funds 28 nutritional therapy & assisted feeding
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
goals of nutritional therapy
treat & manage disease
prevent complications & restore health
specific diet for each pt prescribed & written
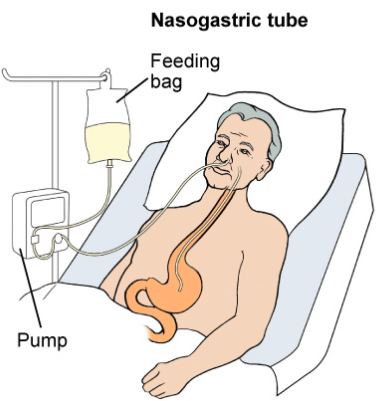
nasogastric & eternal tubes
temporary measure to provide nutritional support
irrigate/ flush to ensure patency
placement must be checked prior to feeding / adm meds
- initial placement, x-ray done. markings on tube are correct
- aspirate (pull back on syringe connected to end of tube) to make sure gastric secretions. look at color, consistency. check pH. (1-4). anything 6+ may be trachea-bronchial
- aspirate to check residual volume to see if food has been digested. amount. some facilities have you put it back
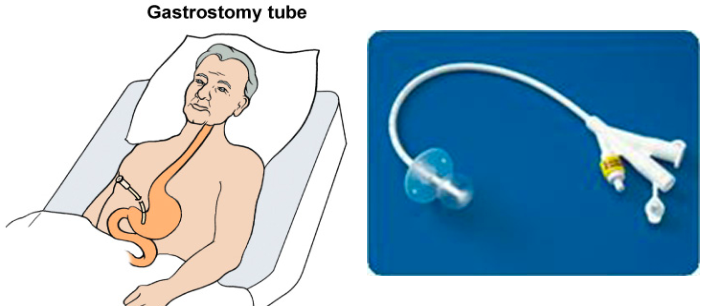
gastrostomy tube
directly into stomach. surgically placed
balloon inside stomach helps it to stay in place
peg (percutaneous endoscopic gastronomy): inserted via mouth
reasons for NGT & eternal tubes
dysphagia
inflammatory bowel disease
obtaining gastric specimens for analysis
gastric feeding
administration of meds
decompression (emptying) of the stomach before / after surgery
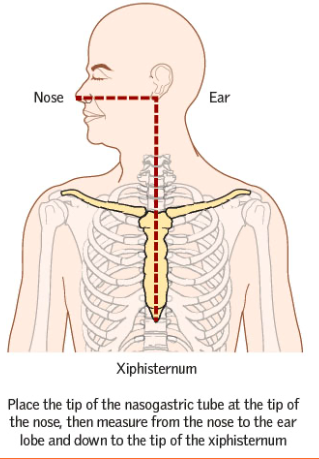
how is determined how far NGT goes in?
N: nose
E: ear
X: typhoid process
PEG tube or Jejungostomy tube
percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube
long-term nutritional support
tube placement should be checked every shift. ac / adm med
assess bowel sounds, soft & non-distended
stomach needs to be bypassed / problems w upper GI or risk for aspirations
assessing gastrostomy tube site
assess site for leakage, breakdown. must be kept clean
if breakdown, notify
some facilities clean w water. others gauze & saline
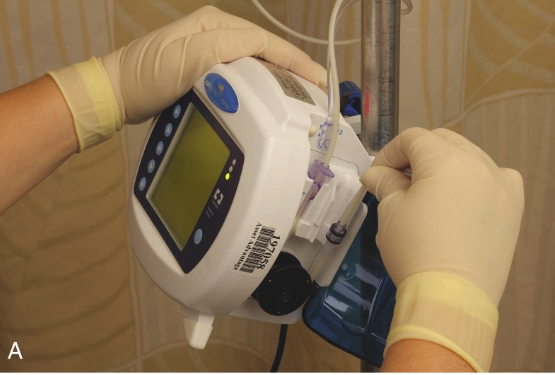
enteral feedings
continuous feedings: via pump. certain mL per hour
intermittent/ bolus feedings: specific times during the day
via syringe (GRAVITY. NOT PUSHED). or via pump.
- 240 - 360 mL per feeding
included in order: type of formula, volume, rate
if can, top needs to be cleaned off before opening.
principals of tube feeding
elevate HOB 30 - 90* ac & leave up 30-60 min ac
keep HOB elevated at least 30* if continuous feeding
if aspiration, nausea or vom, stop feeding and call pcp.
assess bowel sounds at least once q8h
check placement ac / med adm or at least once a shift
tube should be flushed 30-60 mL ac & pc & med adm mL water
maintain accurate I & O. dehydration may occur bc diarrhea or high glucose
if residual > 500mL, replace residual, document & notify. delay next feeding or as appriortire to policy
intermittent feeding steps
check order. formula, volume
check placement
hob 30-90*
flush w water 30-60mL. have formula ready and put in before water empties
gravity feeding
flush w water 30-60mL.
tpn / total parental nutrition
via central line. iv.
malabsorption, GI surgery NPO, burns, bowel disease, aids, cancer
high concentration of carbs. monitor sugar & fluid overload I & O
custom to pt
start slowly for body to adjust to high glucose.
patients needing feeding assistance
pt w paralysis of arms
pt w visual impairment. (fork at 3oclock, mash at 6oclock)
pt w IV lines in their hands
severely impaired, weak or confused
dysphagia
signs: coughing when ingesting, drooling, food remaining in mouth
risk for aspiration. HOB 60-90*. no straw. tuck chin when swallowing
speech pathologist evaluates pt. gives diff foods to see what issues

dietary modifications
liquid
npo
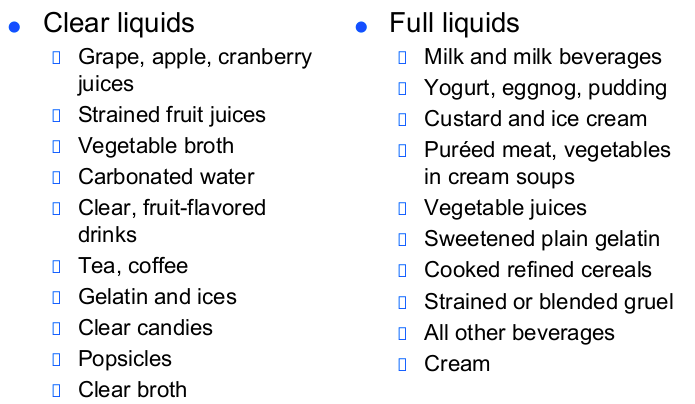
clear liquids (clear fruit juices, gelatin, broth)
full liquids: clear liquids + dairy, all juices. can include pureed veggies
dietary modifications
solid
pureed
mechanical soft
soft/ low residue: low in fiber, easy digest.
low sodium
low cholesterol
diabetic, dysphagia, regular

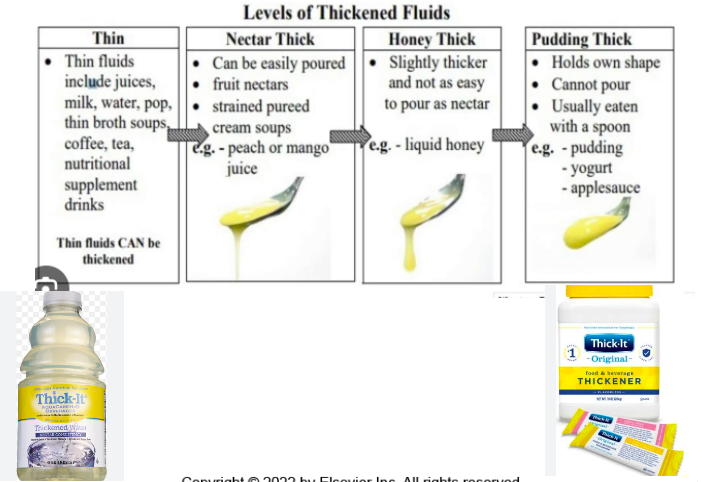
thickened liquids
part of order
post-op patients nutrition
should be well-nourished pre-op. usually npo 6-8h before
post-op: checking for gag reflex and bowel awake → clear liquid to full liquid diet → soft diet → regular diet
clear vs full liquids
anorexia nervosa
refusal to maintain normal weight. fear of becoming obese
treatment: nutritional intervention. counseling
bulimia nervosa
binge episode followed by purging, laxatives, fasting
aware of behavior and often ashamed
treatment: nutritional intervention. counseling
what deficiency is often seen is alcohol abuse?
thiamine aka vitamin b1 deficiency