Blinn College - Geology 1403 - 316 - Dr.Mosely Exam 4
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
What is the role of external processes in the rock cycle?
processes that take place on the outside of the earth
How is mass wasting different from erosion?
mass wasting - rapid movement of rock & soil down a slope
erosion - movement of rock & soil down hill by an agent of transport
What is the water cycle?
the unending circulation of water
What energy source powers the water cycle?
the sun
What is the most important agent in sculpting earth's land surface?
runoff
What factors determine the streams ability to erode?
1.) gradient
2.) size, shape & roughness of the channel
3.) discharge
What is base level?
the lowest elevation that a stream can cut down to
The work of streams include what three processes
1.) erode
2.) transport
3.) deposit
What are the two general types of river valleys?
1.) narrow Valleys
2.) wide Valleys
What are features of a narrow valley?
- v-shaped
- actively downcutting
- stream is high about base level
- high gradient
- swift current
What are features of a wide valley?
- stream is close to base level
- little down cutting
- low gradient
- most energy is forced laterally
- floodplains & meanders
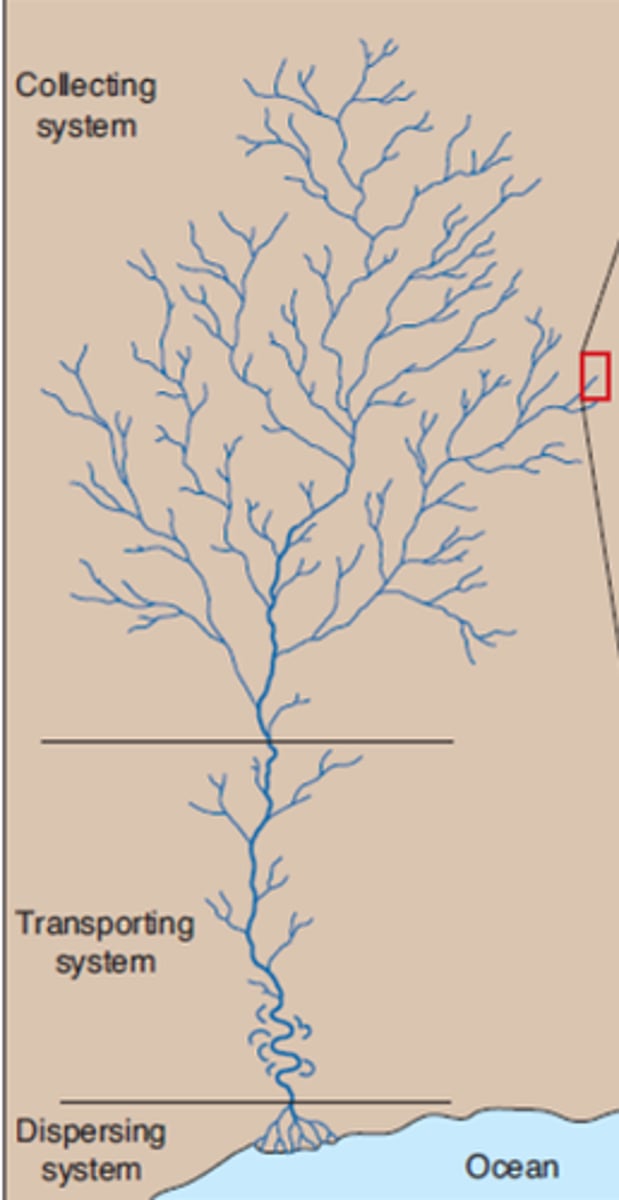
What are some common drainage patterns?
1.) dendritic pattern
2.) rectangular pattern
3.) radial pattern
4.) trellis pattern
What are features of dendritic drainage pattern?
- develops on uniform surface material
- most common
- tree like branching pattern
- determined by the direction of slope in the land
What are features of rectangular drainage pattern?
- develops on highly jointed bedrock
- right angle bends

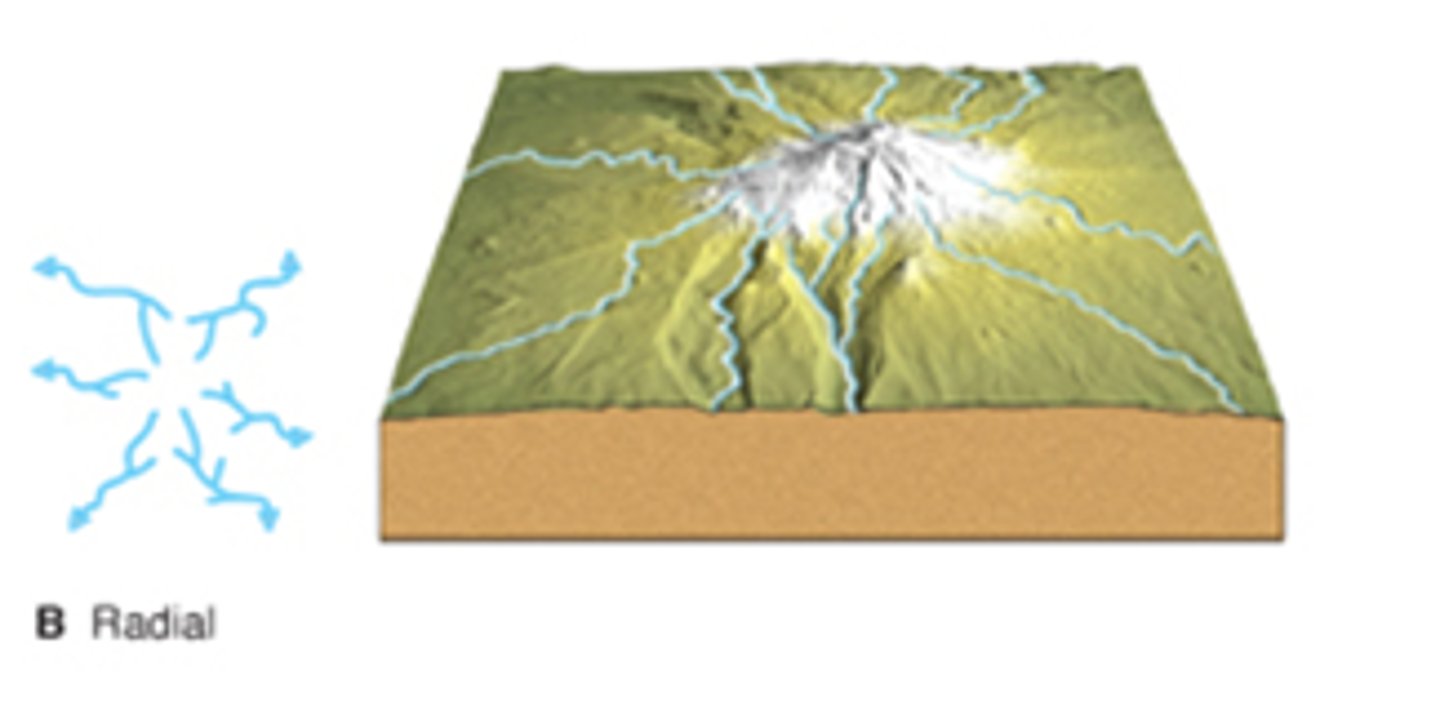
What are features of radial drainage pattern?
- develop on volcanic cones or domes
- streams coverage from a central area
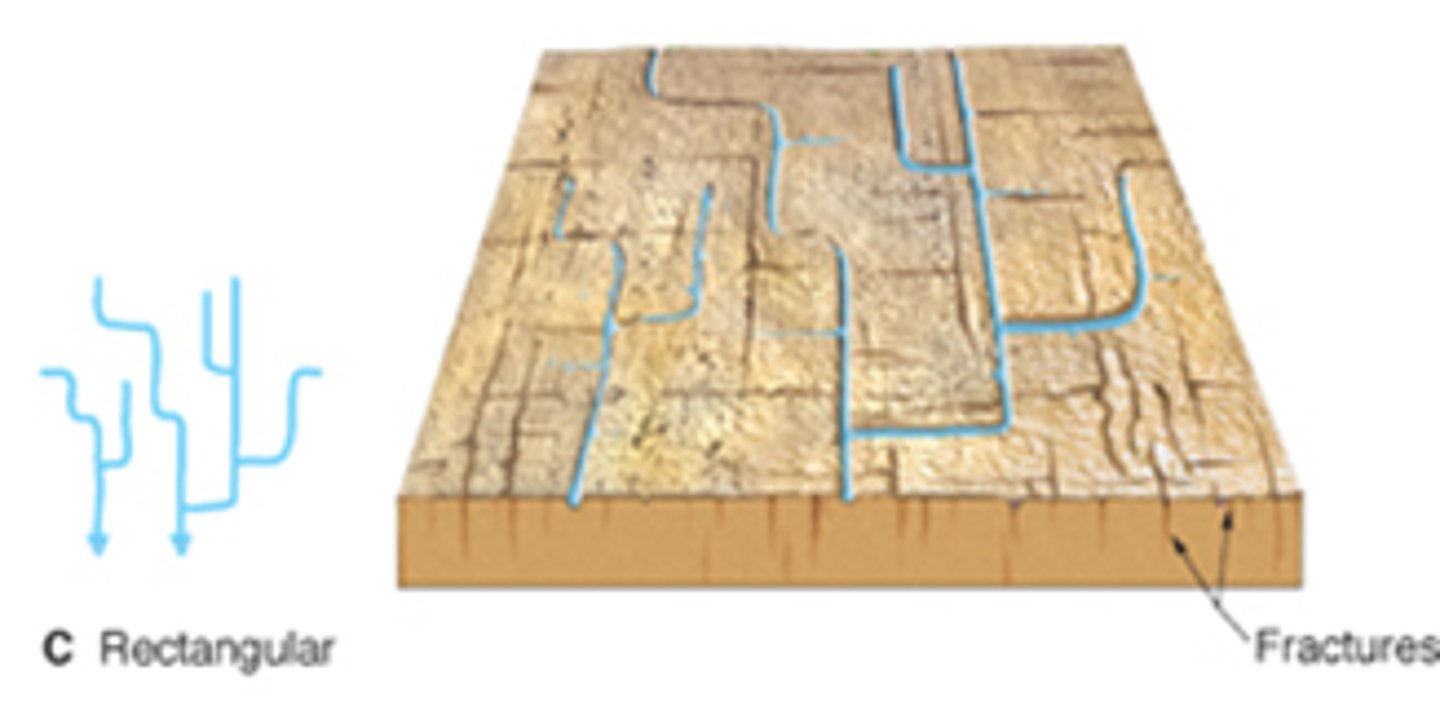
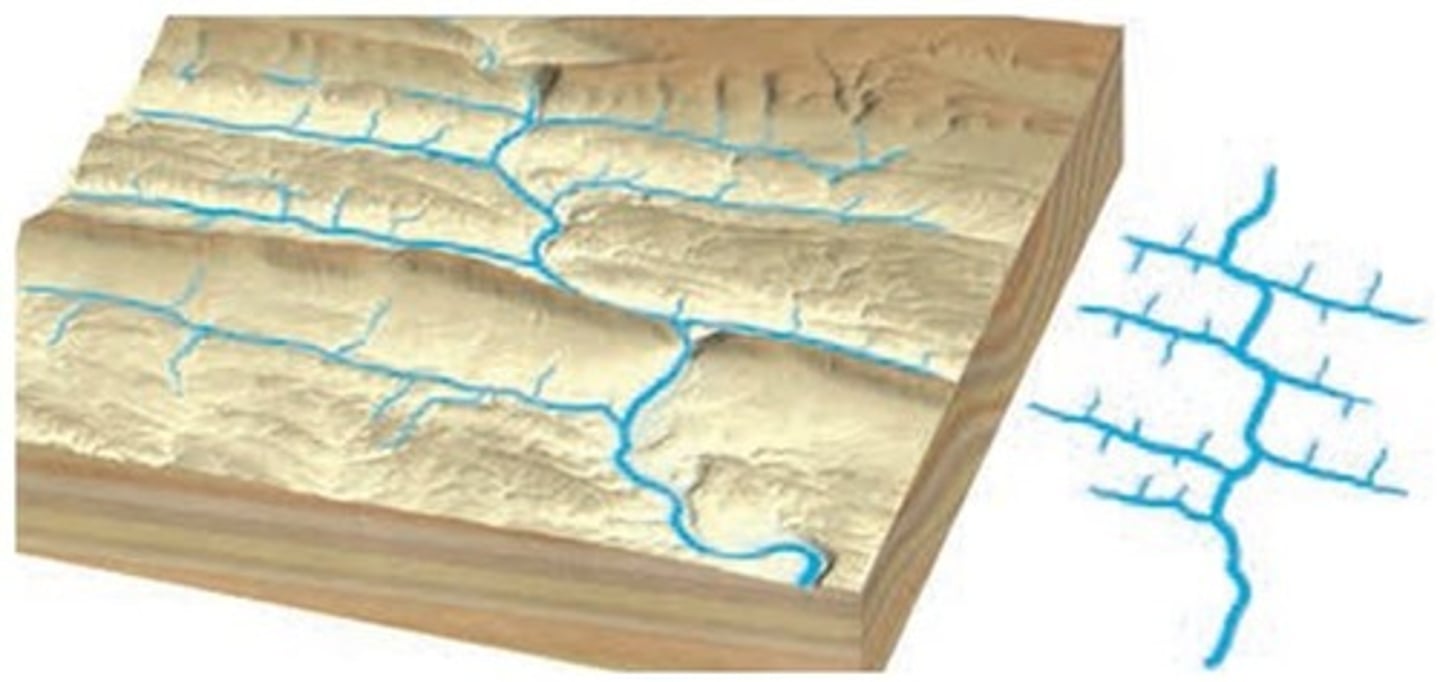
What are features of trellis drainage patter?
- develop in areas of weak and resistant bedrock
- found in Appalachian Mountains
- a rectangular drainage pattern
- streams are nearly parallel to one another
What is the importance of groundwater as a resource?
is used for irrigation & public supply
What is the importance of groundwater as a geologic agent?
- removes sediment as dissolved ions in solutions
- contributes to surface streams
How does groundwater move?
it exists in the pores of rock & moves from pore to pore
What are some natural phenomenas associated with groundwater?
springs, hot springs & geysers
What factors cause infiltration and runoff to vary from place to place and time to time?
1.) the intensity and duration of rainfall
2.) the amount of water already in the soil
3.) the nature of the surface material
4.) the slope of the land
5.) the extent and type of vegetation
What are the three main zones of a river system?
1.) sediment production
2.) sediment transport
3.) sediment deposition
Contrast laminar and turbulent flow
laminar flow - water moves in nearly straight-line paths
turbulent flow - water moves in an erratic fashion (most streamflow is turbulent)
Summarize the factors that influence flow velocity
1.) gradient - slope
2.) channel shape - deep & narrow or wide & shallow
3.) channel size and roughness - irregularities in bed
4.) discharge - amount of water flowing
What is a longitudinal profile?
a cross-sectional view of a stream from its head to its mouth
What happens to channel width, depth, flow velocity, & discharge between the headwaters and the mouth of a stream?
Gradient decreases toward the mouth of a stream, but increases in discharge and channel size + the decrease in roughness makes the flow velocity usually increase towards the mouth
Describe two processes by which streams cut channels in bedrock
1.) abrasion - rocks and sediment grin
2.) corrosion - rock gradually dissolves
In what three ways does a stream transport its load?
1.) dissolved load - in solution
2.) suspended load - muddy
3.) bed load - rolling on the bottom
What part of the load moves most slowly?
bed load
Explain the difference between capacity and competency
capacity - the amount of sediment the stream can carry
competency - the largest grain the steam can move
What is settling velocity?
the speed at which a particle falls through a still fluid
What factors influence settling velocity?
size and shape
-flat grains sink slower than round ones
-large grains sink faster than small ones
Does settling velocity affect the dissolved load?
Are bedrock channels more likely to be found near the head or mouth of a stream?
head
Describe a situation that might cause a stream channel to become braided
where a large portion of a stream's load consists of coarse material (sand & gravel) and the stream has a highly variable discharge (ex: at the end of glaciers)
Does water flow faster or slower on the outside of a meander?
faster
Why does water flow slower on the inside of a meander?
because it is depositing sediment
What is the difference between base level, ultimate base level, and local base level?
base level - the streams limit to erosion
ultimate base level - the lowest level to which stream erosion could lower the land (sea level)
local base level - the level of a lake, resistant rock layer, or any other base level that stands above sea level
What is a graded stream?
a stream that has the correct channel characteristics to maintain exactly the velocity required to transport the material supplied to it
Describe two situation that would trigger the formation of incised meanders
1.) base level dropped
2.) the land on which the river was flowing was uplifted
What are the four types of floods?
1.) regional floods - seasonal
2.) flash floods - occur with little warning
3.) ice-jam floods - water rises under ice and breaks it
4.) dam-failure floods - human caused
Describe three basic flood-control strategies. What are some drawbacks of each?
1.) artificial levees - not built to withstand periods of extreme flooding
2.) channelization (artificial cutoffs) - led to increase in gradient and acceleration of erosion of bank material
3.) flood-control dams - not a permanent solution, have significant costs
What is meant to nonstructural approach to flood control?
floodplain management - appropriate zoning regulations, and no artificial levees or dams
What percentage of earths total freshwater supply is groundwater?
15%
Whats share of earths liquid freshwater is groundwater?
95%
What share of U.S. freshwater is provided by groundwater?
345 bilion gallons
Relate groundwater to the water table
Is a water table usually flat? Why?
no, because it usually replicates the surface topography or is influenced by the way groundwater moves
Contrast a gaining stream and a losing stream
gaining streams - streams gain water from the groundwater
losing streams - streams lose water to the groundwater system
What is the difference between porosity and permeability?
porosity - void space between the grains
permeability - the ability of water to move through the pores in rock
A good aquifer will have high or low porosity & permeability?
high porosity & high permeability
What is most important in an aquifer - porosity or permeability?
permeability
Whats the difference between hydraulic gradient and hydraulic conductivity?
hydraulic gradient - the water table slope
hydraulic conductivity - accounts for permeability
Relate drawdown to cone of depression
How does a heavily pumping well affect the water table?
Why do some artesian wells not flow at earths surface?
How does a spring form?
when the zone of saturation is exposed at the surface
What warms the waters that flow at Hot Springs in the U.S?
when groundwater circulates at great depths it becomes heated - if the hot water rises rapidly to the surface it may emerge as a hot spring
What is the source of heat for most hot springs and geysers?
magma bodies and hot igneous rocks
Describe what occurs to cause a geyser to erupt
heat warms up the water, letting some of it out and reducing pressure - this allows more of the water to boil which expands into steam - and the steam triggers eruption
Describe the problem associated w/ pumping groundwater for irrigation in the southern high plains
it is not replenishing fast enough - because in most parts there isn't as much precipitation with evaporation rates much higher due to warmer weather
Why would ground subside after groundwater is pumped to the surface?
the water pressure drops when water is pumped - the weight is then put on layers of unconsolidated sediment (main result - sinking)
Which aquifer would be MOST effective in purifying polluted groundwater: coarse gravel, sandstone, or cavernous limestone?
sandstone - can be purified after traveling a short time, due to the openings in grains are large enough to permit the water, but slow it down to also purify
Which aquifer would be LEAST effective in purifying polluted groundwater: coarse gravel, sand, or cavernous limestone?
cavernous limestone/coarse gravel - have large openings where the contaminated groundwater can travel long distances without being cleansed
How does groundwater create caverns?
groundwater has carbonic acid and when it interacts with limestone it becomes a soluble material and carried away leaving behind a cavern
What causes cavern formation not stop at one level (depth) but continue or begin at a lower level?
Describe two ways in which sinkholes form
1.) gradually over many years - the limestone below the soil is dissolved by downward sweeping rainwater
2.) abruptly - the roof of a cavern collapses under its own weight
Where are glaciers found today?
earths poles or high mountains (greenland, norway, alaska)
What percentage of earths land surface do glaciers cover today?
10%
How do glaciers fit into the hydrologic cycle?
precipitation becomes part of the glacier and helps with erosion - and eventually makes it way back into the sea
What role do glaciers play in the rock cycle?
can pick up and carry more sediment grains than wind or water
What are the four main types of glaciers?
1.) alpine (valley) glacier - in a mountain valley
2.) outlet glacier - form outward off ice cap or ice sheet
3.) piedmont glacier - when one or more valley glaciers form and create a sheet at the base of a mountain
What is the difference between an ice sheet and an ice shelf?
What are two components of glacial movement?
1.) plastic flow - movement within the ice
2.) basal slip - entire ice mass slips along the ground
How rapidly does glacial ice move? Examples
some are slow - 6.5 ft. (2 meters) per year
some are fast - 2600 ft. (800 meters) per year
What are crevasses, and where do they form?
gaping cracks - as a glacier moves internal stresses cause large cracks to develop in the brittle zone of fracture
Relate glacial budget to zones of a glacier
Under what circumstances will the front of a glacier advance, retreat, remain stationary?
What is the snow line?
the elevation above which snow remains throughout the year
How do glacier acquire their load of sediment?
is trapped within the ice
What are some visible effects of glacial erosion?
What factors influence the capability of a glacier to erode?
1.) plucking - water in cracks freeze & expand breaking off the section of rock and surrounding it in ice
2.) abrasion - sand & gravel trapped in the ice grinds against the walls and floors (creates smooth surface)
3.) striations - grooves cut into the rock caused by the larger rocks within the ice
How does a glaciated mountain valley differ in appearance from a mountain valley that was not glaciated?
glaciate mountain valley - more U-shapped producing a broader, deeper valley
mountain valley - more V-shapped with steep, jagged sides
Describe the features created by glacial erosion in an area where valley glaciers recently existed
arête, tarn, horn, cirques, hanging valley, glacial trough, pater roster lakes
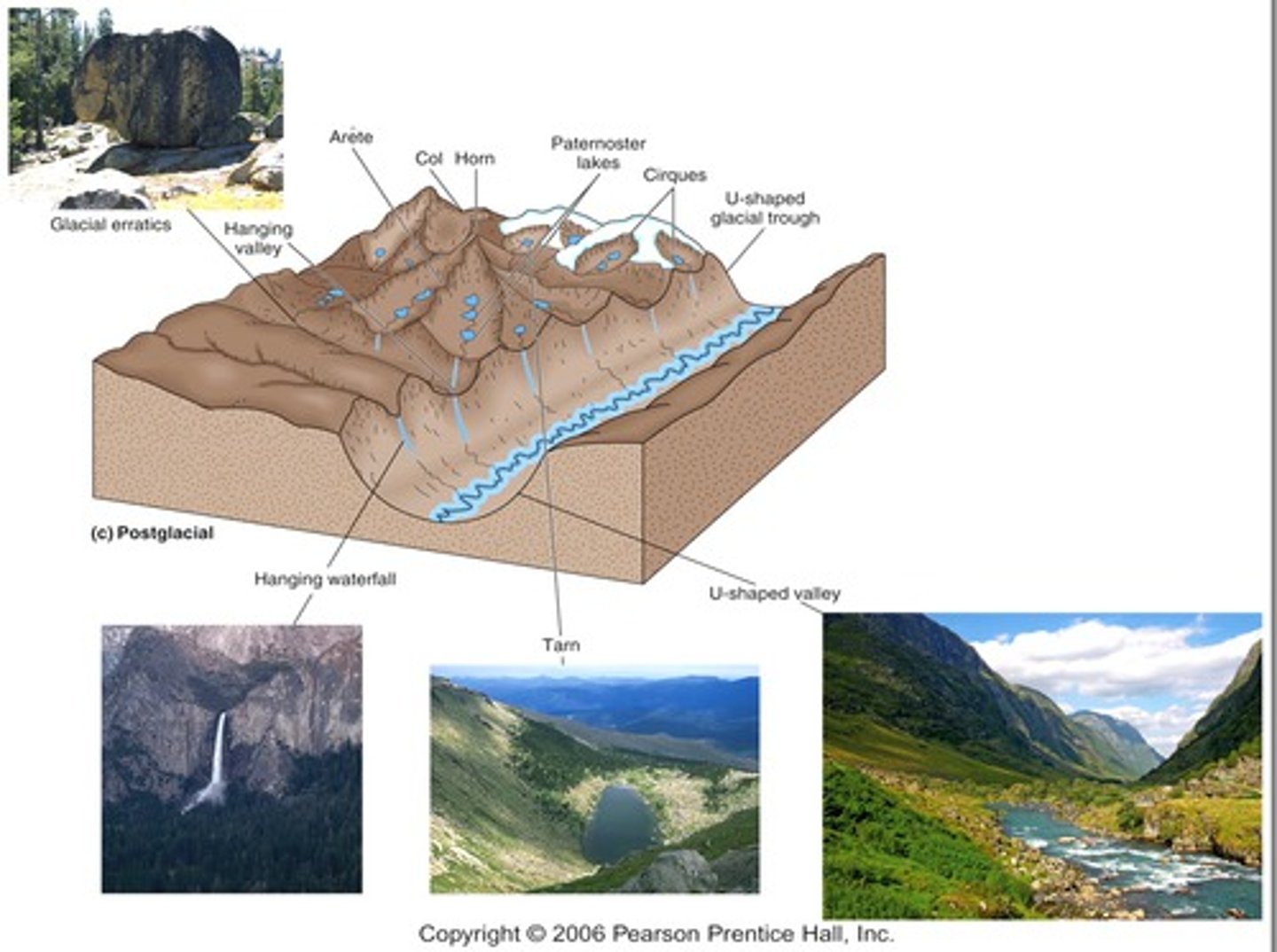
Relate fiords to glacial troughs
fiords are glacial troughs that filled with sea water
Distinguish between till and stratified drift
till - unsorted deposited sediment
stratified drift - sediment that is sorted by glacial melting
How are medial moraines and lateral moraines related?
lateral moraines - form a ridge of till between ice and a valley wall
medial moraines - frome a ridge of till when lateral moraines merge (between ice and ice)

Contrast end moraine and ground moraine
end moraine - sediment deposited at the end of the glacier (zone of wastage = terminus)
ground moraine - the sediment dumped by rapidly melting ice after a glacier retreats
What is an outlaws plain - and how is it different from a valley train?
outwash plain - flat region at the end of a glacier (ice)
valley train - stays within the valley
Describe the formation of kettle lakes
lakes in the outwash plain that form from block of ice that were trapped and then melted
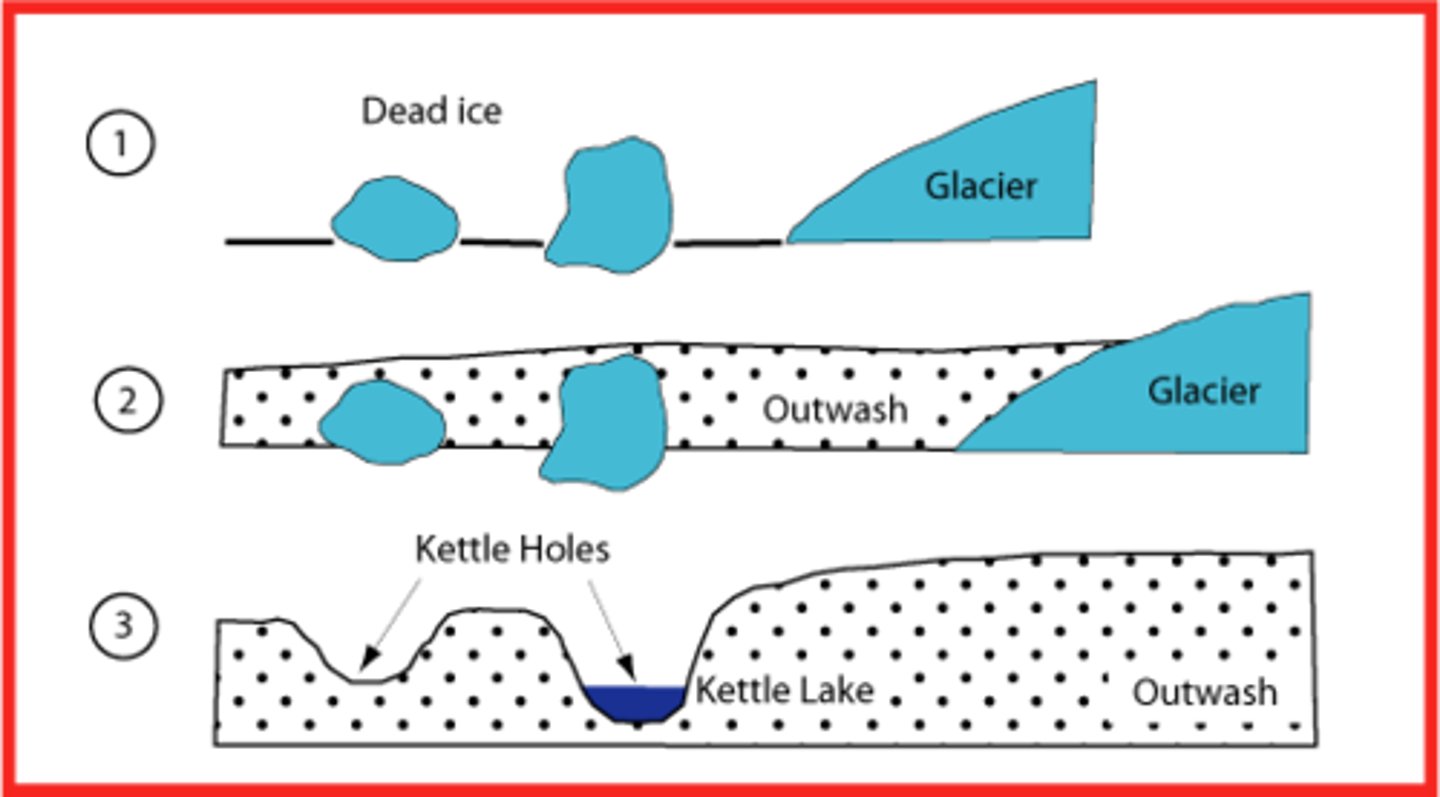
Describe the formation of kames and eskers
sediment deposited by a subglacial stream (names is on steep-sided hills)
What are five effects of Ice Age glaciers?
1.) plants & animals forced to migrate (some extinct)
2.) changes in routes taken by rivers
3.) sea-level changes with melting of ice sheets
4.) glaciers acted as ice dams
5.) adjustments in earths crust due to ice advance & retreat
How much has sea level changed since the last glacial maximum?
was 330 ft. (100 meters) lower about 18,000 years ago
Contrast proglacial lakes and pluvial lakes
pluvial lake - formed with increased rainfall
proglacial lake - a lake crated when a glacier acts as a dam blocking the flow of a river or trapping glacial meltwater
What was the best source of data showing Ice Age climate cycle?
core samples form the sea floor
About what percentage of earths land surface was affected by glaciers during the Quaternary period?
30%
Where were ice sheets more extensive during the Ice Age: Northern or Southern Hemisphere? Why?
Northern Hemisphere was twice as much as southern - northern had more land to spread, where the southern couldn't make it far from antarctica
Does the theory of plate tectonics explain alternating glacial/interglacial climates during the Ice Age?
Summarize the climate change hypothesis that involves variations in earths orbit
based on he premise that variation sin incoming solar radiation are a principal factor in controlling earths climate
- variation sin the shape of earths orbit around the sun
- changes in the angle that the axis makes w/ the plane of earths surface
- the wobbling of earths axis