Ch. 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:00 PM on 9/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
albert lehninger studied/found
•Citric acid cycle in mito
•oxidative phosphorylation mech
•Mito struc & func
•Bioenergetics
•oxidative phosphorylation mech
•Mito struc & func
•Bioenergetics
2
New cards
albert lehninger wrote
classic biochem txtbks
3
New cards
Living organisms conform to
•to all phys & chem laws of behavior of inanimate objects
4
New cards
Macromolecules:
highly ordered polymers that form complex structures in cell
5
New cards
Polymers with a sequence of subunits
generate unique 3D structures for activity
6
New cards
extraction, transform, systematic use of energy
makes, maintains struct, for work
7
New cards
life tries to counteract the universes desire to be
disordered
(tries to reach eq) by envi overall ^disorder
(tries to reach eq) by envi overall ^disorder
8
New cards
microscopic & large structs are higly
coordinated
w/individual chem compounds
w/individual chem compounds
9
New cards
when individual components are interacting w/chem compounds can cause
change in another
whole org display new characteristic
whole org display new characteristic
10
New cards
life responds to the changes in envi by
adapting internal chem
can self-rep (precise enough for evolution
can self-rep (precise enough for evolution
11
New cards
invariant cell
cell mem
ribosomes
DNA
RNA
ribosomes
DNA
RNA
12
New cards
variant cell
mito
chloroplast
nuc membrane
chloroplast
nuc membrane
13
New cards
3 domains of life
bacteria
archaea
eukaryote
archaea
eukaryote
14
New cards
bacteria cell struct (prokaryote)
ribosomes
cell envelope
pili
nucleoid
flagella
dna
membranes
15
New cards
eukaryote structure
nucleus w/nuc membrane
membrane enclosed organelles
* chloroplasts in plants
* lysosome
* golgi
* mito
membrane enclosed organelles
* chloroplasts in plants
* lysosome
* golgi
* mito
16
New cards
eukaryote
spatial separation
spatial separation
of energy making/consuming rxns helps maintain homeotasis
stay away from eq
stay away from eq
17
New cards
smooth ER
lipid synthesis
drug metabolism
18
New cards
rough ER
protein synthesis
19
New cards
cytoplasm
v viscous soln where rxns happen
v dense w/proteins
v dense w/proteins
20
New cards
cytoskeleton
cell struct made by protein filaments that cross to make 3D meshwork
* microtubules, actin, intermediate filaments
* microtubules, actin, intermediate filaments
21
New cards
cytoskeleton funcs
give shape,
org,
transport path,
allow movement
org,
transport path,
allow movement
22
New cards
chemotrophs
chemical
auto- CO2
hetero- (organic compounds) all animals, most fungi, protists, bacteria
23
New cards
phototrophs
light
-auto: CO2 (bacteria & plants)
-hetero: organic compounds (bacteria)
24
New cards
cells organization is
dynamic
changes drastically at diff stages
changes drastically at diff stages
25
New cards
energy from sunlight
plants, some bacteria
26
New cards
energy from fuels
animals, most
27
New cards
28
New cards
biochem studies chem responsible for
* accelling rxns
* org of metabolism & signaling
* store & transfer of info
* org of metabolism & signaling
* store & transfer of info
29
New cards
_ elements essential for life
30
30
New cards
primary elements
C,H,O,N,P,S
31
New cards
metal ions that play role in metabolism
K
Na
Ca
Mg
Zn
Fe
Na
Ca
Mg
Zn
Fe
32
New cards
functional groups in biomolecs
derivatives of hydrocarbons with H replaced by a variety of functional groups (i.e. amino acids have amino and carboxyl groups)
33
New cards
building blocks of biochem
sugars (monosacharides)
lipids (FA’s)
AA’s
nucleotides
lipids (FA’s)
AA’s
nucleotides
34
New cards
chirality
chiral carbon w/4 subs
1 chiral = 2 stereoisomers
1 chiral = 2 stereoisomers
35
New cards
R and S system
assigned by priority
* decreases in clockwise order, configuration is R (rectus, right)
* Counterclockwise configuration is S (sinister, left)
* decreases in clockwise order, configuration is R (rectus, right)
* Counterclockwise configuration is S (sinister, left)
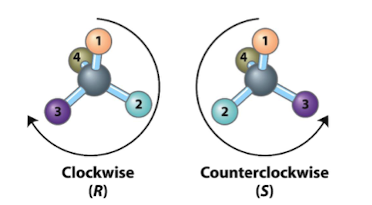
36
New cards
D and L system
(dextrorotatory and levorotatory):
optical activity, rotation of light (natural amino acids are L-form)
optical activity, rotation of light (natural amino acids are L-form)
37
New cards
Structural isomers:
same atoms but dif order of bonding,
dif properties
dif properties
38
New cards
Stereoisomers:
molecs w/same chem bonds but diff configuration, different properties
* enantiomers & diastereomers
* enantiomers & diastereomers
39
New cards
Enantiomers
(mirror images):
identical phys properties (except w/polarized light)
react identically w/achiral reagents, may have diff biological activity
identical phys properties (except w/polarized light)
react identically w/achiral reagents, may have diff biological activity
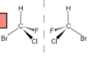
40
New cards
Diastereomers
(not mirror images)
geometric isomers (cis/trans)
* have dif phys and chem properties
geometric isomers (cis/trans)
* have dif phys and chem properties
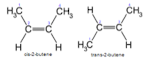
41
New cards
Isomerases
convert between types (racemase, epimerase, cis-trans isomerase)
42
New cards
molec func depends on
3D struct
43
New cards
Macromolecules have unique
binding pockets, and only certain molecules can fit
44
New cards
binding of chiral biomolecules is
stereospecific
(protein AB, enzymes)
(protein AB, enzymes)
45
New cards
binding specificity ex. glucose
fits into pocket on hexokinase, interacting noncovalently.
* enzyme is specific for D -glucose (in body), not L (not made, except in the lab and by one bacterium)
* enzyme is specific for D -glucose (in body), not L (not made, except in the lab and by one bacterium)
46
New cards
Olfactory/taste receptors detect
chirality
47
New cards
Drugs can have different
enantiomers/structures, and sometimes different effects
48
New cards
Racemic mixture is
often cheaper than the enantiopure drug, with similar effects
* more common in drugs than pure
* more common in drugs than pure
49
New cards
Lexapro (Escitalopram) vs. Celexa (Citralopram)
* lexapro: pure, antidepressant SSRI
* celexa: racemic mix of levo isomer (active) & mirror dextro isomer
* need 2x the amt you would bc not pure
* celexa: racemic mix of levo isomer (active) & mirror dextro isomer
* need 2x the amt you would bc not pure
50
New cards
In some cases one enantiomer is required
* Citalopram is not recommended for those with heart or liver issues
* L-thyroxine (Synthroid) – thyroid hormone
* D-thyroxine (Choloxin) – lowers cholesterol w/cardiac side effects
* L-thyroxine (Synthroid) – thyroid hormone
* D-thyroxine (Choloxin) – lowers cholesterol w/cardiac side effects
51
New cards
1st Law of Thermodynamics:
energy can’t be created or destroyed.
* amt of energy added to break a bond = amt released upon its formation
* amt of energy added to break a bond = amt released upon its formation
52
New cards
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
chemical or physical process goes spontaneously in direction of greater disorder (entropy, ΔS)
53
New cards
Cell maintains order at the expense of the
environment
54
New cards
Cells maintain order (-ΔS), which creates
disorder in envi (+ΔS).
**↑S environment > ↓S cell**
**↑S environment > ↓S cell**
55
New cards
The sum of entropy of the system (cell) and surroundings (environment/universe) will be
positive
56
New cards
As metabolic energy is spent to do cellular work, the disorder (randomness) of the system and surroundings (universe)
increases
57
New cards
Organisms return some energy to surroundings as heat and release
end products more disordered than starting fuel
58
New cards
Cells use some energy for anabolic reactions
producing macromolecules: more ordered
* cells ^entropy (+ΔS) of universe
* cells ^entropy (+ΔS) of universe
59
New cards
Free energy is the energy
available to do work
60
New cards
Energy change is expressed as change in
ΔG
61
New cards
enthalpy
ΔH (heat)
62
New cards
movement of a system equation
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
63
New cards
System moves towards
equilibrium concentrations
where ΔG = 0
where ΔG = 0
64
New cards
system energy ex.
NaCl dissolving in solution is favorable -ΔG)
* Heat is absorbed (+ΔH)
* ΔS very positive, thus -TΔS is more negative to offset +ΔH
* Heat is absorbed (+ΔH)
* ΔS very positive, thus -TΔS is more negative to offset +ΔH
65
New cards
endothermic rxn
\+ΔG
66
New cards
exothermic rxn
\-ΔG
67
New cards
activation energy during a rxn
prevents rxn from going downhill (as it should) immediately
68
New cards
small activation energies at each step of a rxn cause
energy only to be extracted in a stepwise manner
69
New cards
activation energy ex. glucose
wants to go downhill but doesn’t turn into co2 & h2o right away has to go thru steps
70
New cards
___ lowers activation energy
enzymes
71
New cards
The sum of all free energy changes in a biosynthetic pathway is
significant
72
New cards
Degradative:
^energy bonds made > consumed
73
New cards
a multistep metabolic path is favorable if
overall sum of ∆Gs is negative
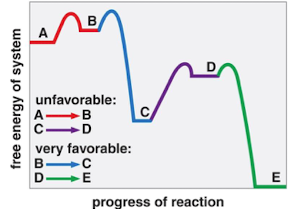
74
New cards
∆G tells ___ of reactions as they go toward equilibrium, but not the **speed** of the reaction
direction
75
New cards
Reaction rates increase with:
^er temp
^er conc
lower conc of prods downstream
coupling to fast rxn
lower activation by catalysis
^er conc
lower conc of prods downstream
coupling to fast rxn
lower activation by catalysis
76
New cards
Reaction rates increasing w temp can cause molecs to be
unstable
77
New cards
rxn rates w/^conc of reactants
more costly
78
New cards
Synthesis of complex molecules and many other metabolic reactions requires
energy (endergonic)
79
New cards
endergonic
if -∆G metabolic rxn may have
if -∆G metabolic rxn may have
too high energy barrier
* Metabolite is kinetically stable
* Metabolite is kinetically stable
80
New cards
Breakdown of some metabolites releases significant amount of energy
exergonic
81
New cards
exergonic metabolites (ATP, NADH, NADPH) can be made from
energy from sun/fuel
* cel conc ^er than eq conc
* cel conc ^er than eq conc
82
New cards
exergonic rxns
cells continuously make
cells continuously make
ATP from ADP +Pi from energy of oxidizing subs (ex.glucose) made by sun
83
New cards
Chemical coupling of exergonic and endergonic rxns lets
unfavorable rxns be able to happen
84
New cards
ATP reacts directly w/metabolite that needs
activation
85
New cards
· ATP → ADP + Pi + Energy
· Glucose + Pi → Glucose 6-phosphate
· Glucose + Pi → Glucose 6-phosphate
Coupled rxns: (not separate).
86
New cards
coupled rxns must be done as a grp transfer to
not lose energy
87
New cards
ATP has 2
phosphoanhydride bonds (high energy)
88
New cards
Free energy source that is released in rxns is from
hydrolysis of ATP (**-∆G**)
89
New cards
effects of ATP hydrolysis
· Consume water
· Electrostatic repulsion of O relieved
· ADP > (∆S) than ATP
· Electrostatic repulsion of O relieved
· ADP > (∆S) than ATP
90
New cards
Grp transfer of ATP is done in coupled rxns so that
energy isn’t released as heat (lost)
91
New cards
ATP grp transfer
Group activation w/AMP or P raises
Group activation w/AMP or P raises
molec energy state
92
New cards
ATP grp transfer
Enzymes must couple
Enzymes must couple
ATP hydrolysis to other rxns
93
New cards
Catalyst:
compound usually metal that increases rate of chem rxn
94
New cards
Catalyst lower
activation free energy ∆G‡
95
New cards
Catalyst do not change
∆G0
cannot go against equilibrium
cannot go against equilibrium
96
New cards
Enzymatic catalysis benefits:
· Accel under mild cond
· High specify
· Regulates
· Couples rxns to atp hydrolysis
· Avoid side rxns
· Substrate channeling
· High specify
· Regulates
· Couples rxns to atp hydrolysis
· Avoid side rxns
· Substrate channeling
97
New cards
enzyme-catalyzed rxns in cells are functionally organized into many sequences of consecutive reactions called
pathways
98
New cards
Metabolic pathways:
make energy or valuable materials
* catabolic or anabolic or amphibolic (both)
* signal transduction pathway transmits info
* catabolic or anabolic or amphibolic (both)
* signal transduction pathway transmits info
99
New cards
regulation of pathways changes
conc of enzymes
100
New cards
regulation is more effective in
bacteria > eukaryote bc rapid growth