk pregnancy include understanding (1)_______ and _______ factors as well as obtaining (2)______ history.
Maternal, Fetal
Family
List the 3 maternal risk factors previously discussed for a high-risk pregnancy.
Blood work or procedure
Vaginal bleeding
Cervical incompetence
A maternal risk factor involving blood work/procedures will look at what 5 tests/procedures?
1st trimester blood work
Quad screen
Amniocentesis
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
Percutaneous cord blood sampling (PUBS)
1st trimester blood work involves what 3 hormones/measurements?
PAPP-A
hCG
NT measurement
A quad screen test is used to indicate if more ________ should be considered.
Testing
What 4 hormones are involved in the quad screen test?
AFP
hCG
Estriol
Inhibin-A
An amniocentesis is when the _____________ is removed.
What are the 2 complications that could occur from an amniocentesis?
Amniotic fluid
Pregnancy loss, Infection
Some reasons for an amniocentesis procedure include…
Abnormal ______ testing
Assess fetal ____ maturity
Reduce the amount of _____________
Genetic
Lung
Amniotic fluid
What does ‘CVS’ stand for?
Chorionic villus sampling
CVS is the biopsy of the _____________.
Chorionic villus
Which two lab procedures are unable to detect neural tube defects?
CVS
PUBS
PUBS is another term for what?
Cordocentesis
What does ‘PUBS’ stand for?
Percutaneous cord blood sampling
A PUBS procedure is done by having a (1)_______ aspiration of the umbilical cord to analyze (2)_________.
Needle
Chromosomes
PUBS procedures detect…
___________ abnormalities
Certain ______ disorders
Chromosomal
Blood
What is the most common reason for vaginal bleeding in the 1st trimester?
SCH (subchorionic hemorrhage)
What are three reasons for vaginal bleeding in the 3rd trimester?
Placenta abruption
Placenta previa
Placenta accreta, increta, and percreta
What is the name of something they use to prevent cervical dilation?
Cervical cerclage (cervical stitch)
List the 4 maternal risk factors for a high-risk pregnancy.
Advanced maternal age (AMA)
Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Hypertension (HTN)
Maternal infections
AMA refers to a patient who will be ___ or older at the time of delivery.
35
In the US, which two treatments are offered to AMA patients?
Why is that?
Genetic counseling
Invasive prenatal testing
Increased risk for genetic abnormalities
Certain syndromes and abnormalities have an increased risk if the patients are…
Advanced for maternal age (AMA)
What is the most common maternal disorder?
Maternal diabetes
Maternal diabetes includes which 3 diabetes?
Type 1
Type 2
Gestational diabetes
Diabetes increases the risk for complications, which includes these two pathologies:
______ and _____ trimester pregnancy loss
___________ anomalies
Early, late
Congenital
What is the primary fuel for fetal growth?
Glucose
If glucose levels are very high and uncontrolled, what could happen to the fetus?
Becomes macrosomic
A macrosomic fetus will be in the ___ percentile in weight.
90th
How is a macrosomic fetus normally delivered?
C-Section
Why is a macrosomic fetus delivered via C-Section?
At a greater risk for shoulder dystocia if delivered vaginally
A macrosomic fetus’ shoulders cannot pass vaginally without…
Manipulation
With maternal diabetes, which diabetes type is more common?
What percentage will it account for?
Type 2
90-95%
With maternal diabetes, which diabetes type is less common?
What percentage will it account for?
Type 1
5-10%
Type 1 diabetes used to be called what?
Juvenile onset diabetes
Type 1 diabetes generally occurs at a ________ age.
Younger
With Type 1 diabetes…
More _______ is produced.
There is an _________ response where the body attacks the ________.
Making the ________ unable to secrete enough ______.
The patient will be ______ dependent.
Glucose
Auto-immune, Pancreas
Pancreas, Insulin
Insulin
Which diabetes type is more common in obese patients?
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes used to be called what?
Non-insulin dependent diabetes
With Type 2 diabetes…
More _______ is produced.
The _______ has to create more ______.
Making the body ______ resistant.
The patient will need ______ shots to manage _______.
Glucose
Pancreas, Insulin
Insulin
Insulin, Glucose
With type 2 diabetes, the pancreas usually produces insulin, but not (1)_______. OR the body’s cells are (2)_________ to it.
Obese people have an insulin (3)__________.
Enough
Resistant
Resistance
Any type 1 or 2 diabetes that predates pregnancy will be termed…
Maternal diabetes mellitus (Pre-Gestational diabetes)
What is another term for maternal diabetes mellitus?
Pre-gestational diabetes
What is another term for pre-gestational diabetes?
Maternal diabetes mellitus
If a patient does not have diabetes, BUT develops it during pregnancy, what is that termed?
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes will typically resolve itself after pregnancy, BUT it will still slightly increase the risk for what diabetes type?
Type 2 diabetes
List the 4 US findings for fetus’ born from a diabetic mother.
Macrosomic fetus
Polyhydramnios
Thick placenta
CCNGGSS
What does ‘CCNGGSS’ stand for?
Cardiovascular malformation
Caudal regression syndrome
Neural tube defects
GU anomalies
GI anomalies
Skeletal anomalies
SUA
What does ‘GU’ stand for?
Genitourinary
What organs do GU anomalies affect?
Kidneys
Bladder
What does ‘SUA’ stand for?
Single umbilical artery
List the 5 possible congenital anomalies of the heart that could be seen in infants of diabetic mothers.
Transposition of the great arteries w/ or w/o VSD
VSD
ASD
Coarctation of the aorta w/ or w/o VSD
Cardiomegaly
List the 3 possible congenital anomalies of the GI tract that could be seen in infants of diabetic mothers.
Duodenal atresia
Anorectal atresia
Small left colon syndrome
List the 3 possible congenital anomalies of the renals that could be seen in infants of diabetic mothers.
Hydronephrosis
Renal agenesis
Ureteral duplication
Fill in the blanks for the 4 possible congenital anomalies of the CNS that could be seen in infants of diabetic mothers.
Caudal _________ syndrome
___________ defects
_____cephaly
_____cephaly
Regression
Neural tube
Anencephaly
Microcephaly
What does ‘CRS’ stand for?
Caudal regression syndrome
CRS is considered a rare ________ anomaly.
Congenital
Caudal regression syndrome is when the ______ part of the spine does not develop properly.
List some examples.
Lower
Absence of the sacrum
Defects of the lower vertebral bodies.
CRS can be associated with what mnemonic of pathologies?
VACTERL
List the pathologies associated with the mnemonic ‘VACTERL’.
Vertebral defects
Anal atresia
Cardiac defects
Trachea-esophageal issues
Renal anomalies
Limb abnormalities
Trachea-esophageal issues can include ______ or _______.
Atresia
Fistula
Patients diagnosed with VACTERL typically have at least ___ of the pathologies.
3
Prognosis for caudal regression syndrome depends on the type of __________.
Abnormalities
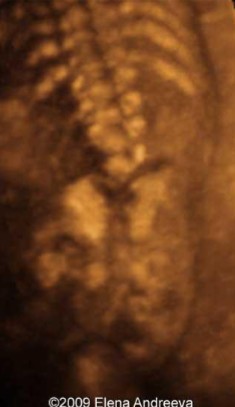
This was found on the scan of a fetus with cardiac defects. What can be assumed here?
Caudal regression syndrome (CRS)
Vertebral defects of CRS present in __-__% of cases.
60-80%
Anal atresia of CRS present in __-__% of cases.
60-90%
Cardiac defects of CRS present in __-__% of cases.
40-80%
Trachea-esophageal fistula/atresia of CRS present in __-__% of cases.
50-80%
Renal anomalies of CRS present in __-__% of cases.
50-80%
Limb abnormalities of CRS present in __% of cases.
50%
Vertebral defects of CRS include the…
Hemivertebrae
__________ vertebrae
_____ or missing vertebrae
Congenital ________
Spina _____
Hypoplastic
Extra
Scoliosis
Bifida
Vertebral defects of CRS can cause what pain later in life?
Back
Anal atresia in CRS will refer to the narrowing or lack of ______ of the anus.
Patency
Anal atresia of CRS may be accompanied by ____ anomalies.
GU
Anal atresia of CRS will have…
No passage of ________
Abdominal ________
Vomiting
Meconium
Distension
Cardiac defects of CRS can have subtle to life threatening ______.
Defects
Common cardiac defects of CRS include:
_________ septal defect
_________ septal defect
Tetralogy of _____
Patent ductus ________
Ventricular
Atrial
Fallot
Arteriosus
What is the shorter form of ‘tracheo-esophageal fistula’?
TEF
What does ‘TEF’ stand for?
Tracheo-esophageal fistula
TEF of CRS is an abnormal connection between the _______ and the _________.
Trachea
Esophagus
What does ‘EA’ stand for?
Esophageal atresia
EA of CRS is a congenital condition characterized by the (1)_______ development of the (2)________.
Incomplete
Esophagus
TEFs are most often found in conjunction with…
EA (esophageal atresia)
TEF/EA of CRS may have patient presenting with…
Vomiting
Copious ____ secretions
Feed _________
Coughing
Cyanosis
Respiratory _______
Oral
Intolerance
Distress
Renal anomalies of CRS include these 4 pathologies:
Renal _______
Renal _______
Vesicouterine _____
_______ or ___-positioned kidneys
Aplasia
Dysplasia
Reflux
Displaced or mal-positioned
Renal anomalies of the CRS may not cause _______ immediately.
Problems
Renal anomalies of CRS may require a ________ or ________ consultation.
Nephrology
Urology
Limb abnormalities of CRS could present with radial aplasia. Define what that is.
Underdevelopment of the radius
Limb abnormalities of CRS include these 4 pathologies:
________ (additional digits)
Missing ______
Lower limb ________
________ (webbing)
Polydactyly
Digits
Hypoplasia
Syndactyly
What blood work is used to determine how controlled each case of diabetes is? (How well controlled someone’s glucose is)
Hemoglobin A1C
Poorly controlled diabetes (1)_______ the pregnancy or (2)_______ the pregnancy, can increase the risk for fetal anatomic anomalies.
Predating
During
A poorly controlled case of diabetes will have the hemoglobin A1C test measuring (1)_____ than (2)___.
More
8
A mildly controlled case of diabetes will have the hemoglobin A1C test measuring (1)_____ than (2)___.
More
7
A well controlled case of diabetes will have the hemoglobin A1C test measuring (1)_____ than (2)___.
Less
7
Hypertension places both the _______ and _______ at a risk.
Mother
Fetus
What does ‘HTN’ stand for?
Hypertension
How does a placenta appear with HTN?
Thin
Prematurely mature
What is something mothers are at an increased risk for relating to the placenta if they have hypertension?
Placenta abruption
Hypertensive pregnancies may also be associated with which two fetal pathologies?
IUGR
Oligohydramnios